Java各版本新增特性, Since Java 8
點(diǎn)擊上方藍(lán)色字體,選擇“標(biāo)星公眾號(hào)”
優(yōu)質(zhì)文章,第一時(shí)間送達(dá)
? 作者?|??Grey Zeng
來源 |? urlify.cn/BvAR3e
66套java從入門到精通實(shí)戰(zhàn)課程分享
Java 8? ? ?
Reactor of Java 這一章來自于《Spring in Action, 5th》?的筆記,因?yàn)檫@本書講Reactor of Java講的太好了,所以作為筆記摘抄了下來。
Reactor of Java
In an imperative programming model, the code would look something like this:
String?name?=?"Craig";
String?capitalName?=?name.toUpperCase();
String?greeting?=?"Hello,?"?+?capitalName?+?"!";
System.out.println(greeting);
In the imperative model, each line of code performs a step, one right after the other, and definitely in the same thread. Each step blocks the executing thread from moving to the next step until complete. In contrast, functional, reactive code could achieve the same thing like this:
Mono.just("Craig")
????????.map(n?->?n.toUpperCase())
????????.map(n?->?"Hello,?"?+?n?+?"?!")
????????.subscribe(System.out::println);
The Mono in the example is one of Reactor’s two core types. Flux is the other. Both are implementations of Reactive Streams’ Publisher.
A Flux represents** a pipeline of zero, one, or many (potentially infinite) data items**.
A Mono is a specialized reactive type that’s optimized for when the dataset is known to have?no more than one data?item.
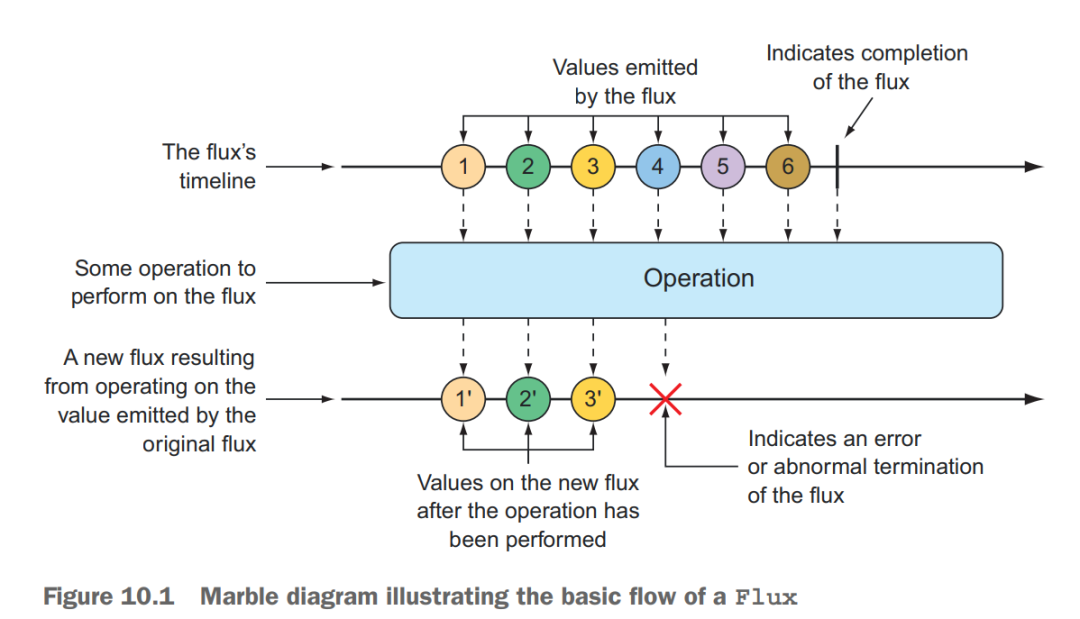
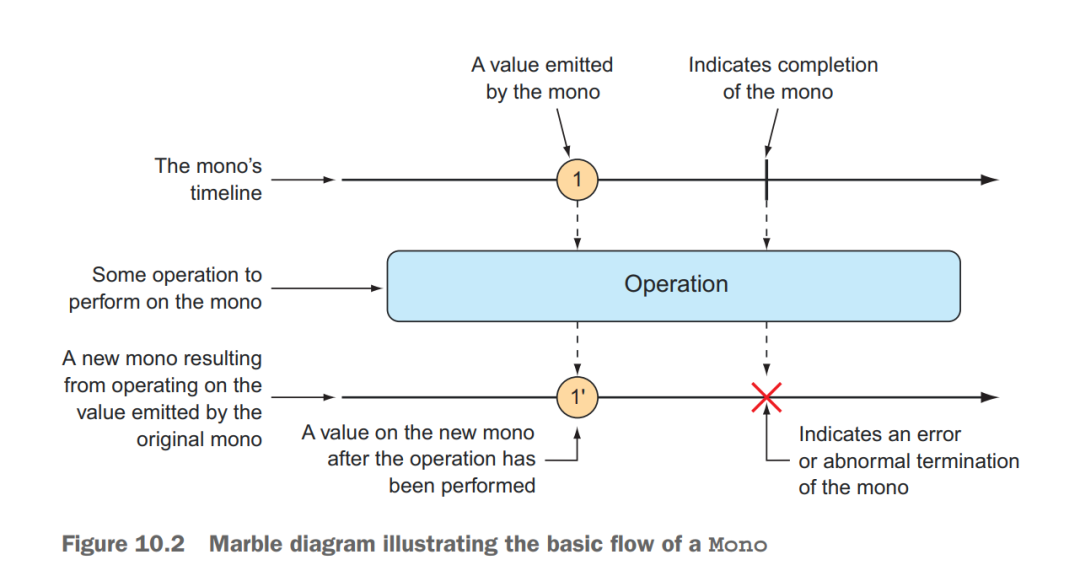
CREATING FROM OBJECTS
????????.just("Apple",?"Orange",?"Grape",?"Banana",?"Strawberry");
????????fruitFlux.subscribe(f?->?System.out.println("Hello?"?+?f));
//?for?test
????????StepVerifier.create(fruitFlux)
????????.expectNext("Apple")
????????.expectNext("Orange")
????????.expectNext("Grape")
????????.expectNext("Banana")
????????.expectNext("Strawberry")
????????.verifyComplete();
CREATING FROM COLLECTIONS
Stream?fruitStream?=?Stream.of("Apple",?"Orange",?"Grape",?"Banana",?"Strawberry");
????????Flux?fruitFlux2?=?Flux.fromStream(fruitStream);
????????fruitFlux2.subscribe(s?->?System.out.println(s));
????????List?fruitList?=?new?ArrayList<>();
????????fruitList.add("Apple");
????????fruitList.add("Orange");
????????fruitList.add("Grape");
????????fruitList.add("Banana");
????????fruitList.add("Strawberry");
????????Flux?fruitFlux3?=?Flux.fromIterable(fruitList);
????????fruitFlux3.subscribe(s?->?System.out.println(s));
????????String[]?fruits?=?new?String[]?{"Apple",?"Orange",?"Grape",?"Banana",?"Strawberry"?};
????????Flux?fruitFlux?=?Flux.fromArray(fruits);
????????fruitFlux.subscribe(s?->?System.out.println(s));
????????StepVerifier.create(fruitFlux)
????????.expectNext("Apple")
????????.expectNext("Orange")
????????.expectNext("Grape")
????????.expectNext("Banana")
????????.expectNext("Strawberry")
????????.verifyComplete();
GENERATING FLUX DATA
Flux?intervalFlux?=
Flux.range(1,?5);
intervalFlux.subscribe(integer?->?System.out.println(integer));
StepVerifier.create(intervalFlux)
.expectNext(1)
.expectNext(2)
