C#: 8.0 & 9.0 常用新特性
在《帶你了解C#每個版本新特性》 一文中介紹了,C# 1.0 到 7.0 的不同特性,本文接著介紹在 8.0 和 9.0 中的一些常用新特性。
C# 8.0
在 dotNET Core 3.1 及以上版本中就可以使用 C# 8 的語法,下面是 C# 8 中我認為比較常用的一些新功能。
默認接口方法
接口是用來約束行為的,在 C# 8 以前,接口中只能進行方法的定義,下面的代碼在 C# 8 以前是會報編譯錯誤的:
public interface IUser
{
string GetName() => "oec2003";
}
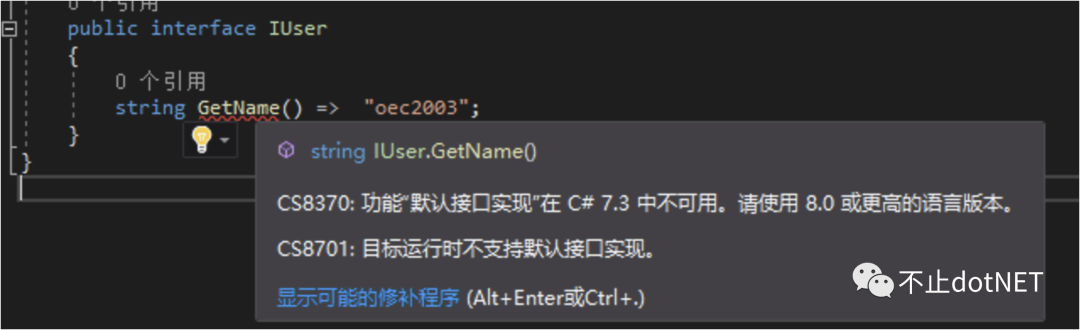
那么在 C# 8 中,可以正常使用上面的代碼,也就是說可以對接口中的方法提供默認實現(xiàn)。
接口默認方法最大的好處是,當(dāng)在接口中進行方法擴展時,之前的實現(xiàn)類可以不受影響,而在 C# 8 之前,接口中如果要添加方法,所有的實現(xiàn)類需要進行新增接口方法的實現(xiàn),否則編譯失敗。
C# 中不支持多重繼承,主要的原因是會導(dǎo)致菱形問題:
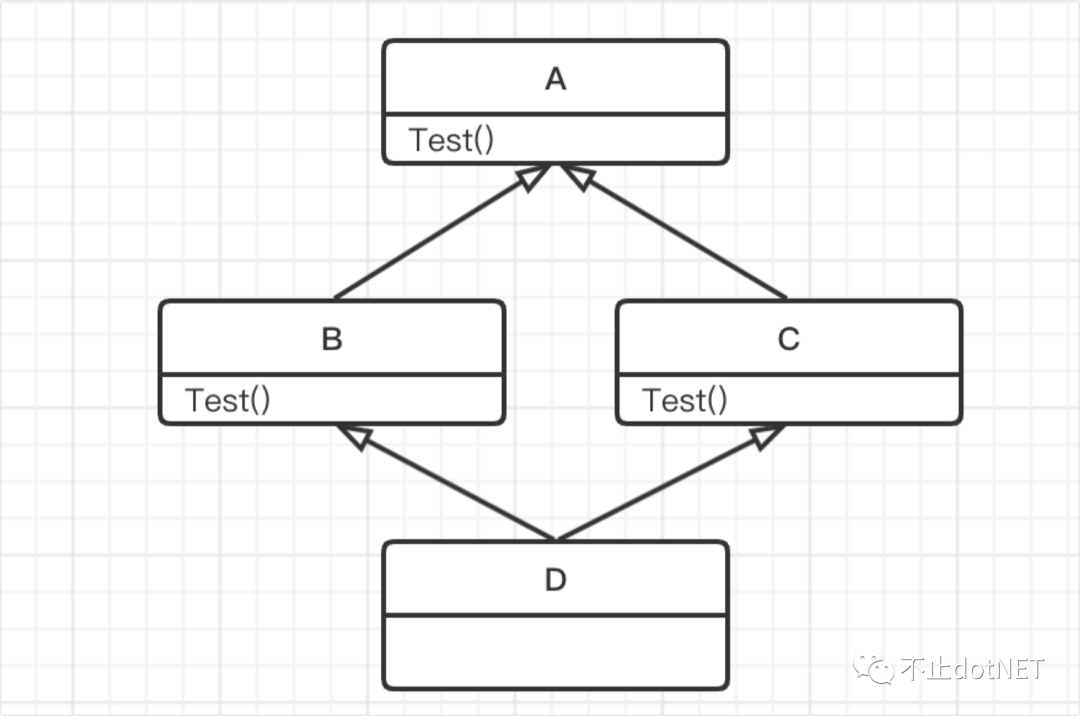
類 A 是一個抽象類,定義有一個 方法 Test; 類 B 和 類 C 繼承自抽象類 A,并有各自的實現(xiàn); 類 D 同時繼承類 B 和類 C;
當(dāng)調(diào)用類 D 的 Test 方法時,就不知道應(yīng)該使用 B 的 Test 還是 C 的 Test,這個就是菱形問題。
而接口是允許多繼承的,那么當(dāng)接口支持默認方法時,是否也會導(dǎo)致菱形問題呢?看下面代碼:
public interface IA
{
void Test() => Console.WriteLine("Invoke IA.Test");
}
public interface IB:IA
{
void Test() => Console.WriteLine("Invoke IB.Test");
}
public interface IC:IA
{
void Test() => Console.WriteLine("Invoke IC.Test");
}
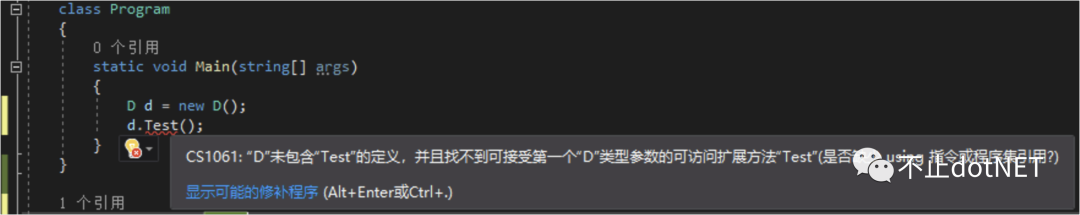
public class D : IB, IC { }
static void Main(string[] args)
{
D d = new D();
d.Test();
}
上面的代碼是無法通過編譯的,因為接口的默認方法不能被繼承,所以類 D 中沒有 Test 方法可以調(diào)用,如下圖:
所以,必須通過接口類型來進行相關(guān)方法的調(diào)用:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IA d1 = new D();
IB d2 = new D();
IC d3 = new D();
d1.Test(); // Invoke IA.Test
d2.Test(); // Invoke IB.Test
d3.Test(); // Invoke IC.Test
}
也正是因為必須通過接口類型來進行調(diào)用,所以也就不存在菱形問題。而當(dāng)具體的類中有對接口方法實現(xiàn)的時候,就會調(diào)用類上實現(xiàn)的方法:
public interface IA
{
void Test() => Console.WriteLine("Invoke IA.Test");
}
public interface IB:IA
{
void Test() => Console.WriteLine("Invoke IB.Test");
}
public interface IC:IA
{
void Test() => Console.WriteLine("Invoke IC.Test");
}
public class D : IB, IC
{
public void Test() => Console.WriteLine("Invoke D.Test");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IA d1 = new D();
IB d2 = new D();
IC d3 = new D();
d1.Test(); // Invoke D.Test
d2.Test(); // Invoke D.Test
d3.Test(); // Invoke D.Test
}
類可能同時繼承類和接口,這時會優(yōu)先調(diào)用類中的方法:
public class A
{
public void Test() => Console.WriteLine("Invoke A.Test");
}
public interface IA
{
void Test() => Console.WriteLine("Invoke IA.Test");
}
