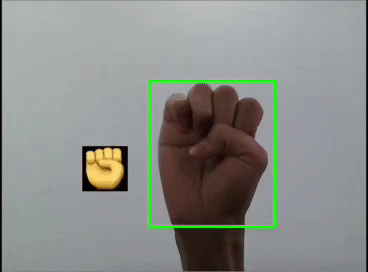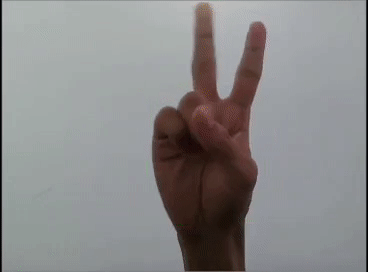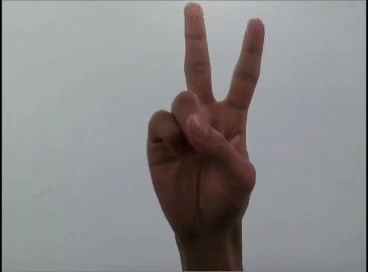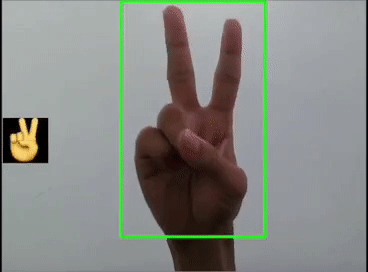
用YOLOv5模型識(shí)別出表情!
本文利用YOLOV5對(duì)手勢(shì)進(jìn)行訓(xùn)練識(shí)別,并識(shí)別顯示出對(duì)應(yīng)的emoji,如同下圖:
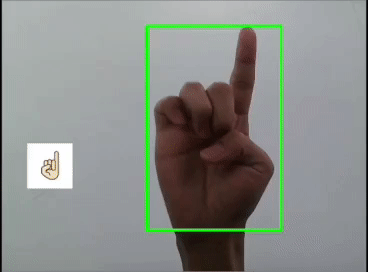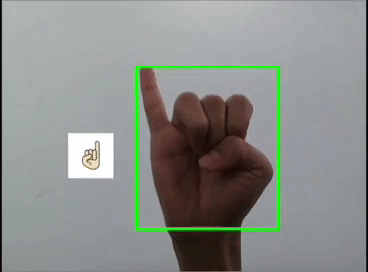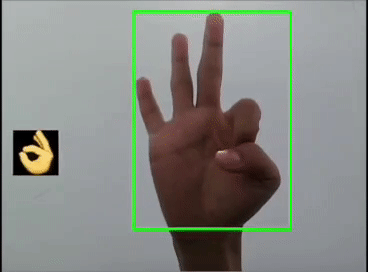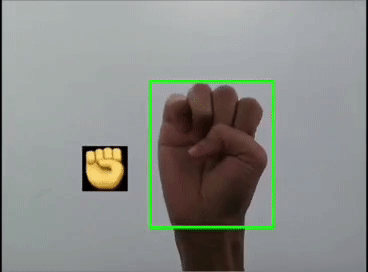
一 、YOLOV5訓(xùn)練數(shù)據(jù)集
1. 安裝環(huán)境依賴
本教程所用環(huán)境:YOLOV5版本是V3.1。
通過(guò)git clone 將源碼下載到本地,通過(guò)pip install -r requirements.txt 安裝依賴包 (其中官方要求python>=3.8 and torch>=1.6)。
我的環(huán)境是:系統(tǒng)環(huán)境Ubuntu16.04;cuda版本10.2;cudnn版本7.6.5;torch版本1.6.0;python版本3.8
2. 準(zhǔn)備手勢(shì)識(shí)別數(shù)據(jù)集
其中手勢(shì)數(shù)據(jù)集已上傳至開(kāi)源數(shù)據(jù)平臺(tái)Graviti,包含了完整代碼。
手勢(shì)數(shù)據(jù)集地址:https://gas.graviti.cn/dataset/datawhale/HandPose?utm_medium=0831datawhale
2.1 數(shù)據(jù)集的采集以及標(biāo)注
手勢(shì)數(shù)據(jù)采集的代碼:
import cv2
def main():
total_pics = 1000
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
pic_no = 0
flag_start_capturing = False
frames = 0
while True:
ret,frame = cap.read()
frame = cv2.flip(frame,1)
cv2.imwrite("hand_images/" +str(pic_no) +".jpg",frame)
cv2.imshow("Capturing gesture",frame)
cv2.waitKey(10)
pic_no += 1
if pic_no == total_pics:
break
main()
在yolov5目錄下創(chuàng)建VOC2012文件夾(名字自己定義的),目錄結(jié)構(gòu)就是VOC數(shù)據(jù)集的,對(duì)應(yīng)如下:
VOC2012 ../Annotations #這個(gè)是存放數(shù)據(jù)集圖片對(duì)應(yīng)的xml文件 ../images #這個(gè)存放圖片的 ../ImageSets/Main #這個(gè)主要是存放train.txt,test.txt,val.txt和trainval.txt四個(gè)文件。里面的內(nèi)容是訓(xùn)練集、測(cè)試集、驗(yàn)證集以及訓(xùn)練驗(yàn)證集的名字(不帶擴(kuò)展后綴名)。
示例:
VOC2012文件夾下內(nèi)容:
Annotations文件中是xml文件(labelimg標(biāo)注的):
images為VOC數(shù)據(jù)集格式中的JPRGImages:
ImageSets文件中Main子文件夾主要存放訓(xùn)練,測(cè)試驗(yàn)證集的劃分txt。這個(gè)劃分通過(guò)以下腳本代碼生成:
# coding:utf-8
import os
import random
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
