Threejs 地圖3D可視化
大廠(chǎng)技術(shù) 高級(jí)前端 Node進(jìn)階
點(diǎn)擊上方 程序員成長(zhǎng)指北,關(guān)注公眾號(hào)
回復(fù)1,加入高級(jí)Node交流群
可以直接去github github.com/1023byte/3Dmap
前言
threejs小練習(xí),從頭實(shí)現(xiàn)如何加載地理數(shù)據(jù),并將其映射到三維場(chǎng)景中的對(duì)象上。
獲取數(shù)據(jù)
在開(kāi)始繪制圖形前,需要一份包含地理信息數(shù)據(jù),我們可以從阿里云提供的小工具獲取datav.aliyun.com/portal/school/atlas/area_selector
在范圍選擇器中,可以選擇整個(gè)或者各個(gè)省份的地理信息數(shù)據(jù)。
生成圖形
獲取數(shù)據(jù)后,先分析一下JSON的結(jié)構(gòu)
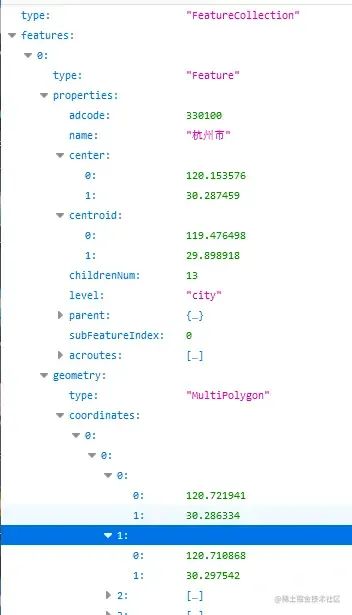
properties 中包含了名字、中心、質(zhì)心等信息, geometry.coordinates 則是地理的坐標(biāo)點(diǎn),我們需要做的是將這些點(diǎn)連成線(xiàn)。
THREE.Shpae
const createMap = (data) => {
const map = new THREE.Object3D();
data.features.forEach((feature) => {
const unit = new THREE.Object3D();
const { coordinates, type } = feature.geometry;
coordinates.forEach((coordinate) => {
if (type === "MultiPolygon") coordinate.forEach((item) => fn(item));
if (type === "Polygon") fn(coordinate);
function fn(coordinate) {
const mesh = createMesh(coordinate);
unit.add(mesh);
}
});
map.add(unit);
});
return map;
};
這里需要注意在geometry中的type分為MultiPolygon和Polygon,需要分別處理,不然會(huì)造成個(gè)別區(qū)域缺失,二者區(qū)別是MultiPolygon的坐標(biāo)多一層嵌套數(shù)據(jù),所以這里多做一次遍歷。
const createMesh = (data, color, depth) => {
const shape = new THREE.Shape();
data.forEach((item, idx) => {
cosnt [x,y] =item
if (idx === 0) shape.moveTo(x, -y);
else shape.lineTo(x, -y);
});
const shapeGeometry = new THREE.ShapeGeometry(shape);
const shapematerial = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({
color: 0xfff,
side: THREE.DoubleSide
});
const mesh = new THREE.Mesh(shapeGeometry, shapematerial);
return mesh;
};
通過(guò)THREE.Shape繪制一個(gè)二維的形狀平面后,但是打開(kāi)網(wǎng)頁(yè)后會(huì)發(fā)現(xiàn)頁(yè)面中并沒(méi)有出現(xiàn)圖形,這是因?yàn)槭莏son中的坐標(biāo)非常大,在縮小后才能勉強(qiáng)看到,所以我們需要對(duì)坐標(biāo)進(jìn)行相應(yīng)的處理。
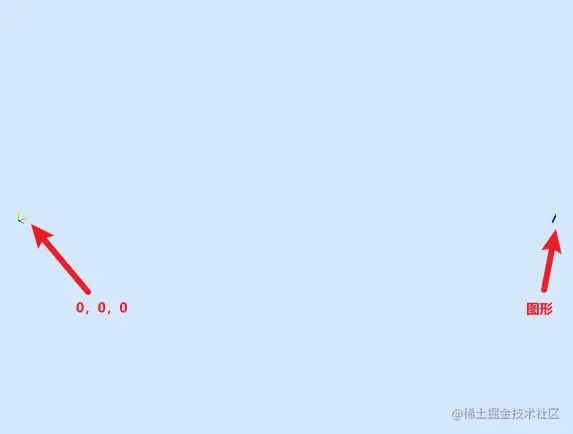
坐標(biāo)矯正1
這里先介紹第一種矯正的方法
import * as d3 from "d3";
...
