獨(dú)家 | 使用Python的LDA主題建模(附鏈接)
作者:Kamil Polak 翻譯:劉思婧
校對(duì):孫韜淳
本文約2700字,建議閱讀5分鐘
本文為大家介紹了主題建模的概念、LDA算法的原理,示例了如何使用Python建立一個(gè)基礎(chǔ)的LDA主題模型,并使用pyLDAvis對(duì)主題進(jìn)行可視化。
引言
發(fā)現(xiàn)數(shù)據(jù)集中隱藏的主題;
將文檔分類(lèi)到已經(jīng)發(fā)現(xiàn)的主題中;
使用分類(lèi)來(lái)組織/總結(jié)/搜索文檔。
潛在語(yǔ)義索引(Latent semantic indexing)
潛在狄利克雷分配(Latent Dirichlet Allocation,LDA)
非負(fù)矩陣分解(Non-negative matrix factorization,NMF)
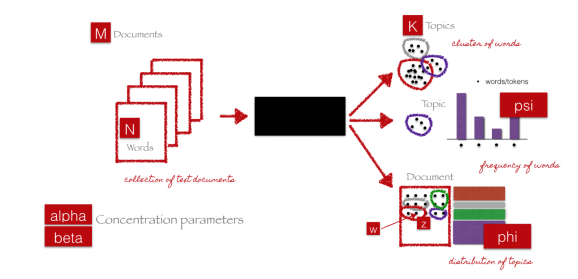
什么是潛在狄利克雷分配(LDA, Latent Dirichlet allocation);
LDA算法如何工作;
如何使用Python建立LDA主題模型。
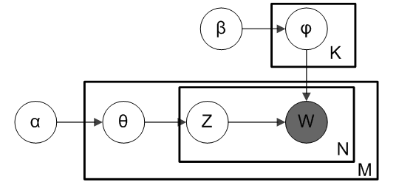
什么是潛在狄利克雷分配(LDA, Latent Dirichlet allocation)?
LDA算法如何工作?
我們已知的屬于文件的單詞;
需要計(jì)算的屬于一個(gè)主題的單詞或?qū)儆谝粋€(gè)主題的單詞的概率。
P(T | D):文檔D中,指定給主題T的單詞的比例;
P(W | T):所有包含單詞W的文檔中,指定給主題T的比例。
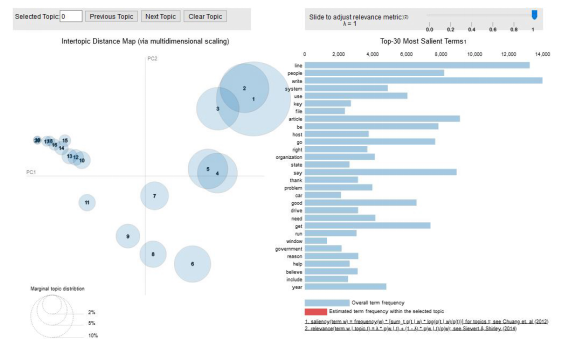
LDA主題模型的圖示如下。

如何使用Python建立LDA主題模型
1. import re2. import numpy as np3. import pandas as pd4. from pprint import pprint5.6. # Gensim7. import gensim8. import gensim.corpora as corpora9. from gensim.utils import simple_preprocess10. from gensim.models import CoherenceModel11.12. # spacy for lemmatization13. import spacy14.15. # Plotting tools16. import pyLDAvis17. import pyLDAvis.gensim # don't skip this18. import matplotlib.pyplot as plt19. %matplotlib inline20.21. # Enable logging for gensim - optional22. import logging23. logging.basicConfig(format='%(asctime)s : %(levelname)s : %(message)s', level=logging.ERROR)24.25. import warnings26. warnings.filterwarnings("ignore",category=DeprecationWarning)
1. # NLTK Stop words2. from nltk.corpus import stopwords3. stop_words = stopwords.words('english')4. stop_words.extend(['from', 'subject', 're', 'edu', 'use'])
1. # Import Dataset2. df = pd.read_json('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/newsgroups.json')3. print(df.target_names.unique())4. df.head()