#xml文件的地址,根據(jù)自己的數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行修改 xml一般存放在Annotations下
parser.add_argument('--xml_path', default='C:\\Users\\Lenovo\\Desktop\\hand_datasets\\VOC2012\\Annotations\\', type=str, help='input xml label path')
#數(shù)據(jù)集的劃分,地址選擇自己數(shù)據(jù)下的ImageSets/Main
parser.add_argument('--txt_path', default='C:\\Users\\Lenovo\\Desktop\\hand_datasets\\VOC2012\\ImageSets\\Main\\', type=str, help='output txt label path')
opt = parser.parse_args()
trainval_percent = 1.0
train_percent = 0.99
xmlfilepath = opt.xml_path
txtsavepath = opt.txt_path
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
if not os.path.exists(txtsavepath):
os.makedirs(txtsavepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list_index = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list_index, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
file_trainval = open(txtsavepath + 'trainval.txt', 'w')
file_test = open(txtsavepath + 'test.txt', 'w')
file_train = open(txtsavepath + 'train.txt', 'w')
file_val = open(txtsavepath + 'val.txt', 'w')
for i in list_index:
name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'
if i in trainval:
file_trainval.write(name)
if i in train:
file_train.write(name)
else:
file_val.write(name)
else:
file_test.write(name)
file_trainval.close()
file_train.close()
file_val.close()
file_test.close()
運(yùn)行代碼在Main文件下生成txt文檔如下:

2.2 生成yolo訓(xùn)練格式labels
把xml標(biāo)注信息轉(zhuǎn)換成yolo的txt格式。其中yolo的txt標(biāo)簽格式信息:每個(gè)圖像對(duì)應(yīng)一個(gè)txt文件,文件每一行為一個(gè)目標(biāo)信息,包括classx_center, y_center, width, height 格式。如下圖所示:
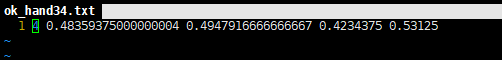
創(chuàng)建voc_label.py文件,將訓(xùn)練集,驗(yàn)證集以及測(cè)試集生成txt標(biāo)簽,代碼如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
from os import getcwd
sets = ['train', 'val', 'test']
classes = ["four_fingers","hand_with_fingers_splayed","index_pointing_up","little_finger","ok_hand","raised_fist","raised_hand","sign_of_the_horns","three","thumbup","victory_hand"]
