代理模式,拿下!!!
代理模式是給一個對象提供一個代理對象,并由代理對象控制對原對象的引用。
通俗來講,代理模式就是我們所熟知的中介。
以我們熟知的商品代購為例:
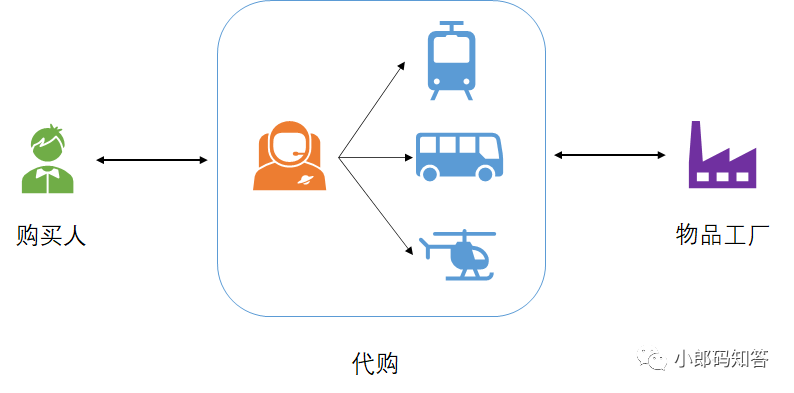
假如我們需要買一個物品,我們可以直接去工廠里購買;也可以找代購。
如果直接去工廠購買,我們在購買前需要對自己要買的物品做一些調(diào)研,然后去工廠直接去提貨,這樣什么事情都需要自己親力親為。
如果我們通過代購購買,我們只需要告訴代購我們需要什么,剩下的事情代購會幫我們處理(調(diào)研、拿貨),最終給我們需要的相應的物品。
因此,代理模式的目標如下:
(1)通過引用代理對象的方式來間接訪問目標對象,防止直接訪問目標對象給系統(tǒng)帶來不必要的復雜性。
(2)通過代理對象對原有的業(yè)務進行增強。
通常情況下,按照代理的創(chuàng)建時期,一般可以分為兩種:
靜態(tài)代理
靜態(tài)代理是由程序員或者特定的工具自動生成的源代碼,再對其編譯,在程序運行之前,代理類編譯的生成的.class文件就已經(jīng)存在了
動態(tài)代理
動態(tài)代理是在程序運行時,通過反射機制動態(tài)創(chuàng)建而成。
1、靜態(tài)代理模式
靜態(tài)代理中的代理類和委托類的關系在運行前就確定了,如圖所示:
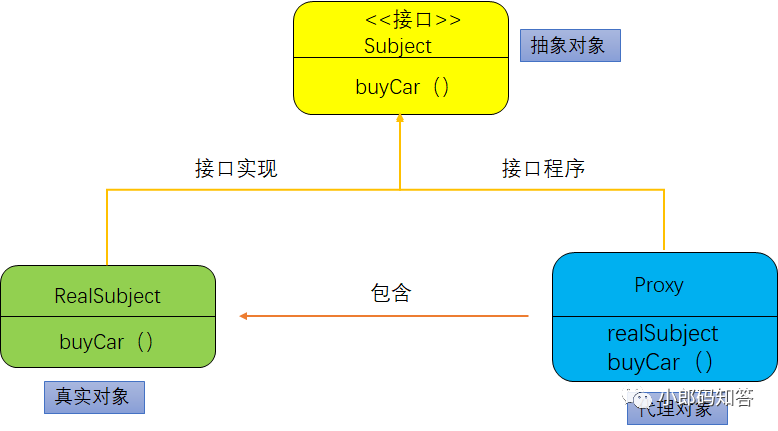
特別注意幾個概念:
抽象對象
抽象對象聲明了真實對象和代理對象的公共接口。
真實對象
代理對象所代表的真實對象,最終被引用的對象。
代理對象
包含真實對象進而操作真實對象,相當于訪問者與真實對象直接的中介。
下面,我們來舉個例子:
(1)創(chuàng)建服務類接口
public interface BuyCar {
void buycar();
}
(2)服務實現(xiàn)類
public class BuyCarImpl implements BuyCar{
public void buycar() {
System.out.println("買一輛奧迪");
}
}
(3)創(chuàng)建代理類
public class BuyCarProxy implements BuyCar{
private BuyCar buyCar;
public BuyCarProxy(BuyCar buyCar){
this.buyCar = buyCar;
}
public void buycar() {
System.out.println("買車前的調(diào)研......");
buyCar.buycar();
System.out.println("買車后的保養(yǎng)......");
}
}
(4)編寫測試類
public class ProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BuyCarImpl buyCar = new BuyCarImpl();
BuyCarProxy buyCarProxy = new BuyCarProxy(buyCar);
buyCarProxy.buycar();
}
}
優(yōu)點:靜態(tài)代理在不修改目標對象的前提下,可以通過代理對象對目標對象進行擴展。
代理類可以使得客戶端不需要知道具體的實現(xiàn)類是什么,怎么做的,客戶端只需知道代理即可(解耦合)
缺點:代理類和具體的實現(xiàn)類實現(xiàn)了相同的接口,代理類通過實現(xiàn)類實現(xiàn)了相同的方法。這樣就出現(xiàn)了大量的代碼重復。如果接口增加一個方法,除了所有實現(xiàn)類需要實現(xiàn)這個方法外,所有代理類也需要實現(xiàn)此方法。增加了代碼維護的復雜度。
代理對象只服務于一種類型的對象,如果要服務多類型的對象。勢必要為每一種對象都進行代理,靜態(tài)代理在程序規(guī)模稍大時就無法勝任了。
2、動態(tài)代理模式
2.1 JDK自帶
事實上,單一的代理是不存的,一個代理可以同時身兼數(shù)職。既可以代購車,也可以代購房。
在動態(tài)代理中我們不再需要手動的創(chuàng)建代理類,我們只需要一個動態(tài)處理器就可以了,而真正的代理對象由JDK運行時動態(tài)的創(chuàng)建。
(1)創(chuàng)建服務類接口
//買車接口
public interface BuyCar {
void buycar();
}
//買房接口
public interface BuyHouse {
void buyHouse();
}
(2)服務實現(xiàn)類
//買車接口的實現(xiàn)類
public class BuyCarImpl implements BuyCar {
public void buycar() {
System.out.println("買一輛奧迪");
}
}
//買房接口的實現(xiàn)類
public class BuyHouseImpl implements BuyHouse{
public void buyHouse() {
System.out.println("買一棟大別墅");
}
}
(3)動態(tài)代理類
//通過實現(xiàn) InvocationHandler 接口創(chuàng)建自己的調(diào)用處理器;
public class ProxyHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private Object object;
//通過構造函數(shù)創(chuàng)建動態(tài)代理類實例,構造時調(diào)用處理器對象作為參數(shù)被傳入。
public ProxyHandler(Object object){
this.object = object;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("Before invoke "+method.getName());
