力扣 (LeetCode)-棧,括號(hào)生成 |刷題打卡
Github來(lái)源:力扣 (LeetCode)|刷題打卡 | 求星星 ? | 給個(gè)??關(guān)注,??點(diǎn)贊,??鼓勵(lì)一下作者
[已開(kāi)啟]任務(wù)一:刷題打卡 * 10 篇
大家好,我是魔王哪吒,很高興認(rèn)識(shí)你~~
哪吒人生信條:如果你所學(xué)的東西 處于喜歡 才會(huì)有強(qiáng)大的動(dòng)力支撐。
每天學(xué)習(xí)編程,讓你離夢(mèng)想更新一步,感謝不負(fù)每一份熱愛(ài)編程的程序員,不論知識(shí)點(diǎn)多么奇葩,和我一起,讓那一顆四處流蕩的心定下來(lái),一直走下去,加油,2021加油!歡迎關(guān)注加我vx:xiaoda0423,歡迎點(diǎn)贊、收藏和評(píng)論
時(shí)間:3 月 1 日 ~ 3 月 13 日
力扣 (LeetCode)-兩數(shù)之和,有效的括號(hào),兩數(shù)相加|刷題打卡-3月1日 力扣 (LeetCode)-合并兩個(gè)有序鏈表,刪除排序數(shù)組中的重復(fù)項(xiàng),JavaScript筆記|刷題打卡-3月2日 力扣 (LeetCode)-最大子序和,JavaScript數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)與算法(數(shù)組)|刷題打卡-3月3日 針對(duì)CSS說(shuō)一說(shuō)|技術(shù)點(diǎn)評(píng)-3月4日
前言
如果這篇文章有幫助到你,給個(gè)??關(guān)注,??點(diǎn)贊,??鼓勵(lì)一下作者,接收好挑戰(zhàn)了嗎?文章公眾號(hào)首發(fā),關(guān)注 程序員哆啦A夢(mèng) 第一時(shí)間獲取最新的文章
??筆芯??~
棧
棧是一種 后進(jìn)先出 的有序集合。新添加或待刪除的元素都保存在棧的同一端,叫做棧頂,另外一端叫棧底。
創(chuàng)建棧
創(chuàng)建一個(gè)類來(lái)表示棧:(如何使用Stack類)
function Stack() {
// 各種屬性和方法的聲明
}
聲明數(shù)組,保存棧里的元素:
let items = []
push(),添加一個(gè)或幾個(gè)新元素到棧頂pop(),移除棧頂?shù)脑兀瑫r(shí)返回被移除的元素peek(),返回棧頂?shù)脑兀粚?duì)棧做任何修改isEmpty(),如果棧里沒(méi)有任何元素就返回true,否則返回falseclear(),移除棧里的所有元素size(),返回棧里的元素個(gè)數(shù)
向棧添加元素(往棧里添加新元素)
示例:
// 只添加元素到棧頂,也就是棧的末尾
this.push = function(element) {
items.push(element);
});
從棧移除元素(移出的是最后添加進(jìn)去的元素)
示例:
this.pop = function() {
return items.pop();
};
查看棧頂元素(用于想找到棧里面最后添加的元素是什么)
示例,返回棧頂?shù)脑兀?/p>
this.peek = function() {
return items[items.length-1];
};
檢查棧是否為空
如果棧為空的話將返回true,否則就返回false。
示例:
this.isEmpty = function() {
return items.length == 0;
};
返回棧的長(zhǎng)度:
this.size = function() {
return items.length;
};
清空和打印棧元素
clear方法用來(lái)移除棧里所有的元素,把棧清空。
this.clear = function() {
items = [];
};
把棧里的元素都輸出來(lái):
this.print = function() {