# 11 classes # 改成自己的類別
abs_path = os.getcwd()
print(abs_path)
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / (size[0])
dh = 1. / (size[1])
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0 - 1
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return x, y, w, h
def convert_annotation(image_id):
in_file = open('/home/yanyq/Ryan/yolov5/VOC2012/Annotations/%s.xml' % (image_id), encoding='UTF-8')
out_file = open('/home/yanyq/Ryan/yolov5/VOC2012/labels/%s.txt' % (image_id), 'w')
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
# difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
b1, b2, b3, b4 = b
# 標(biāo)注越界修正
if b2 > w:
b2 = w
if b4 > h:
b4 = h
b = (b1, b2, b3, b4)
bb = convert((w, h), b)
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
wd = getcwd()
for image_set in sets:
if not os.path.exists('/home/yanyq/Ryan/yolov5/VOC2012/labels/'):
os.makedirs('/home/yanyq/Ryan/yolov5/VOC2012/labels/')
image_ids = open('/home/yanyq/Ryan/yolov5/VOC2012/ImageSets/Main/%s.txt' % (image_set)).read().strip().split()
list_file = open('%s.txt' % (image_set), 'w')
for image_id in image_ids:
list_file.write(abs_path + '/images/%s.jpg\n' % (image_id))
convert_annotation(image_id)
list_file.close()
運(yùn)行上述腳本后會(huì)生成labels文件夾和三個(gè)包含數(shù)據(jù)集的txt文件,其中l(wèi)abels中為圖像的yolo格式標(biāo)注文件,train.txt,test.txt, val.txt文件為劃分后圖像所在位置的絕對(duì)路徑。
三個(gè)txt文件內(nèi)容:
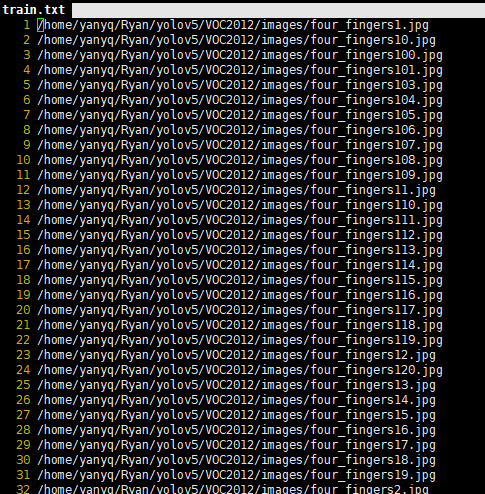
2.3 配置文件
1)數(shù)據(jù)集的配置
在yolov5目錄的data文件夾新建一個(gè)Emoji.yaml文件(自己定義)。用來(lái)存放訓(xùn)練集驗(yàn)證集的劃分文件train.txt和val.txt(其中這兩個(gè)文件是voc_label.py生成的)。具體內(nèi)容如下:
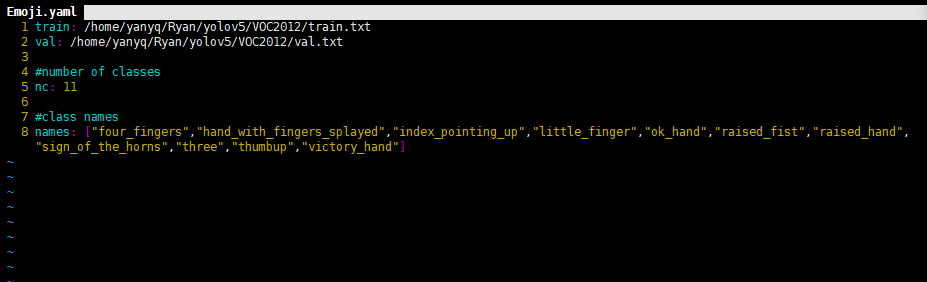
2)模型的配置文件
一般訓(xùn)練yolo模型的時(shí)候,是可以聚類自己標(biāo)注的框作為先驗(yàn)框(這樣可以保證標(biāo)注樣本最大化的利用)。我們這里就直接采用默認(rèn)值了。
選擇一個(gè)需要的模型,YOLOV5有提供s、m、l、x版本,其是逐漸增大的架構(gòu),也就是訓(xùn)練時(shí)間和推理時(shí)間都對(duì)應(yīng)增加,我們這里選擇s版本。在yolov5文件夾下的models文件夾中打開(kāi)yolov5s.yaml文件,修改內(nèi)容如下圖(我們選擇默認(rèn)anchor,所以不做修改,只需要更改nc中的類別數(shù),由于我們是11類,所以改成11就可以了):
