5分鐘掌握 Python 隨機爬山算法

爬山是用于功能優(yōu)化的隨機局部搜索算法。 如何在Python中從頭開始實現爬山算法。 如何應用爬山算法并檢查算法結果。
爬山算法 爬山算法的實現 應用爬山算法的示例
#?objective?function
def?objective(x):
?return?0
?
#?define?range?for?input
bounds?=?asarray([[-5.0,?5.0]])
#?generate?an?initial?point
solution?=?bounds[:,?0]?+?rand(len(bounds))?*?(bounds[:,?1]?-?bounds[:,?0])
#?evaluate?the?initial?point
solution_eval?=?objective(solution)
“ n_iterations”的算法的預定義迭代次數,例如100或1,000。#?run?the?hill?climb
for?i?in?range(n_iterations):
“ step_size”參數,該參數相對于搜索空間的邊界。我們將采用高斯分布的隨機步驟,其中均值是我們的當前點,標準偏差由“ step_size”定義。這意味著大約99%的步驟將在當前點的(3 * step_size)之內。#?take?a?step
candidate?=?solution?+?randn(len(bounds))?*?step_size
#?take?a?step
candidate?=?solution?+?rand(len(bounds))?*?step_size
#?evaluate?candidate?point
candidte_eval?=?objective(candidate)
#?check?if?we?should?keep?the?new?point
if?candidte_eval?<=?solution_eval:
?#?store?the?new?point
?solution,?solution_eval?=?candidate,?candidte_eval
?#?report?progress
?print('>%d?f(%s)?=?%.5f'?%?(i,?solution,?solution_eval))
#?hill?climbing?local?search?algorithm
def?hillclimbing(objective,?bounds,?n_iterations,?step_size):
?#?generate?an?initial?point
?solution?=?bounds[:,?0]?+?rand(len(bounds))?*?(bounds[:,?1]?-?bounds[:,?0])
?#?evaluate?the?initial?point
?solution_eval?=?objective(solution)
?#?run?the?hill?climb
?for?i?in?range(n_iterations):
??#?take?a?step
??candidate?=?solution?+?randn(len(bounds))?*?step_size
??#?evaluate?candidate?point
??candidte_eval?=?objective(candidate)
??#?check?if?we?should?keep?the?new?point
??if?candidte_eval?<=?solution_eval:
???#?store?the?new?point
???solution,?solution_eval?=?candidate,?candidte_eval
???#?report?progress
???print('>%d?f(%s)?=?%.5f'?%?(i,?solution,?solution_eval))
?return?[solution,?solution_eval]
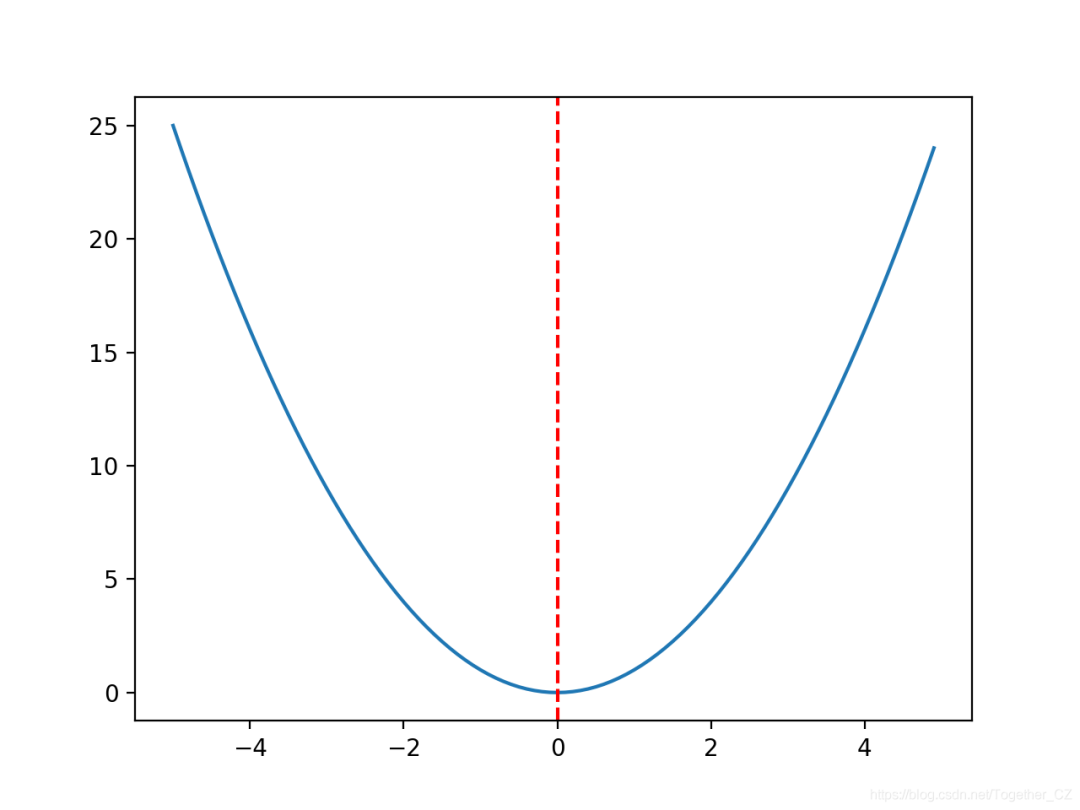
f(0.0)= 0.0處的最佳值。#?convex?unimodal?optimization?function
