React 之生命周期實(shí)現(xiàn)原理
生命周期是指組件從創(chuàng)建、更新到最終銷(xiāo)毀的完整過(guò)程。在不同的階段,React 內(nèi)置了一些函數(shù)以便開(kāi)發(fā)者用來(lái)執(zhí)行不同的邏輯處理。
裝載階段
-
constructor -
static getDerivedStateFromProps -
UNSAFE_componentWillMount -
render -
componentDidMount
更新階段
-
UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps -
static getDerivedStateFromProps -
shouldComponentUpdate -
UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate -
render -
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate -
componentDidUpdate
卸載階段
-
componentWillUnMount
錯(cuò)誤捕獲
-
static getDerivedStateFromError -
componentDidCatch
React 的作者 Dan Abramov 畫(huà)了一張圖來(lái)幫助我們更好地理解 React 的生命周期。
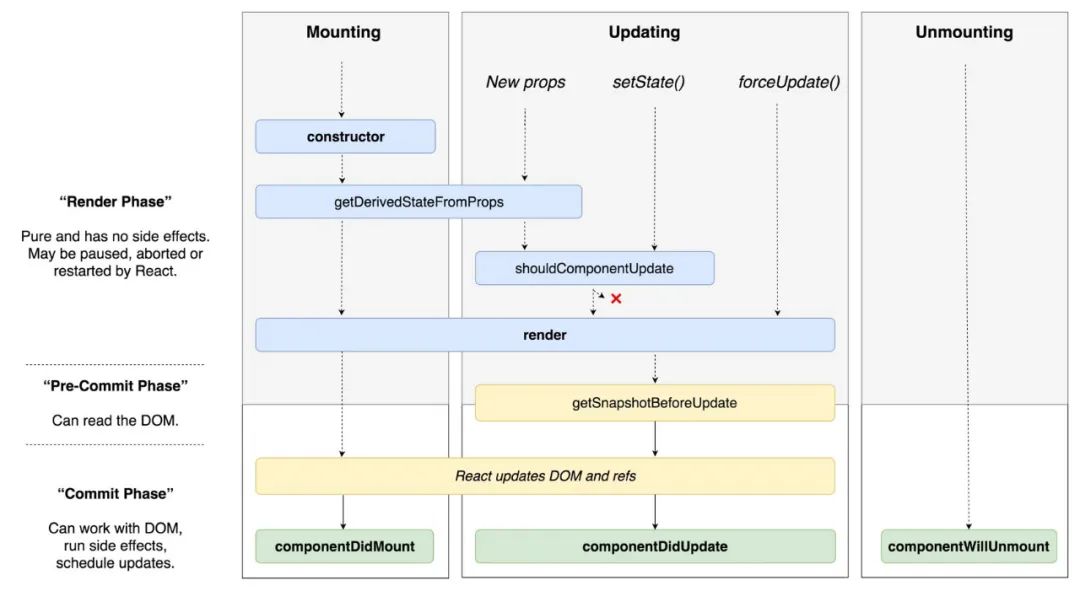
為什么部分生命周期要加 UNSAFE_
在 React 16 之前,React 的更新都是采用遞歸的方式同步更新。生命周期一但開(kāi)始,結(jié)束結(jié)束之前是不會(huì)停止的,所以像 componentWillMount、componentWillReceiveProps、componentWillUpdate 都能順序地正常執(zhí)行。
而在 React16 中,采用 Fiber + Time Slice 的方式處理每個(gè)任務(wù),任務(wù)是可以暫停和繼續(xù)執(zhí)行的。這意味著一次完整的執(zhí)行中,掛載和更新之前的生命周期可能多次執(zhí)行。所以在 React 16.3.0 中,將 componentWillMount、componentWillReceiveProps、componentWillUpdate 前面加上了 UNSAFE_,一來(lái)是為了漸進(jìn)式升級(jí) React,不能一刀切。二來(lái)來(lái)提示使用者,這幾個(gè)方法在新版本的 React 中使用起來(lái)可能會(huì)存在一些風(fēng)險(xiǎn),建議使用最新的生命周期來(lái)開(kāi)發(fā),以防止出現(xiàn)一些意外的 bug。
對(duì)于不同生命周期的作用,想必大家都有所了解,不清楚的可以查看 官方文檔 https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/react-component.html 進(jìn)行學(xué)習(xí)。
接下來(lái),我們從一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單的例子入手,順著它的執(zhí)行來(lái)看看生命周期在源碼中是如何實(shí)現(xiàn)的。
Demo 組件代碼
初始化一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單組件,組件會(huì)展示一個(gè)數(shù)字和一個(gè)按鈕,每次點(diǎn)擊按鈕時(shí),數(shù)字都會(huì) + 1。
// App.jsx
import { useState } from 'react';
import ChildComponent from './ChildComponent';
function App() {
const [show, setShow] = useState(true);
return (
<>
{ show && <ChildComponent count={count} />}
<button onClick={() => setShow(pre => !pre)}>toggle</button>
</>
)
}
export default App;
// ChildComponent.jsx
import { Component } from 'react';
export default class ChildComponent extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
num: 1
}
}
render() {
const { num } = this.state;
return (
<>
<h1>{num}</h1>
<button onClick={() => this.setState({ num: num + 1 })}>點(diǎn)擊我+1</button>
</>
)
}
}
效果截圖如下所示:

當(dāng)首次進(jìn)來(lái)時(shí),會(huì)進(jìn)入裝載 Mounting 階段。
裝載階段