.expectNext(3)
.expectNext(4)
.expectNext(5)
.verifyComplete();
Flux?intervalFlux?=
Flux.interval(Duration.ofSeconds(1))
.take(5);
intervalFlux.subscribe(i?->?System.out.println(i));
StepVerifier.create(intervalFlux)
.expectNext(0L)
.expectNext(1L)
.expectNext(2L)
.expectNext(3L)
.expectNext(4L)
.verifyComplete();
MERGING REACTIVE TYPES
Flux?characterFlux?=?Flux
.just("Garfield",?"Kojak",?"Barbossa")
.delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(500));
Flux?foodFlux?=?Flux
.just("Lasagna",?"Lollipops",?"Apples")
.delaySubscription(Duration.ofMillis(250))
.delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(500));
Flux?mergedFlux?=?characterFlux.mergeWith(foodFlux);
mergedFlux.subscribe(s?->?System.out.println(s));
StepVerifier.create(mergedFlux)
.expectNext("Garfield")
.expectNext("Lasagna")
.expectNext("Kojak")
.expectNext("Lollipops")
.expectNext("Barbossa")
.expectNext("Apples")
.verifyComplete();
Flux?characterFlux?=?Flux
.just("Garfield",?"Kojak",?"Barbossa");
Flux?foodFlux?=?Flux
.just("Lasagna",?"Lollipops",?"Apples");
Flux>?zippedFlux?=
Flux.zip(characterFlux,?foodFlux);
zippedFlux.subscribe(x?->?System.out.println(x));
StepVerifier.create(zippedFlux)
.expectNextMatches(p?->
p.getT1().equals("Garfield")?&&
p.getT2().equals("Lasagna"))
.expectNextMatches(p?->
p.getT1().equals("Kojak")?&&
p.getT2().equals("Lollipops"))
.expectNextMatches(p?->
p.getT1().equals("Barbossa")?&&
p.getT2().equals("Apples"))
.verifyComplete();
Flux?characterFlux?=?Flux
.just("Garfield",?"Kojak",?"Barbossa");
Flux?foodFlux?=?Flux
.just("Lasagna",?"Lollipops",?"Apples");
Flux?zippedFlux?=
Flux.zip(characterFlux,?foodFlux,?(c,?f)?->?c?+?"?eats?"?+?f);
zippedFlux.subscribe(x?->?System.out.println(x));
StepVerifier.create(zippedFlux)
.expectNext("Garfield?eats?Lasagna")
.expectNext("Kojak?eats?Lollipops")
.expectNext("Barbossa?eats?Apples")
.verifyComplete();
SELECTING THE FIRST REACTIVE TYPE TO PUBLISH
Flux?slowFlux?=?Flux.just("tortoise",?"snail",?"sloth")
.delaySubscription(Duration.ofMillis(100));
Flux?fastFlux?=?Flux.just("hare",?"cheetah",?"squirrel");
Flux?firstFlux?=?Flux.first(slowFlux,?fastFlux);
StepVerifier.create(firstFlux)
.expectNext("hare")
.expectNext("cheetah")
.expectNext("squirrel")
.verifyComplete();
FILTERING DATA FROM REACTIVE TYPES
Flux?skipFlux?=?Flux.just(
"one",?"two",?"skip?a?few",?"ninety?nine",?"one?hundred")
.skip(3);
StepVerifier.create(skipFlux)
.expectNext("ninety?nine",?"one?hundred")
.verifyComplete();
Flux?skipFlux?=?Flux.just(
"one",?"two",?"skip?a?few",?"ninety?nine",?"one?hundred")
.delayElements(Duration.ofSeconds(1))
.skip(Duration.ofSeconds(4));
StepVerifier.create(skipFlux)
.expectNext("ninety?nine",?"one?hundred")
.verifyComplete();
Flux?nationalParkFlux?=?Flux.just(
"Yellowstone",?"Yosemite",?"Grand?Canyon",
"Zion",?"Grand?Teton")
.take(3);
StepVerifier.create(nationalParkFlux)