const offsetXY = d3.geoMercator();
在createMap中新增獲取第一個(gè)子數(shù)據(jù)的centroid以及偏移代碼,這里的centroid也就是杭州的質(zhì)心。
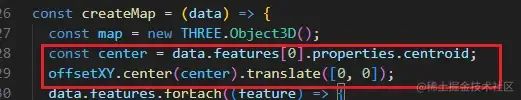
d3.geoMercator()是一個(gè)地理投影函數(shù),用于將地球表面的經(jīng)緯度坐標(biāo)映射到二維平面上。
在代碼中,.center(center)是用于指定投影的中心點(diǎn),這個(gè)中心點(diǎn)決定了投影的中心位置,地圖上的所有要素都將以該點(diǎn)為中心進(jìn)行投影轉(zhuǎn)換。
.translate([0, 0])是指定投影的平移量。這里的 [0, 0] 表示在平面坐標(biāo)系中的 x 和 y 方向上都沒(méi)有平移,也就是將地圖的投影結(jié)果放置在平面坐標(biāo)系的原點(diǎn)位置。
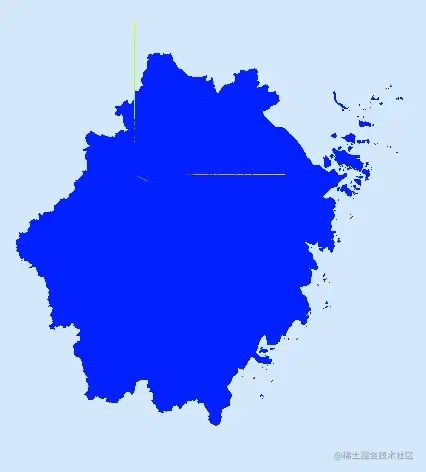
這份數(shù)據(jù)是浙江省的地理信息,所以根據(jù)以上代碼,圖形的中心點(diǎn)已經(jīng)以到杭州的質(zhì)心上,并且坐標(biāo)為[0,0]
THREE.ExtrudeGeometry
接著再通過(guò) THREE.ExtrudeGeometry將shape從二維擠出成三維。為了方便查看剛才代碼使用了new THREE.ShapeGeometry(shape);我們替換成ExtrudeGeometry
const shapeGeometry = new THREE.ExtrudeGeometry(shape, {
depth: 1,
bevelEnabled: false,
});
depth:圖形擠出的深度,默認(rèn)值為1
bevelEnabled:對(duì)擠出的形狀應(yīng)用是否斜角,默認(rèn)值為true
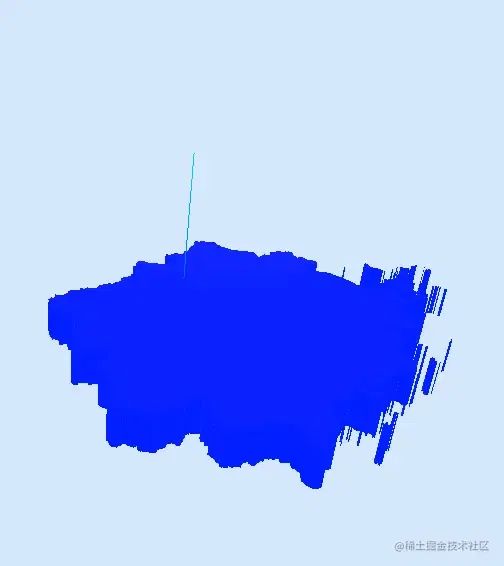
區(qū)域劃分
現(xiàn)在的圖形全都是一個(gè)顏色,看不出區(qū)域
const color = new THREE.Color(`hsl(
${233},
${Math.random() * 30 + 55}%,
${Math.random() * 30 + 55}%)`).getHex();
const depth = Math.random() * 0.3 + 0.3;
...
