Spring Cache 緩存原理與 Redis 實(shí)踐
說到Spring Boot緩存,那就不得不提JSR-107規(guī)范,它告訴我們?cè)贘ava中如何規(guī)范地使用緩存。
JSR是Java Specification Requests的簡(jiǎn)稱,通常譯為”Java 規(guī)范提案“。具體而言,是指向JCP(Java Community Process,Java標(biāo)準(zhǔn)制定組織)提出新增一個(gè)標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化技術(shù)規(guī)范的正式請(qǐng)求。任何人都可以提交JSR,通過一定的標(biāo)準(zhǔn)測(cè)試后,就可以向Java平臺(tái)增添新的API和服務(wù)。JSR已成為Java界的一個(gè)重要標(biāo)準(zhǔn)。
JSR-107規(guī)范即JCache API,JCache規(guī)范定義了一種對(duì)Java對(duì)象臨時(shí)在內(nèi)存中進(jìn)行緩存的方法,包括對(duì)象的創(chuàng)建、共享訪問、假脫機(jī)(spooling)、失效、各JVM的一致性等,可被用于緩存JSP內(nèi)最經(jīng)常讀取的數(shù)據(jù),如產(chǎn)品目錄和價(jià)格列表。利用JCache的緩存數(shù)據(jù),可以加快大多數(shù)查詢的反應(yīng)時(shí)間(內(nèi)部測(cè)試表明反應(yīng)時(shí)間大約快15倍)。
一、JCache
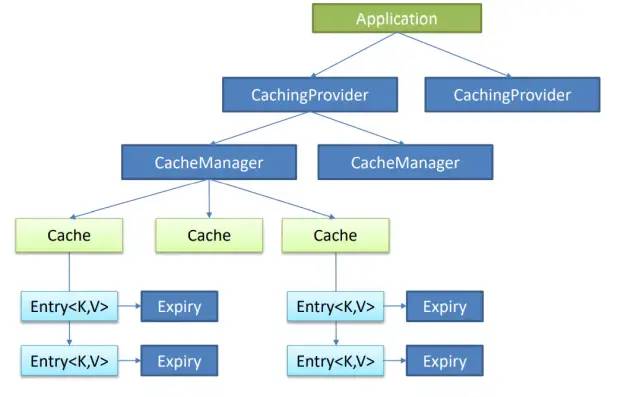
在Spring Boot中使用緩存之前,我們有必要了解一下JCache。JCache定義了五個(gè)核心接口,分別是CachingProvider,CacheManager,Cache,Entry和Expiry。
一個(gè)CachingProvider可以創(chuàng)建和管理多個(gè)CacheManager,并且一個(gè)CacheManager只能被一個(gè)CachingProvider所擁有,而一個(gè)應(yīng)用可以在運(yùn)行期間訪問多個(gè)CachingProvider。
一個(gè)CacheManager可以創(chuàng)建和管理多個(gè)唯一命名的Cache,且一個(gè)Cache只能被一個(gè)CacheManager所擁有,這些Cache存在于CacheManager的上下文中。
Cache是一個(gè)類似Map的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)
Entry是一個(gè)存儲(chǔ)在Cache中的key-value對(duì)
Expiry是指存儲(chǔ)在Cache中的Entry的有效期,一旦超過這個(gè)時(shí)間,Entry將處于過期狀態(tài),即不可訪問、更新和刪除。緩存有效期可以通過ExpiryPolicy設(shè)置。
二、Spring Cache原理
Spring 3.1開始,引入了Spring Cache,即Spring 緩存抽象。通過定義org.springframework.cache.Cache和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口來統(tǒng)一不同的緩存技術(shù),并支持使用JCache注解簡(jiǎn)化開發(fā)過程。
Cache接口為緩存的組件規(guī)范定義,包含緩存的各種操作集合。Spring中為Cache接口提供了各種xxxCache的實(shí)現(xiàn):RedisCache,EhCacheCache,ConcurrentMapCache等。
我們通過部分源碼詳細(xì)了解一下Cache接口和CacheManager接口。
Cache接口
public interface Cache {//Cache名稱String getName();//Cache負(fù)責(zé)緩存的對(duì)象Object getNativeCache();/*** 獲取key對(duì)應(yīng)的ValueWrapper* 沒有對(duì)應(yīng)的key,則返回null* key對(duì)應(yīng)的value是null,則返回null對(duì)應(yīng)的ValueWrapper*/Cache.ValueWrapper get(Object key);//返回key對(duì)應(yīng)type類型的value<T> T get(Object key, Class<T> type);//返回key對(duì)應(yīng)的value,沒有則緩存Callable::call,并返回<T> T get(Object key, Callable<T> valueLoader);//緩存目標(biāo)key-value(替換舊值),不保證實(shí)時(shí)性void put(Object key, Object value);//插入緩存,并返回該key對(duì)應(yīng)的value;先調(diào)用get,不存在則用put實(shí)現(xiàn)default Cache.ValueWrapper putIfAbsent(Object key, Object value) {Cache.ValueWrapper existingValue = this.get(key);if (existingValue == null) {this.put(key, value);}return existingValue;}//刪除緩存,不保證實(shí)時(shí)性void evict(Object key);//立即刪除緩存:返回false表示剔除前不存在制定key活不確定是否存在;返回true,表示該key之前存在default boolean evictIfPresent(Object key) {this.evict(key);return false;}//清除所有緩存,不保證實(shí)時(shí)性void clear();//立即清楚所有緩存,返回false表示清除前沒有緩存或不能確定是否有;返回true表示清除前有緩存default boolean invalidate() {this.clear();return false;}public static class ValueRetrievalException extends RuntimeException {private final Object key;public ValueRetrievalException( Object key, Callable<?> loader, Throwable ex) {super(String.format("Value for key '%s' could not be loaded using '%s'", key, loader), ex);this.key = key;}public Object getKey() {return this.key;}}//緩存值的一個(gè)包裝器接口,實(shí)現(xiàn)類為SimpleValueWrapperpublic interface ValueWrapper {Object get();}}
