半小時(shí)快速上手 TypeScript 類型編程!(附手摸手實(shí)戰(zhàn)案例)
1. Why
在介紹什么叫 TypeScript 類型編程和為什么需要學(xué)習(xí) TypeScript 類型編程之前,我們先看一個(gè)例子,這里例子里包含一個(gè) promisify 的函數(shù),這個(gè)函數(shù)用于將 NodeJS 中 callback style 的函數(shù)轉(zhuǎn)換成 promise style 的函數(shù)。
import * as fs from "fs";
function promisify(fn) {
return function(...args) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fn(...args, (err, data) => {
if(err) {
return reject(err);
}
resolve(data);
});
});
}
}
(async () => {
let file = await promisify(fs.readFile)("./xxx.json");
})();
如果我們直接套用上述的代碼,那么 file 的類型和 promisify(fs.readFile)(...) 中 (...) 的類型也會(huì)丟失,也就是我們有兩個(gè)目標(biāo):
我們需要知道
promisify(fs.readFile)(...)這里能夠接受的類型。我們需要知道
let file = await ...這里 file 的類型。
這個(gè)問題的答案在實(shí)戰(zhàn)演練環(huán)節(jié)會(huì)結(jié)合本文的內(nèi)容給出答案,如果你覺得這個(gè)問題簡單得很,那么恭喜你,你已經(jīng)具備本文將要介紹的大部分知識(shí)點(diǎn)。如何讓類似于 promisify這樣的函數(shù)保留類型信息是“體操”或者我稱之為類型編程的意義所在。
2. 前言 (Preface)
最近在國內(nèi)的前端圈流行一個(gè)名詞“TS 體操”,簡稱為“TC”,體操這個(gè)詞是從 Haskell 社區(qū)來的,本意就是高難度動(dòng)作,關(guān)于“體操”能夠?qū)崿F(xiàn)到底多高難度的動(dòng)作,可以參照下面這篇文章。
https://www.zhihu.com/question/418792736/answer/1448121319[1]
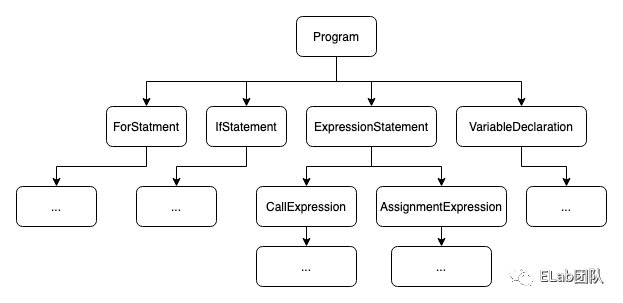
3. 建模 (Modeling)
4. 語法分類 (Grammar Classification)
4.1 基本類型 (Basic Types)
Boolean[4] Number[5] String[6] Array[7] Tuple[8] (TypeScript 獨(dú)有) Enum[9] (TypeScript 獨(dú)有) Unknown[10] (TypeScript 獨(dú)有) Any[11] (TypeScript 獨(dú)有) Void[12] (TypeScript 獨(dú)有) Null and Undefined[13] Never[14] (TypeScript 獨(dú)有) Object[15]
type A = {
attrA: string,
attrB: number,
attrA: true, // Boolean 的枚舉
...
}
4.2 函數(shù) (Function)
類比 let func = (argA, argB, ...) => expression;
// 函數(shù)定義
type B<T> = T & {
attrB: "anthor value"
}
// 變量
class CCC {
...
}
type DDD = {
...
