Linux 進(jìn)程管理之任務(wù)綁定
什么是進(jìn)程的 CPU 親和性?
在多核結(jié)構(gòu)中,每個(gè)核有各自的L1緩存,相同類(lèi)型的核被劃分在同一個(gè)cluster中,而不同cluster之間又有共用的L2緩存。講負(fù)載均衡的時(shí)候我們講過(guò)一個(gè)進(jìn)程在核之間來(lái)回切換的時(shí)候,各個(gè)核之間的緩存命中率會(huì)降低,所以,將進(jìn)程與 CPU 進(jìn)行綁定可以提高 CPU 緩存的命中率,從而提高性能。這種綁定關(guān)系就叫做:進(jìn)程的 CPU 親和性。
如何設(shè)置進(jìn)程的 CPU 親和性?
Linux 系統(tǒng)提供了一個(gè)名為 sched_setaffinity 的系統(tǒng)調(diào)用,此系統(tǒng)調(diào)用可以設(shè)置進(jìn)程的 CPU 親和性。
sched_setaffinity(pid_t pid, size_t cpusetsize, const cpu_set_t *mask)
pid:進(jìn)行綁定 CPU 的進(jìn)程ID號(hào) cpusetsize:參數(shù) mask 指向的 CPU 集合的大小 mask:與進(jìn)程綁定的 CPU 集合
cpu_set_t 類(lèi)型是個(gè)位圖,可以理解為 CPU 集,通過(guò)宏來(lái)進(jìn)行清除、設(shè)置以及判斷:
//初始化,設(shè)為空
void CPU_ZERO (cpu_set_t *set);
//將某個(gè)cpu加入cpu集中
void CPU_SET (int cpu, cpu_set_t *set);
//將某個(gè)cpu從cpu集中移出
void CPU_CLR (int cpu, cpu_set_t *set);
//判斷某個(gè)cpu是否已在cpu集中設(shè)置了
int CPU_ISSET (int cpu, const cpu_set_t *set);
CPU 集可以認(rèn)為是一個(gè)掩碼,每個(gè)設(shè)置的位都對(duì)應(yīng)一個(gè)可以合法調(diào)度的 CPU,而未設(shè)置的位則對(duì)應(yīng)一個(gè)不可調(diào)度的 CPU。換言之,線程都被綁定了,只能在那些對(duì)應(yīng)位被設(shè)置了的處理器上運(yùn)行。通常,掩碼中的所有位都被置位了,也就是可以在所有的 CPU 中調(diào)度。
我們來(lái)看看 sched_setaffinity 系統(tǒng)調(diào)用的例子,將進(jìn)程綁定到 CPU2 上運(yùn)行:
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <sched.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int cpus = 0;
int i = 0;
cpu_set_t mask;
cpu_set_t get;
cpus = sysconf(_SC_NPROCESSORS_ONLN);
printf("cpus: %d\n", cpus);
CPU_ZERO(&mask); /* 初始化set集,將set置為空*/
CPU_SET(2, &mask); /*將本進(jìn)程綁定到CPU2上*/
if (sched_setaffinity(0, sizeof(mask), &mask) == -1) {
printf("Set CPU affinity failue, ERROR:%s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
CPU 親和性的實(shí)現(xiàn)
我們知道每個(gè) CPU 都擁有一個(gè)獨(dú)立的可運(yùn)行進(jìn)程隊(duì)列,系統(tǒng)運(yùn)行的時(shí)候 CPU 只會(huì)從屬于自己的可運(yùn)行進(jìn)程隊(duì)列中按照 CFS 策略,選擇一個(gè)進(jìn)程來(lái)運(yùn)行。所以,把進(jìn)程放置在 CPU 對(duì)應(yīng)的可運(yùn)行進(jìn)程隊(duì)列上,也就可將進(jìn)程綁定到指定的 CPU 上。