從 第一棵 Fiber 樹(shù)是如何生成的? 我們了解到,第一個(gè)組件、節(jié)點(diǎn)都會(huì)經(jīng)歷 beginWork、completeWork,首先來(lái)看一下,最早執(zhí)行的 constructor 是在什么地方實(shí)現(xiàn)的。
constructor
beginWork 中判斷當(dāng)前 workInProgress.tag 的類(lèi)型,由于 ChildComponent 的 tag 是 ClassComponent,所以進(jìn)入:
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberBeginWork.old.js
function beginWork(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderLanes: Lanes,
): Fiber | null {
// ...
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
// ...
case ClassComponent: {
// ...
return updateClassComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
Component,
resolvedProps,
renderLanes,
);
}
}
// ...
}
這個(gè)方法是返回 updateClassComponent 方法執(zhí)行后的返回值。
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberBeginWork.old.js
function updateClassComponent(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
Component: any,
nextProps: any,
renderLanes: Lanes,
) {
// ...
const instance = workInProgress.stateNode;
let shouldUpdate;
// 根據(jù)組件 stateNode(組件實(shí)例)的值是否為 null,以此來(lái)判斷應(yīng)該創(chuàng)建組件還是更新組件
if (instance === null) {
// In the initial pass we might need to construct the instance.
// 實(shí)例化組件,將組件實(shí)例與對(duì)應(yīng)的 fiber 節(jié)點(diǎn)關(guān)聯(lián)
constructClassInstance(workInProgress, Component, nextProps);
// 將 fiber 上的 state 和 props 更新至組件上
// 并且會(huì)檢查是否聲明了 getDervedStateFromProps 生命周期
// 有的話(huà)則會(huì)調(diào)用并且使用 getDerivedStateFromProps 生命周期函數(shù)中返回的 state 來(lái)更新組件實(shí)例上的 state
// 檢查是否聲明了 componentDidMount 生命周期,有的話(huà)則會(huì)收集標(biāo)示添加到 fiber 的 flags 屬性上
mountClassInstance(workInProgress, Component, nextProps, renderLanes);
// 創(chuàng)建組件肯定是需要更新的,所以直接為 shouldUpdate 賦值為 true
shouldUpdate = true;
}
// ...
}
這里我們能看到兩個(gè)關(guān)鍵方法,constructClassInstance、mountClassInstance。從字面意思上看,我們大概能猜出,這里可能會(huì)和 React 生命周期的 constructor 有關(guān)。
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberClassComponent.old.js
function constructClassInstance(
workInProgress: Fiber,
ctor: any, // ChildComponent
props: any,
): any {
// ...
// 實(shí)例化組件
let instance = new ctor(props, context);
// 將獲取到的組件上的 state 屬性復(fù)制給 workInProgress.memoizedState
const state = (workInProgress.memoizedState =
instance.state !== null && instance.state !== undefined
? instance.state
: null);
// 將 fiber 節(jié)點(diǎn)與組件實(shí)例相互關(guān)聯(lián),在之前更新時(shí)可復(fù)用
adoptClassInstance(workInProgress, instance);
// ...