...
const mesh = createMesh(coordinate, color, depth);
我們寫(xiě)一個(gè)隨機(jī)顏色和隨機(jī)的深度,在data.features中寫(xiě)入,確保每一個(gè)子區(qū)域一個(gè)顏色,如果在createMesh中實(shí)現(xiàn)會(huì)產(chǎn)生以下區(qū)別,舟山、寧波、溫州的島嶼會(huì)產(chǎn)生不同的顏色。
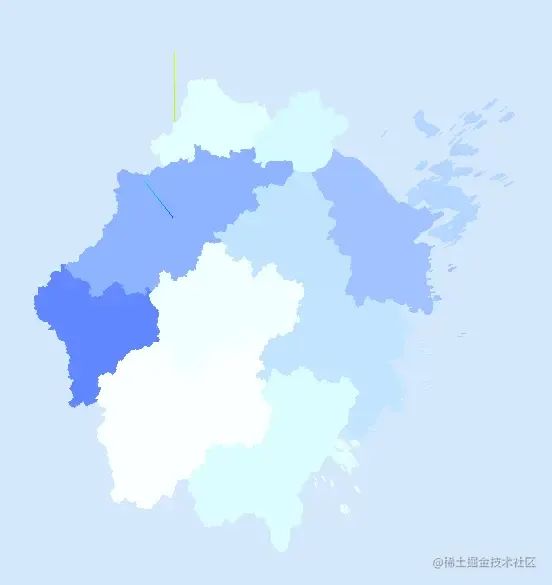
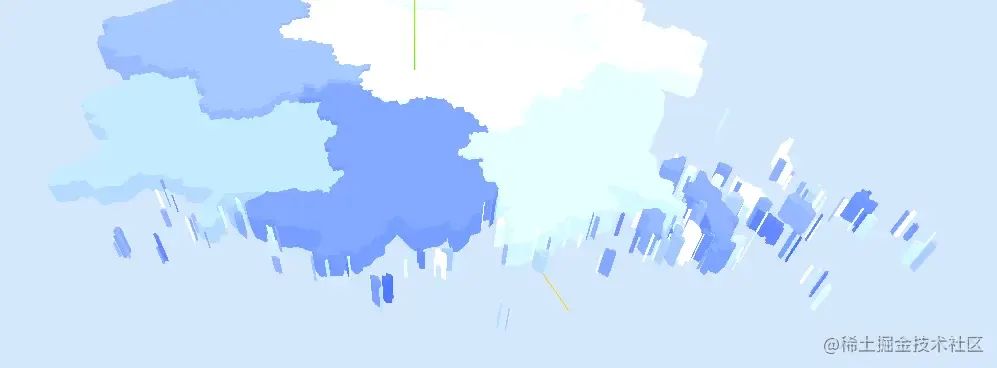
繪制描邊
繪制描邊的方法和之前的shape有所不同
創(chuàng)建一個(gè)THREE.BufferGeometry對(duì)象,并通過(guò)一組給定的點(diǎn)來(lái)設(shè)置其幾何形狀,再通過(guò)LineBasicMaterial材質(zhì)渲染基本的線(xiàn)條
const createLine = (data, depth) => {
const points = [];
data.forEach((item) => {
const [x, y] = offsetXY(item);
points.push(new THREE.Vector3(x, -y, 0));
});
const lineGeometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry().setFromPoints(points);
const uplineMaterial = new THREE.LineBasicMaterial({ color: 0xffffff });
const downlineMaterial = new THREE.LineBasicMaterial({ color: 0xffffff });
const upLine = new THREE.Line(lineGeometry, uplineMaterial);
const downLine = new THREE.Line(lineGeometry, downlineMaterial);
downLine.position.z = -0.0001;
upLine.position.z = depth + 0.0001;
return [upLine, downLine];
};
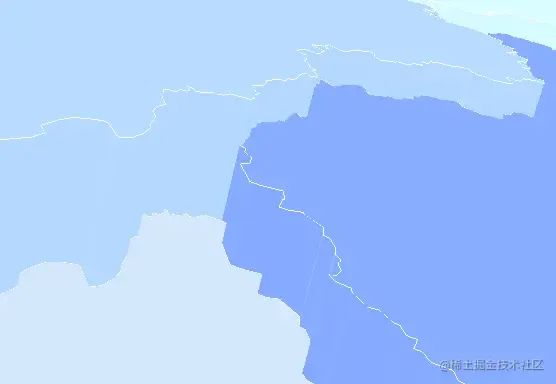
繪制標(biāo)簽信息
接下來(lái)我們通過(guò)css2d的方式向圖形中添加城市名稱(chēng)
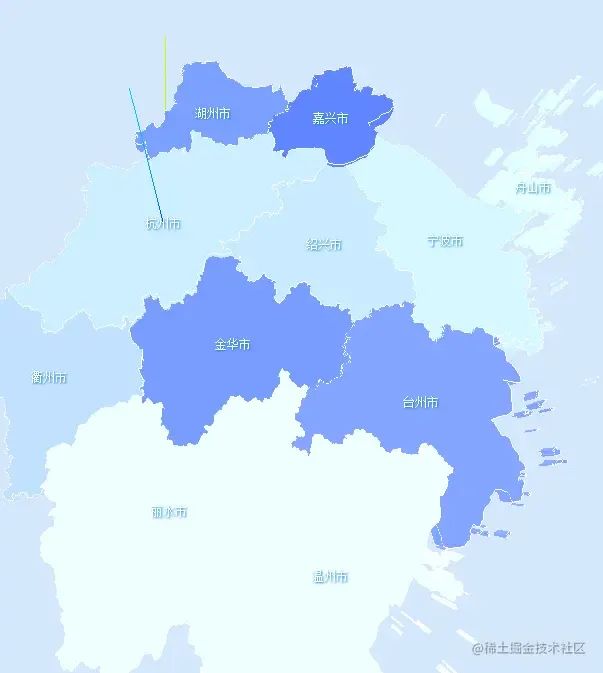
使用css2d需要相應(yīng)的引用以及設(shè)置
import {
CSS2DRenderer,
CSS2DObject,
} from "three/examples/jsm/renderers/CSS2DRenderer.js";
...
...
const labelRenderer = new CSS2DRenderer();
labelRenderer.domElement.style.position = "absolute";
labelRenderer.domElement.style.top = "0px";
labelRenderer.domElement.style.pointerEvents = "none";
labelRenderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
document.getElementById("map").appendChild(labelRenderer.domElement);
除了能使用css的樣式,通過(guò)new CSS2DObject() 這一步后可以操作threejs元素一樣操作div,其實(shí)原理是仍是使用transform屬性進(jìn)行3d變換操作。
const createLabel = (name, point, depth) => {
const div = document.createElement("div");
div.style.color = "#fff";
div.style.fontSize = "12px";
div.style.textShadow = "1px 1px 2px #047cd6";
div.textContent = name;
const label = new CSS2DObject(div);
label.scale.set(0.01, 0.01, 0.01);
const [x, y] = offsetXY(point);
label.position.set(x, -y, depth);
return label;
};
繪制圖標(biāo)
繪制圖標(biāo)也可以使用css2d的方式,但是除了css2d,我們還有多種方式:css3d,svg,Sprite。這里我們使用Sprite。
const createIcon = (point, depth) => {
const url = new URL("../assets/icon.png", import.meta.url).href;
const map = new THREE.TextureLoader().load(url);
const material = new THREE.SpriteMaterial({
map: map,
transparent: true,
});
const sprite = new THREE.Sprite(material);
const [x, y] = offsetXY(point);
sprite.scale.set(0.3, 0.3, 0.3);
sprite.position.set(x, -y, depth + 0.2);
sprite.renderOrder = 1;
return sprite;
};
SPrite是一個(gè)總是面朝著攝像機(jī)的平面,這一點(diǎn)似乎和css2d的效果一樣,不過(guò)二者還略有不同。
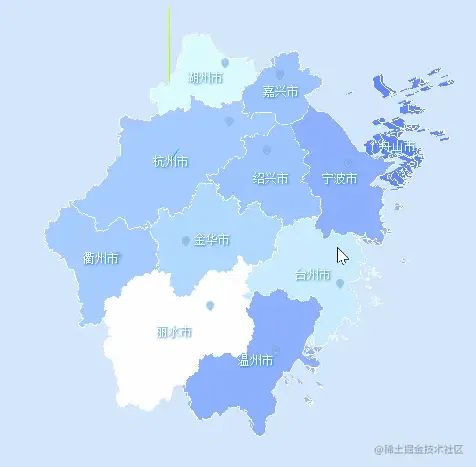
圖中我們可以看到,SPrite會(huì)隨著相機(jī)的距離而改變大小。
坐標(biāo)矯正2
之前的坐標(biāo)矯正我們可以將中心移到某個(gè)點(diǎn)上,那如果想把中心移到整個(gè)圖形的中心該如何實(shí)現(xiàn)?通過(guò)已有的數(shù)據(jù)我們只能將中心移到某個(gè)區(qū)域的中心或者質(zhì)心,并不知道圖形的中心在哪里,當(dāng)然我們可以手動(dòng)調(diào)試,不過(guò)換一份地理數(shù)據(jù)又的重新調(diào)試。
對(duì)此,我們可以使用threejs中的包圍盒