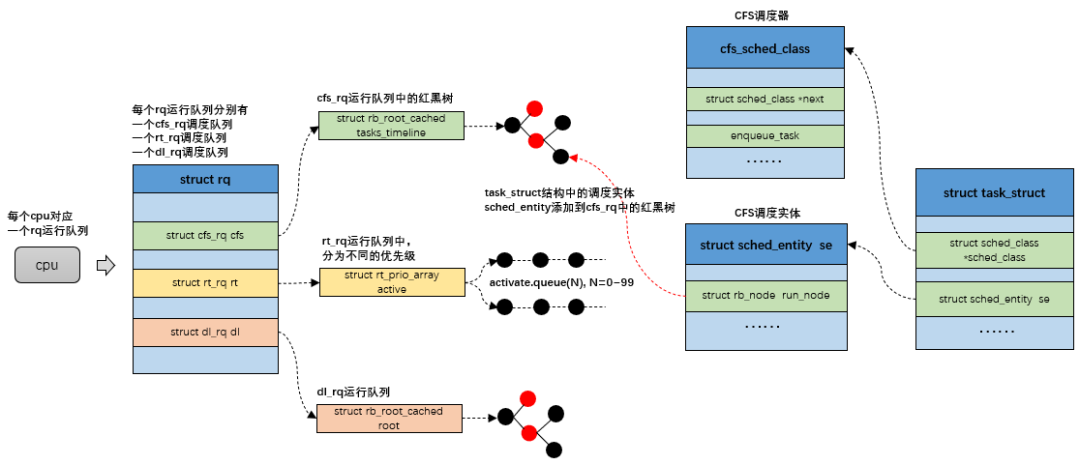
下面我們追蹤函數(shù) sched_setaffinity 的調(diào)用順序,分析一下進(jìn)程如何與 CPU 進(jìn)行綁定的。
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(sched_setaffinity, pid_t, pid, unsigned int, len, unsigned long __user *, user_mask_ptr)
-- sched_setaffinity(pid_t pid, const struct cpumask *in_mask)
--- __set_cpus_allowed_ptr(struct task_struct *p, const struct cpumask *new_mask, bool check)
---- stop_one_cpu(unsigned int cpu, cpu_stop_fn_t fn, void *arg)
----- migration_cpu_stop(void *data)
------ __migrate_task(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int dest_cpu)
------- move_queued_task(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int new_cpu)
-------- enqueue_task(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p, int flags)
--------- returns the new run queue of destination CPU

__set_cpus_allowed_ptr 函數(shù)主要分兩種情況來(lái)將進(jìn)程綁定到某個(gè) CPU 上:
stop_one_cpu(cpu_of(rq), migration_cpu_stop, &arg):把還沒(méi)運(yùn)行且在源運(yùn)行隊(duì)列中進(jìn)程,放到指定的 CPU 可運(yùn)行隊(duì)列中 move_queued_task(rq, &rf, p, dest_cpu):把已經(jīng)運(yùn)行的進(jìn)程遷移到指定的 CPU 可運(yùn)行隊(duì)列中
這兩種情況最終都會(huì)調(diào)用 move_queued_task:
static struct rq *move_queued_task(struct rq *rq, struct rq_flags *rf,
struct task_struct *p, int new_cpu)
{
lockdep_assert_held(&rq->lock);
p->on_rq = TASK_ON_RQ_MIGRATING;
dequeue_task(rq, p, DEQUEUE_NOCLOCK);
set_task_cpu(p, new_cpu);
rq_unlock(rq, rf);
rq = cpu_rq(new_cpu);
rq_lock(rq, rf);
BUG_ON(task_cpu(p) != new_cpu);
enqueue_task(rq, p, 0);
p->on_rq = TASK_ON_RQ_QUEUED;
check_preempt_curr(rq, p, 0);
return rq;
}
這里首先根據(jù)目標(biāo) CPU 找到對(duì)應(yīng)的工作隊(duì)列 rq,然后通過(guò) enqueue_task 把任務(wù)遷移到目標(biāo) CPU 對(duì)應(yīng)的工作隊(duì)列中,CFS 調(diào)度器的話(huà)會(huì)調(diào)用到函數(shù) enqueue_task_fair。
enqueue_task_fair 的執(zhí)行流程如下:
如果通過(guò)struct sched_entity 的 on_rq 成員判斷進(jìn)程已經(jīng)在就緒隊(duì)列上, 則無(wú)事可。 否則, 具體的工作委托給 enqueue_entity,將任務(wù)插入到 CFS 紅黑樹(shù)中合適的結(jié)點(diǎn)。