from?numpy?import?arange
from?matplotlib?import?pyplot
?
#?objective?function
def?objective(x):
?return?x[0]**2.0
?
#?define?range?for?input
r_min,?r_max?=?-5.0,?5.0
#?sample?input?range?uniformly?at?0.1?increments
inputs?=?arange(r_min,?r_max,?0.1)
#?compute?targets
results?=?[objective([x])?for?x?in?inputs]
#?create?a?line?plot?of?input?vs?result
pyplot.plot(inputs,?results)
#?define?optimal?input?value
x_optima?=?0.0
#?draw?a?vertical?line?at?the?optimal?input
pyplot.axvline(x=x_optima,?ls='--',?color='red')
#?show?the?plot
pyplot.show()
#?seed?the?pseudorandom?number?generator
seed(5)
n_iterations?=?1000
#?define?the?maximum?step?size
step_size?=?0.1
#?perform?the?hill?climbing?search
best,?score?=?hillclimbing(objective,?bounds,?n_iterations,?step_size)
print('Done!')
print('f(%s)?=?%f'?%?(best,?score))
#?hill?climbing?search?of?a?one-dimensional?objective?function
from?numpy?import?asarray
from?numpy.random?import?randn
from?numpy.random?import?rand
from?numpy.random?import?seed
?
#?objective?function
def?objective(x):
?return?x[0]**2.0
?
#?hill?climbing?local?search?algorithm
def?hillclimbing(objective,?bounds,?n_iterations,?step_size):
?#?generate?an?initial?point
?solution?=?bounds[:,?0]?+?rand(len(bounds))?*?(bounds[:,?1]?-?bounds[:,?0])
?#?evaluate?the?initial?point
?solution_eval?=?objective(solution)
?#?run?the?hill?climb
?for?i?in?range(n_iterations):
??#?take?a?step
??candidate?=?solution?+?randn(len(bounds))?*?step_size
??#?evaluate?candidate?point
??candidte_eval?=?objective(candidate)
??#?check?if?we?should?keep?the?new?point
??if?candidte_eval?<=?solution_eval:
???#?store?the?new?point
???solution,?solution_eval?=?candidate,?candidte_eval
???#?report?progress
???print('>%d?f(%s)?=?%.5f'?%?(i,?solution,?solution_eval))
?return?[solution,?solution_eval]
?
