現(xiàn)代 C++ 智能指針使用入門
引用計(jì)數(shù)
了解?Objective-C/Swift?的程序員應(yīng)該知道引用計(jì)數(shù)的概念。引用計(jì)數(shù)這種計(jì)數(shù)是為了防止內(nèi)存泄露而產(chǎn)生的。
基本想法是對(duì)于動(dòng)態(tài)分配的對(duì)象,進(jìn)行引用計(jì)數(shù),每當(dāng)增加一次對(duì)同一個(gè)對(duì)象的引用,那么引用對(duì)象的引用計(jì)數(shù)就會(huì)增加一次, 每刪除一次引用,引用計(jì)數(shù)就會(huì)減一,當(dāng)一個(gè)對(duì)象的引用計(jì)數(shù)減為零時(shí),就自動(dòng)刪除指向的堆內(nèi)存。
在傳統(tǒng)C++中,『記得』手動(dòng)釋放資源,總不是最佳實(shí)踐。因?yàn)槲覀兒苡锌赡芫屯浟巳メ尫刨Y源而導(dǎo)致泄露。所以通常的做法是對(duì)于一個(gè)對(duì)象而言,我們?cè)跇?gòu)造函數(shù)的時(shí)候申請(qǐng)空間,而在析構(gòu)函數(shù)(在離開(kāi)作用域時(shí)調(diào)用)的時(shí)候釋放空間, 也就是我們常說(shuō)的 RAII 資源獲取即初始化技術(shù)。
凡事都有例外,我們總會(huì)有需要將對(duì)象在自由存儲(chǔ)上分配的需求,在傳統(tǒng) C++ 里我們只好使用 new 和 delete 去 『記得』對(duì)資源進(jìn)行釋放。而 C++11 引入了智能指針的概念,使用了引用計(jì)數(shù)的想法,讓程序員不再需要關(guān)心手動(dòng)釋放內(nèi)存。
這些智能指針就包括?std::shared_ptr std::unique_ptr std::weak_ptr,使用它們需要包含頭文件
注意:引用計(jì)數(shù)不是垃圾回收,引用計(jì)數(shù)能夠盡快收回不再被使用的對(duì)象,同時(shí)在回收的過(guò)程中也不會(huì)造成長(zhǎng)時(shí)間的等待, 更能夠清晰明確的表明資源的生命周期。
std::shared_ptr
std::shared_ptr 是一種智能指針,它能夠記錄多少個(gè) shared_ptr 共同指向一個(gè)對(duì)象,從而消除顯式的調(diào)用 delete,當(dāng)引用計(jì)數(shù)變?yōu)榱愕臅r(shí)候就會(huì)將對(duì)象自動(dòng)刪除。
但還不夠,因?yàn)槭褂?std::shared_ptr 仍然需要使用 new 來(lái)調(diào)用,這使得代碼出現(xiàn)了某種程度上的不對(duì)稱。
std::make_shared 就能夠用來(lái)消除顯式的使用 new,所以 std::make_shared 會(huì)分配創(chuàng)建傳入?yún)?shù)中的對(duì)象, 并返回這個(gè)對(duì)象類型的 std::shared_ptr 指針。例如:
#include |
std::shared_ptr 可以通過(guò) get() 方法來(lái)獲取原始指針,通過(guò) reset() 來(lái)減少一個(gè)引用計(jì)數(shù), 并通過(guò) use_count() 來(lái)查看一個(gè)對(duì)象的引用計(jì)數(shù)。例如:
auto pointer = std::make_shared<int>(10); |
std::unique_ptr
