每日一例 | 流式編程時(shí)代,效率之王了解下?

前言
大家在找工作的時(shí)候,面試官經(jīng)常會(huì)問到JDK1.8的一些新特性,不知道大家回答的時(shí)候是真的已經(jīng)在用這些新特性,還是說僅僅停留在了解這些新特性的基礎(chǔ)上,實(shí)話實(shí)說,以前我用JDK1.8和用1.6沒太大的區(qū)別,新特性除了接口的默認(rèn)default實(shí)現(xiàn)方法,其他的新特性確實(shí)沒咋用過,一個(gè)重要的原因就是沒有深入了解過,而且當(dāng)時(shí)公司用的還是JDK1.6,所以這些新特性就算真的學(xué)會(huì)了,也不咋用,會(huì)忘記(借口),直到這一次入職以后,公司的生產(chǎn)環(huán)境大規(guī)模地使用lambda表達(dá)式、函數(shù)下編程、stream編程等,才真正為我打開這些新特性的大門,用起來是真的香呀
好了,話不多說,直接開干!
忘了說了,今天我們主要講下流式編程(stream),lambda表達(dá)式之前分享過了,感興趣的小伙伴去爬樓吧
流式編程
流式編程(stream),顧名思義,就是讓數(shù)據(jù)的流轉(zhuǎn)像水一樣絲滑,當(dāng)然用起來確實(shí)也是如此絲滑,美滋滋。官方給的解釋是:通過將集合轉(zhuǎn)換為這么一種叫做 “流” 的元素序列,通過聲明性方式,能夠?qū)现械拿總€(gè)元素進(jìn)行一系列并行或串行的流水線操作。大同小異哈,流式編程的流程圖:
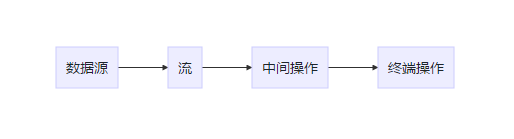
簡(jiǎn)單來說,就是把數(shù)據(jù)源轉(zhuǎn)換為流stream,然后對(duì)stream進(jìn)行一些操作,最后拿到你想要的數(shù)據(jù),可以是list、map、string或者count等。就像你把水導(dǎo)入凈水器,然后最后拿到純凈水;或者從水中提取你想要的元素,最終的結(jié)果取決于你的操作過程。
從jdk1.8開始,collection增加了一個(gè)stream方法,而且還是默認(rèn)實(shí)現(xiàn),也正是如此,我們也才能實(shí)現(xiàn)流式編程:
下面我們通過一些簡(jiǎn)單示例來演示說明一下。
集合過濾
在1.8以前,我們?nèi)绻^來集合中的元素,我們需要自己手動(dòng)遍歷集合,然后過濾,生成新的集合,但是如果用流式編程,一行代碼搞定:
private static void listStreamTest1() {
TestEntity testEntity = new TestEntity();
ChildEntriy childEntriy = new ChildEntriy();
testEntity.setChildEntriy(childEntriy);
testEntity.setAge(20);
testEntity.setId(34124234L);
testEntity.setName("name-test");
TestEntity testEntity2 = new TestEntity();
ChildEntriy childEntriy2 = new ChildEntriy();
testEntity2.setChildEntriy(childEntriy2);
testEntity2.setAge(12);
testEntity2.setId(34124234L);
testEntity2.setName("name-test2");
List<TestEntity> testEntityList = Lists.newArrayList(testEntity, testEntity2);
List<TestEntity> collect = testEntityList.stream().filter(t -> t.getAge() > 18).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);
}
解釋下,上面我們先構(gòu)建了一個(gè)TestEntity的list,我們的需求是獲取testEntityList中年齡大于18的元素,我們只用了一行代碼:
List<TestEntity> collect = testEntityList.stream().filter(t -> t.getAge() > 18).collect(Collectors.toList());
其中,關(guān)鍵地方有兩個(gè),一個(gè)是.filter(t -> t.getAge() > 18),這里是我們的過濾條件,過濾條件就是我們要保留的元素,只是條件為true的時(shí)候,才會(huì)被保留,同樣也用到了lambda表達(dá)式;一個(gè)是collect(Collectors.toList()),作用是將符合條件的元素收集起來
我們也可以對(duì)過濾之后的元素做其他操作,以滿足我們不同需求:
統(tǒng)計(jì)條數(shù)
過濾完直接返回符合條件的元素個(gè)數(shù)
