C# ConcurrentBag的實(shí)現(xiàn)原理

一、前言
筆者最近在做一個(gè)項(xiàng)目,項(xiàng)目中為了提升吞吐量,使用了消息隊(duì)列,中間實(shí)現(xiàn)了生產(chǎn)消費(fèi)模式,在生產(chǎn)消費(fèi)者模式中需要有一個(gè)集合,來存儲(chǔ)生產(chǎn)者所生產(chǎn)的物品,筆者使用了最常見的List<T>集合類型。
由于生產(chǎn)者線程有很多個(gè),消費(fèi)者線程也有很多個(gè),所以不可避免的就產(chǎn)生了線程同步的問題。開始筆者是使用lock關(guān)鍵字,進(jìn)行線程同步,但是性能并不是特別理想,然后有網(wǎng)友說可以使用SynchronizedList<T>來代替使用List<T>達(dá)到線程安全的目的。于是筆者就替換成了SynchronizedList<T>,但是發(fā)現(xiàn)性能依舊糟糕,于是查看了SynchronizedList<T>的源代碼,發(fā)現(xiàn)它就是簡單的在List<T>提供的API的基礎(chǔ)上加了lock,所以性能基本與筆者實(shí)現(xiàn)方式相差無幾。
最后筆者找到了解決的方案,使用ConcurrentBag<T>類來實(shí)現(xiàn),性能有很大的改觀,于是筆者查看了ConcurrentBag<T>的源代碼,實(shí)現(xiàn)非常精妙,特此在這記錄一下。
二、ConcurrentBag類
ConcurrentBag<T>實(shí)現(xiàn)了IProducerConsumerCollection<T>接口,該接口主要用于生產(chǎn)者消費(fèi)者模式下,可見該類基本就是為生產(chǎn)消費(fèi)者模式定制的。然后還實(shí)現(xiàn)了常規(guī)的IReadOnlyCollection<T>類,實(shí)現(xiàn)了該類就需要實(shí)現(xiàn)IEnumerable<T>、IEnumerable、 ICollection類。
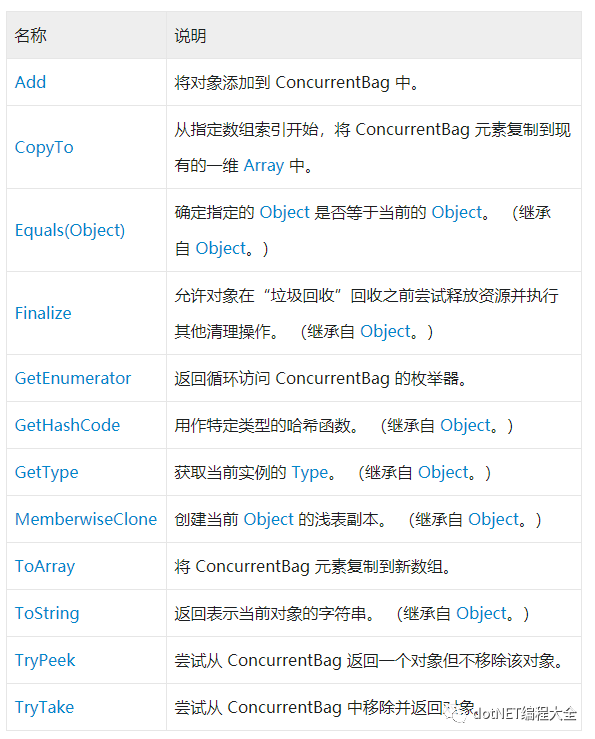
ConcurrentBag<T>對(duì)外提供的方法沒有List<T>那么多,但是同樣有Enumerable實(shí)現(xiàn)的擴(kuò)展方法。類本身提供的方法如下所示。
三、 ConcurrentBag線程安全實(shí)現(xiàn)原理
1. ConcurrentBag的私有字段
ConcurrentBag線程安全實(shí)現(xiàn)主要是通過它的數(shù)據(jù)存儲(chǔ)的結(jié)構(gòu)和細(xì)顆粒度的鎖。
public class ConcurrentBag<T> : IProducerConsumerCollection<T>, IReadOnlyCollection<T>{ // ThreadLocalList對(duì)象包含每個(gè)線程的數(shù)據(jù)ThreadLocal<ThreadLocalList> m_locals;// 這個(gè)頭指針和尾指針指向中的第一個(gè)和最后一個(gè)本地列表,這些本地列表分散在不同線程中// 允許在線程局部對(duì)象上枚舉volatile ThreadLocalList m_headList, m_tailList;// 這個(gè)標(biāo)志是告知操作線程必須同步操作// 在GlobalListsLock 鎖中 設(shè)置bool m_needSync;}
首選我們來看它聲明的私有字段,其中需要注意的是集合的數(shù)據(jù)是存放在ThreadLocal線程本地存儲(chǔ)中的。也就是說訪問它的每個(gè)線程會(huì)維護(hù)一個(gè)自己的集合數(shù)據(jù)列表,一個(gè)集合中的數(shù)據(jù)可能會(huì)存放在不同線程的本地存儲(chǔ)空間中,所以如果線程訪問自己本地存儲(chǔ)的對(duì)象,那么是沒有問題的,這就是實(shí)現(xiàn)線程安全的第一層,使用線程本地存儲(chǔ)數(shù)據(jù)。
然后可以看到ThreadLocalList m_headList, m_tailList;這個(gè)是存放著本地列表對(duì)象的頭指針和尾指針,通過這兩個(gè)指針,我們就可以通過遍歷的方式來訪問所有本地列表。它使用volatile修飾,所以它是線程安全的。
最后又定義了一個(gè)標(biāo)志,這個(gè)標(biāo)志告知操作線程必須進(jìn)行同步操作,這是實(shí)現(xiàn)了一個(gè)細(xì)顆粒度的鎖,因?yàn)橹挥性趲讉€(gè)條件滿足的情況下才需要進(jìn)行線程同步。
2. 用于數(shù)據(jù)存儲(chǔ)的TrehadLocalList類
接下來我們來看一下ThreadLocalList類的構(gòu)造,該類就是實(shí)際存儲(chǔ)了數(shù)據(jù)的位置。實(shí)際上它是使用雙向鏈表這種結(jié)構(gòu)進(jìn)行數(shù)據(jù)存儲(chǔ)。