.expectNext("Yellowstone",?"Yosemite",?"Grand?Canyon")
.verifyComplete();
Flux?nationalParkFlux?=?Flux.just(
"Yellowstone",?"Yosemite",?"Grand?Canyon",
"Zion",?"Grand?Teton")
.delayElements(Duration.ofSeconds(1))
.take(Duration.ofMillis(3500));
StepVerifier.create(nationalParkFlux)
.expectNext("Yellowstone",?"Yosemite",?"Grand?Canyon")
.verifyComplete();
Flux?nationalParkFlux?=?Flux.just(
"Yellowstone",?"Yosemite",?"Grand?Canyon",
"Zion",?"Grand?Teton")
.filter(np?->?!np.contains("?"));
StepVerifier.create(nationalParkFlux)
.expectNext("Yellowstone",?"Yosemite",?"Zion")
.verifyComplete();
Flux?animalFlux?=?Flux.just(
"dog",?"cat",?"bird",?"dog",?"bird",?"anteater")
.distinct();
StepVerifier.create(animalFlux)
.expectNext("dog",?"cat",?"bird",?"anteater")
.verifyComplete();
MAPPING REACTIVE DATA
Flux?playerFlux?=?Flux
.just("Michael?Jordan",?"Scottie?Pippen",?"Steve?Kerr")
.map(n?->?{
String[]?split?=?n.split("\\s");
return?new?Player(split[0],?split[1]);
});
StepVerifier.create(playerFlux)
.expectNext(new?Player("Michael",?"Jordan"))
.expectNext(new?Player("Scottie",?"Pippen"))
.expectNext(new?Player("Steve",?"Kerr"))
.verifyComplete();
Flux?playerFlux?=?Flux
.just("Michael?Jordan",?"Scottie?Pippen",?"Steve?Kerr")
.flatMap(n?->?Mono.just(n)
.map(p?->?{
String[]?split?=?p.split("\\s");
return?new?Player(split[0],?split[1]);
})
.subscribeOn(Schedulers.parallel())
);
List?playerList?=?Arrays.asList(
new?Player("Michael",?"Jordan"),
new?Player("Scottie",?"Pippen"),
new?Player("Steve",?"Kerr"));
StepVerifier.create(playerFlux)
.expectNextMatches(p?->?playerList.contains(p))
.expectNextMatches(p?->?playerList.contains(p))
.expectNextMatches(p?->?playerList.contains(p))
.verifyComplete();
BUFFERING DATA ON A REACTIVE STREAM
Flux?fruitFlux?=?Flux.just(
"apple",?"orange",?"banana",?"kiwi",?"strawberry");
Flux>?bufferedFlux?=?fruitFlux.buffer(3);
StepVerifier
.create(bufferedFlux)
.expectNext(Arrays.asList("apple",?"orange",?"banana"))
.expectNext(Arrays.asList("kiwi",?"strawberry"))
.verifyComplete();
Buffering?values?from?a?reactive?Flux?into?non-reactive?List?collections?seems?counterproductive.?But?when?you?combine?buffer()?with?flatMap(),?it?enables?each?of?the?List?collections?to?be?processed?in?parallel:
Flux.just(
"apple",?"orange",?"banana",?"kiwi",?"strawberry")
.buffer(3)
.flatMap(x?->
Flux.fromIterable(x)
.map(y?->?y.toUpperCase())
.subscribeOn(Schedulers.parallel())
.log()
).subscribe();
Flux?fruitFlux?=?Flux.just(
"apple",?"orange",?"banana",?"kiwi",?"strawberry");
Mono>?fruitListMono?=?fruitFlux.collectList();
StepVerifier
.create(fruitListMono)
.expectNext(Arrays.asList(
"apple",?"orange",?"banana",?"kiwi",?"strawberry"))
.verifyComplete();
Flux?animalFlux?=?Flux.just(
"aardvark",?"elephant",?"koala",?"eagle",?"kangaroo");
Mono>?animalMapMono?=
animalFlux.collectMap(a?->?a.charAt(0));
StepVerifier
.create(animalMapMono)
.expectNextMatches(map?->?{
return