method.invoke(object,args);
System.out.println("After invoke "+method.getName());
return null;
}
}
(4)測試類
public class DynamicProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
BuyHouse buyHouse = new BuyHouseImpl();
BuyCar buyCar = new BuyCarImpl();
InvocationHandler handler = new ProxyHandler(buyHouse);
InvocationHandler handler1 = new ProxyHandler(buyCar);
/**
* 通過為 Proxy 類指定 ClassLoader 對象和一組 interface 來創(chuàng)建動態(tài)代理類;
*/
BuyHouse proxyHouse = (BuyHouse) Proxy.newProxyInstance(buyHouse.getClass().getClassLoader(), buyHouse.getClass().getInterfaces(),handler);
BuyCar proxyCar = (BuyCar) Proxy.newProxyInstance(buyCar.getClass().getClassLoader(), buyCar.getClass().getInterfaces(),handler1);
proxyHouse.buyHouse();
proxyCar.buycar();
}
}
注意Proxy.newProxyInstance()方法接受三個參數(shù):
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h)
ClassLoader loader:指定當前目標對象使用類加載器,獲取加載器的方法是固定的 Class<?>[] interfaces:指定目標對象實現(xiàn)的接口的類型,使用泛型方式確認類型 InvocationHandler h:指定動態(tài)處理器,執(zhí)行目標對象的方法時,會觸發(fā)事件處理器的方法。
2.2 CGLIB
CGLIB相比于JDK動態(tài)代理更加強大,JDK動態(tài)代理雖然簡單易用,但是其有一個致命缺陷是,只能對接口進行代理。如果要代理的類為一個普通類、沒有接口,那么Java動態(tài)代理就沒法使用了。
在使用cglib前,需要先添加依賴。
<dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib</artifactId>
<version>3.2.12</version>
</dependency>
(1)目標類
Dao
public class Dao {
public void update() {
System.out.println("PeopleDao.update()");
}
}
Dao1
public class Dao1 {
public void select(){
System.out.println("PeopleDao.select");
}
}
(2)代理類
public class DaoProxy implements MethodInterceptor {
public Object intercept(Object object, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("Befor Metod Invoke");
methodProxy.invokeSuper(object,objects);
System.out.println("After Method Invoke");
return null;
}
}
參數(shù)解釋:
Object表示要進行增強的對象 Method表示攔截的方法 Object[]數(shù)組表示參數(shù)列表,基本數(shù)據(jù)類型需要傳入其包裝類型,如int-->Integer、long-Long、double-->Double MethodProxy表示對方法的代理,invokeSuper方法表示對被代理對象方法的調(diào)用
(3)測試
public class CglibProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DaoProxy daoProxy = new DaoProxy();
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
Enhancer enhancer1 = new Enhancer();
//設置要繼承的父類
enhancer.setSuperclass(Dao.class);
enhancer1.setSuperclass(Dao1.class);
//設置回調(diào)方法
enhancer.setCallback(daoProxy);
enhancer1.setCallback(daoProxy);
//創(chuàng)建動態(tài)代理類
Dao dao = (Dao)enhancer.create();
Dao1 dao1= (Dao1) enhancer1.create();
dao.update();
System.out.println("...................................");
dao1.select();
}
}
公眾號回復:Java全套、Java架構、大數(shù)據(jù)、電子書、算法和刷題筆記、面經(jīng),即可獲得對應的學習資源。

點個在看你最好看