[]// 構(gòu)造了雙向鏈表的節(jié)點(diǎn)internal class Node{ public Node(T value) {m_value = value;} public readonly T m_value; public Node m_next; public Node m_prev;}/// <summary>/// 集合操作類型/// </summary>internal enum ListOperation{None,Add,Take};/// <summary>/// 線程鎖定的類/// </summary>internal class ThreadLocalList{ // 雙向鏈表的頭結(jié)點(diǎn) 如果為null那么表示鏈表為空internal volatile Node m_head; // 雙向鏈表的尾節(jié)點(diǎn)private volatile Node m_tail; // 定義當(dāng)前對(duì)List進(jìn)行操作的種類// 與前面的 ListOperation 相對(duì)應(yīng)internal volatile int m_currentOp; // 這個(gè)列表元素的計(jì)數(shù)private int m_count; // The stealing count// 這個(gè)不是特別理解 好像是在本地列表中 刪除某個(gè)Node 以后的計(jì)數(shù)internal int m_stealCount; // 下一個(gè)列表 可能會(huì)在其它線程中internal volatile ThreadLocalList m_nextList; // 設(shè)定鎖定是否已進(jìn)行internal bool m_lockTaken; // The owner thread for this listinternal Thread m_ownerThread; // 列表的版本,只有當(dāng)列表從空變?yōu)榉强战y(tǒng)計(jì)是底層internal volatile int m_version; /// <summary>/// ThreadLocalList 構(gòu)造器/// </summary>/// <param name="ownerThread">擁有這個(gè)集合的線程</param>internal ThreadLocalList(Thread ownerThread) {m_ownerThread = ownerThread;} /// <summary>/// 添加一個(gè)新的item到鏈表首部/// </summary>/// <param name="item">The item to add.</param>/// <param name="updateCount">是否更新計(jì)數(shù).</param>internal void Add(T item, bool updateCount) { checked{m_count++;}Node node = new Node(item); if (m_head == null){Debug.Assert(m_tail == null);m_head = node;m_tail = node;m_version++; // 因?yàn)檫M(jìn)行初始化了,所以將空狀態(tài)改為非空狀態(tài)} else{ // 使用頭插法 將新的元素插入鏈表node.m_next = m_head;m_head.m_prev = node;m_head = node;} if (updateCount) // 更新計(jì)數(shù)以避免此添加同步時(shí)溢出{m_count = m_count - m_stealCount;m_stealCount = 0;}} /// <summary>/// 從列表的頭部刪除一個(gè)item/// </summary>/// <param name="result">The removed item</param>internal void Remove(out T result) { // 雙向鏈表刪除頭結(jié)點(diǎn)數(shù)據(jù)的流程Debug.Assert(m_head != null);Node head = m_head;m_head = m_head.m_next; if (m_head != null){m_head.m_prev = null;} else{m_tail = null;}m_count--;result = head.m_value;} /// <summary>/// 返回列表頭部的元素/// </summary>/// <param name="result">the peeked item</param>/// <returns>True if succeeded, false otherwise</returns>internal bool Peek(out T result) {Node head = m_head; if (head != null){result = head.m_value; return true;}result = default(T); return false;} /// <summary>/// 從列表的尾部獲取一個(gè)item/// </summary>/// <param name="result">the removed item</param>/// <param name="remove">remove or peek flag</param>internal void Steal(out T result, bool remove) {Node tail = m_tail;Debug.Assert(tail != null); if (remove) // Take operation{m_tail = m_tail.m_prev; if (m_tail != null){m_tail.m_next = null;} else{m_head = null;} // Increment the steal countm_stealCount++;}result = tail.m_value;} /// <summary>/// 獲取總計(jì)列表計(jì)數(shù), 它不是線程安全的, 如果同時(shí)調(diào)用它, 則可能提供不正確的計(jì)數(shù)/// </summary>internal int Count{ get{ return m_count - m_stealCount;}}}