long count = testEntityList.stream().filter(t -> t.getAge() > 18).count();
轉(zhuǎn)成map
這里直接用Collectors.toMap就可以了。
Map<Long, String> collect1 = testEntityList.stream().filter(t -> t.getAge() > 18).collect(Collectors.toMap(TestEntity::getId, TestEntity::getName));
上面這行代碼,是將過濾后的元素構(gòu)建成key為id,value為name的map,寫法看起來很高端,比如TestEntity::getId其實(shí)就是獲取元素的id,也是lambda表達(dá)式的寫法,常規(guī)的lambda表達(dá)式寫法是這樣的:
Map<Long, String> collect3 = testEntityList.stream().filter(t -> t.getAge() > 18).collect(Collectors.toMap(t -> t.getId(), t -> t.getName()));
t -> t.getName()寫法就等同于TestEntity::getName,看習(xí)慣就好了
如果你想要構(gòu)建key為id,value為當(dāng)前元素的集合,這樣寫就可以了:
Map<Long, TestEntity> collect2 = testEntityList.stream().filter(t -> t.getAge() > 18).collect(Collectors.toMap(TestEntity::getId, t -> t));
補(bǔ)充說明
其實(shí)不通過filter也是可以直接操作的,從這一點(diǎn)上來說,straem式編程確實(shí)很靈活,就像你們家的凈水器一樣,不需要中間哪個(gè)功能段,可以直接拿掉,很靈活有沒有:
List<TestEntity> collect1 = testEntityList.stream().collect(Collectors.toList());
long count = testEntityList.stream().filter(t -> t.getAge() > 18).count();
Map<Long, String> collect2 = testEntityList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(TestEntity::getId, TestEntity::getName));
Map<Long, String> collect3 = testEntityList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(t -> t.getId(), t -> t.getName()));
Map<Long, TestEntity> collect4 = testEntityList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(TestEntity::getId, t -> t));
其他應(yīng)用
內(nèi)容未完待續(xù)……明天我們繼續(xù),今天時(shí)間不夠了,六點(diǎn)半起床,一個(gè)小時(shí)沒搞完 ,但是早起感覺不錯(cuò)喲,繼續(xù)堅(jiān)持,奧里給
,但是早起感覺不錯(cuò)喲,繼續(xù)堅(jiān)持,奧里給 !
!
結(jié)語
今天我們分享了流式編程(stream)常用的接口和用法,從實(shí)際意義上講,這些確實(shí)很方便,也確實(shí)很實(shí)用,一方面讓你的代碼更簡(jiǎn)潔,更好看,逼格也更高;另外一方面,免去了繁瑣的循環(huán)遍歷,代碼的性能也上來了,豈不是美滋滋 。
。
更現(xiàn)實(shí)的意義是,如果你不去主動(dòng)學(xué)這些東西,不去主動(dòng)用這些東西,也行未來有一天你入職新公司了,你可能連java原生的代碼寫法都看不懂了,一臉懵逼??,你說你問身邊人吧,人比人家資深,應(yīng)該懂得更多,結(jié)果還不如新人,你說尷尬不 ?再多說一句,其實(shí)大家都很鄙視那些比你資深,拿的工資可能還比你高
?再多說一句,其實(shí)大家都很鄙視那些比你資深,拿的工資可能還比你高 ,但知道的還沒你多的人,所以你想成為這樣的人嗎?不想就得學(xué)習(xí)新東西,這是現(xiàn)實(shí),你說呢?
,但知道的還沒你多的人,所以你想成為這樣的人嗎?不想就得學(xué)習(xí)新東西,這是現(xiàn)實(shí),你說呢?
項(xiàng)目路徑:
https://github.com/Syske/example-everyday
本項(xiàng)目會(huì)每日更新,讓我們一起學(xué)習(xí),一起進(jìn)步,遇見更好的自己,加油呀
- END -