可以看出,Cache接口抽象了緩存的 get put evict 等相關(guān)操作。
AbstractValueAdaptingCache
public abstract class AbstractValueAdaptingCache implements Cache {//是否允許Null值private final boolean allowNullValues;protected AbstractValueAdaptingCache(boolean allowNullValues) {this.allowNullValues = allowNullValues;}public final boolean isAllowNullValues() {return this.allowNullValues;}public ValueWrapper get(Object key) {return this.toValueWrapper(this.lookup(key));}public <T> T get(Object key, Class<T> type) {//查詢到的緩存值做fromStoreValue轉(zhuǎn)換Object value = this.fromStoreValue(this.lookup(key));//轉(zhuǎn)換后非null值且無法轉(zhuǎn)換為type類型則拋出異常if (value != null && type != null && !type.isInstance(value)) {throw new IllegalStateException("Cached value is not of required type [" + type.getName() + "]: " + value);} else {return value;}}//從緩存中獲取key對(duì)應(yīng)的value,子類實(shí)現(xiàn)protected abstract Object lookup(Object key);//對(duì)于從緩存中獲取的值,允許為空且值為NullValue時(shí),處理為nullprotected Object fromStoreValue( Object storeValue) {return this.allowNullValues && storeValue == NullValue.INSTANCE ? null : storeValue;}//對(duì)于要插入緩存的null值,在允許null值的情況下處理為NullValue;否則拋出異常IllegalArgumentExceptionprotected Object toStoreValue( Object userValue) {if (userValue == null) {if (this.allowNullValues) {return NullValue.INSTANCE;} else {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cache '" + this.getName() + "' is configured to not allow null values but null was provided");}} else {return userValue;}}//get操作依據(jù),查詢到緩存值非null,則fromStoreValue轉(zhuǎn)換后包裝成SimpleValueWrapper返回protected ValueWrapper toValueWrapper( Object storeValue) {return storeValue != null ? new SimpleValueWrapper(this.fromStoreValue(storeValue)) : null;}}
抽象類AbstractValueAdaptingCache實(shí)現(xiàn)了Cache接口,主要抽象了對(duì)NULL值的處理邏輯。
allowNullValues屬性表示是否允許處理NULL值的緩存
fromStoreValue方法處理NULL值的get操作,在屬性allowNullValues為true的情況下,將NullValue處理為NULL
toStoreValue方法處理NULL值得put操作,在屬性allowNullValues為true的情況下,將NULL處理為NullValue,否則拋出異常
toValueWrapper方法提供Cache接口中g(shù)et方法的默認(rèn)實(shí)現(xiàn),從緩存中讀取值,再通過fromStoreValue轉(zhuǎn)化,最后包裝為SimpleValueWrapper返回
ValueWrapper get(Object key)和T get(Object key, @Nullable Class<T> type)方法基于上述方法實(shí)現(xiàn)
ValueWrapper get(Object key)和@Nullable Class<T> type)方法基于上述方法實(shí)現(xiàn)
lookup抽象方法用于給子類獲取真正的緩存值
ConcurrentMapCache