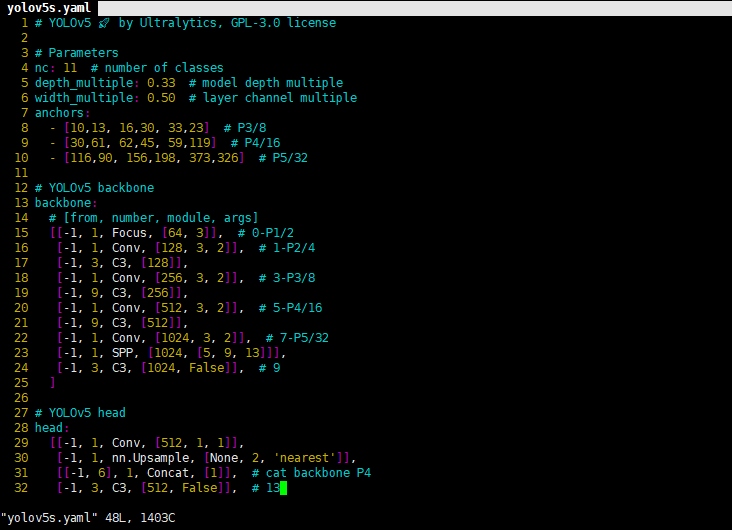
到這里我們的自定義數(shù)據(jù)集以及配置文件創(chuàng)建完畢,下面就是訓(xùn)練模型了。
3.模型訓(xùn)練
3.1、下載預(yù)訓(xùn)練模型
在源碼yolov5目錄下的weights文件夾下提供了下載smlx模型的腳本--download_weights.sh,執(zhí)行這個(gè)腳本就可以下載這四個(gè)模型的預(yù)訓(xùn)練模型了。
3.2、訓(xùn)練模型
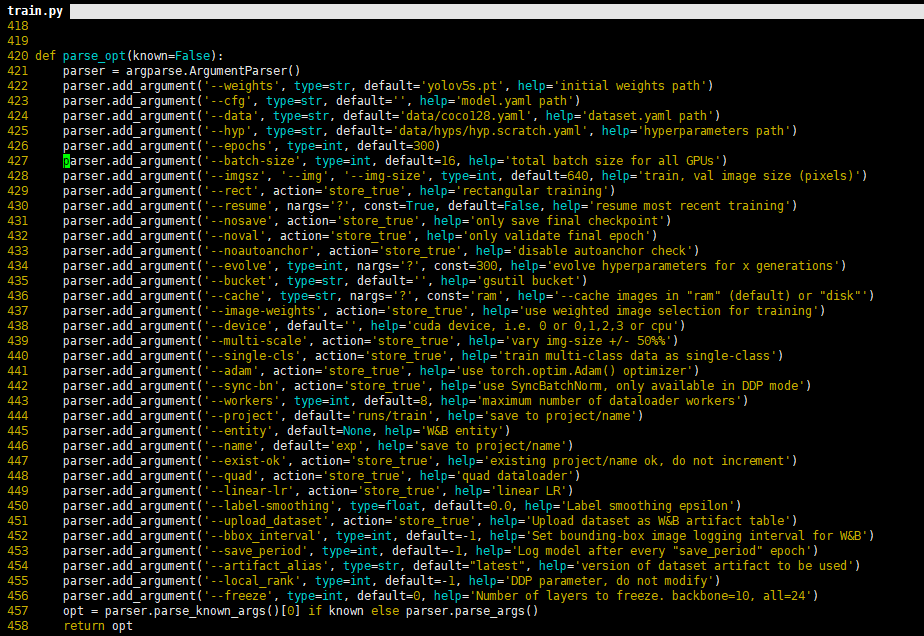
以上參數(shù)解釋如下:epochs:指的就是訓(xùn)練過(guò)程中整個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)集將被迭代多少次,顯卡不行你就調(diào)小點(diǎn)。batch-size:一次看完多少?gòu)垐D片才進(jìn)行權(quán)重更新,梯度下降的mini-batch,顯卡不行你就調(diào)小點(diǎn)。cfg:存儲(chǔ)模型結(jié)構(gòu)的配置文件。data:存儲(chǔ)訓(xùn)練、測(cè)試數(shù)據(jù)的文件。img-size:輸入圖片寬高,顯卡不行你就……。rect:進(jìn)行矩形訓(xùn)練。resume:恢復(fù)最近保存的模型開(kāi)始訓(xùn)練。nosave:僅保存最終checkpoint。notest:僅測(cè)試最后的epoch。evolve:進(jìn)化超參數(shù)。bucket:gsutil bucket。 cache-images:緩存圖像以加快訓(xùn)練速度。 weights:權(quán)重文件路徑。name:重命名results.txt to results_name.txt。device:cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu。adam:使用adam優(yōu)化。multi-scale:多尺度訓(xùn)練,img-size +/- 50%。single-cls:單類別的訓(xùn)練集
訓(xùn)練只需要運(yùn)行訓(xùn)練命令就可以了,如下:
$ python train.py --data Emoji.yaml --cfg yolov5s.yaml --weights weights/yolov5s.pt --batch-size 64 --device "0,1,2,3" --epochs 200 --img-size 640
其中device batch-size 等需要根據(jù)自己機(jī)器進(jìn)行設(shè)置。
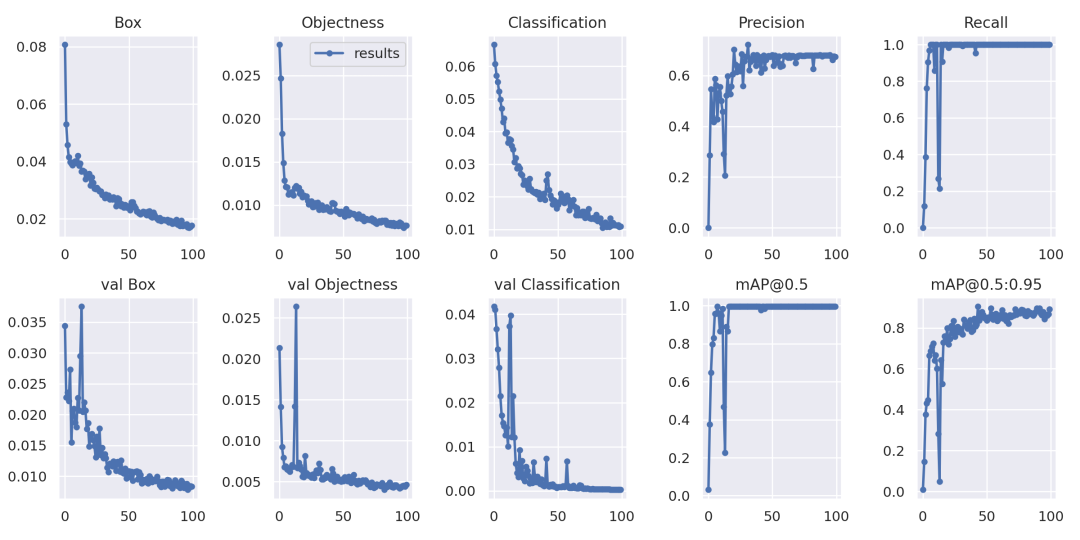
4.模型測(cè)試
評(píng)估模型好壞就是在有標(biāo)注的測(cè)試集或驗(yàn)證集上進(jìn)行模型效果的評(píng)估,在目標(biāo)檢測(cè)中最常使用的評(píng)估指標(biāo)為mAP。yolov5文件下的test.py文件中指定了數(shù)據(jù)集的配置文件和訓(xùn)練結(jié)果模型如下:
通過(guò)以下命令進(jìn)行模型測(cè)試:
python test.py --data data/Emoji.yaml --weights runs/train/exp2/weights/best.pt --augment
模型測(cè)試效果:

測(cè)試結(jié)果圖:

二、YOLOV5模型轉(zhuǎn)換
1.安裝依賴庫(kù)
pip install onnx coremltools onnx-simplifier
2.導(dǎo)出ONNX模型
python models/export.py --weights runs/train/exp2/weights/best.pt --img 640 --batch 1
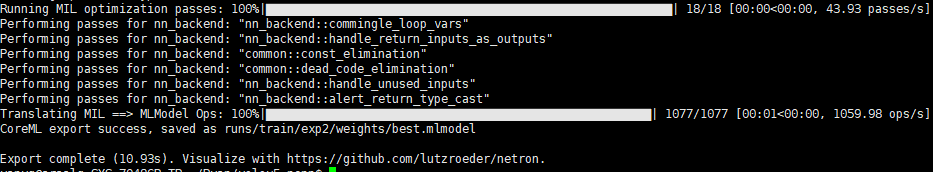
此時(shí)在best.pt同級(jí)目錄下生成了best.mlmodel best.onnx best.torchscript.pt三個(gè)文件,我們只需best.onnx,這個(gè)文件可以直接用netron打開(kāi)查看模型結(jié)構(gòu)。
3.用onnx-simplifer簡(jiǎn)化模型
為什么要簡(jiǎn)化?