public class D : A, IA { }
static void Main(string[] args)
{
D d = new D();
IA d1 = new D();
d.Test(); // Invoke A.Test
d1.Test(); // Invoke A.Test
}
關(guān)于默認接口方法,總結(jié)如下:
默認接口方法可以讓我們在往底層接口中擴展方法的時候變得比較平滑; 默認方法,會優(yōu)先調(diào)用類中的實現(xiàn),如果類中沒有實現(xiàn),才會去調(diào)用接口中的默認方法; 默認方法不能夠被繼承,當(dāng)類中沒有自己實現(xiàn)的時候是不能從類上直接調(diào)用的。
using 變量聲明
我們都知道 using 關(guān)鍵字可以導(dǎo)入命名空間,也能定義別名,還能定義一個范圍,在范圍結(jié)束時銷毀對象,在 C# 8.0 中的 using 變量聲明可以讓代碼看起來更優(yōu)雅。
在沒有 using 變量聲明的時候,我們是這樣使用的:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var connString = "Host=221.234.36.41;Username=gpadmin;Password=123456;Database=postgres;Port=54320";
using (var conn = new NpgsqlConnection(connString))
{
conn.Open();
using (var cmd = new NpgsqlCommand("select * from user_test", conn))
{
using (var reader = cmd.ExecuteReader())
{
while (reader.Read())
Console.WriteLine(reader["user_name"]);
}
}
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
當(dāng)調(diào)用層級比較多時,會出現(xiàn) using 的嵌套,對影響代碼的可讀性,當(dāng)然,當(dāng)兩個 using 語句中間沒有其他代碼時,可以這樣來優(yōu)化:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var connString = "Host=221.234.36.41;Username=gpadmin;Password=123456;Database=postgres;Port=54320";
using (var conn = new NpgsqlConnection(connString))
{
conn.Open();
using (var cmd = new NpgsqlCommand("select * from user_test", conn))
using (var reader = cmd.ExecuteReader())
while (reader.Read())
Console.WriteLine(reader["user_name"]);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
使用 using 變量聲明后的代碼如下:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var connString = "Host=221.234.36.41;Username=gpadmin;Password=123456;Database=postgres;Port=54320";
using var conn = new NpgsqlConnection(connString);
conn.Open();
using var cmd = new NpgsqlCommand("select * from user_test", conn);
using var reader = cmd.ExecuteReader();
while (reader.Read())
Console.WriteLine(reader["user_name"]);
Console.ReadKey();
}
Null 合并賦值
這是一個很有用的語法糖,在 C# 中如果調(diào)用一個為 Null 的引用類型上的方法,會出現(xiàn)經(jīng)典的錯誤:”未將對應(yīng)引用到對象的實例“,所以我們在返回引用類型時,需要做些判斷:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<string> list = GetUserNames();
if(list==null)
{
list = new List<string>();
}
Console.WriteLine(list.Count);
}
public static List<string> GetUserNames()
{