}
// 函數(shù)調(diào)用
type AnotherType = B<CCC>;
type YetAnotherType = B<DDD>;
<T> 就相當(dāng)于函數(shù)括弧和參數(shù)列表,= 后面的就相當(dāng)于函數(shù)定義。或者按照這個(gè)思路你可以開始沉淀很多工具類 TC 函數(shù)了,例如// 將所有屬性變成可選的
type Optional<T> = {
[key in keyof T]?: T[key];
}
// 將某些屬性變成必選的
type MyRequired<T, K extends keyof T> = T &
{
[key in K]-?: T[key];
};
// 例如我們有個(gè)實(shí)體
type App = {
_id?: string;
appId: string;
name: string;
description: string;
ownerList: string[];
createdAt?: number;
updatedAt?: number;
};
// 我們在更新這個(gè)對象/類型的時(shí)候,有些 key 是必填的,有些 key 是選填的,這個(gè)時(shí)候就可以這樣子生成我們需要的類型
type AppUpdatePayload = MyRequired<Optional<App>, '_id'>
<K extends keyof T> 這樣的語法來表達(dá)。TypeScript 函數(shù)的缺陷 (Defect)
高版本才能支持遞歸
函數(shù)不能作為參數(shù)
function map(s, mapper) { return s.map(mapper) }
map([1, 2, 3], (t) => s);
type Map<T, Mapper> = {
[k in keyof T]: Mapper<T[k]>; // 語法報(bào)錯(cuò)
}
支持閉包,但是沒有辦法修改閉包中的值
type ClosureValue = string;
type Map<T> = {
[k in keyof T]: ClosureValue; // 筆者沒有找到語法能夠修改 ClosureValue
}
type ClosureValue = string;
type Map<T> = {
[k in keyof T]: ClosureValue & T[k]; // 筆者沒有找到語法能夠修改 ClosureValue
}
4.3 語句 (Statements)
變量聲明語句 (Variable Declaration)
類比:let a = Expression;
type ToDeclareType = Expresion 這樣子的變量名加表達(dá)式的語法來實(shí)現(xiàn),表達(dá)式有很多種類,我們接下來會(huì)詳細(xì)到介紹到,type ToDeclareType<T> = T extends (args: any) => PromiseLike<infer R> ? R : never; // 條件表達(dá)式/帶三元運(yùn)算符的條件表達(dá)式
type ToDeclareType = Omit<App>; // 函數(shù)調(diào)用表達(dá)式
type ToDeclareType<T>= { // 循環(huán)表達(dá)式
[key in keyof T]: Omit<T[key], '_id'>
}
4.4 表達(dá)式 (Expressions)
帶三元運(yùn)算符的條件表達(dá)式 (IfExpression with ternary operator)
類比:a == b ? 'hello' : 'world';
Condition ? ExpressionIfTrue : ExpressionIfFalse 這樣的形式,在 TypeScript 中則可以用以下的語法來表示:type TypeOfWhatPromiseReturn<T> = T extends (args: any) => PromiseLike<infer R> ? R : never;
T extends (args: any) => PromiseLike<infer R> 就相當(dāng)條件判斷,R : never 就相當(dāng)于為真時(shí)的表達(dá)式和為假時(shí)的表達(dá)式。async function hello(name: string): Promise<string> {
return Promise.resolve(name);
}
// type CCC: string = ReturnType<typeof hello>; doesn't work
type MyReturnType<T extends (...args) => any> = T extends (
...args
) => PromiseLike<infer R>
? R
: ReturnType<T>;
type CCC: string = MyReturnType<typeof hello>; // it works
函數(shù)調(diào)用/定義表達(dá)式 (CallExpression)
類比:call(a, b, c);
循環(huán)相關(guān) (Loop Related)(Object.keys、Array.map等)
類比:for (let k in b) { ... }
循環(huán)實(shí)現(xiàn)思路 (Details Explained )
注意:遞歸只有在 TS 4.1.0 才支持
type IntSeq<N, S extends any[] = []> =
S["length"] extends N ? S :
IntSeq<N, [...S, S["length"]]>
對對象進(jìn)行遍歷 (Loop Object)
type AnyType = {
[key: string]: any;
};
type OptionalString<T> = {
[key in keyof T]?: string;
};
type CCC = OptionalString<AnyType>;
對數(shù)組(Tuple)進(jìn)行遍歷 (Loop Array/Tuple)
map
類比:Array.map
const a = ['123', 1, {}];
type B = typeof a;
type Map<T> = {
[k in keyof T]: T[k] extends (...args) => any ? 0 : 1;
};
type C = Map<B>;
type D = C[0];
reduce
類比:Array.reduce
const a = ['123', 1, {}];
type B = typeof a;
type Reduce<T extends any[]> = T[number] extends (...arg: any[]) => any ? 1 : 0;
type C = Reduce<B>;
4.5 成員表達(dá)式 (Member Expression)
a.b.c 這樣的成員表達(dá)式主要是因?yàn)槲覀冎懒四硞€(gè)對象/變量的結(jié)構(gòu),然后想拿到其中某部分的值,在 TypeScript 中有個(gè)比較通用的方法,就是用 infer 語法,例如我們想拿到函數(shù)的某個(gè)參數(shù)就可以這么做:function hello(a: any, b: string) {