在訓(xùn)練完深度學(xué)習(xí)的pytorch或者tensorflow模型后,有時(shí)候需要把模型轉(zhuǎn)成 onnx,但是很多時(shí)候,很多節(jié)點(diǎn)比如cast節(jié)點(diǎn),Identity 這些節(jié)點(diǎn)可能都不需要,我們需要進(jìn)行簡(jiǎn)化,這樣會(huì)方便我們把模型轉(zhuǎn)成ncnn或者mnn等這些端側(cè)部署的模型格式或者通過(guò)tensorRT進(jìn)行部署。
python -m onnxsim best.onnx yolov5-best-sim.onnx

完成后就生成了簡(jiǎn)化版本的模型yolov5-best-sim.onnx。
三、YOLOV5轉(zhuǎn)換成ncnn模型
1、onnx轉(zhuǎn).param .bin
由上述生成了yolov5-best-sim.onnx這個(gè)模型,我們利用ncnn自帶的工具onnx2ncnn.exe(這個(gè)工具是自己編譯生成的,我這里是在windows下編譯生成的,可以用linux下的可執(zhí)行文件)生成yolov5s.param yolov5s.bin兩個(gè)文件。
在windows平臺(tái)下ctrl+r cmd命令行窗口輸入:
onnx2ncnn.exe yolov5-best-sim.onnx yolov5s.param yolov5s.bin
2、修改.param 參數(shù)去除不支持的網(wǎng)絡(luò)層
去掉不支持的網(wǎng)絡(luò)層,打開(kāi)轉(zhuǎn)換得到的yolov5s.param文件,前面幾行需要?jiǎng)h除的是標(biāo)紅部分。(注意我們訓(xùn)練yoloV5的版本是V3.1,這里不同的版本可能會(huì)不同。)
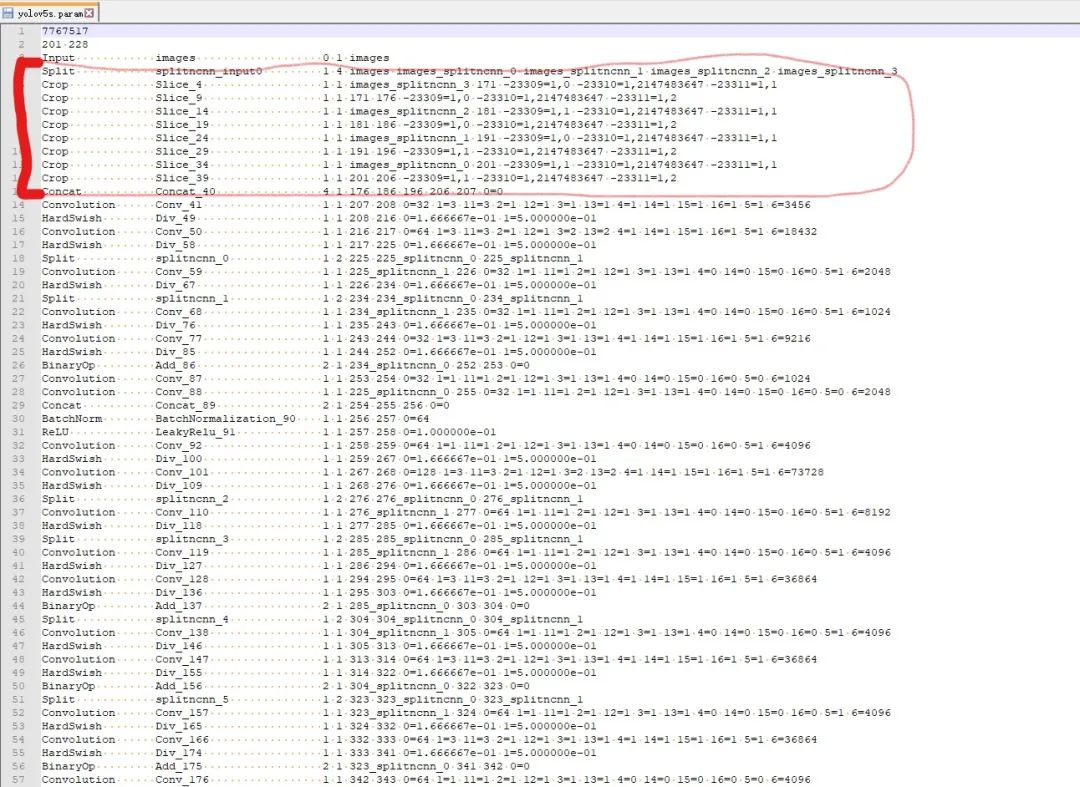
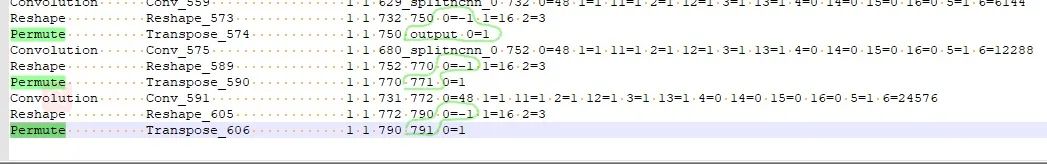
修改結(jié)果如下綠色框和紅色框中的。因?yàn)槿サ袅?0層所以變成191 228。并用YoloV5Focus網(wǎng)絡(luò)層代替去掉的10層,而YoloV5Focus網(wǎng)絡(luò)層中的images代表該層的輸入,207代表的輸出名,這個(gè)是根據(jù)下邊一層的卷積層輸入層數(shù)寫的。
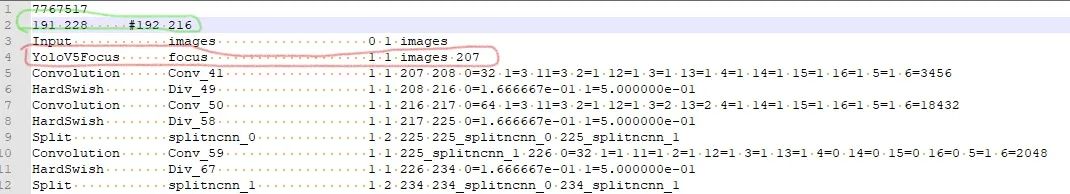
修改網(wǎng)路的輸出shape:
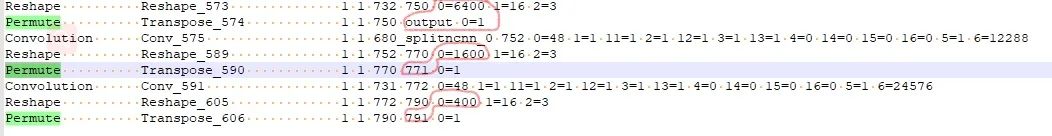
當(dāng)基于修改后的網(wǎng)路使用ncnn/examples/yolov5測(cè)試時(shí)會(huì)發(fā)現(xiàn)出現(xiàn)圖片中一堆亂框,這種情況需要修改網(wǎng)路的輸出部分。在保證輸出名一致的情況下,修改Reshape中的0=-1,使的最終的輸出shape不固定。具體的修改地方以及修改之前和之后見(jiàn)下圖。
3、ncnn的c++測(cè)試代碼實(shí)現(xiàn)
以下是用C++實(shí)現(xiàn)的完整代碼。建議一劃到底,先看最后的整體思路
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include "iostream"
//#include <fstream>
//#include < ctime >
//#include <direct.h>
//#include <io.h>
// ncnn
#include "ncnn/layer.h"
#include "ncnn/net.h"
#include "ncnn/benchmark.h"
//#include "gpu.h"
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
static ncnn::UnlockedPoolAllocator g_blob_pool_allocator;
static ncnn::PoolAllocator g_workspace_pool_allocator;
static ncnn::Net yolov5;
class YoloV5Focus : public ncnn::Layer
{
public:
YoloV5Focus()
{
one_blob_only = true;
}
virtual int forward(const ncnn::Mat& bottom_blob, ncnn::Mat& top_blob, const ncnn::Option& opt) const
{
int w = bottom_blob.w;
int h = bottom_blob.h;
int channels = bottom_blob.c;
int outw = w / 2;
int outh = h / 2;
int outc = channels * 4;
top_blob.create(outw, outh, outc, 4u, 1, opt.blob_allocator);
if (top_blob.empty())
return -100;
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(opt.num_threads)
for (int p = 0; p < outc; p++)
{
const float* ptr = bottom_blob.channel(p % channels).row((p / channels) % 2) + ((p / channels) / 2);
float* outptr = top_blob.channel(p);
for (int i = 0; i < outh; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < outw; j++)
{
*outptr = *ptr;
outptr += 1;
ptr += 2;
}
ptr += w;
}
}
return 0;
}
};
DEFINE_LAYER_CREATOR(YoloV5Focus)
struct Object
{
float x;
float y;
float w;
float h;
int label;
float prob;
};
static inline float intersection_area(const Object& a, const Object& b)
{
if (a.x > b.x + b.w || a.x + a.w < b.x || a.y > b.y + b.h || a.y + a.h < b.y)
{
// no intersection
return 0.f;
}