從上面的代碼中我們可以更加驗(yàn)證之前的觀點(diǎn),就是ConcurentBag<T>在一個(gè)線程中存儲(chǔ)數(shù)據(jù)時(shí),使用的是雙向鏈表,ThreadLocalList實(shí)現(xiàn)了一組對(duì)鏈表增刪改查的方法。
3. ConcurrentBag實(shí)現(xiàn)新增元素
接下來我們看一看ConcurentBag<T>是如何新增元素的。
/// <summary>/// 嘗試獲取無主列表,無主列表是指線程已經(jīng)被暫停或者終止,但是集合中的部分?jǐn)?shù)據(jù)還存儲(chǔ)在那里/// 這是避免內(nèi)存泄漏的方法/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>private ThreadLocalList GetUnownedList(){ //此時(shí)必須持有全局鎖Contract.Assert(Monitor.IsEntered(GlobalListsLock)); // 從頭線程列表開始枚舉 找到那些已經(jīng)被關(guān)閉的線程// 將它所在的列表對(duì)象 返回ThreadLocalList currentList = m_headList; while (currentList != null){ if (currentList.m_ownerThread.ThreadState == System.Threading.ThreadState.Stopped){currentList.m_ownerThread = Thread.CurrentThread; // the caller should acquire a lock to make this line thread safereturn currentList;}currentList = currentList.m_nextList;} return null;}/// <summary>/// 本地幫助方法,通過線程對(duì)象檢索線程線程本地列表/// </summary>/// <param name="forceCreate">如果列表不存在,那么創(chuàng)建新列表</param>/// <returns>The local list object</returns>private ThreadLocalList GetThreadList(bool forceCreate){ThreadLocalList list = m_locals.Value; if (list != null){ return list;} else if (forceCreate) { // 獲取用于更新操作的 m_tailList 鎖lock (GlobalListsLock){ // 如果頭列表等于空,那么說明集合中還沒有元素// 直接創(chuàng)建一個(gè)新的if (m_headList == null){list = new ThreadLocalList(Thread.CurrentThread);m_headList = list;m_tailList = list;} else{ // ConcurrentBag內(nèi)的數(shù)據(jù)是以雙向鏈表的形式分散存儲(chǔ)在各個(gè)線程的本地區(qū)域中// 通過下面這個(gè)方法 可以找到那些存儲(chǔ)有數(shù)據(jù) 但是已經(jīng)被停止的線程// 然后將已停止線程的數(shù)據(jù) 移交到當(dāng)前線程管理list = GetUnownedList(); // 如果沒有 那么就新建一個(gè)列表 然后更新尾指針的位置if (list == null){list = new ThreadLocalList(Thread.CurrentThread);m_tailList.m_nextList = list;m_tailList = list;}}m_locals.Value = list;}} else{ return null;}Debug.Assert(list != null); return list;}/// <summary>/// Adds an object to the <see cref="ConcurrentBag{T}"/>./// </summary>/// <param name="item">The object to be added to the/// <see cref="ConcurrentBag{T}"/>. The value can be a null reference/// (Nothing in Visual Basic) for reference types.