map.size()?==?3?&&
map.get('a').equals("aardvark")?&&
map.get('e').equals("eagle")?&&
map.get('k').equals("kangaroo");
})
.verifyComplete();
Performing?logic?operations?on?reactive?types
Flux?animalFlux?=?Flux.just(
"aardvark",?"elephant",?"koala",?"eagle",?"kangaroo");
Mono?hasAMono?=?animalFlux.all(a?->?a.contains("a"));
StepVerifier.create(hasAMono)
.expectNext(true)
.verifyComplete();
Mono?hasKMono?=?animalFlux.all(a?->?a.contains("k"));
StepVerifier.create(hasKMono)
.expectNext(false)
.verifyComplete();
Flux?animalFlux?=?Flux.just(
"aardvark",?"elephant",?"koala",?"eagle",?"kangaroo");
Mono?hasAMono?=?animalFlux.any(a?->?a.contains("a"));
StepVerifier.create(hasAMono)
.expectNext(true)
.verifyComplete();
Mono?hasZMono?=?animalFlux.any(a?->?a.contains("z"));
StepVerifier.create(hasZMono)
.expectNext(false)
.verifyComplete();
Spring MVC change to Spring WebFlux
@GetMapping("/recent")
public?Iterable?recentTacos()?{
PageRequest?page?=?PageRequest.of(
0,?12,?Sort.by("createdAt").descending());
return?tacoRepo.findAll(page).getContent();
}
@GetMapping("/recent")
public?Flux?recentTacos()?{
return?Flux.fromIterable(tacoRepo.findAll()).take(12);
}
@PostMapping(consumes="application/json")
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public?Taco?postTaco(@RequestBody?Taco?taco)?{
return?tacoRepo.save(taco);
}
@PostMapping(consumes="application/json")
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public?Mono?postTaco(@RequestBody?Mono?tacoMono)?{
return?tacoRepo.saveAll(tacoMono).next();
}
public?interface?TacoRepository
extends?ReactiveCrudRepository?{
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public?Taco?tacoById(@PathVariable("id")?Long?id)?{
Optional?optTaco?=?tacoRepo.findById(id);
if?(optTaco.isPresent())?{
return?optTaco.get();
}
return?null;
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public?Mono?tacoById(@PathVariable("id")?Long?id)?{
return?tacoRepo.findById(id);
}
WORKING WITH RXJAVA TYPES
@GetMapping("/recent")
public?Observable?recentTacos()?{
return?tacoService.getRecentTacos();
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public?Single?tacoById(@PathVariable("id")?Long?id)?{
return?tacoService.lookupTaco(id);
}
Developing Reactive APIs
@Configuration
public?class?RouterFunctionConfig?{
@Autowired
private?TacoRepository?tacoRepo;
@Bean
public?RouterFunction?routerFunction()?{
return?route(GET("/design/taco"),?this::recents)
Testing?reactive?controllers?279
.andRoute(POST("/design"),?this::postTaco);
}
public?Mono?recents(ServerRequest?request)?{
return?ServerResponse.ok()
.body(tacoRepo.findAll().take(12),?Taco.class);
}
public?Mono?postTaco(ServerRequest?request)?{
Mono?taco?=?request.bodyToMono(Taco.class);
Mono?savedTaco?=?tacoRepo.save(taco);
return?ServerResponse
.created(URI.create(
"http://localhost:8080/design/taco/"?+
savedTaco.getId()))
.body(savedTaco,?Taco.class);
}
}
Test Reactive Rest APIs