std::unique_ptr?是一種獨(dú)占的智能指針,它禁止其他智能指針與其共享同一個(gè)對(duì)象,從而保證代碼的安全:
std::unique_ptr<int> pointer = std::make_unique<int>(10); // make_unique 從 C++14 引入 |
make_unique 并不復(fù)雜,C++11 沒(méi)有提供 std::make_unique,可以自行實(shí)現(xiàn):
template<typename T, typename ...Args> |
至于為什么沒(méi)有提供,C++ 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)委員會(huì)主席 Herb Sutter 在他的博客中提到原因是因?yàn)椤罕凰麄兺浟恕弧?/span>
既然是獨(dú)占,換句話說(shuō)就是不可復(fù)制。但是,我們可以利用 std::move 將其轉(zhuǎn)移給其他的 unique_ptr,例如:
#include |
std::weak_ptr
如果你仔細(xì)思考?std::shared_ptr?就會(huì)發(fā)現(xiàn)依然存在著資源無(wú)法釋放的問(wèn)題。看下面這個(gè)例子:
struct A; |
運(yùn)行結(jié)果是 A, B 都不會(huì)被銷毀,這是因?yàn)?a,b 內(nèi)部的 pointer 同時(shí)又引用了 a,b,這使得 a,b 的引用計(jì)數(shù)均變?yōu)榱?2,而離開(kāi)作用域時(shí),a,b 智能指針被析構(gòu),卻只能造成這塊區(qū)域的引用計(jì)數(shù)減一。
這樣就導(dǎo)致了?a,b?對(duì)象指向的內(nèi)存區(qū)域引用計(jì)數(shù)不為零,而外部已經(jīng)沒(méi)有辦法找到這塊區(qū)域了,也就造成了內(nèi)存泄露,如圖 1:
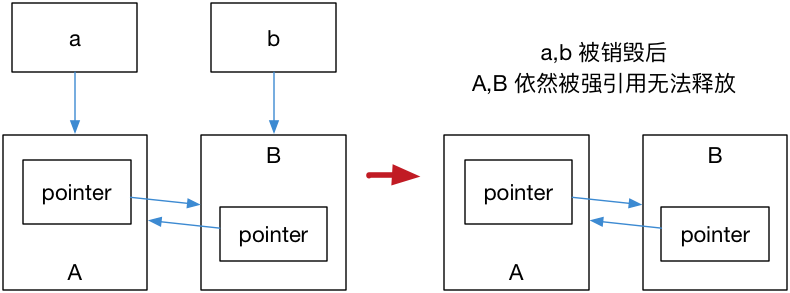
圖 1
解決這個(gè)問(wèn)題的辦法就是使用弱引用指針?std::weak_ptr,std::weak_ptr是一種弱引用(相比較而言 std::shared_ptr 就是一種強(qiáng)引用)。
弱引用不會(huì)引起引用計(jì)數(shù)增加,當(dāng)換用弱引用時(shí)候,最終的釋放流程如圖 2 所示:
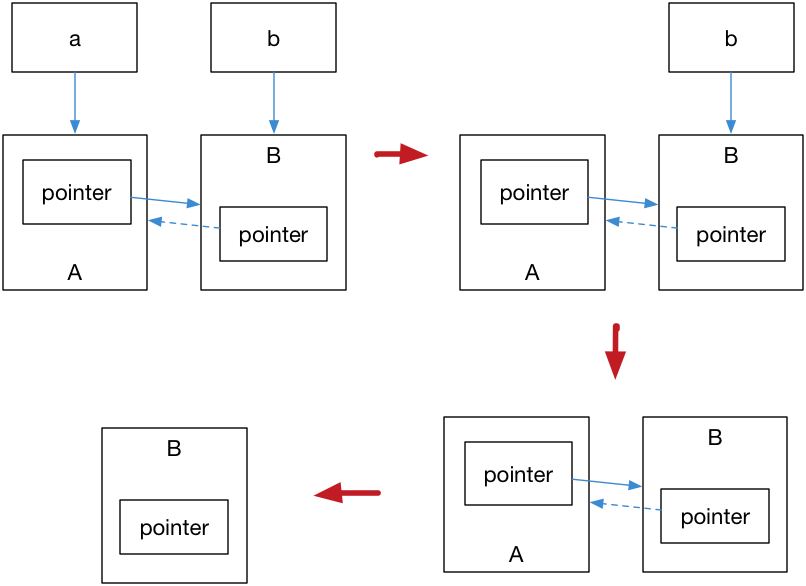
圖 2
在上圖中,最后一步只剩下 B,而 B 并沒(méi)有任何智能指針引用它,因此這塊內(nèi)存資源也會(huì)被釋放。
std::weak_ptr?沒(méi)有?*?運(yùn)算符和?->?運(yùn)算符,所以不能夠?qū)Y源進(jìn)行操作,它的唯一作用就是用于檢查 std::shared_ptr 是否存在,其 expired()?方法能在資源未被釋放時(shí),會(huì)返回 false,否則返回 true。
總結(jié)
智能指針這種技術(shù)并不新奇,在很多語(yǔ)言中都是一種常見(jiàn)的技術(shù),現(xiàn)代 C++ 將這項(xiàng)技術(shù)引進(jìn),在一定程度上消除了?new/delete?的濫用,是一種更加成熟的編程范式。
來(lái)源:https://changkun.de/modern-cpp/zh-cn/05-pointers/index.html
推薦:
Android FFmpeg 實(shí)現(xiàn)帶濾鏡的微信小視頻錄制功能