if (__DEV__) {
if (
typeof ctor.getDerivedStateFromProps === 'function' ||
typeof instance.getSnapshotBeforeUpdate === 'function'
) {
if (
foundWillMountName !== null ||
foundWillReceivePropsName !== null ||
foundWillUpdateName !== null
) {
const componentName = getComponentNameFromType(ctor) || 'Component';
const newApiName =
typeof ctor.getDerivedStateFromProps === 'function'
? 'getDerivedStateFromProps()'
: 'getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()';
if (!didWarnAboutLegacyLifecyclesAndDerivedState.has(componentName)) {
didWarnAboutLegacyLifecyclesAndDerivedState.add(componentName);
console.error(
'Unsafe legacy lifecycles will not be called for components using new component APIs.\n\n' +
'%s uses %s but also contains the following legacy lifecycles:%s%s%s\n\n' +
'The above lifecycles should be removed. Learn more about this warning here:\n' +
'https://reactjs.org/link/unsafe-component-lifecycles',
componentName,
newApiName,
foundWillMountName !== null ? `\n ${foundWillMountName}` : '',
foundWillReceivePropsName !== null
? `\n ${foundWillReceivePropsName}`
: '',
foundWillUpdateName !== null ? `\n ${foundWillUpdateName}` : '',
);
}
}
}
// ...
return instance;
}
這個(gè)方法中,調(diào)用 new ctor(props, context) 方法,向上找 ctor 是什么?在 beginWork 對(duì)就的 case ClassComponent 中可以看到,ctor 其它就是 const Component = workInProgress.type;,而 workInProgress.type 指向的就是 ChildComponent 這個(gè) class。
通過(guò) new ctor(props, context) 新建一個(gè) class 的實(shí)例,自然,也就會(huì)執(zhí)行這個(gè) class 對(duì)應(yīng)的 constructor 構(gòu)造函數(shù)了。
此外,在開(kāi)發(fā)環(huán)境中,如果我們使用了 getDerivedStateFromProps 或者 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate,同時(shí)又使用了 UNSAFE_componentWillMount、UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps、UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate 鉤子方法,控制臺(tái)中會(huì)進(jìn)行報(bào)錯(cuò)提示,這也是在 constructClassInstance 方法中執(zhí)行的。
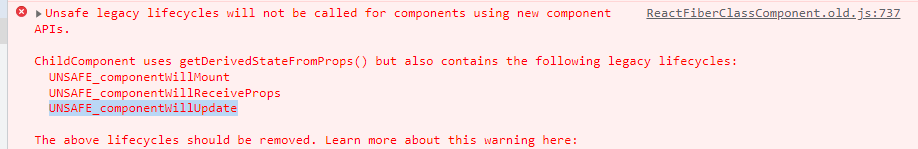
小結(jié):
constructor的執(zhí)行位置是:beginWork > updateClassComponent > constructClassInstance。
getDerivedStateFromProps & UNSAFE_componentWillMount
執(zhí)行完 constructor 生命周期后,繼續(xù)執(zhí)行 mountClassInstance(workInProgress, Component, nextProps, renderLanes);。
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberClassComponent.old.js
function mountClassInstance(
workInProgress: Fiber,
ctor: any,
newProps: any,
renderLanes: Lanes,
): void {
// ...
// 檢查當(dāng)前組件是否聲明了 getDerivedStateFromProps 生命周期函數(shù)
const getDerivedStateFromProps = ctor.getDerivedStateFromProps;
if (typeof getDerivedStateFromProps === 'function') {
// 有聲明的話(huà)則會(huì)調(diào)用并且使用 getDerivedStateFromProps 生命周期函數(shù)中返回的 state 來(lái)更新 workInProgress.memoizedState
applyDerivedStateFromProps(
workInProgress,
ctor,
getDerivedStateFromProps,
newProps,
);
// 將更新了的 state 賦值給組件實(shí)例的 state 屬性
instance.state = workInProgress.memoizedState;
}
}
這個(gè)方法會(huì)判斷組件中是否定義了 getDerivedStateFromProps,如果有就會(huì)執(zhí)行 applyDerivedStateFromProps 方法:
applyDerivedStateFromProps(
workInProgress,
ctor,
getDerivedStateFromProps,
newProps,
);
在 applyDerivedStateFromProps 這個(gè)方法中,會(huì)調(diào)用組件的 getDerivedStateFromProps 方法,將方法的返回值賦值給 workInProgress.memoizedState,具體的實(shí)現(xiàn)方法如下所示:
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberClassComponent.old.js
function applyDerivedStateFromProps(
workInProgress: Fiber,
ctor: any,
getDerivedStateFromProps: (props: any, state: any) => any,
nextProps: any,
) {
const prevState = workInProgress.memoizedState;
let partialState = getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState);
// Merge the partial state and the previous state.
const memoizedState =
partialState === null || partialState === undefined
? prevState
: assign({}, prevState, partialState);
workInProgress.memoizedState = memoizedState;
// ...