1. # Convert to list2. data = df.content.values.tolist()3.4. # Remove Emails5. data = [re.sub('\S*@\S*\s?', '', sent) for sent in data]6.7. # Remove new line characters8. data = [re.sub('\s+', ' ', sent) for sent in data]9.10. # Remove distracting single quotes11. data = [re.sub("\'", "", sent) for sent in data]12.13. pprint(data[:1])

1. def sent_to_words(sentences):2. for sentence in sentences:3. yield(gensim.utils.simple_preprocess(str(sentence), deacc=True)) # deacc=True removes punctuations4.5. data_words = list(sent_to_words(data))6.7. print(data_words[:1])

1. # Build the bigram and trigram models2. bigram = gensim.models.Phrases(data_words, min_count=5, threshold=100) # higher threshold fewer phrases.3. trigram = gensim.models.Phrases(bigram[data_words], threshold=100)4.5. # Faster way to get a sentence clubbed as a trigram/bigram6. bigram_mod = gensim.models.phrases.Phraser(bigram)7. trigram_mod = gensim.models.phrases.Phraser(trigram)8.9. # See trigram example10. print(trigram_mod[bigram_mod[data_words[0]]])
1. # Define functions for stopwords, bigrams, trigrams and lemmatization2. def remove_stopwords(texts):3. return [[word for word in simple_preprocess(str(doc)) if word not in stop_words] for doc in texts]4.5. def make_bigrams(texts):6. return [bigram_mod[doc] for doc in texts]7.8. def make_trigrams(texts):9. return [trigram_mod[bigram_mod[doc]] for doc in texts]10.11. def lemmatization(texts, allowed_postags=['NOUN', 'ADJ', 'VERB', 'ADV']):12. """https://spacy.io/api/annotation"""13. texts_out = []14. for sent in texts:15. doc = nlp(" ".join(sent))16. texts_out.append([token.lemma_ for token in doc if token.pos_ in allowed_postags])17. return texts_out1. # Remove Stop Words2. data_words_nostops = remove_stopwords(data_words)3.4. # Form Bigrams5. data_words_bigrams = make_bigrams(data_words_nostops)6.7. # Initialize spacy 'en' model, keeping only tagger component (for efficiency)8. # python3 -m spacy download en9. nlp = spacy.load('en', disable=['parser', 'ner'])10.11. # Do lemmatization keeping only noun, adj, vb, adv12. data_lemmatized = lemmatization(data_words_bigrams, allowed_postags=['NOUN', 'ADJ', 'VERB', 'ADV'])13.14. print(data_lemmatized[:1])

1. # Create Dictionary2. id2word = corpora.Dictionary(data_lemmatized)3.4. # Create Corpus5. texts = data_lemmatized6.7. # Term Document Frequency8. corpus = [id2word.doc2bow(text) for text in texts]9.10. # View11. print(corpus[:1])

num_topics —需要預(yù)先定義的主題數(shù)量;
chunksize — 每個(gè)訓(xùn)練塊(training chunk)中要使用的文檔數(shù)量;
alpha — 影響主題稀疏性的超參數(shù);
passess — 訓(xùn)練評(píng)估的總數(shù)。
1. # Build LDA model2. lda_model = gensim.models.ldamodel.LdaModel(corpus=corpus,3. id2word=id2word,4. num_topics=20,5. random_state=100,6. update_every=1,7. chunksize=100,8. passes=10,9. alpha='auto',10. per_word_topics=True)
1. # Print the Keyword in the 10 topics2. pprint(lda_model.print_topics())3. doc_lda = lda_model[corpus]