return null;
}
在 C# 8 中可以使用 ??= 操作符更簡單地實現(xiàn):
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<string> list = GetUserNames();
list ??= new List<string>();
Console.WriteLine(list.Count);
}
當(dāng) list 為 null 時,會將右邊的值分配給 list 。
C# 9.0
在 .NET 5 中可以使用 C# 9 ,下面是 C# 9 中幾個常用的新特性。
init
init 是屬性的一種修飾符,可以設(shè)置屬性為只讀,但在初始化的時候卻可以指定值:
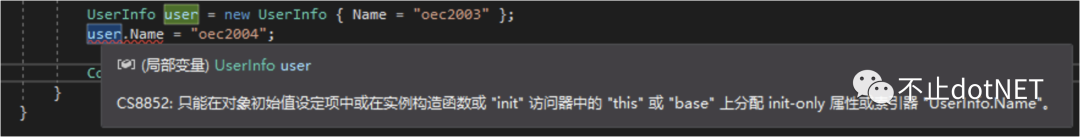
public class UserInfo
{
public string Name { get; init; }
}
UserInfo user = new UserInfo { Name = "oec2003" };
//當(dāng) user 初始化完了之后就不能再改變 Name 的值
user.Name = "oec2004";
上面代碼中給 Name 屬性賦值會出現(xiàn)編譯錯誤:
record
在 C# 9 中新增了 record 修飾符,record 是一種引用類型的修飾符,使用 record 修飾的類型是一種特別的 class,一種不可變的引用類型。
我們創(chuàng)建一個名為 UserInfo 的 class ,不同的實例中即便屬性值完全相同,這兩個實例也是不相等的,看下面代碼:
public class UserInfo
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
UserInfo user1 = new UserInfo { Name = "oec2003" };
UserInfo user2 = new UserInfo { Name = "oec2003" };
Console.WriteLine(user1== user2); //False
}
如果使用 record ,將會看到不一樣的結(jié)果,因為 record 中重寫了 ==、Equals 等 ,是按照屬性值的方式來進行比較的:
public record UserInfo
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
UserInfo user1 = new UserInfo { Name = "oec2003" };
UserInfo user2 = new UserInfo { Name = "oec2003" };
Console.WriteLine(user1== user2); //True
}
在 class 中我們經(jīng)常將一個對象的實例賦值給另一個值,對賦值后的對象實例進行屬性值的改變會影響到原對象實例:
public class UserInfo
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
UserInfo user = new UserInfo { Name = "oec2003" };
UserInfo user1 = user;
user1.Name = "oec2004";
Console.WriteLine(user.Name); // oec2004
}
如果想要不影響原對象實例,就需要使用到深拷貝,在 record 中,可以使用 with 語法簡單地達到目的:
public record UserInfo
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
UserInfo user = new UserInfo { Name = "oec2003" };
UserInfo user1 = user with { Name="eoc2004"};
Console.WriteLine(user.Name); // oec2003
Console.WriteLine(user1.Name); // oec2004
}
模式匹配增強
模式匹配中我覺得最有用的就是對 Null 類型的判斷,在 9.0 中支持這樣的寫法了:
public static string GetUserName(UserInfo user)
{
if(user is not null)
{
return user.Name;
}
return string.Empty;
}
頂級語句
這個不知道有啥用?但挺好玩的,創(chuàng)建一個控制臺程序,將 Program.cs 中的內(nèi)容替換為下面這一行,程序也能正常運行:
System.Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
除此之外,在 C# 8.0 和 9.0 中還有一些其他的新功能,我目前沒有用到或者我覺得不太常用,就沒有寫在本文中了。
希望本文對您有所幫助。