}
在 mountClassInstance 方法中,還有這樣的判斷
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberClassComponent.old.js
function mountClassInstance(
workInProgress: Fiber,
ctor: any,
newProps: any,
renderLanes: Lanes,
): void {
// ...
// In order to support react-lifecycles-compat polyfilled components,
// Unsafe lifecycles should not be invoked for components using the new APIs.
// 調(diào)用 componentWillMount 生命周期
if (
typeof ctor.getDerivedStateFromProps !== 'function' &&
typeof instance.getSnapshotBeforeUpdate !== 'function' &&
(typeof instance.UNSAFE_componentWillMount === 'function' ||
typeof instance.componentWillMount === 'function')
) {
callComponentWillMount(workInProgress, instance);
// If we had additional state updates during this life-cycle, let's
// process them now.
processUpdateQueue(workInProgress, newProps, instance, renderLanes);
instance.state = workInProgress.memoizedState;
}
// 判斷是否聲明了 componentDidMount 聲明周期,聲明了則會(huì)添加標(biāo)識(shí) Update 至 flags 中,在 commit 階段使用
if (typeof instance.componentDidMount === 'function') {
const fiberFlags: Flags = Update | LayoutStatic;
workInProgress.flags |= fiberFlags;
}
// ...
}
它的意思是,如果組件沒(méi)有定義過(guò) getDerivedStateFromProps、getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 方法,并且有定義 componentWillMount || UNSAFE_componentWillMount 方法,就會(huì)調(diào)用 callComponentWillMount 去執(zhí)行 componentWillMount || UNSAFE_componentWillMount 方法。
function callComponentWillMount(workInProgress, instance) {
const oldState = instance.state;
if (typeof instance.componentWillMount === 'function') {
instance.componentWillMount();
}
if (typeof instance.UNSAFE_componentWillMount === 'function') {
instance.UNSAFE_componentWillMount();
}
if (oldState !== instance.state) {
classComponentUpdater.enqueueReplaceState(instance, instance.state, null);
}
}
執(zhí)行會(huì)判斷 oldState 和 instance.state 是否相等,如果不相等,就會(huì)執(zhí)行 classComponentUpdater.enqueueReplaceState(instance, instance.state, null);。
小結(jié):
getDerivedStateFromProps()的調(diào)用位置是beginWork > updateClassComponent > mountClassInstance > applyDerivedStateFromProps。如果沒(méi)有定義
getDerivedStateFromProps、getSnapshotBeforeUpdate,有定義componentWillMount、UNSAFE_componentWillMount鉤子會(huì)在beginWork > updateClassComponent > mountClassInstance > callComponentWillMount調(diào)用。
執(zhí)行完對(duì)應(yīng)的 beginWork 和 completeWork 后,就會(huì)進(jìn)入到 commit 階段。
引用一下 React 的核心思想
const state = reconcile(update);
const UI = commit(state);
通過(guò) const UI = commit(state); 我們可以看出,render 應(yīng)該是和 commit 階段有關(guān)。
render
beginWork 階段執(zhí)行了 constructor、static getDerivedStateFromProps、UNSAFE_componentWillMount 生命周期。如何將 Fiber 渲染到頁(yè)面上,這就是 render 階段。
具體將 Fiber 渲染到頁(yè)面上的邏輯在 commitRootImpl > commitMutationEffects 處。完整的流程可以查看上一篇文章 React 之第一棵樹(shù)是如何渲染到頁(yè)面上的?,這里不再贅述。
componentDidMount
在 commitRootImpl 方法中執(zhí)行完 commitMutationEffects 將 Fiber 渲染到頁(yè)面上后,繼續(xù)執(zhí)行 commitRootImpl 方法中的 commitLayoutEffects 方法。
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberCommitWork.old.js
export function commitLayoutEffects(
finishedWork: Fiber,
root: FiberRoot,
committedLanes: Lanes,
): void {
// ...
commitLayoutEffectOnFiber(root, current, finishedWork, committedLanes);
}
commitLayoutEffects 方法里執(zhí)行 commitLayoutEffectOnFiber 方法。
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberCommitWork.old.js
function commitLayoutEffectOnFiber(
finishedRoot: FiberRoot,
current: Fiber | null,
finishedWork: Fiber,
committedLanes: Lanes,
): void {
// ...
case ClassComponent: {
recursivelyTraverseLayoutEffects(
finishedRoot,
finishedWork,
committedLanes,
);
if (flags & Update) {
commitClassLayoutLifecycles(finishedWork, current);
}
// ...
}
// ...