//?Test?Get?Method
Taco[]?tacos?=?{
testTaco(1L),?testTaco(2L),
testTaco(3L),?testTaco(4L),
testTaco(5L),?testTaco(6L),
testTaco(7L),?testTaco(8L),
testTaco(9L),?testTaco(10L),
testTaco(11L),?testTaco(12L),
testTaco(13L),?testTaco(14L),
testTaco(15L),?testTaco(16L)};
Flux?tacoFlux?=?Flux.just(tacos);
TacoRepository?tacoRepo?=?Mockito.mock(TacoRepository.class);
when(tacoRepo.findAll()).thenReturn(tacoFlux);
WebTestClient?testClient?=?WebTestClient.bindToController(
new?DesignTacoController(tacoRepo))
.build();
testClient.get().uri("/design/recent")
.exchange()
.expectStatus().isOk()
.expectBody()
.jsonPath("$").isArray()
.jsonPath("$").isNotEmpty()
.jsonPath("$[0].id").isEqualTo(tacos[0].getId().toString())
.jsonPath("$[0].name").isEqualTo("Taco?1").jsonPath("$[1].id")
.isEqualTo(tacos[1].getId().toString()).jsonPath("$[1].name")
.isEqualTo("Taco?2").jsonPath("$[11].id")
.isEqualTo(tacos[11].getId().toString())
.jsonPath("$[11].name").isEqualTo("Taco?12").jsonPath("$[12]")
.doesNotExist().jsonPath("$[12]").doesNotExist();
//?Test?POST?Method
TacoRepository?tacoRepo?=?Mockito.mock(
TacoRepository.class);
Mono?unsavedTacoMono?=?Mono.just(testTaco(null));
Taco?savedTaco?=?testTaco(null);
savedTaco.setId(1L);
Mono?savedTacoMono?=?Mono.just(savedTaco);
when(tacoRepo.save(any())).thenReturn(savedTacoMono);
WebTestClient?testClient?=?WebTestClient.bindToController(
new?DesignTacoController(tacoRepo)).build();
testClient.post()
.uri("/design")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.body(unsavedTacoMono,?Taco.class)
.exchange()
.expectStatus().isCreated()
.expectBody(Taco.class)
.isEqualTo(savedTaco);
//?Testing?with?a?live?server
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment=WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
public?class?DesignTacoControllerWebTest?{
@Autowired
private?WebTestClient?testClient;
@Test
public?void?shouldReturnRecentTacos()?throws?IOException?{
testClient.get().uri("/design/recent")
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).exchange()
.expectStatus().isOk()
.expectBody()
.jsonPath("$[?(@.id?==?'TACO1')].name")
.isEqualTo("Carnivore")
.jsonPath("$[?(@.id?==?'TACO2')].name")
.isEqualTo("Bovine?Bounty")
.jsonPath("$[?(@.id?==?'TACO3')].name")
.isEqualTo("Veg-Out");
}
}
Consume Reactive APIs
Flux?ingredients?=?WebClient.create()
.get()
.uri("http://localhost:8080/ingredients")
.retrieve()
.bodyToFlux(Ingredient.class);
ingredients.subscribe(i?->?{?...})
Flux?ingredients?=?WebClient.create()
.get()
.uri("http://localhost:8080/ingredients")
.retrieve()
.bodyToFlux(Ingredient.class);
ingredients
.timeout(Duration.ofSeconds(1))
.subscribe(
i?->?{?...?},
e?->?{
//?handle?timeout?error
})
//Handing?errors
ingredientMono.subscribe(
ingredient?->?{
//?handle?the?ingredient?data
...
},
error->?{
//?deal?with?the?error
...
});
Mono?ingredientMono?=?webClient
.get()