float inter_width = std::min(a.x + a.w, b.x + b.w) - std::max(a.x, b.x);
float inter_height = std::min(a.y + a.h, b.y + b.h) - std::max(a.y, b.y);
return inter_width * inter_height;
}
static void qsort_descent_inplace(std::vector<Object>& faceobjects, int left, int right)
{
int i = left;
int j = right;
float p = faceobjects[(left + right) / 2].prob;
while (i <= j)
{
while (faceobjects[i].prob > p)
i++;
while (faceobjects[j].prob < p)
j--;
if (i <= j)
{
// swap
std::swap(faceobjects[i], faceobjects[j]);
i++;
j--;
}
}
#pragma omp parallel sections
{
#pragma omp section
{
if (left < j) qsort_descent_inplace(faceobjects, left, j);
}
#pragma omp section
{
if (i < right) qsort_descent_inplace(faceobjects, i, right);
}
}
}
static void qsort_descent_inplace(std::vector<Object>& faceobjects)
{
if (faceobjects.empty())
return;
qsort_descent_inplace(faceobjects, 0, faceobjects.size() - 1);
}
static void nms_sorted_bboxes(const std::vector<Object>& faceobjects, std::vector<int>& picked, float nms_threshold)
{
picked.clear();
const int n = faceobjects.size();
std::vector<float> areas(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
areas[i] = faceobjects[i].w * faceobjects[i].h;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
const Object& a = faceobjects[i];
int keep = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < (int)picked.size(); j++)
{
const Object& b = faceobjects[picked[j]];
// intersection over union
float inter_area = intersection_area(a, b);
float union_area = areas[i] + areas[picked[j]] - inter_area;
// float IoU = inter_area / union_area
if (inter_area / union_area > nms_threshold)
keep = 0;
}
if (keep)
picked.push_back(i);
}
}
static inline float sigmoid(float x)
{
return static_cast<float>(1.f / (1.f + exp(-x)));
}
static void generate_proposals(const ncnn::Mat& anchors, int stride, const ncnn::Mat& in_pad, const ncnn::Mat& feat_blob, float prob_threshold, std::vector<Object>& objects)
{
const int num_grid = feat_blob.h;
int num_grid_x;
int num_grid_y;
if (in_pad.w > in_pad.h)
{
num_grid_x = in_pad.w / stride;
num_grid_y = num_grid / num_grid_x;
}
else
{
num_grid_y = in_pad.h / stride;
num_grid_x = num_grid / num_grid_y;
}
const int num_class = feat_blob.w - 5;
const int num_anchors = anchors.w / 2;
for (int q = 0; q < num_anchors; q++)
{
const float anchor_w = anchors[q * 2];
const float anchor_h = anchors[q * 2 + 1];
const ncnn::Mat feat = feat_blob.channel(q);
for (int i = 0; i < num_grid_y; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < num_grid_x; j++)
{
const float* featptr = feat.row(i * num_grid_x + j);
// find class index with max class score
int class_index = 0;
float class_score = -FLT_MAX;
for (int k = 0; k < num_class; k++)
{
float score = featptr[5 + k];
if (score > class_score)
{
class_index = k;
class_score = score;
}
}
float box_score = featptr[4];
float confidence = sigmoid(box_score) * sigmoid(class_score);
if (confidence >= prob_threshold)
{
float dx = sigmoid(featptr[0]);
float dy = sigmoid(featptr[1]);
float dw = sigmoid(featptr[2]);