}
經(jīng)歷過(guò)一些判斷以及遍歷,最后會(huì)進(jìn)入 case ClassComponent 階段的 commitClassLayoutLifecycles 中。
// packages\react-reconciler\src\ReactFiberCommitWork.old.js
function commitClassLayoutLifecycles(
finishedWork: Fiber,
current: Fiber | null,
) {
const instance = finishedWork.stateNode;
if (current === null) {
if (shouldProfile(finishedWork)) {
// ...
} else {
try {
instance.componentDidMount();
} catch (error) {
captureCommitPhaseError(finishedWork, finishedWork.return, error);
}
}
} else {
const prevProps =
finishedWork.elementType === finishedWork.type
? current.memoizedProps
: resolveDefaultProps(finishedWork.type, current.memoizedProps);
const prevState = current.memoizedState;
if (shouldProfile(finishedWork)) {
// ...
} else {
try {
instance.componentDidUpdate(
prevProps,
prevState,
instance.__reactInternalSnapshotBeforeUpdate,
);
} catch (error) {
captureCommitPhaseError(finishedWork, finishedWork.return, error);
}
}
}
}
從這個(gè)方法中可以看出,如果 current === null (首次加載),就會(huì)調(diào)用 instance.componentDidMount();。如果 current !== null(更新),就會(huì)調(diào)用 instance.componentDidUpdate。
小結(jié):
componentDidMount的執(zhí)行位置是:commitRoot > commitRootImpl > commitLayoutEffects > commitLayoutEffectOnFiber > recursivelyTraverseLayoutEffects > commitClassLayoutLifecycles。
完成的代碼執(zhí)行流程圖如下所示:
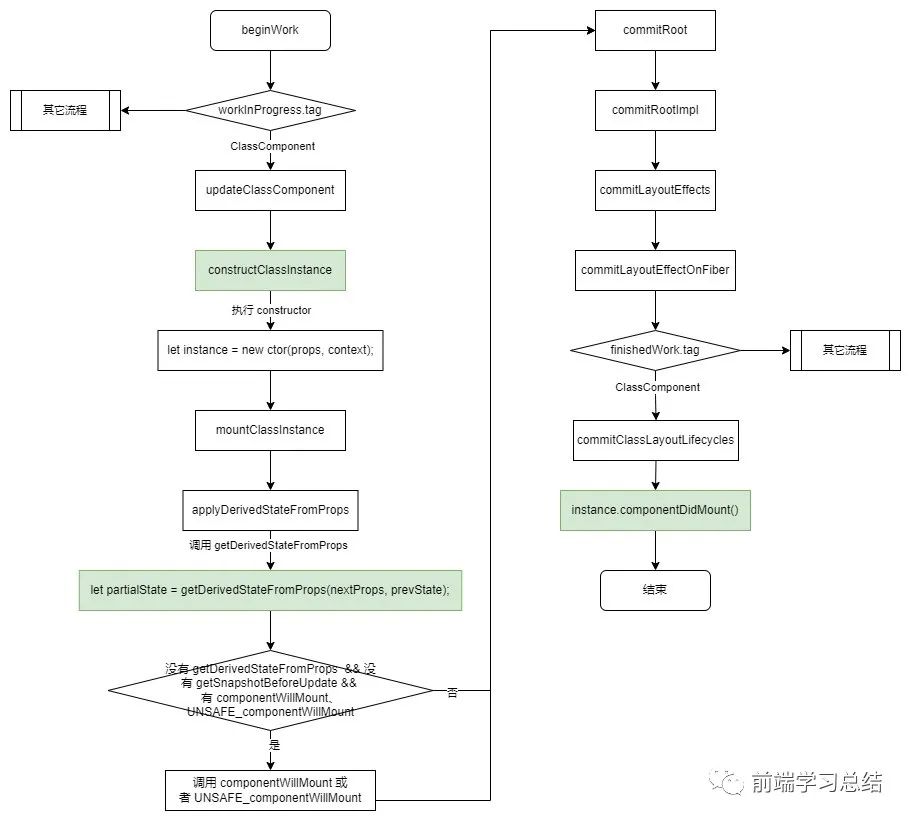
到目前為止,裝載階段的生命周期就完成了,下面,來(lái)看一下更新階段的生命周期是如何實(shí)現(xiàn)的。
更新階段
當(dāng)我們點(diǎn)擊 Demo 中的 點(diǎn)擊我+1 按鈕,數(shù)字 1 將變成 2,在此期間,會(huì)怎樣執(zhí)行呢?