#?seed?the?pseudorandom?number?generator
seed(5)
#?define?range?for?input
bounds?=?asarray([[-5.0,?5.0]])
#?define?the?total?iterations
n_iterations?=?1000
#?define?the?maximum?step?size
step_size?=?0.1
#?perform?the?hill?climbing?search
best,?score?=?hillclimbing(objective,?bounds,?n_iterations,?step_size)
print('Done!')
print('f(%s)?=?%f'?%?(best,?score))
>1?f([-2.74290923])?=?7.52355
>3?f([-2.65873147])?=?7.06885
>4?f([-2.52197291])?=?6.36035
>5?f([-2.46450214])?=?6.07377
>7?f([-2.44740961])?=?5.98981
>9?f([-2.28364676])?=?5.21504
>12?f([-2.19245939])?=?4.80688
>14?f([-2.01001538])?=?4.04016
>15?f([-1.86425287])?=?3.47544
>22?f([-1.79913002])?=?3.23687
>24?f([-1.57525573])?=?2.48143
>25?f([-1.55047719])?=?2.40398
>26?f([-1.51783757])?=?2.30383
>27?f([-1.49118756])?=?2.22364
>28?f([-1.45344116])?=?2.11249
>30?f([-1.33055275])?=?1.77037
>32?f([-1.17805016])?=?1.38780
>33?f([-1.15189314])?=?1.32686
>36?f([-1.03852644])?=?1.07854
>37?f([-0.99135322])?=?0.98278
>38?f([-0.79448984])?=?0.63121
>39?f([-0.69837955])?=?0.48773
>42?f([-0.69317313])?=?0.48049
>46?f([-0.61801423])?=?0.38194
>48?f([-0.48799625])?=?0.23814
>50?f([-0.22149135])?=?0.04906
>54?f([-0.20017144])?=?0.04007
>57?f([-0.15994446])?=?0.02558
>60?f([-0.15492485])?=?0.02400
>61?f([-0.03572481])?=?0.00128
>64?f([-0.03051261])?=?0.00093
>66?f([-0.0074283])?=?0.00006
>78?f([-0.00202357])?=?0.00000
>119?f([0.00128373])?=?0.00000
>120?f([-0.00040911])?=?0.00000
>314?f([-0.00017051])?=?0.00000
Done!
f([-0.00017051])?=?0.000000
#?hill?climbing?local?search?algorithm
def?hillclimbing(objective,?bounds,?n_iterations,?step_size):
?#?generate?an?initial?point
?solution?=?bounds[:,?0]?+?rand(len(bounds))?*?(bounds[:,?1]?-?bounds[:,?0])
?#?evaluate?the?initial?point
?solution_eval?=?objective(solution)
?#?run?the?hill?climb
?scores?=?list()