</param>public void Add(T item){ // 獲取該線程的本地列表, 如果此線程不存在, 則創(chuàng)建一個(gè)新列表 (第一次調(diào)用 add)ThreadLocalList list = GetThreadList(true); // 實(shí)際的數(shù)據(jù)添加操作 在AddInternal中執(zhí)行AddInternal(list, item);}/// <summary>/// </summary>/// <param name="list"></param>/// <param name="item"></param>private void AddInternal(ThreadLocalList list, T item){ bool lockTaken = false; try{Interlocked.Exchange(ref list.m_currentOp, (int)ListOperation.Add);// 同步案例:// 如果列表計(jì)數(shù)小于兩個(gè), 因?yàn)槭请p向鏈表的關(guān)系 為了避免與任何竊取線程發(fā)生沖突 必須獲取鎖// 如果設(shè)置了 m_needSync, 這意味著有一個(gè)線程需要凍結(jié)包 也必須獲取鎖if (list.Count < 2 || m_needSync){ // 將其重置為None 以避免與竊取線程的死鎖list.m_currentOp = (int)ListOperation.None; // 鎖定當(dāng)前對(duì)象Monitor.Enter(list, ref lockTaken);} // 調(diào)用 ThreadLocalList.Add方法 將數(shù)據(jù)添加到雙向鏈表中// 如果已經(jīng)鎖定 那么說明線程安全 可以更新Count 計(jì)數(shù)list.Add(item, lockTaken);} finally{list.m_currentOp = (int)ListOperation.None; if (lockTaken){Monitor.Exit(list);}}}
從上面代碼中,我們可以很清楚的知道Add()方法是如何運(yùn)行的,其中的關(guān)鍵就是GetThreadList()方法,通過該方法可以獲取當(dāng)前線程的數(shù)據(jù)存儲(chǔ)列表對(duì)象,假如不存在數(shù)據(jù)存儲(chǔ)列表,它會(huì)自動(dòng)創(chuàng)建或者通過GetUnownedList()方法來尋找那些被停止但是還存儲(chǔ)有數(shù)據(jù)列表的線程,然后將數(shù)據(jù)列表返回給當(dāng)前線程中,防止了內(nèi)存泄漏。
在數(shù)據(jù)添加的過程中,實(shí)現(xiàn)了細(xì)顆粒度的lock同步鎖,所以性能會(huì)很高。刪除和其它操作與新增類似,本文不再贅述。
4. ConcurrentBag 如何實(shí)現(xiàn)迭代器模式
看完上面的代碼后,我很好奇ConcurrentBag<T>是如何實(shí)現(xiàn)IEnumerator來實(shí)現(xiàn)迭代訪問的,因?yàn)?code>ConcurrentBag<T>是通過分散在不同線程中的ThreadLocalList來存儲(chǔ)數(shù)據(jù)的,那么在實(shí)現(xiàn)迭代器模式時(shí),過程會(huì)比較復(fù)雜。
后面再查看了源碼之后,發(fā)現(xiàn)ConcurrentBag<T>為了實(shí)現(xiàn)迭代器模式,將分在不同線程中的數(shù)據(jù)全都存到一個(gè)List<T>集合中,然后返回了該副本的迭代器。所以每次訪問迭代器,它都會(huì)新建一個(gè)List<T>的副本,這樣雖然浪費(fèi)了一定的存儲(chǔ)空間,但是邏輯上更加簡單了。
/// <summary>/// 本地幫助器方法釋放所有本地列表鎖/// </summary>private void ReleaseAllLocks(){ // 該方法用于在執(zhí)行線程同步以后 釋放掉所有本地鎖// 通過遍歷每個(gè)線程中存儲(chǔ)的 ThreadLocalList對(duì)象 釋放所占用的鎖ThreadLocalList currentList = m_headList; while (currentList != null){ if (currentList.m_lockTaken){currentList.m_lockTaken = false;Monitor.Exit(currentList);}currentList = currentList.m_nextList;}}/// <summary>/// 從凍結(jié)狀態(tài)解凍包的本地幫助器方法/// </summary>/// <param name="lockTaken">The lock taken result from the Freeze method</param>private void UnfreezeBag(bool lockTaken){ // 首先釋放掉 每個(gè)線程中 本地變量的鎖// 然后釋放全局鎖ReleaseAllLocks();m_needSync = false; if (lockTaken){Monitor.Exit(GlobalListsLock);}}/// <summary>/// 本地幫助器函數(shù)等待所有未同步的操作/// </summary>private