1. # Compute Perplexity2. print('\nPerplexity: ', lda_model.log_perplexity(corpus)) # a measure of how good the model is. lower the better.3.4. # Compute Coherence Score5. coherence_model_lda = CoherenceModel(model=lda_model, texts=data_lemmatized, dictionary=id2word, coherence='c_v')6. coherence_lda = coherence_model_lda.get_coherence()7. print('\nCoherence Score: ', coherence_lda)

1. # Visualize the topics2. pyLDAvis.enable_notebook()3. vis = pyLDAvis.gensim.prepare(lda_model, corpus, id2word)4. vis
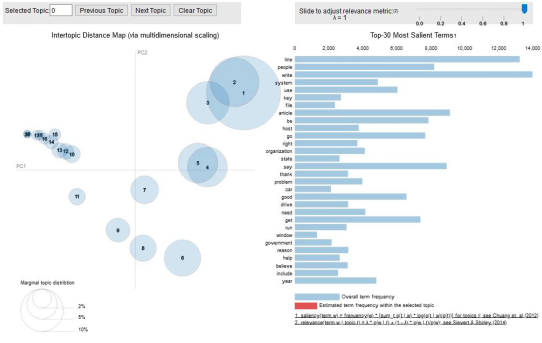
結(jié)語(yǔ)
主題建模是自然語(yǔ)言處理的主要應(yīng)用之一。本文的目的是解釋什么是主題建模,以及如何在實(shí)際使用中實(shí)現(xiàn)潛在狄利克雷分配(LDA)模型。
希望您喜歡該文并有所收獲。
References:
編輯:王菁
校對(duì):林亦霖
譯者簡(jiǎn)介
劉思婧,清華大學(xué)新聞系研一在讀,數(shù)據(jù)傳播方向。文理兼愛(ài),有點(diǎn)小情懷的數(shù)據(jù)愛(ài)好者。希望結(jié)識(shí)更多不同專(zhuān)業(yè)、不同專(zhuān)長(zhǎng)的伙伴,拓寬眼界、優(yōu)化思維、日日自新。
翻譯組招募信息
工作內(nèi)容:需要一顆細(xì)致的心,將選取好的外文文章翻譯成流暢的中文。如果你是數(shù)據(jù)科學(xué)/統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)/計(jì)算機(jī)類(lèi)的留學(xué)生,或在海外從事相關(guān)工作,或?qū)ψ约和庹Z(yǔ)水平有信心的朋友歡迎加入翻譯小組。
你能得到:定期的翻譯培訓(xùn)提高志愿者的翻譯水平,提高對(duì)于數(shù)據(jù)科學(xué)前沿的認(rèn)知,海外的朋友可以和國(guó)內(nèi)技術(shù)應(yīng)用發(fā)展保持聯(lián)系,THU數(shù)據(jù)派產(chǎn)學(xué)研的背景為志愿者帶來(lái)好的發(fā)展機(jī)遇。
其他福利:來(lái)自于名企的數(shù)據(jù)科學(xué)工作者,北大清華以及海外等名校學(xué)生他們都將成為你在翻譯小組的伙伴。
點(diǎn)擊文末“閱讀原文”加入數(shù)據(jù)派團(tuán)隊(duì)~
轉(zhuǎn)載須知
如需轉(zhuǎn)載,請(qǐng)?jiān)陂_(kāi)篇顯著位置注明作者和出處(轉(zhuǎn)自:數(shù)據(jù)派ID:DatapiTHU),并在文章結(jié)尾放置數(shù)據(jù)派醒目二維碼。有原創(chuàng)標(biāo)識(shí)文章,請(qǐng)發(fā)送【文章名稱(chēng)-待授權(quán)公眾號(hào)名稱(chēng)及ID】至聯(lián)系郵箱,申請(qǐng)白名單授權(quán)并按要求編輯。
發(fā)布后請(qǐng)將鏈接反饋至聯(lián)系郵箱(見(jiàn)下方)。未經(jīng)許可的轉(zhuǎn)載以及改編者,我們將依法追究其法律責(zé)任。
點(diǎn)擊“閱讀原文”擁抱組織