const box = new THREE.Box3().setFromObject(map);
const boxHelper = new THREE.Box3Helper(box, 0xffff00);
scene.add(boxHelper);
創(chuàng)建一個(gè)Box3對(duì)象,并通過(guò)調(diào)用setFromObject(map)方法,將map的包圍盒信息存儲(chǔ)在box變量中。,box變量現(xiàn)在包含了map對(duì)象的邊界范圍。為了便于觀(guān)察再加一個(gè)輔助器。
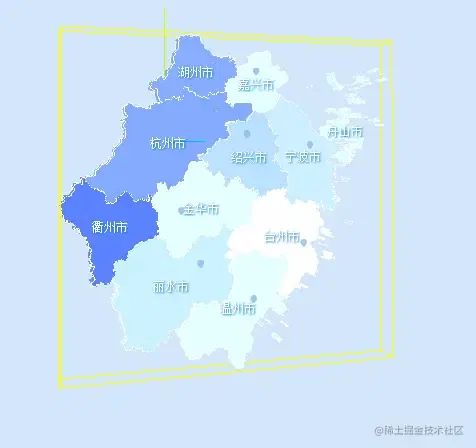
接著通過(guò)const center = box.getCenter(new THREE.Vector3());獲取包圍盒的中心點(diǎn)坐標(biāo)。
map.position.x = map.position.x - center.x ;
map.position.y = map.position.y - center.y ;
對(duì)中心點(diǎn)進(jìn)行計(jì)算后便是一個(gè)相對(duì)中心的位置,因?yàn)橛械牡匦紊婕皪u嶼海域或者形狀不太規(guī)整,得出的中心點(diǎn)可能不是理想效果。
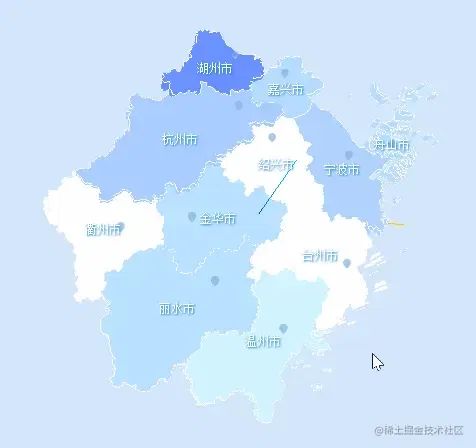
鼠標(biāo)交互
最后我們來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn)圖形與鼠標(biāo)的交互, THREE.Raycaster可以從指定的原點(diǎn)(起點(diǎn))沿著指定的方向(射線(xiàn))發(fā)射一條射線(xiàn)。這條射線(xiàn)可以與場(chǎng)景中的對(duì)象進(jìn)行相交檢測(cè),以確定射線(xiàn)是否與對(duì)象相交,從而獲取與射線(xiàn)相交的對(duì)象或交點(diǎn)信息,常用于用戶(hù)交互、拾取物體、碰撞檢測(cè)等場(chǎng)景。
const mouse = new THREE.Vector2();
//將鼠標(biāo)位置歸一化為設(shè)備坐標(biāo)。x 和 y 方向的取值范圍是 (-1 to +1)
mouse.x = (event.clientX / window.innerWidth) * 2 - 1;
mouse.y = -(event.clientY / window.innerHeight) * 2 + 1;
const raycaster = new THREE.Raycaster();
// 通過(guò)攝像機(jī)和鼠標(biāo)位置更新射線(xiàn)
raycaster.setFromCamera(mouse, camera);
// 計(jì)算物體和射線(xiàn)的焦點(diǎn)
const intersects = raycaster.intersectObjects(map.children)
通過(guò)以上代碼我們可以在intersects里獲取到鼠標(biāo)都觸發(fā)了哪些對(duì)象。
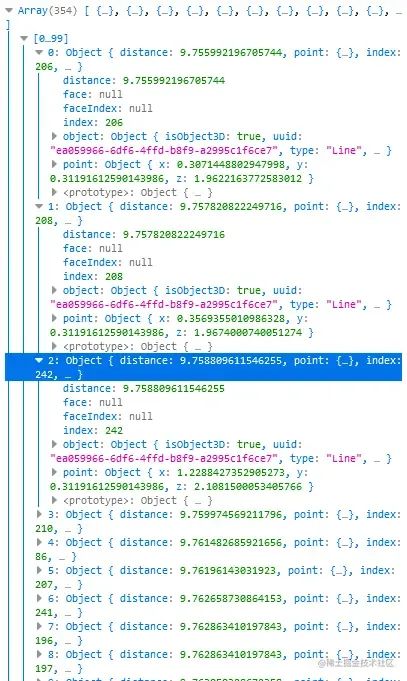
可以看到我們觸發(fā)很多對(duì)象,但是大部分type都是Line,也就是之前繪制的描邊,這些線(xiàn)段會(huì)干擾到正常的點(diǎn)擊,所以我們要將它過(guò)濾掉。