?scores.append(solution_eval)
?for?i?in?range(n_iterations):
??#?take?a?step
??candidate?=?solution?+?randn(len(bounds))?*?step_size
??#?evaluate?candidate?point
??candidte_eval?=?objective(candidate)
??#?check?if?we?should?keep?the?new?point
??if?candidte_eval?<=?solution_eval:
???#?store?the?new?point
???solution,?solution_eval?=?candidate,?candidte_eval
???#?keep?track?of?scores
???scores.append(solution_eval)
???#?report?progress
???print('>%d?f(%s)?=?%.5f'?%?(i,?solution,?solution_eval))
?return?[solution,?solution_eval,?scores]
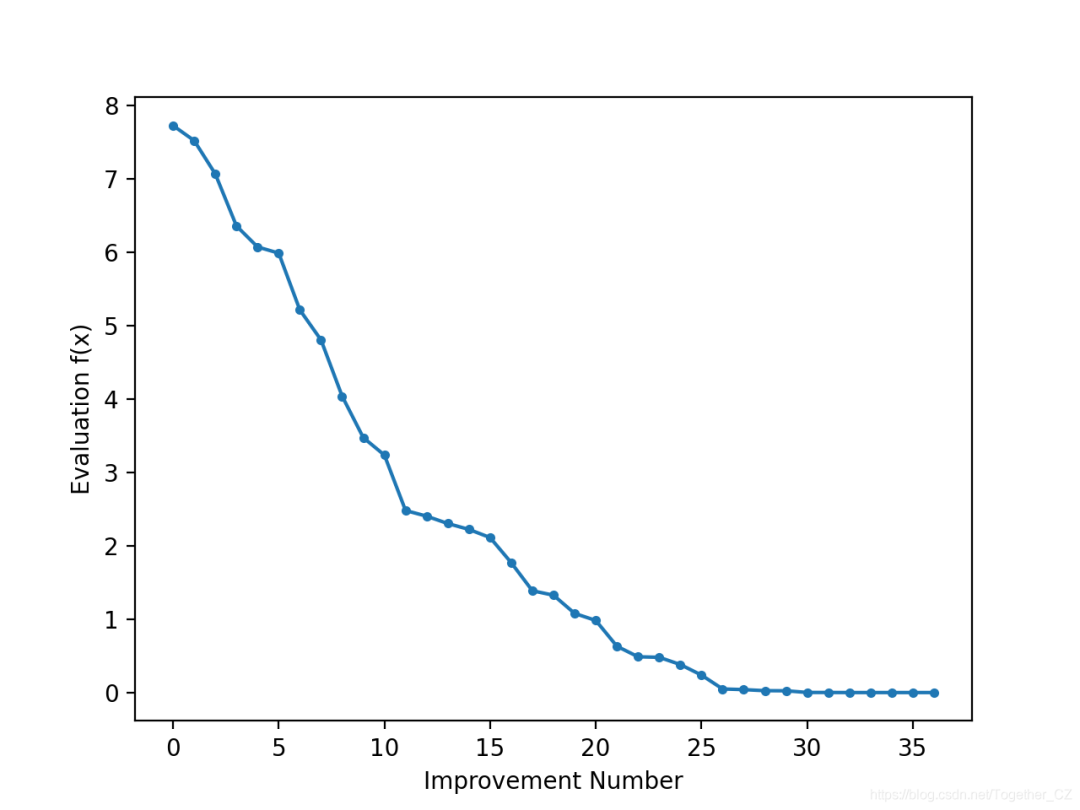
#?line?plot?of?best?scores
pyplot.plot(scores,?'.-')
pyplot.xlabel('Improvement?Number')
pyplot.ylabel('Evaluation?f(x)')
pyplot.show()
#?hill?climbing?search?of?a?one-dimensional?objective?function
from?numpy?import?asarray
from?numpy.random?import?randn
from?numpy.random?import?rand
from?numpy.random?import?seed
from?matplotlib?import?pyplot
?
#?objective?function
def?objective(x):
?return?x[0]**2.0
?
#?hill?climbing?local?search?algorithm
def?hillclimbing(objective,?bounds,?n_iterations,?step_size):
?#?generate?an?initial?point
?solution?=?bounds[:,?0]?+?rand(len(bounds))?*?(bounds[:,?1]?-?bounds[:,?0])
?#?evaluate?the?initial?point
?solution_eval?=?objective(solution)
?#?run?the?hill?climb
?scores?=?list()
?scores.append(solution_eval)
?for?i?in?range(n_iterations):
??#?take?a?step
??candidate?=?solution?+?randn(len(bounds))?*?step_size
??#?evaluate?candidate?point
??candidte_eval?=?objective(candidate)
??#?check?if?we?should?keep?the?new?point
??if?candidte_eval?<=?solution_eval:
???#?store?the?new?point
???solution,?solution_eval?=?candidate,?candidte_eval
???#?keep?track?of?scores
???scores.append(solution_eval)
???#?report?progress
???print('>%d?f(%s)?=?%.5f'?%?(i,?solution,?solution_eval))
?return?[solution,?solution_eval,?scores]
?