return b;
}
type getSecondParameter<T> = T extends (a: any, b: infer U) => any ? U : never;
type P = getSecondParameter<typeof hello>;
T extends (a: any, b: infer U) => any 就是在表示結(jié)構(gòu),并拿其中某個(gè)部分。type A = {
a: string;
b: string;
};
type B = [string, string, boolean];
type C = A['a'];
type D = B[number];
type E = B[0];
// eslint-disable-next-line prettier/prettier
type Last<T extends any[]> = T extends [...infer _, infer L] ? L : never;
type F = Last<B>;
4.6 常見數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)和操作 (Common Datastructures and Operations)
Set
Add
type S = '1' | 2 | a;
S = S | 3;
Remove
type S = '1' | 2 | a;
S = Exclude<S, '1'>;
Has
type S = '1' | 2 | a;
type isInSet = 1 extends S ? true : false;
Intersection
type SA = '1' | 2;
type SB = 2 | 3;
type interset = Extract<SA, SB>;
Diff
type SA = '1' | 2;
type SB = 2 | 3;
type diff = Exclude<SA, SB>;
Symmetric Diff
type SA = '1' | 2;
type SB = 2 | 3;
type sdiff = Exclude<SA, SB> | Exclude<SB, SA>;
ToIntersectionType
type A = {
a: string;
b: string;
};
type B = {
b: string;
c: string;
};
type ToIntersectionType<U> = (
U extends any ? (arg: U) => any : never
) extends (arg: infer I) => void
? I
: never;
type D = ToIntersectionType <A | B>;
ToArray
注意:遞歸只有在 TS 4.1.0 才支持
type Input = 1 | 2;
type UnionToIntersection<U> = (
U extends any ? (arg: U) => any : never
) extends (arg: infer I) => void
? I
: never;
type ToArray<T> = UnionToIntersection<(T extends any ? (t: T) => T : never)> extends (_: any) => infer W
? [...ToArray<Exclude<T, W>>, W]
: [];
type Output = ToArray<Input>;
type C = ((arg: any) => true) & ((arg: any) => false);
type D = C extends (arg: any) => infer R ? R : never; // false;
Size
type Input = 1 | 2;
type Size = ToArray<Input>['length'];
Map/Object
Merge/Object.assign
type C = A & B;
Intersection
interface A {
a: string;
b: string;
c: string;
}
interface B {
b: string;
c: number;
d: boolean;
}
type Intersection<A, B> = {
[KA in Extract<keyof A, keyof B>]: A[KA] | B[KA];
};
type AandB = Intersection<A, B>;
Filter
type Input = { foo: number; bar?: string };
type FilteredKeys<T> = {
[P in keyof T]: T[P] extends number ? P : never;
}[keyof T];
type Filter<T> = {
[key in FilteredKeys<T>]: T[key];
};
type Output = Filter<Input>;
Array
成員訪問
type B = [string, string, boolean];
type D = B[number];
type E = B[0];
// eslint-disable-next-line prettier/prettier
type Last<T extends any[]> = T extends [...infer _, infer L] ? L : never;
type F = Last<B>;
type G = B['length'];
Append
type Append<T extends any[], V> = [...T, V];
Pop
type Pop<T extends any[]> = T extends [...infer I, infer _] ? I : never
Dequeue
type Dequeue<T extends any[]> = T extends [infer _, ...infer I] ? I : never
Prepend
type Prepend<T extends any[], V> = [V, ...T];
Concat
type Concat<T extends any[], V extends any[] > = [...T, ...V];
Filter
注意:遞歸只有在 TS 4.1.0 才支持
type Filter<T extends any[]> = T extends [infer V, ...infer R]
? V extends number
? [V, ...Filter<R>]
: Filter<R>
: [];
type Input = [1, 2, string];
type Output = Filter<Input>;
Slice
注意:遞歸只有在 TS 4.1.0 才支持 注意:為了實(shí)現(xiàn)簡單,這里 Slice 的用法和 Array.slice 用法不一樣:N 表示剩余元素的個(gè)數(shù)。
type Input = [string, string, boolean];
type Slice<N extends number, T extends any[]> = T['length'] extends N
? T
: T extends [infer _, ...infer U]