.uri("http://localhost:8080/ingredients/{id}",?ingredientId)
.retrieve()
.onStatus(HttpStatus::is4xxClientError,
response?->?Mono.just(new?UnknownIngredientException()))
.bodyToMono(Ingredient.class);
Java 9
jshell
無法用單個(gè)下劃線作為變量名稱
int _ = 3; // java9 or above , error
String?a?=?Objects.requireNonNullElse(m,"Bc");?//?若m不為null,則a?=?m,若m為null,則a?=?"Bc"
-cp, -classpath, --class-path(Java9新增)
Multi-Release JAR Files
--release
--class-path?instead?of?-classpath
--version?instead?of?-version
--module-path?option?has?a?shortcut?-p
更多,見jeps
Java8中,接口可以有靜態(tài)方法的默認(rèn)實(shí)現(xiàn),例:
public?interface?Test?{
????public?static?void?print()?{
????????System.out.println("interface?print");
????}
????default?void?pout()?{
????????System.out.println();
????}
}
Java9中,可以支持private的靜態(tài)方法實(shí)現(xiàn)。
public?interface?Test?{
????private?static?void?print()?{
????????System.out.println("interface?print");
????}
????static?void?pout()?{
????????print();
????}
}
Optional.ofNullable(date).orElseGet(()?->?newDate());?//?date為null,才會(huì)執(zhí)行newDate()方法,否則不執(zhí)行newDate()方法
Optional.ofNullable(date).orElse(newDate());?//?無論date是否為null,都會(huì)執(zhí)行newDate()方法
Java7中,可以使用try-with-Resources
try(Resouce?res?=?...)?{
????work?with?res
}
res.close()會(huì)被自動(dòng)執(zhí)行
例:
try?(var?in?=?new?Scanner(new?FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\Young\\Desktop\\新建文件夾\\1.tx.txt"),?StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
?????????????var?out?=?new?PrintWriter("C:\\Users\\Young\\Desktop\\新建文件夾\\out.txt",?StandardCharsets.UTF_8))?{
????????????while?(in.hasNext())?{
????????????????out.println(in.next().toUpperCase());
????????????}
????????}
in 和 out執(zhí)行完畢后都會(huì)自動(dòng)關(guān)閉資源
在Java9 中,你可以在try中預(yù)先聲明資源
例:
??public?static?void?printAll(String[]?lines,?PrintWriter?out)?{
???????try?(out)?{?//?effectively?final?variable
???????????for?(String?line?:?lines)?{
???????????????out.println(line);
???????????}?//?out.close()?called?here
???????}
???}
StackWalker用法示例
public?class?App?{
????/**
?????*?Computes?the?factorial?of?a?number
?????*
?????*?@param?n?a?non-negative?integer
?????*?@return?n!?=?1?*?2?*?.?.?.?*?n
?????*/
????public?static?int?factorial(int?n)?{
????????System.out.println("factorial("?+?n?+?"):");
????????var?walker?=?StackWalker.getInstance();
????????walker.forEach(System.out::println);
????????int?r;
????????if?(n?<=?1)?{
????????????r?=?1;
????????}?else?{
????????????r?=?n?*?factorial(n?-?1);
????????}
????????System.out.println("return?"?+?r);
????????return?r;
????}
????public?static?void?main(String[]?args)?{
????????try?(var?in?=?new?Scanner(System.in))?{
????????????System.out.print("Enter?n:?");
????????????int?n?=?in.nextInt();
????????????factorial(n);
????????}
????}
}
Java 9 expands the use of the diamond syntax to situations where it was previously not accepted. For example , you can now use diamonds with anonymous subclasses.