#?seed?the?pseudorandom?number?generator
seed(5)
#?define?range?for?input
bounds?=?asarray([[-5.0,?5.0]])
#?define?the?total?iterations
n_iterations?=?1000
#?define?the?maximum?step?size
step_size?=?0.1
#?perform?the?hill?climbing?search
best,?score,?scores?=?hillclimbing(objective,?bounds,?n_iterations,?step_size)
print('Done!')
print('f(%s)?=?%f'?%?(best,?score))
#?line?plot?of?best?scores
pyplot.plot(scores,?'.-')
pyplot.xlabel('Improvement?Number')
pyplot.ylabel('Evaluation?f(x)')
pyplot.show()
#?hill?climbing?local?search?algorithm
def?hillclimbing(objective,?bounds,?n_iterations,?step_size):
?#?generate?an?initial?point
?solution?=?bounds[:,?0]?+?rand(len(bounds))?*?(bounds[:,?1]?-?bounds[:,?0])
?#?evaluate?the?initial?point
?solution_eval?=?objective(solution)
?#?run?the?hill?climb
?solutions?=?list()
?solutions.append(solution)
?for?i?in?range(n_iterations):
??#?take?a?step
??candidate?=?solution?+?randn(len(bounds))?*?step_size
??#?evaluate?candidate?point
??candidte_eval?=?objective(candidate)
??#?check?if?we?should?keep?the?new?point
??if?candidte_eval?<=?solution_eval:
???#?store?the?new?point
???solution,?solution_eval?=?candidate,?candidte_eval
???#?keep?track?of?solutions
???solutions.append(solution)
???#?report?progress
???print('>%d?f(%s)?=?%.5f'?%?(i,?solution,?solution_eval))
?return?[solution,?solution_eval,?solutions]
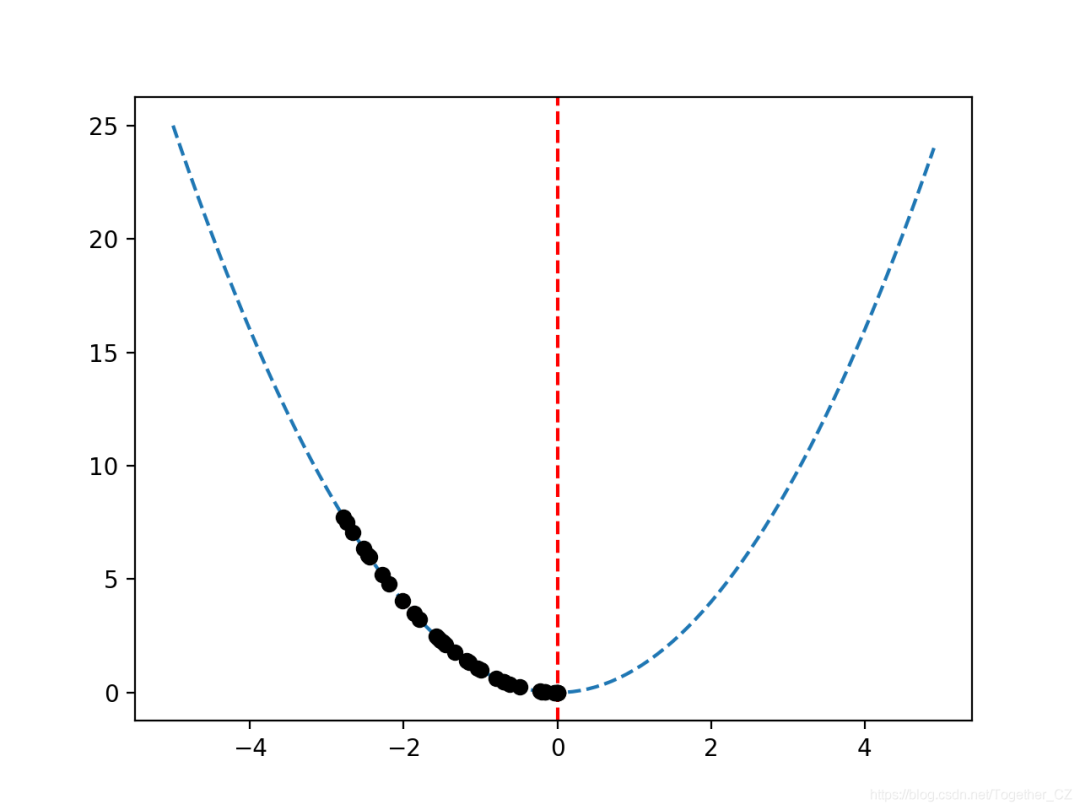
#?sample?input?range?uniformly?at?0.1?increments
inputs?=?arange(bounds[0,0],?bounds[0,1],?0.1)
#?create?a?line?plot?of?input?vs?result
pyplot.plot(inputs,?[objective([x])?for?x?in?inputs],?'--')
#?draw?a?vertical?line?at?the?optimal?input
pyplot.axvline(x=[0.0],?ls='--',?color='red')
#?plot?the?sample?as?black?circles
pyplot.plot(solutions,?[objective(x)?for?x?in?solutions],?'o',?color='black')
#?hill?climbing?search?of?a?one-dimensional?objective?function
from?numpy?import?asarray
from?numpy?import?arange
from?numpy.random?import?randn