public class ConcurrentMapCache extends AbstractValueAdaptingCache { private final String name;//定義ConcurrentMap緩存private final ConcurrentMap<Object, Object> store;//如果要緩存的是值對(duì)象的copy,則由此序列化代理類處理private final SerializationDelegate serialization;public ConcurrentMapCache(String name) {this(name, new ConcurrentHashMap(256), true);}//默認(rèn)允許處理nullpublic ConcurrentMapCache(String name, boolean allowNullValues) {this(name, new ConcurrentHashMap(256), allowNullValues);}//默認(rèn)serialization = nullpublic ConcurrentMapCache(String name, ConcurrentMap<Object, Object> store, boolean allowNullValues) {this(name, store, allowNullValues, (SerializationDelegate)null);}protected ConcurrentMapCache(String name, ConcurrentMap<Object, Object> store, boolean allowNullValues, SerializationDelegate serialization) {super(allowNullValues);Assert.notNull(name, "Name must not be null");Assert.notNull(store, "Store must not be null");this.name = name;this.store = store;this.serialization = serialization;}//serialization不為空,緩存值對(duì)象的copypublic final boolean isStoreByValue() {return this.serialization != null;}public final String getName() {return this.name;}public final ConcurrentMap<Object, Object> getNativeCache() {return this.store;}//實(shí)現(xiàn)lookup:store#getprotected Object lookup(Object key) {return this.store.get(key);}//基于ConcurrentMap::computeIfAbsent方法實(shí)現(xiàn);get和put的值由fromStoreValue和toStoreValue處理Nullpublic <T> T get(Object key, Callable<T> valueLoader) {return this.fromStoreValue(this.store.computeIfAbsent(key, (k) -> {try {return this.toStoreValue(valueLoader.call());} catch (Throwable var5) {throw new ValueRetrievalException(key, valueLoader, var5);}}));}public void put(Object key, Object value) {this.store.put(key, this.toStoreValue(value));}public ValueWrapper putIfAbsent(Object key, Object value) {Object existing = this.store.putIfAbsent(key, this.toStoreValue(value));return this.toValueWrapper(existing);}public void evict(Object key) {this.store.remove(key);}public boolean evictIfPresent(Object key) {return this.store.remove(key) != null;}public void clear() {this.store.clear();}public boolean invalidate() {boolean notEmpty = !this.store.isEmpty();this.store.clear();return notEmpty;}protected Object toStoreValue( Object userValue) {Object storeValue = super.toStoreValue(userValue);if (this.serialization != null) {try {return this.serialization.serializeToByteArray(storeValue);} catch (Throwable var4) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Failed to serialize cache value '" + userValue + "'. Does it implement Serializable?", var4);}} else {return storeValue;}}protected Object fromStoreValue( Object storeValue) {if (storeValue != null && this.serialization != null) {try {return super.fromStoreValue(this.serialization.deserializeFromByteArray((byte[])((byte[])storeValue)));} catch (Throwable var3) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Failed to deserialize cache value '" + storeValue + "'", var3);}} else {return super.fromStoreValue(storeValue);}}}
ConcurrentMapCache繼承了抽象類AbstractValueAdaptingCache,是Spring的默認(rèn)緩存實(shí)現(xiàn)。它支持對(duì)緩存對(duì)象copy的緩存,由SerializationDelegate serialization 處理序列化,默認(rèn)為 null 即基于引用的緩存。緩存相關(guān)操作基于基類 AbstractValueAdaptingCache 的 null 值處理,默認(rèn)允許為 null。