ArrayList?list?=?new?ArrayList<>(){
????????????@Override
????????????public?String?get(int?index)?{
????????????????return?super.get(index).replaceAll(".","*");
????????????}
????????};
Java 10
無需定義變量類型,通過var關(guān)鍵字+初始化的值,可以推測(cè)出變量類型
var?a?=?2;?//?a表示int
var?b?=?"hello";?//?b?表示String
var?date?=?new?java.util.Date();
var?obj?=?new?Custome();?//?自定義對(duì)象
Java 11
String?repeated?=?"Java".repeat(3);?//?三個(gè)Java字符串連接
JDK提供了jdeprscan?來檢查你的代碼是否使用了deprecated的方法
專題
Lambda Expression
| Method Reference | Equivalent Lambda Expression | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| separator::equals | x -> separator.equals(x) | This is a method expression with an object and an instance method. The lambda parameter is passed as the explicit parameter of the method |
| String::trim | x -> x.trim() | This is a method expression with a class and an instance method. The lambda parameter becomes the explicit parameter of the method |
| String::concat | (x, y) -> x.concat(y) | Again, we have an instance method, but this time, with an explicit parameter. As before, the first lambda parameter becomes the implicit parameter, and the remaining ones are passed to the method |
| Integer::valueOf | x -> Integer::valueOf(x) | This is a method expression with a static method. The lambda parameter is passed to the static method |
| Integer::sum | (x, y) -> Integer::sum(x, y) | This is another static method, but this time with two parameters. Both lambda parameters are passed to the static method. The Integer.sum method was specifically created to be used as a method reference. As a lmbda, you could just write (x, y)->x + y |
| Integer::new | x -> new Integer(x) | This is a constructor reference. The lambda parameters are passed to the constructor |
| Integer[]::new | n -> new Integer[n] | This is an array constructor reference. The lambda paramter is the array length |
| Functional Interface | Parameter Types | Return Types | Abstract Method Name | Description | Other Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Runnable | none | void | run | Runs an action without arguments or return value | |
| Supplier | none | T | get | Supplies a value of type T | |
| Consumer | T | void | accept | Consumes a value of type T | andThen |
| BiConsumer | T,U | void | accept | Consumes ?value of types T and U | andThen |
| Function | T | R | apply | A function with argument of type T | compose, andThen, identity |
| BiFunction | T,U | R | apply | A function with arguments of types T and U | andThen |
| UnaryOperator | T | T | apply | A unary operator on the type T | compose, andThen, identity |
| BinaryOperator | T,T | T | apply | A binary operator on the type T | andThen, maxBy, minBy |
| Predicate | T | boolean | test | A boolean-valued function | and, or, negate, isEqual |
| BiPredicate | T,U | boolean | test | A boolean-valued function with two argumnets | and,or,negate |