float dh = sigmoid(featptr[3]);
float pb_cx = (dx * 2.f - 0.5f + j) * stride;
float pb_cy = (dy * 2.f - 0.5f + i) * stride;
float pb_w = pow(dw * 2.f, 2) * anchor_w;
float pb_h = pow(dh * 2.f, 2) * anchor_h;
float x0 = pb_cx - pb_w * 0.5f;
float y0 = pb_cy - pb_h * 0.5f;
float x1 = pb_cx + pb_w * 0.5f;
float y1 = pb_cy + pb_h * 0.5f;
Object obj;
obj.x = x0;
obj.y = y0;
obj.w = x1 - x0;
obj.h = y1 - y0;
obj.label = class_index;
obj.prob = confidence;
objects.push_back(obj);
}
}
}
}
}
extern "C" {
void release()
{
fprintf(stderr, "YoloV5Ncnn finished!");
//ncnn::destroy_gpu_instance();
}
int init()
{
fprintf(stderr, "YoloV5Ncnn init!\n");
ncnn::Option opt;
opt.lightmode = true;
opt.num_threads = 4;
opt.blob_allocator = &g_blob_pool_allocator;
opt.workspace_allocator = &g_workspace_pool_allocator;
opt.use_packing_layout = true;
yolov5.opt = opt;
yolov5.register_custom_layer("YoloV5Focus", YoloV5Focus_layer_creator);
// init param
{
int ret = yolov5.load_param("yolov5s.param");
if (ret != 0)
{
std::cout << "ret= " << ret << std::endl;
fprintf(stderr, "YoloV5Ncnn, load_param failed");
return -301;
}
}
// init bin
{
int ret = yolov5.load_model("yolov5s.bin");
if (ret != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "YoloV5Ncnn, load_model failed");
return -301;
}
}
return 0;
}
int detect(cv::Mat img, std::vector<Object> &objects)
{
double start_time = ncnn::get_current_time();
const int target_size = 320;
// letterbox pad to multiple of 32
const int width = img.cols;//1280
const int height = img.rows;//720
int w = img.cols;//1280
int h = img.rows;//720
float scale = 1.f;
if (w > h)
{
scale = (float)target_size / w;//640/1280
w = target_size;//640
h = h * scale;//360
}
else
{
scale = (float)target_size / h;
h = target_size;
w = w * scale;
}
cv::resize(img, img, cv::Size(w, h));
ncnn::Mat in = ncnn::Mat::from_pixels(img.data, ncnn::Mat::PIXEL_BGR2RGB, w, h);
// pad to target_size rectangle
// yolov5/utils/datasets.py letterbox
int wpad = (w + 31) / 32 * 32 - w;
int hpad = (h + 31) / 32 * 32 - h;
ncnn::Mat in_pad;
ncnn::copy_make_border(in, in_pad, hpad / 2, hpad - hpad / 2, wpad / 2, wpad - wpad / 2, ncnn::BORDER_CONSTANT, 114.f);
// yolov5
//std::vector<Object> objects;
{
const float prob_threshold = 0.4f;
const float nms_threshold = 0.51f;
const float norm_vals[3] = { 1 / 255.f, 1 / 255.f, 1 / 255.f };
in_pad.substract_mean_normalize(0, norm_vals);
ncnn::Extractor ex = yolov5.create_extractor();
//ex.set_vulkan_compute(use_gpu);
ex.input("images", in_pad);
std::vector<Object> proposals;
// anchor setting from yolov5/models/yolov5s.yaml
// stride 8
{
ncnn::Mat out;
ex.extract("output", out);
ncnn::Mat anchors(6);
anchors[0] = 10.f;
anchors[1] = 13.f;
anchors[2] = 16.f;
anchors[3] = 30.f;
anchors[4] = 33.f;
anchors[5] = 23.f;
std::vector<Object> objects8;
generate_proposals(anchors, 8, in_pad, out, prob_threshold, objects8);
proposals.insert(proposals.end(), objects8.begin(), objects8.end());
}
// stride 16
{
ncnn::Mat out;
ex.extract("771", out);
ncnn::Mat anchors(6);
anchors[0] = 30.f;