CacheManager
public interface CacheManager {//獲取指定name的Cache,可能延遲創(chuàng)建Cache getCache(String name);//獲取當(dāng)前CacheManager下的Cache name集合Collection<String> getCacheNames();}
CacheManager 基于 name 管理一組 Cache。當(dāng)然,CacheManager也有很多實(shí)現(xiàn)類,如ConcurrentMapCacheManager、AbstractCacheManager及SimpleCacheManager,這些xxxCacheManager類都是為了制定Cache的管理規(guī)則,這里就不再深入探討了。
三、Spring Cache實(shí)踐
除了第二章中提到的Cache接口和CacheManager接口,在使用Spring 緩存抽象時(shí),我們還會(huì)用到一些JCache注解。
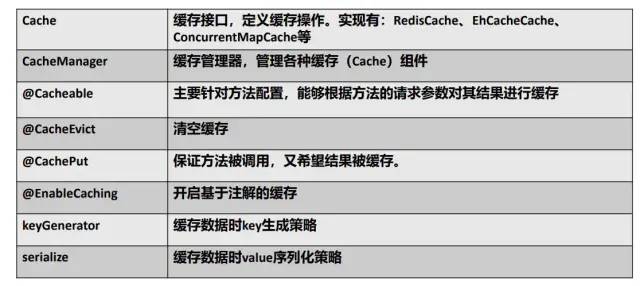
Spring Cache中一些概念和注解
@Cacheable、@CacheEvict和@CachePut三個(gè)注解都是對(duì)方法進(jìn)行配置,主要參數(shù)如下圖所示:

Cache中可用的SpEL表達(dá)式如下圖所示:

@EnableCaching
這個(gè)注解表示開啟基于注解的緩存,一般放在主程序類前面,如下所示:
public class SpringBootCacheApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(SpringBootCacheApplication.class, args);}}
@Cacheable
這個(gè)注解放在方法前,可以將方法的運(yùn)行結(jié)果進(jìn)行緩存,之后就不用調(diào)用方法了,直接從緩存中取值即可。常用屬性可以見上圖。以下是常見用法:
public Employee getEmp(Integer id) {Employee emp = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id);return emp;}}
@Cacheable注解中常用的參數(shù)有cacheNames/value(指定緩存組件的名字,可以指定多個(gè))、key(緩存數(shù)據(jù)時(shí)使用的key,默認(rèn)使用方法參數(shù)的值,也可以自定義)、keyGenerator(key的生成器,可以自定義,key與keyGenerator二選一)、cacheManager(指定緩存管理器,或者使用cacheResolver指定獲取解析器)、condition(符合條件才緩存)、unless(符合條件則不緩存,可以獲取方法運(yùn)行結(jié)果進(jìn)行判斷)、sync(是否使用異步模式,不可與unless一起使用)。@Cacheable的運(yùn)行原理:
方法運(yùn)行前,程序會(huì)使用cacheManager根據(jù)cacheNames獲取Cache,如果沒有對(duì)應(yīng)名稱的Cache,則自動(dòng)創(chuàng)建一個(gè)Cache。
使用key去Cache中查找對(duì)應(yīng)的緩存內(nèi)容。key默認(rèn)使用SimpleKeyGenerator生成,其生成策略如下:
如果沒有參數(shù),key=new SimpleKey()
如果只有一個(gè)參數(shù),key=參數(shù)值
如果有多個(gè)參數(shù),key=new SimpleKey(params)
沒有查到緩存值,則調(diào)用目標(biāo)方法
以步驟二中返回的key,目標(biāo)方法返回的結(jié)果為value,存入緩存
@CachePut
@CachePut注解先調(diào)用目標(biāo)方法,然后再緩存目標(biāo)方法的結(jié)果。
public Employee updateEmp(Employee employee) {employeeMapper.updateEmp(employee);return employee;}
@CacheEvict
@CacheEvict用于清除緩存,可以通過key指定需要清除的緩存,allEntries置為true表示刪除所有緩存。
@CacheEvict(value = "emp", key = "#id", allEntries = true)public void deleteEmp(Integer id) {employeeMapper.deleteEmpById(id);}
默認(rèn)刪除緩存行為在方法執(zhí)行之后(beforeInvocation=false),如果方法運(yùn)行異常,則該緩存不會(huì)被刪除。但可以通過設(shè)置beforeInvocation = true,將刪除緩存行為在方法執(zhí)行之前。
@Caching&@CacheConfig
@Caching注解中包含了@Cacheable、@CachePut和@CacheEvict注解,可以同時(shí)指定多個(gè)緩存規(guī)則。示例如下所示:
@Caching(cacheable = {@Cacheable(value = "emp", key = "#lastName")}, put = {@CachePut(value = "emp", key = "#result.id")@CachePut(value = "emp", key = "#result.email")})
@CacheConfig注解放在類上,抽取緩存的公共配置,如cacheNames、cacheManager等,這樣就不用在每個(gè)緩存注解中重復(fù)配置了。
四、Redis測(cè)試
Spring Boot里面默認(rèn)使用的Cache和CacheManager分別是ConcurrentMapCache和ConcurrentMapCacheManager,將數(shù)據(jù)存儲(chǔ)在ConcurrentMap<Object,Object>中。
然而,在實(shí)際開發(fā)過程中,一般會(huì)使用一些緩存中間件,如Redis、Memcached和Encache等。接下來,演示一下Redis環(huán)境搭建與測(cè)試。