Functional interfaces for Primitive Types
p, q is int ,long double; P, Q is Int, Long, Double
| Functional Interface | Parameter Types | Return Types | Abstract Method Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| BooleanSupplier | none | boolean | getAsBoolean |
| PSupplier | none | p | getAsP |
| PConsumer | p | void | accept |
| ObjPConsumer | T,p | void | accept |
| PFunction | p | T | apply |
| PToQFunction | p | q | applyAsQ |
| ToPFunction | T | p | applyAsP |
| ToPBiFunction | T,U | p | applyAsP |
| PUnaryOperator | p | p | applyAsP |
| PBinaryOperator | p,p | p | applyAsP |
| PPredicate | p | boolean | test |
Service Loaders
Proxies
Logging
Generic Programming
E for the element type of a collection
K and V for key and value type of a table
T(and the neighboring letters U and S, if neccessary) for "any type at all"
Pair?a?=?new?Pair<>("A",?"B");
Pair?b?=?new?Pair<>(1.1,?1.11);
System.out.println(a.getClass()?==?b.getClass());?//?TRUE
in Java8
public?static??Pair?makePair(Supplier?constr)?{
????return?new?Pair<>(constr.get(),?constr.get());
}
Pair?p?=?Pair.makePair(String:new);
In general, there is no relationship between?Pair?and?Pair, no matter how S and T are related.
BUT
var?managerBuiddies?=?new?Pair(ceo,?cfo);
Pair?buddies?=?managerBuddies;
Collections
Concurrency
Stream
Java 8
//?流操作
List?list?=?new?ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.parallelStream().filter(i?->?i?>?1).count();
list.stream().filter(i?->?i?>?1).count();
Stream?words?=?Stream.of(contents.split(","));
//?創(chuàng)建流
var?limits?=?new?BigInteger("1000");
Stream?integerStream?=?Stream.iterate(BigInteger.ZERO,?n?->?n.compareTo(limits)??n.add(BigInteger.ONE));
System.out.println(integerStream.count());
如果我們持有的iterable對(duì)象不是集合,那么可以通過下面的調(diào)用將其轉(zhuǎn)換成一個(gè)流
StreamSupport.stream(iterable.spliterator(),false);
如果我們持有的是Iterator對(duì)象,并且希望得到一個(gè)由它的結(jié)果構(gòu)成的流,那么可以使用下面的語句
StreamSupport.stream(Spliterators.spliteratorUnknowSize(iterator,?Spliterator.ORDERED),false);
至關(guān)重要的是,在執(zhí)行流的操作時(shí),我們并沒有修改流背后的集合。記住,流并沒有收集其數(shù)據(jù),數(shù)據(jù)一直存儲(chǔ)在單獨(dú)的集合中
Optional
String?result?=?optionalString.orElse("");?//?The?wrapped?string?,?or?""?if?none
String?result?=?optionalString.orElseGet(()?->?System.getProperty("myapp.default"));
String?result?=?optionalString.orElseThrow(IllegalStateException::new);
消費(fèi)Optinal值
optionalValue.ifPresent(v?->?result.add(v));
optionalValue.ifPresentOrElse(v?->?System.out.println("Found"?+?v),
()->?logger.warning("no?match"));
管道化Optional
Optional?transformed?=?optionalString.filter(s?->?s.length()?>=?8).map(String::toUpperCase);
in Java9
//?如果optionalString的值存在,那么result為optionalString,如果值不存在,那么就會(huì)計(jì)算lambda表達(dá)式,并使用計(jì)算出來的結(jié)果
Optional?transformed?=?optionalString.or(()?->?alternatives.stream().findFirst());
粉絲福利:Java從入門到入土學(xué)習(xí)路線圖
???

?長按上方微信二維碼?2 秒
感謝點(diǎn)贊支持下哈?