console.log(item.toString());
};
使用Stack類
初始化Stack類:
let stack = new Stack();
console.log(stack.isEmpty()); //輸出為true
往棧里添加一些元素
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
如果調(diào)用peek方法,將會(huì)輸出2
console.log(stack.peek()); //輸出2
如何用ES6聲明Stack類
代碼:
// 在類的構(gòu)造函數(shù)constructor里聲明, ES6的類是基于原型的。
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.items = [];
}
push(element) {
this.items.push(element);
}
}
基于原型的類比基于函數(shù)的類更節(jié)省內(nèi)存,也更適合創(chuàng)建多個(gè)實(shí)例,卻不能夠聲明私有屬性或方法。
用 ES6的限定作用域Symbol實(shí)現(xiàn)類
ES6新增了一種叫做Symbol的基本類型,它是不可變的,可以用作對(duì)象的屬性。
示例:
// 聲明了Symbol類型的變量_items,在類的constructor函數(shù)中初始化它的值
let _items = Symbol();
class Stack {
constructor() {
this[_items] = [];
}
}
使用ES6新增的Object.getOwnPropertySymbols方法能夠取到類里面聲明的所有Symbols屬性。
let stack = new Stack();
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
let objectSymbols = Object.getOwnPropertySymbols(stack);
console.log(objectSymbols.length); // 1
console.log(objectSymbols); // [Symbol()] 數(shù)組Symbols屬性
console.log(objectSymbols[0]); // Symbol()
stack[objectSymbols[0]].push(1);
stack.print(); //輸出 2, 3, 1
訪問(wèn)
stack[objectSymbols[0]]獲得_items的,_items屬性是一個(gè)數(shù)組,可以進(jìn)行任意的數(shù)組操作。所以不該使用這種方法。
ES6中的WeakMap實(shí)現(xiàn)類
使用WeakMap確保屬性是私有的,WeakMap可以存儲(chǔ)鍵值對(duì),其中鍵是對(duì)象,值可以是任意數(shù)據(jù)類型。
示例:
// 聲明了一個(gè)WeakMap類型的變量items
const items = new WeakMap(); // 誰(shuí)都可以改動(dòng)它
class Stack {
constructor () {
// 在constructor中,以this為鍵,把代表?xiàng)5臄?shù)組存入items
items.set(this, []);
}
push(element) {
// 從WeakMap中取出值,即以this為鍵從items中取值
let s = items.get(this);
s.push(element);
}
pop() {
let s = items.get(this);
let r = s.pop();
return r;
}
//其他方法
}
itmes在Stack類里是真正的所有屬性了。
使用閉包:
// 當(dāng)Stack函數(shù)里的構(gòu)造函數(shù)被調(diào)用時(shí),會(huì)返回Stack類的一個(gè)實(shí)例