? Slice<N, U>
: never;
type Out = Slice<2, Input>;
Array.slice(s) 這種效果,實(shí)現(xiàn) Array.slice(s, e) 涉及減法,比較麻煩,暫不在這里展開了。4.7 運(yùn)算符 (Operators)
注意:運(yùn)算符的實(shí)現(xiàn)涉及遞歸,遞歸只有在 TS 4.1.0 才支持
注意:下面的運(yùn)算符只能適用于整型
注意:原理依賴于遞歸、效率較低
基本原理 (Details Explained)
type IntSeq<N, S extends any[] = []> =
S["length"] extends N ? S :
IntSeq<N, [...S, S["length"]]>;
===
type IfEquals<X, Y, A = X, B = never> = (<T>() => T extends X ? 1 : 2) extends <
T
>() => T extends Y ? 1 : 2
? A
: B;
+
type NumericPlus<A extends Numeric, B extends Numeric> = [...IntSeq<A>, ...IntSeq<B>]["length"];
-
注意:減法結(jié)果不支持負(fù)數(shù) ...
type NumericMinus<A extends Numeric, B extends Numeric> = _NumericMinus<B, A, []>;
type ToNumeric<T extends number> = T extends Numeric ? T : never;
type _NumericMinus<A extends Numeric, B extends Numeric, M extends any[]> = NumericPlus<A, ToNumeric<M["length"]>> extends B ? M["length"] : _NumericMinus<A, B, [...M, 0]>;
4.8 其他 (MISC)
inferface
inteface A extends B {
attrA: string
}
Utility Types
5. 實(shí)戰(zhàn)演練 (Excercise)
Promisify
import * as fs from "fs";
function promisify(fn) {
return function(...args: XXXX) {
return new Promise<XXXX>((resolve, reject) => {
fn(...args, (err, data) => {
if(err) {
return reject(err);
}
resolve(data);
});
});
}
}
(async () => {
let file = await promisify(fs.readFile)("./xxx.json");
})();
我們需要知道 promisify(fs.readFile)(...)這里能夠接受的類型。我們需要 let file = await ...這里 file 的類型。
答案
import * as fs from "fs";
// 基于數(shù)據(jù)的基本操作 Last 和 Pop
type Last<T extends any[]> = T extends [...infer _, infer L] ? L : never;
type Pop<T extends any[]> = T extends [...infer I, infer _] ? I : never;
// 對數(shù)組進(jìn)行操作
type GetParametersType<T extends (...args: any) => any> = Pop<Parameters<T>>;
type GetCallbackType<T extends (...args: any) => any> = Last<Parameters<T>>;
// 類似于成員變量取值
type GetCallbackReturnType<T extends (...args: any) => any> = GetCallbackType<T> extends (err: Error, data: infer R) => void ? R : any;
function promisify<T extends (...args: any) => any>(fn: T) {
return function(...args: GetParametersType<T>) {
return new Promise<GetCallbackReturnType<T>>((resolve, reject) => {
fn(...args, (err, data) => {
if(err) {
return reject(err);
}
resolve(data);
});
});
}
}
(async () => {
let file = await promisify(fs.readFile)("./xxx.json");
})();
MyReturnType[19]
const fn = (v: boolean) => {
if (v) return 1;
else return 2;
};
type MyReturnType<F> = F extends (...args) => infer R ? R : never;
type a = MyReturnType<typeof fn>;
Readonly 2[20]
interface Todo {
title: string;
description: string;
completed: boolean;
}
type MyReadonly2<T, KEYS extends keyof T> = T &
{
readonly [k in KEYS]: T[k];
};
const todo: MyReadonly2<Todo, 'title' | 'description'> = {
title: 'Hey',
description: 'foobar',
completed: false,
};
todo.title = 'Hello'; // Error: cannot reassign a readonly property
todo.description = 'barFoo'; // Error: cannot reassign a readonly property
todo.completed = true; // O
Type Lookup[21]
interface Cat {
type: 'cat';
breeds: 'Abyssinian' | 'Shorthair' | 'Curl' | 'Bengal';
}
interface Dog {
type: 'dog';
breeds: 'Hound' | 'Brittany' | 'Bulldog' | 'Boxer';
color: 'brown' | 'white' | 'black';
}
type LookUp<T, K extends string> = T extends { type: string }
? T['type'] extends K
? T
: never
: never;