from?numpy.random?import?rand
from?numpy.random?import?seed
from?matplotlib?import?pyplot
?
#?objective?function
def?objective(x):
?return?x[0]**2.0
?
#?hill?climbing?local?search?algorithm
def?hillclimbing(objective,?bounds,?n_iterations,?step_size):
?#?generate?an?initial?point
?solution?=?bounds[:,?0]?+?rand(len(bounds))?*?(bounds[:,?1]?-?bounds[:,?0])
?#?evaluate?the?initial?point
?solution_eval?=?objective(solution)
?#?run?the?hill?climb
?solutions?=?list()
?solutions.append(solution)
?for?i?in?range(n_iterations):
??#?take?a?step
??candidate?=?solution?+?randn(len(bounds))?*?step_size
??#?evaluate?candidate?point
??candidte_eval?=?objective(candidate)
??#?check?if?we?should?keep?the?new?point
??if?candidte_eval?<=?solution_eval:
???#?store?the?new?point
???solution,?solution_eval?=?candidate,?candidte_eval
???#?keep?track?of?solutions
???solutions.append(solution)
???#?report?progress
???print('>%d?f(%s)?=?%.5f'?%?(i,?solution,?solution_eval))
?return?[solution,?solution_eval,?solutions]
?
#?seed?the?pseudorandom?number?generator
seed(5)
#?define?range?for?input
bounds?=?asarray([[-5.0,?5.0]])
#?define?the?total?iterations
n_iterations?=?1000
#?define?the?maximum?step?size
step_size?=?0.1
#?perform?the?hill?climbing?search
best,?score,?solutions?=?hillclimbing(objective,?bounds,?n_iterations,?step_size)
print('Done!')
print('f(%s)?=?%f'?%?(best,?score))
#?sample?input?range?uniformly?at?0.1?increments
inputs?=?arange(bounds[0,0],?bounds[0,1],?0.1)
#?create?a?line?plot?of?input?vs?result
pyplot.plot(inputs,?[objective([x])?for?x?in?inputs],?'--')
#?draw?a?vertical?line?at?the?optimal?input
pyplot.axvline(x=[0.0],?ls='--',?color='red')
#?plot?the?sample?as?black?circles
pyplot.plot(solutions,?[objective(x)?for?x?in?solutions],?'o',?color='black')
pyplot.show()
作者:沂水寒城,CSDN博客專家,個人研究方向:機器學習、深度學習、NLP、CV
Blog:?http://yishuihancheng.blog.csdn.net
贊 賞 作 者

更多閱讀
特別推薦

點擊下方閱讀原文加入社區(qū)會員
評論
圖片
表情