let Stack = (function () {
const items = new WeakMap();
class Stack {
constructor () {
items.set(this, []);
}
//其他方法
}
return Stack; //當(dāng)被調(diào)用時(shí),會(huì)返回Stack類的一個(gè)實(shí)例
})();
// 使用這種方法,擴(kuò)展類無(wú)法繼承私有屬性
十進(jìn)制轉(zhuǎn)二進(jìn)制問(wèn)題算法
示例:
function divideBy2(decNumber){
var remStack = new Stack(),
rem,
binaryString = '';
while (decNumber > 0){
rem = Math.floor(decNumber % 2);
remStack.push(rem);
decNumber = Math.floor(decNumber / 2);
}
while (!remStack.isEmpty()){
binaryString += remStack.pop().toString();
}
return binaryString;
}
十進(jìn)制轉(zhuǎn)換成任何進(jìn)制
示例:
function baseConverter(decNumber, base){
var remStack = new Stack(),
rem,
baseString = '',
// 多了digits
digits = '0123456789ABCDEF';
// 基數(shù)
while (decNumber > 0){
rem = Math.floor(decNumber % base);
remStack.push(rem);
decNumber = Math.floor(decNumber / base);
}
while (!remStack.isEmpty()){
baseString += digits[remStack.pop()];
}
return baseString;
}
兩數(shù)之和
解題思路:
暴力法 哈希表法
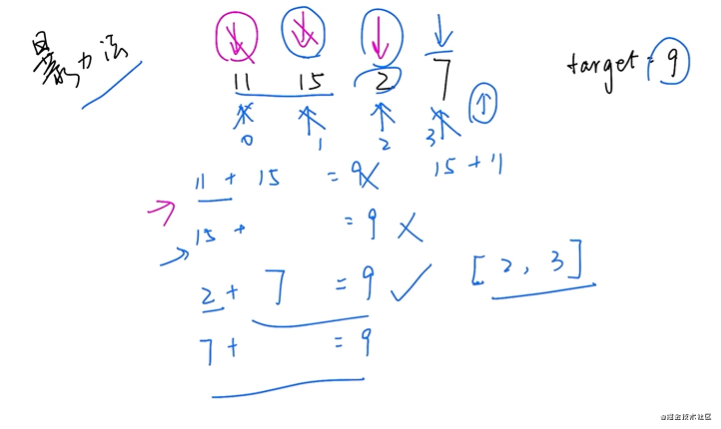
示例偽代碼:
func(nums,target) -> []
result = []; [0,1] 長(zhǎng)度為2
for i in [0, len(nums)]; // 不動(dòng)
for j in [i+1, len(nums)]; // 移動(dòng)
sum = nums[i]+nums[j];
if sm == target;
result[0] = i
result[1] = j
result result
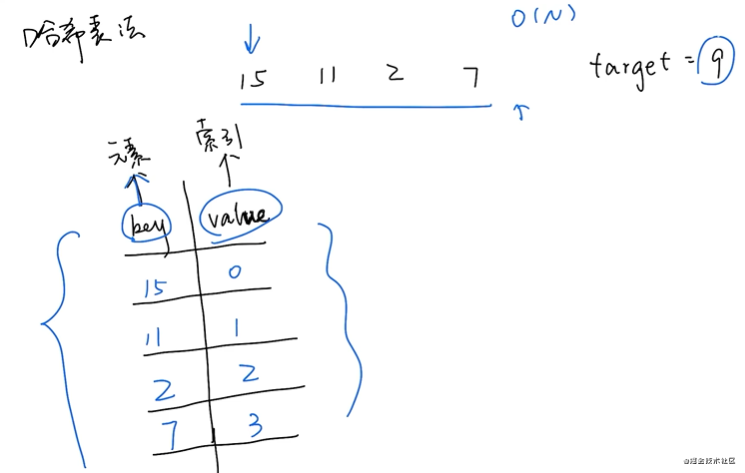
偽代碼:
func(nums, target) -> [];
result = []
map = HashTable()
for i in [0, len(nums)];
map.add(nums[i], i);
for j in [0, len(nums)];
diff = target - nums[j]
if(map.containskey(diff) and map.get(diff) != j)
result[0] = j
result[1] = map.get(diff)
return result
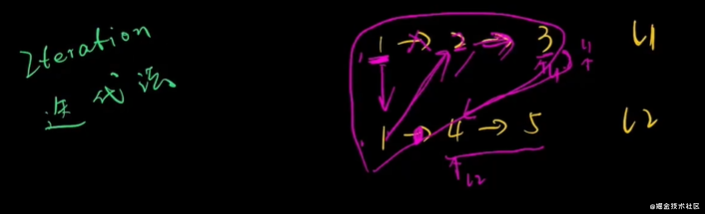
兩數(shù)相加
迭代法 遞歸法

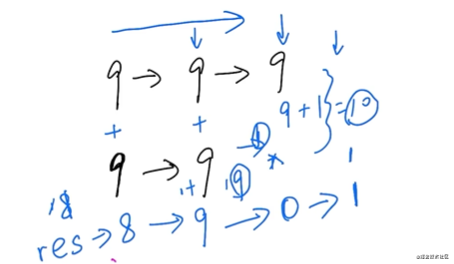
偽代碼:
func (l1, l2) -> Listnode
total = 0 // 兩個(gè)相加的和是多少
next1 = 0 // 下一個(gè)進(jìn)位
result = ListNode()
cur = result