const intersects = raycaster
.intersectObjects(map.children)
.filter((item) => item.object.type !== "Line");

這里簡(jiǎn)單處理一下,點(diǎn)擊Mesh使其透明,點(diǎn)擊Sprite打印對(duì)象。
if (intersects.length > 0) {
if (intersects[0].object.type === "Mesh") {
if (intersect) isAplha(intersect, 1);
intersect = intersects[0].object.parent;
isAplha(intersect, 0.4);
}
if (intersects[0].object.type === "Sprite") {
console.log(intersects[0].object);
}
} else {
if (intersect) isAplha(intersect, 1);
}
function isAplha(intersect, opacity) {
intersect.children.forEach((item) => {
if (item.type === "Mesh") {
item.material.opacity = opacity;
}
});
}
有一點(diǎn)需要注意在獲取Mesh對(duì)象時(shí),我們使用的是intersects[0].object.parent;,拿到了觸發(fā)對(duì)象的的父級(jí)對(duì)象。以舟山為例,我們點(diǎn)擊了其中一個(gè)島嶼,但是想要整個(gè)區(qū)域都發(fā)生變化,所以需要獲取父級(jí)對(duì)象再遍歷處理。
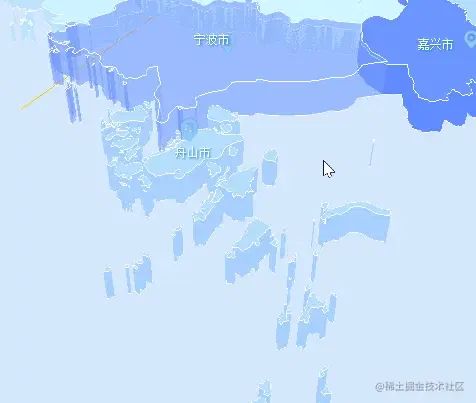

其他設(shè)置
大致的功能都實(shí)現(xiàn)完成了,我們還可以在視覺(jué)上增加一些風(fēng)格。
const ambientLight = new THREE.AmbientLight(0xd4e7fd, 4);
scene.add(ambientLight);
const directionalLight = new THREE.DirectionalLight(0xe8eaeb, 0.2);
directionalLight.position.set(0, 10, 5);
const directionalLight2 = directionalLight.clone();
directionalLight2.position.set(0, 10, -5);
const directionalLight3 = directionalLight.clone();
directionalLight3.position.set(5, 10, 0);
const directionalLight4 = directionalLight.clone();
directionalLight4.position.set(-5, 10, 0);
scene.add(directionalLight);
scene.add(directionalLight2);
scene.add(directionalLight3);
scene.add(directionalLight4);
...