通過(guò) setState 觸發(fā) React 更新。React 會(huì)從 FiberRoot 開(kāi)始進(jìn)行處理。
提個(gè)問(wèn)題:為什么每次更新
React都要從根節(jié)點(diǎn)開(kāi)始執(zhí)行?它是如何保證性能的?這樣做的原因是什么?為什么它不從更新的組件開(kāi)始?這個(gè)問(wèn)題先提到這里,后面再單獨(dú)總結(jié)。
為方便理解,這里將代碼的執(zhí)行流程做成了一個(gè)流程圖,具體如下所示:
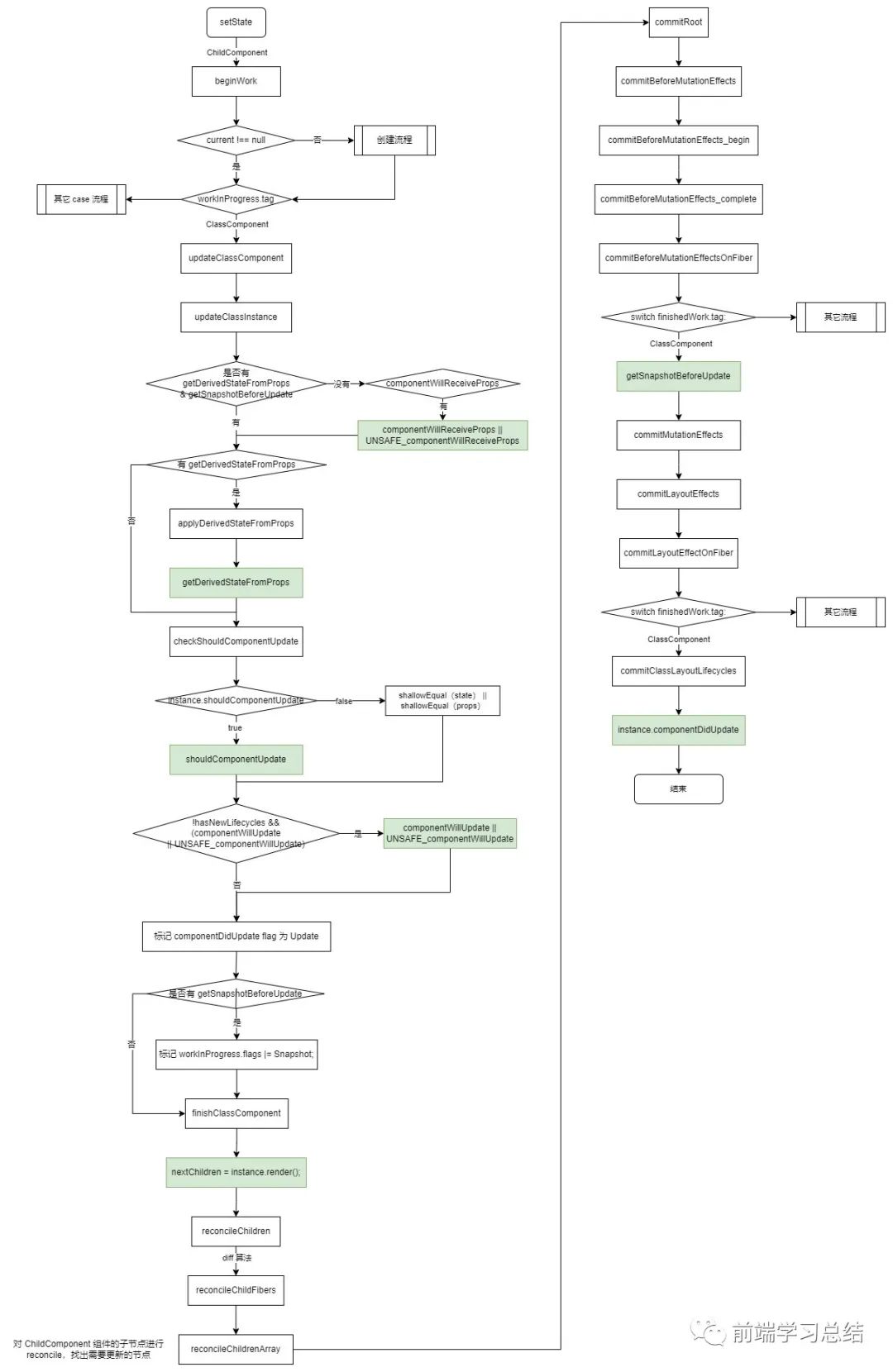
當(dāng) workInProgress 經(jīng)過(guò) workLoop 遍歷到 ChildComponent 時(shí),又會(huì)開(kāi)始進(jìn)入它的 beginWork。通過(guò)之前的學(xué)習(xí),我們了解到,在 Mounting 階段,current 為 null,更新階段 current 不為 null。再加上 ChildComponent 的 type 類(lèi)型為 ClassComponent,所以 ChildComponent 會(huì)執(zhí)行 updateClassComponent 方法。
執(zhí)行 updateClassInstance 方法,在這個(gè)方法中會(huì)判斷組件中是否定義了 getDerivedStateFromProps 或者 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate。如果沒(méi)有定義,才會(huì)檢查是否有定義 *_componentWillReceiveProps 方法并執(zhí)行它。如果這兩種都存在,在 Mounting 階段執(zhí)行 constructClassInstance 就會(huì)打印 error 信息。

繼續(xù)執(zhí)行后面的代碼,發(fā)現(xiàn)如果組件中有定義 getDerivedStateFromProps 就會(huì)執(zhí)行 getDerivedStateFromProps 方法,將方法的返回值掛載到 workInProgress.memoizedState,所以這個(gè)方法可以用來(lái)在渲染前根據(jù)新的 props 和舊的 state 計(jì)算衍生數(shù)據(jù)。
執(zhí)行完 getDerivedStateFromProps 就會(huì)開(kāi)始檢查是否定義了 shouldComponentUpdate,如果有定義,執(zhí)行 shouldComponentUpdate 方法,并將方法的返回值用于判斷頁(yè)面是否需要更新的依據(jù)。如果返回 true,說(shuō)明需要更新,如果此時(shí)組件中有定義 componentWillUpdate 也會(huì)執(zhí)行它,然后根據(jù)條件修改 workInProgress.flags 的值為 Update 或者 Snapshot。在 commit 階段,會(huì)根據(jù)不同的 flags 對(duì)組件進(jìn)行不同的處理。
調(diào)用 render 方法,拿到當(dāng)前組件的子節(jié)點(diǎn)內(nèi)容。