void WaitAllOperations(){Contract.Assert(Monitor.IsEntered(GlobalListsLock));ThreadLocalList currentList = m_headList; // 自旋等待 等待其它操作完成while (currentList != null){ if (currentList.m_currentOp != (int)ListOperation.None){SpinWait spinner = new SpinWait(); // 有其它線程進(jìn)行操作時(shí),會(huì)將cuurentOp 設(shè)置成 正在操作的枚舉while (currentList.m_currentOp != (int)ListOperation.None){spinner.SpinOnce();}}currentList = currentList.m_nextList;}}/// <summary>/// 本地幫助器方法獲取所有本地列表鎖/// </summary>private void AcquireAllLocks(){Contract.Assert(Monitor.IsEntered(GlobalListsLock)); bool lockTaken = false;ThreadLocalList currentList = m_headList;// 遍歷每個(gè)線程的ThreadLocalList 然后獲取對(duì)應(yīng)ThreadLocalList的鎖while (currentList != null){ // 嘗試/最后 bllock 以避免在獲取鎖和設(shè)置所采取的標(biāo)志之間的線程港口try{Monitor.Enter(currentList, ref lockTaken);} finally{ if (lockTaken){currentList.m_lockTaken = true;lockTaken = false;}}currentList = currentList.m_nextList;}}/// <summary>/// Local helper method to freeze all bag operations, it/// 1- Acquire the global lock to prevent any other thread to freeze the bag, and also new new thread can be added/// to the dictionary/// 2- Then Acquire all local lists locks to prevent steal and synchronized operations/// 3- Wait for all un-synchronized operations to be done/// </summary>/// <param name="lockTaken">Retrieve the lock taken result for the global lock, to be passed to Unfreeze method</param>private void FreezeBag(ref bool lockTaken){Contract.Assert(!Monitor.IsEntered(GlobalListsLock)); // 全局鎖定可安全地防止多線程調(diào)用計(jì)數(shù)和損壞 m_needSyncMonitor.Enter(GlobalListsLock, ref lockTaken); // 這將強(qiáng)制同步任何將來的添加/執(zhí)行操作m_needSync = true; // 獲取所有列表的鎖AcquireAllLocks(); // 等待所有操作完成WaitAllOperations();}/// <summary>/// 本地幫助器函數(shù)返回列表中的包項(xiàng), 這主要由 CopyTo 和 ToArray 使用。/// 這不是線程安全, 應(yīng)該被稱為凍結(jié)/解凍袋塊/// 本方法是私有的 只有使用 Freeze/UnFreeze之后才是安全的 /// </summary>/// <returns>List the contains the bag items</returns>private List<T> ToList(){Contract.Assert(Monitor.IsEntered(GlobalListsLock)); // 創(chuàng)建一個(gè)新的ListList<T> list = new List<T>();ThreadLocalList currentList = m_headList; // 遍歷每個(gè)線程中的ThreadLocalList 將里面的Node的數(shù)據(jù) 添加到list中while (currentList != null){Node currentNode = currentList.m_head; while (currentNode != null){list.Add(currentNode.m_value);currentNode = currentNode.m_next;}currentList = currentList.m_nextList;} return list;}/// <summary>/// Returns an enumerator that iterates through the <see/// cref="ConcurrentBag{T}"/>./// </summary>/// <returns>An enumerator for the contents of the <see/// cref="ConcurrentBag{T}"/>.