Redis環(huán)境搭建
Redis是一個(gè)開源的、內(nèi)存中的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)存儲(chǔ)系統(tǒng),可以作為數(shù)據(jù)庫、緩存和消息中間件。這里選擇用Docker搭建Redis環(huán)境。首先需要下載鏡像,然后啟動(dòng),具體命令如下:
// 默認(rèn)拉取最新的Redis鏡像docker pull redis// 啟動(dòng)Redis容器docker run -d -p 6379:6379 --name myredis redis
接下來,我們使用Redis Desktop Manager軟件連接Redis,Redis的端口號(hào)默認(rèn)為6379。
RedisAutoConfiguration.java文件里面定義了StringRedisTemplate(操作字符串)和RedisTemplate組件,將組件自動(dòng)注入代碼中,即可使用。兩個(gè)組件都有針對(duì)Redis不同數(shù)據(jù)類型的處理方法。Redis常見的五大數(shù)據(jù)類型:
String(字符串)、List(列表)、Set(集合)、Hash(散列)、ZSet(有序集合)
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue()[字符串]stringRedisTemplate.opsForList()[列表]stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet()[集合]stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash()[散列]stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet()[有序集合]
下面是使用示例:
public class RedisTest {@AutowiredStringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;@AutowiredRedisTemplate redisTemplate;// 測(cè)試保存數(shù)據(jù)public void test01 {stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().append("msg","hello");//存入數(shù)據(jù)String s = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("msg");//獲取數(shù)據(jù)stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush("mylist","1");}//測(cè)試保存對(duì)象public void test02 {Employee emp = new Employee();//默認(rèn)使用jdk序列化機(jī)制,將對(duì)象序列化后的數(shù)據(jù)保存至Redis中redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("emp-01", empById);}}
如果想將對(duì)象以json的方式保存,可將對(duì)象轉(zhuǎn)換為json或改變RedisTemplate中的默認(rèn)序列化規(guī)則。后者的參考代碼如下,首先找到Redis的自動(dòng)加載類RedisAutoConfiguration,自定義一個(gè)RedisTemplate,然后放入容器中。
public class MyRedisConfig {@Beanpublic RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> empRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) throws UnknownHostException {RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> template = new RedisTemplate<Object, Employee>();template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Employee> ser = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Employee>(Employee.class);template.setDefaultSerizlizer(ser);return template;}}
自定義CacheManager
當(dāng)Spring Boot項(xiàng)目中引入Redis的starter依賴時(shí),會(huì)將RedisCacheManager作為默認(rèn)的CacheManager。RedisCacheManager管理RedisCache,后者使用RedisTemplate<Object,Object>操作Redis,默認(rèn)序列化機(jī)制是jdk。如果需要改變Redis序列化機(jī)制,可以自定義CacheManager。參考代碼如下:
public RedisCacheManager employeeCacheManager(RedisTemplate<Object,Object> employeeRedisTemplate) {RedisCacheManager cacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(employeeRedisTemplate);// 將cacheNames作為key的前綴cacheManager.setUserPrefix(true);return cacheManager;}
自定義RedisCache和CacheManager都可以更改緩存方式,兩者區(qū)別在于:前者用于自定義緩存層,后者將緩存交給spring管理(spring cache中不止Redis)。
作者:lynnnnyl鏈接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/0865248ddd74
記得點(diǎn)「贊」和「在看」↓
愛你們