while (l1 != null and l2 != null);
total = l1.val + l2.vale + next1
cur.next = ListNode(total%10)
next1 = total / 10
l1 = l1.next
l2 = l2.next
cur = cur.next
while l1 != null
total = l1.val + next1
cur.next = ListNode(total%10)
nextl = total / 10
l1 = l1.next
cur = cur.next
while l2 != null
total = l2.val + next1
cur.next = ListNode(total%10)
next1 = total / 10
l2 = l2.next
cur = cur.next
if next1 ! = 0
cur.next = ListNode(next1)
return reult.next
遞歸法:
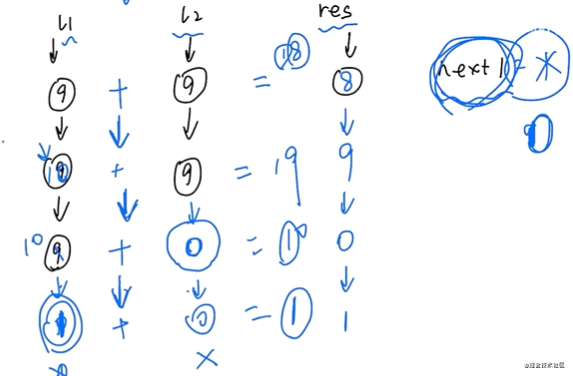
偽代碼:
func (l1, l2) -> ListNode
total = l1.val + l2.val
next1 = total / 10
res = ListNode(total % 10)
if( l1.next != null or l2.next != null or next1 != 0 )
if(l1.next ! = null)
l1 = l1.next
else
l2 = ListNode(0)
if(l2.next != null)
l2 = l2.next
else
l2 = ListNode(0)
l1.val = l1.val + next1
res.next = fun(l1,l2)
return res
有效的括號(hào)
棧的解法:
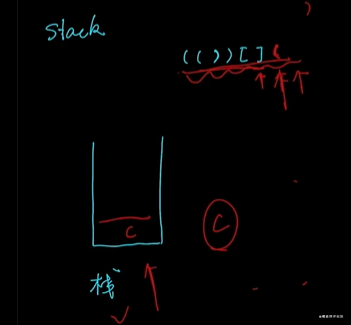
var isValid = function (s) {
let valid = true;
const stack = [];
const mapper = {
"{": "}",
"[": "]",
"(": ")",
};
for (let i in s) {
const v = s[i];
if (["(", "[", "{"].indexOf(v) > -1) {
stack.push(v);
} else {
const peak = stack.pop();
if (v !== mapper[peak]) {
return false;
}
}
}
if (stack.length > 0) return false;
return valid;
};
合并兩個(gè)有序鏈表
迭代法 遞歸法
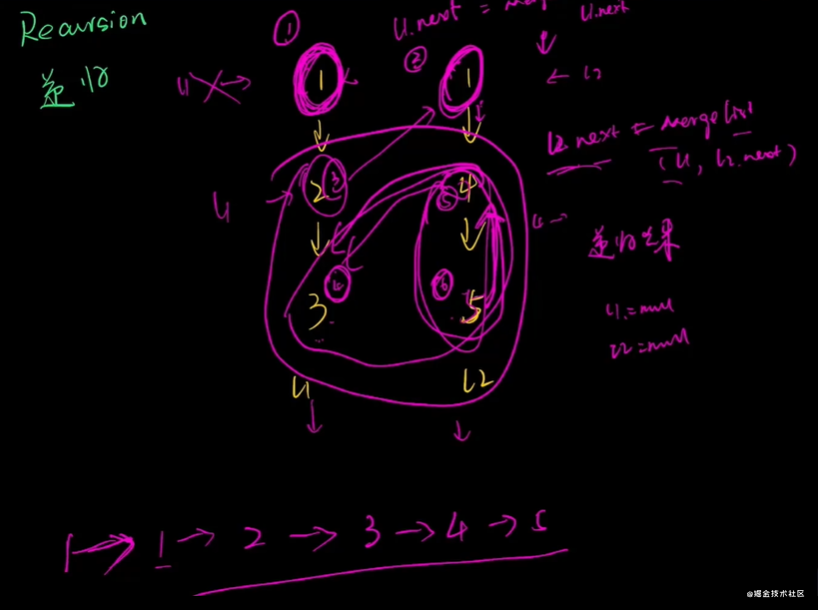
/**
* @param {ListNode} l1
* @param {ListNode} l2
* @return {ListNode}
*/
const mergeTwoLists = function (l1, l2) {
if (l1 === null) {
return l2;
}
if (l2 === null) {
return l1;
}
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
};
22. 括號(hào)生成
一、題目描述
數(shù)字 n 代表生成括號(hào)的對(duì)數(shù),請(qǐng)你設(shè)計(jì)一個(gè)函數(shù),用于能夠生成所有可能的并且 有效的 括號(hào)組合。
示例 1:
輸入:n = 3
輸出:["((()))","(()())","(())()","()(())","()()()"]
示例 2:
輸入:n = 1
輸出:["()"]
提示:
1 <= n <= 8
二、思路分析
回溯法