</returns>/// <remarks>/// The enumeration represents a moment-in-time snapshot of the contents/// of the bag. It does not reflect any updates to the collection after /// <see cref="GetEnumerator"/> was called. The enumerator is safe to use/// concurrently with reads from and writes to the bag./// </remarks>public IEnumerator<T> GetEnumerator(){ // Short path if the bag is emptyif (m_headList == null) return new List<T>().GetEnumerator(); // empty listbool lockTaken = false; try{ // 首先凍結(jié)整個(gè) ConcurrentBag集合FreezeBag(ref lockTaken); // 然后ToList 再拿到 List的 IEnumeratorreturn ToList().GetEnumerator();} finally{UnfreezeBag(lockTaken);}}
由上面的代碼可知道,為了獲取迭代器對(duì)象,總共進(jìn)行了三步主要的操作。
使用FreezeBag()方法,凍結(jié)整個(gè)ConcurrentBag<T>集合。因?yàn)樾枰杉系腖ist<T>副本,生成副本期間不能有其它線程更改損壞數(shù)據(jù)。將ConcurrrentBag<T>生成List<T>副本。因?yàn)镃oncurrentBag<T>存儲(chǔ)數(shù)據(jù)的方式比較特殊,直接實(shí)現(xiàn)迭代器模式困難,考慮到線程安全和邏輯,最佳的辦法是生成一個(gè)副本。完成以上操作以后,就可以使用UnfreezeBag()方法解凍整個(gè)集合。
那么FreezeBag()方法是如何來凍結(jié)整個(gè)集合的呢?也是分為三步走。
首先獲取全局鎖,通過Monitor.Enter(GlobalListsLock, ref lockTaken);這樣一條語句,這樣其它線程就不能凍結(jié)集合。然后獲取所有線程中ThreadLocalList的鎖,通過`AcquireAllLocks()方法來遍歷獲取。這樣其它線程就不能對(duì)它進(jìn)行操作損壞數(shù)據(jù)。等待已經(jīng)進(jìn)入了操作流程線程結(jié)束,通過WaitAllOperations()方法來實(shí)現(xiàn),該方法會(huì)遍歷每一個(gè)ThreadLocalList對(duì)象的m_currentOp屬性,確保全部處于None操作。
完成以上流程后,那么就是真正的凍結(jié)了整個(gè)ConcurrentBag<T>集合,要解凍的話也類似。在此不再贅述。
四、總結(jié)
下面給出一張圖,描述了ConcurrentBag<T>是如何存儲(chǔ)數(shù)據(jù)的。通過每個(gè)線程中的ThreadLocal來實(shí)現(xiàn)線程本地存儲(chǔ),每個(gè)線程中都有這樣的結(jié)構(gòu),互不干擾。然后每個(gè)線程中的m_headList總是指向ConcurrentBag<T>的第一個(gè)列表,m_tailList指向最后一個(gè)列表。列表與列表之間通過m_locals 下的 m_nextList相連,構(gòu)成一個(gè)單鏈表。
數(shù)據(jù)存儲(chǔ)在每個(gè)線程的m_locals中,通過Node類構(gòu)成一個(gè)雙向鏈表。
PS: 要注意m_tailList和m_headList并不是存儲(chǔ)在ThreadLocal中,而是所有的線程共享一份。

【推薦】.NET Core開發(fā)實(shí)戰(zhàn)視頻課程 ★★★
.NET Core實(shí)戰(zhàn)項(xiàng)目之CMS 第一章 入門篇-開篇及總體規(guī)劃
【.NET Core微服務(wù)實(shí)戰(zhàn)-統(tǒng)一身份認(rèn)證】開篇及目錄索引
Redis基本使用及百億數(shù)據(jù)量中的使用技巧分享(附視頻地址及觀看指南)
.NET Core中的一個(gè)接口多種實(shí)現(xiàn)的依賴注入與動(dòng)態(tài)選擇看這篇就夠了
10個(gè)小技巧助您寫出高性能的ASP.NET Core代碼
用abp vNext快速開發(fā)Quartz.NET定時(shí)任務(wù)管理界面
在ASP.NET Core中創(chuàng)建基于Quartz.NET托管服務(wù)輕松實(shí)現(xiàn)作業(yè)調(diào)度
現(xiàn)身說法:實(shí)際業(yè)務(wù)出發(fā)分析百億數(shù)據(jù)量下的多表查詢優(yōu)化