...
THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({
color: color,
emissive: 0x000000,
roughness: 0.45,
metalness: 0.8,
transparent: true,
side: THREE.DoubleSide,
});
配合燈光以及MeshStandardMaterial材質(zhì)實(shí)現(xiàn)反光效果。
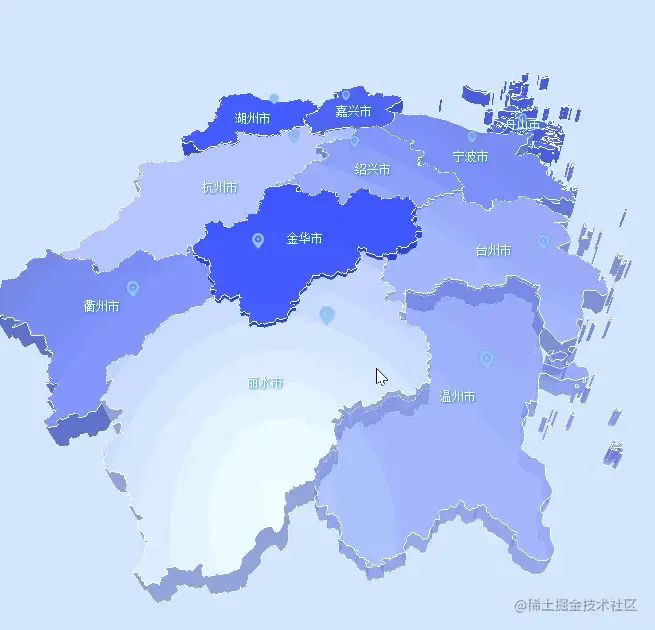
結(jié)尾
代碼寫(xiě)的有些匆忙,功能也還有沒(méi)寫(xiě)的,本來(lái)是打算加上飛線(xiàn)、熱力、柱狀圖這類(lèi)的功能。但是最近剛?cè)胧至恕冬F(xiàn)代JavaScript庫(kù)開(kāi)發(fā):原理、技術(shù)與實(shí)戰(zhàn)》,想著到時(shí)候讀完看看能不能試著寫(xiě)一個(gè)相關(guān)的庫(kù),給自己畫(huà)個(gè)大餅先
假如有后續(xù)的話(huà)可以前往github.com/1023byte/3Dmap
關(guān)于本文
作者:Defineee
https://juejin.cn/post/7247027696822304827
最后
Node 社群
我組建了一個(gè)氛圍特別好的 Node.js 社群,里面有很多 Node.js小伙伴,如果你對(duì)Node.js學(xué)習(xí)感興趣的話(huà)(后續(xù)有計(jì)劃也可以),我們可以一起進(jìn)行Node.js相關(guān)的交流、學(xué)習(xí)、共建。下方加 考拉 好友回復(fù)「Node」即可。
“分享、點(diǎn)贊、在看” 支持一下