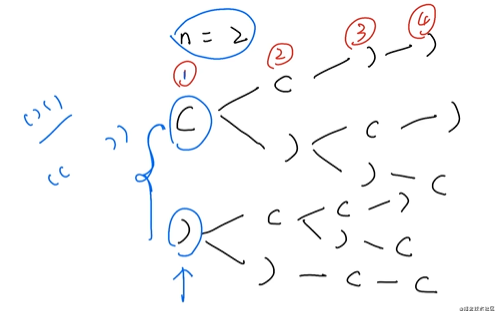

偽代碼:
fun(n) -> []
result = []
backtracking(n,result,0,0, "")
return result
backtracking(n,result,left,right,str) -> void
if right > left
return
if left == right == n
result.add(str)
return
if left<n
backtracking(n,result,left+1,right,str+"(")
if right<left
backtracking(n,result,left,right+1,str+")")
三、答案代碼
示例:
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {string[]}
* @param l 左括號(hào)已經(jīng)用了幾個(gè)
* @param r 右括號(hào)已經(jīng)用了幾個(gè)
* @param str 當(dāng)前遞歸得到的拼接字符串結(jié)果
* @param res 結(jié)果集
*/
const generateParenthesis = function (n) {
const res = [];
function dfs(l, r, str) {
if (l == n && r == n) {
return res.push(str);
}
// l 小于 r 時(shí)不滿足條件 剪枝
if (l < r) {
return;
}
// l 小于 n 時(shí)可以插入左括號(hào),最多可以插入 n 個(gè)
if (l < n) {
dfs(l + 1, r, str + "(");
}
// r < l 時(shí) 可以插入右括號(hào)
if (r < l) {
dfs(l, r + 1, str + ")");
}
}
dfs(0, 0, "");
return res;
};
四、總結(jié)
棧,括號(hào)生成分析
回看筆者往期高贊文章,也許能收獲更多喔!
一個(gè)合格的初級(jí)前端工程師需要掌握的模塊筆記 Vue.js筆試題解決業(yè)務(wù)中常見(jiàn)問(wèn)題 【初級(jí)】個(gè)人分享Vue前端開(kāi)發(fā)教程筆記 長(zhǎng)篇總結(jié)之JavaScript,鞏固前端基礎(chǔ) 前端面試必備ES6全方位總結(jié) 達(dá)達(dá)前端個(gè)人web分享92道JavaScript面試題附加回答 【圖文并茂,點(diǎn)贊收藏哦!】重學(xué)鞏固你的Vuejs知識(shí)體系 【思維導(dǎo)圖】前端開(kāi)發(fā)-鞏固你的JavaScript知識(shí)體系 14期-連肝7個(gè)晚上,總結(jié)了計(jì)算機(jī)網(wǎng)絡(luò)的知識(shí)點(diǎn)!(共66條)
??關(guān)注+點(diǎn)贊+收藏+評(píng)論+轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)??,原創(chuàng)不易,鼓勵(lì)筆者創(chuàng)作更好的文章
點(diǎn)贊、收藏和評(píng)論
我是Jeskson(達(dá)達(dá)前端),感謝各位人才的:點(diǎn)贊、收藏和評(píng)論,我們下期見(jiàn)!(如本文內(nèi)容有地方講解有誤,歡迎指出?謝謝,一起學(xué)習(xí)了)
我們下期見(jiàn)!
文章持續(xù)更新,可以微信搜一搜「 程序員哆啦A夢(mèng) 」第一時(shí)間閱讀,回復(fù)【資料】有我準(zhǔn)備的一線大廠資料,本文 http://www.dadaqianduan.cn/#/ 已經(jīng)收錄
github收錄,歡迎Star:https://github.com/webVueBlog/WebFamily