在將新的內(nèi)容 commitMutationEffects (將新節(jié)點(diǎn)渲染到頁(yè)面之前),調(diào)用 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate。所以在 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 中,我們可以訪(fǎng)問(wèn)更新前的 props 和 state 以及舊的 DOM 節(jié)點(diǎn)信息,并且它的返回值會(huì)綁定到當(dāng)前 Fiber 節(jié)點(diǎn)的 __reactInternalSnapshotBeforeUpdate 屬性上面,這個(gè)參數(shù)會(huì)作為后面的 componentDidUpdate 鉤子的第三個(gè)參數(shù)調(diào)用。
這個(gè)特性在處理渲染頁(yè)面前,需要獲取之前的頁(yè)面信息,并根據(jù)之前的頁(yè)面信息執(zhí)行一些新的交互上有奇效。比如:收到新消息時(shí),需要自動(dòng)滾動(dòng)到新消息處。
執(zhí)行完 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate,繼續(xù)執(zhí)行 commitLayoutEffects,然后在 commitLayoutEffectOnFiber 里面經(jīng)過(guò)不同的 case 調(diào)用 recursivelyTraverseLayoutEffects 方法,這個(gè)方法又會(huì)將 parentFiber.child 作為參數(shù)繼續(xù)調(diào)用 commitLayoutEffectOnFiber,直到找到 ChildComponent。執(zhí)行完 case ClassComponent 里面的 recursivelyTraverseLayoutEffects 方法,就會(huì)開(kāi)始調(diào)用 commitClassLayoutLifecycles 方法,這個(gè)方法中就會(huì)判斷,如果有定義 componentDidUpdate 就會(huì)執(zhí)行它。如果有執(zhí)行 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate,還會(huì)將它的返回值作為第三個(gè)參數(shù)傳給 componentDidUpdate 來(lái)執(zhí)行。
小結(jié):到目前為止,更新階段就執(zhí)行完了。有一些不再維護(hù)的生命周期,會(huì)根據(jù)組件中是否有定義最新的一些生命周期來(lái)判斷是否需要執(zhí)行。
卸載階段
當(dāng)點(diǎn)擊 Demo 中的 toggle 按鈕時(shí),會(huì)觸發(fā) setShow(false)。此時(shí)頁(yè)面的展示代碼如下:
<div style={{ padding: 20 }}>
{ false && <ChildComponent count={count} />}
<button onClick={() => setShow(pre => !pre)}>toggle</button>