anchors[1] = 61.f;
anchors[2] = 62.f;
anchors[3] = 45.f;
anchors[4] = 59.f;
anchors[5] = 119.f;
std::vector<Object> objects16;
generate_proposals(anchors, 16, in_pad, out, prob_threshold, objects16);
proposals.insert(proposals.end(), objects16.begin(), objects16.end());
}
// stride 32
{
ncnn::Mat out;
ex.extract("791", out);
ncnn::Mat anchors(6);
anchors[0] = 116.f;
anchors[1] = 90.f;
anchors[2] = 156.f;
anchors[3] = 198.f;
anchors[4] = 373.f;
anchors[5] = 326.f;
std::vector<Object> objects32;
generate_proposals(anchors, 32, in_pad, out, prob_threshold, objects32);
proposals.insert(proposals.end(), objects32.begin(), objects32.end());
}
// sort all proposals by score from highest to lowest
qsort_descent_inplace(proposals);
// apply nms with nms_threshold
std::vector<int> picked;
nms_sorted_bboxes(proposals, picked, nms_threshold);
int count = picked.size();
objects.resize(count);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
objects[i] = proposals[picked[i]];
// adjust offset to original unpadded
float x0 = (objects[i].x - (wpad / 2)) / scale;
float y0 = (objects[i].y - (hpad / 2)) / scale;
float x1 = (objects[i].x + objects[i].w - (wpad / 2)) / scale;
float y1 = (objects[i].y + objects[i].h - (hpad / 2)) / scale;
// clip
x0 = std::max(std::min(x0, (float)(width - 1)), 0.f);
y0 = std::max(std::min(y0, (float)(height - 1)), 0.f);
x1 = std::max(std::min(x1, (float)(width - 1)), 0.f);
y1 = std::max(std::min(y1, (float)(height - 1)), 0.f);
objects[i].x = x0;
objects[i].y = y0;
objects[i].w = x1;
objects[i].h = y1;
}
}
return 0;
}
}
static const char* class_names[] = {
"four_fingers","hand_with_fingers_splayed","index_pointing_up","little_finger",
"ok_hand","raised_fist","raised_hand","sign_of_the_horns","three","thumbup","victory_hand"
};
void draw_face_box(cv::Mat& bgr, std::vector<Object> object) //主要的emoji顯示函數(shù)
{
for (int i = 0; i < object.size(); i++)
{
const auto obj = object[i];
cv::rectangle(bgr, cv::Point(obj.x, obj.y), cv::Point(obj.w, obj.h), cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 3, 8, 0);
std::cout << "label:" << class_names[obj.label] << std::endl;
string emoji_path = "emoji\\" + string(class_names[obj.label]) + ".png"; //這個(gè)是emoji圖片的路徑
cv::Mat logo = cv::imread(emoji_path);
if (logo.empty()) {
std::cout << "imread logo failed!!!" << std::endl;
return;
}
resize(logo, logo, cv::Size(80, 80));
cv::Mat imageROI = bgr(cv::Range(obj.x, obj.x + logo.rows), cv::Range(obj.y, obj.y + logo.cols)); //emoji的圖片放在圖中的位置,也就是手勢(shì)框的旁邊
logo.copyTo(imageROI); //把emoji放在原圖中
}
}
int main()
{
Mat frame;
VideoCapture capture(0);
init();
while (true)
{
capture >> frame;
if (!frame.empty()) {
std::vector<Object> objects;
detect(frame, objects);
draw_face_box(frame, objects);
imshow("window", frame);
}
if (waitKey(20) == 'q')
break;
}
capture.release();
return 0;
}
這里是首先用yolov5s識(shí)別出手勢(shì),然后利用圖像ROI融合,把相應(yīng)的Emoji縮放到80x80大小顯示在手勢(shì)框的旁邊,實(shí)現(xiàn)根據(jù)不同的手勢(shì)顯示相應(yīng)的Emoji。
4、實(shí)現(xiàn)emoji和手勢(shì)的映射
到這里,我們終于大功告成!達(dá)成了開(kāi)頭的效果。