type MyDogType = LookUp<Cat | Dog, 'dog'>; // expected to be `Dog`
Get Required[22]
type GetRequiredKeys<T> = {
[key in keyof T]-?: {} extends Pick<T, key> ? never : key;
}[keyof T];
type GetRequired<T> = {
[key in GetRequiredKeys<T>]: T[key];
};
type I = GetRequired<{ foo: number; bar?: string }>; // expected to be { foo: number }
6. 想法 (Thoughts)
沉淀類型編程庫 (Supplementary Utility Types)
https://github.com/piotrwitek/utility-types
https://github.com/sindresorhus/type-fest
直接用 JS 做類型編程 (Doing Type Computing in Plain TS)
type Test = {
a: string
}
typecomp function Map(T, mapper) {
for (let key of Object.keys(T)) {
T[key] = mapper(T[key]);
}
}
typecomp AnotherType = Map(Test, typecomp (T) => {
if (T extends 'hello') {
return number;
} else {
return string;
}
});
7. Reference
https://github.com/type-challenges/type-challenges https://www.zhihu.com/question/418792736/answer/1448121319 https://github.com/piotrwitek/utility-types#requiredkeyst
參考資料
[1] https://www.zhihu.com/question/418792736/answer/1448121319
[2] 有趣的 brain teaser: https://github.com/type-challenges/type-challenges
[3] AST(抽象語法樹)的角度來看: https://github.com/babel/babel/blob/main/packages/babel-types/src/definitions/core.js
[4] Boolean: https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/basic-types.html#boolean
[5] Number: https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/basic-types.html#number
[6] String: https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/basic-types.html#string
[7] Array: https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/basic-types.html#array
[8] Tuple: https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/basic-types.html#tuple
[9] Enum: https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/basic-types.html#enum
[10] Unknown: https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/basic-types.html#unknown
[11] Any: https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/basic-types.html#any
[12] Void: https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/basic-types.html#void
[13] Null and Undefined: https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/basic-types.html#null-and-undefined
[14] Never: https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/basic-types.html#never
[15] Object: https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/basic-types.html#object
[16] Declaration Merging: https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/declaration-merging.html
[17] 這個(gè)鏈接: https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/utility-types.html
[18] https://github.com/DefinitelyTyped/DefinitelyTyped/blob/master/types/util.promisify/implementation.d.ts
[19] https://github.com/type-challenges/type-challenges/blob/master/questions/2-medium-return-type/README.md
[20] https://github.com/type-challenges/type-challenges/blob/master/questions/8-medium-readonly-2/README.md
[21] https://github.com/type-challenges/type-challenges/blob/master/questions/62-medium-type-lookup/README.md
[22] https://github.com/type-challenges/type-challenges/blob/master/questions/57-hard-get-required/README.md
最后
如果你覺得這篇內(nèi)容對你挺有啟發(fā),我想邀請你幫我三個(gè)小忙:
點(diǎn)個(gè)「在看」,讓更多的人也能看到這篇內(nèi)容(喜歡不點(diǎn)在看,都是耍流氓 -_-)
歡迎加我微信「qianyu443033099」拉你進(jìn)技術(shù)群,長期交流學(xué)習(xí)...
關(guān)注公眾號(hào)「前端下午茶」,持續(xù)為你推送精選好文,也可以加我為好友,隨時(shí)聊騷。