</div>
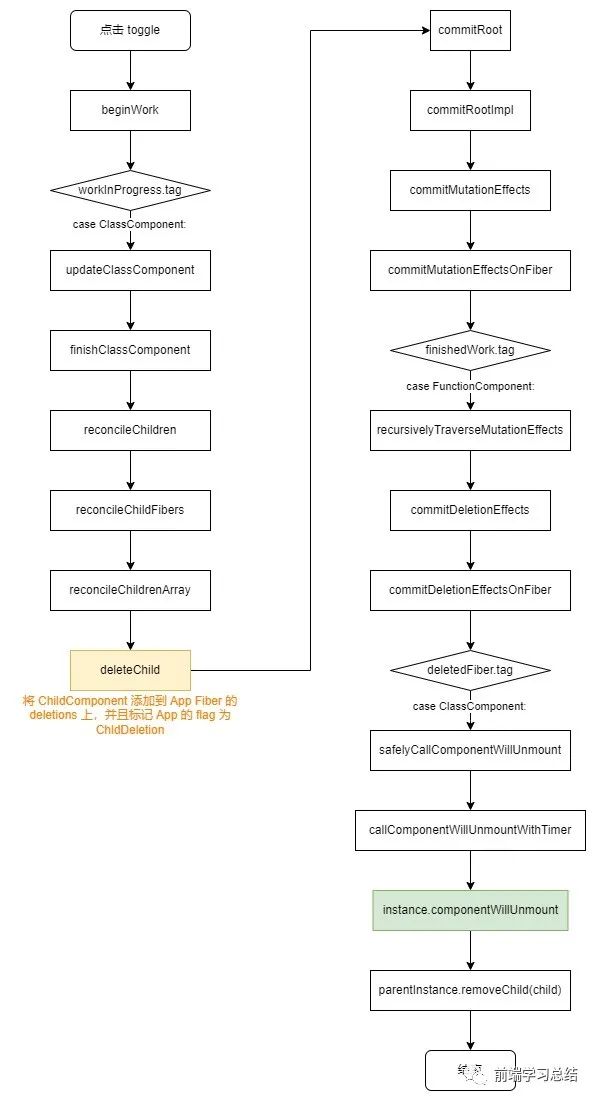
React 又開(kāi)始對(duì)每個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)進(jìn)行 beginWork。當(dāng)遍歷到 App 節(jié)點(diǎn)時(shí),它下面有兩個(gè)子節(jié)點(diǎn),false & <button> 按鈕。進(jìn)入 reconcileChildrenArray 進(jìn)行 diff 算法的比較。當(dāng)比較 { false && <ChildComponent count={count} />} 時(shí),發(fā)現(xiàn)這個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)的值是 boolean,它是一個(gè)條件判斷值,和需要渲染的任何類(lèi)型都不相關(guān),此時(shí),會(huì)將這個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)對(duì)應(yīng)的原來(lái)的 <ChildComponent count={count} /> 添加到它的 returnFiber 也就是 App Fiber 的 deleteChild 屬性中,并添加 App Fiber 的 Flag 為 ChildDeletion。這個(gè)在 commit 階段,也會(huì)遍歷節(jié)點(diǎn),如果發(fā)現(xiàn)節(jié)點(diǎn)有 deleteChild 值,在 commitMutationEffects 時(shí)就會(huì)對(duì)這個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)進(jìn)行刪除。
真正執(zhí)行刪除前,如果組件中有定義 componentWillUnmount,會(huì)對(duì) componentWillUnmount 進(jìn)行調(diào)用。調(diào)用結(jié)束后,會(huì)執(zhí)行 parentInstance.removeChild(child) 將節(jié)點(diǎn)從頁(yè)面中真正的移除。
完整的執(zhí)行流程圖如下所示:
總結(jié)
通過(guò)上面的學(xué)習(xí)以及每個(gè)步驟的小結(jié),我們知道了 裝載、更新、卸載 的具體實(shí)現(xiàn)原理。但也留下了幾個(gè)疑問(wèn):
-
為什么每次更新都要從 FiberRoot節(jié)點(diǎn)開(kāi)始? -
錯(cuò)誤處理是如何實(shí)現(xiàn)的? -
diff算法的具體實(shí)現(xiàn)邏輯是什么? -
現(xiàn)在都推薦使用 Hooks寫(xiě)法,Class寫(xiě)法以及它的生命周期還有什么作用,還需要這樣深入學(xué)習(xí)嗎? -
Hooks的生命周期是如何實(shí)現(xiàn)的?
這里的每一個(gè)疑問(wèn)都值得好好思考,后面再單獨(dú)總結(jié)。
最后,文章如果有寫(xiě)得不對(duì)的地方,歡迎指正、一起探討!!!
