Pytorch并行訓練
來源:知乎—魔法學院的Chilia
作者:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/501510475
01
只需要一行代碼就可以實現(xiàn)DataParallel:
if torch.cuda.device_count() > 1: #判斷是不是有多個GPUprint("Let's use", torch.cuda.device_count(), "GPUs!")model = nn.DataParallel(model,device_ids=range(torch.cuda.device_count()))
DataParallel方法雖然代碼非常簡單,但是GPU會出現(xiàn)負載不均衡的問題("一個gpu干活,其它gpu看戲")。第一個GPU(12GB)可能占用了10GB,剩余的GPU卻只使用了2GB -- 這是極大的浪費。那么,為什么會出現(xiàn)這樣的現(xiàn)象呢?我們來仔細研究一下下面這個流程圖就明白了:
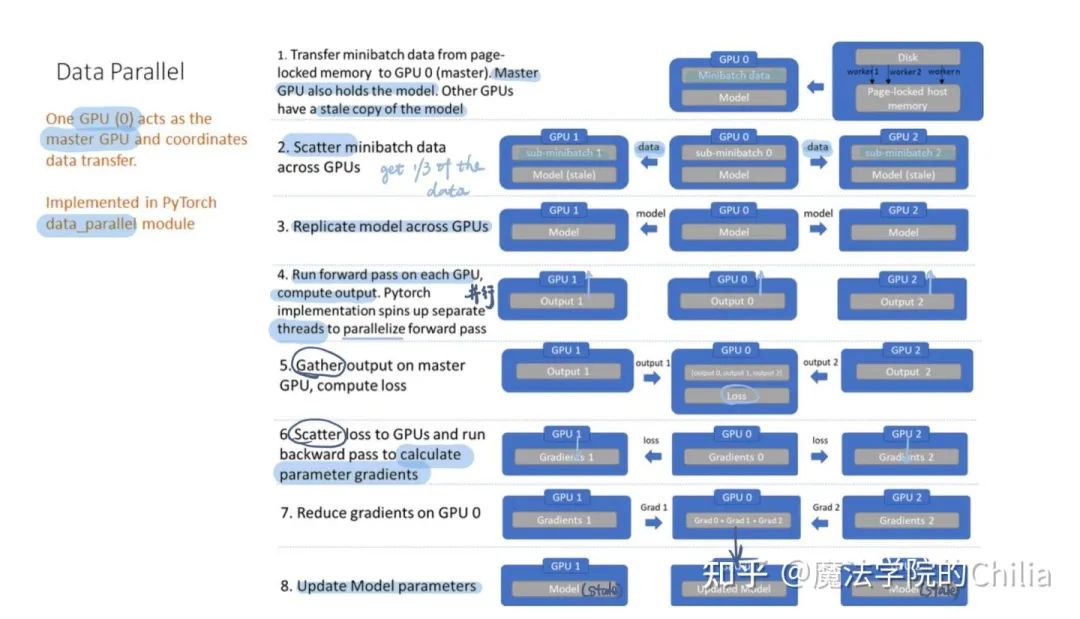
我們首先需要指定一個GPU(0)作為master GPU,它必須承擔最多的負載。
第一步:GPU(0)從鎖頁內(nèi)存(分配主機內(nèi)存時鎖定該頁,讓其不與磁盤交換。必須保證自己內(nèi)存空間充足的時候才用鎖頁內(nèi)存!)中取得一個minibatch。
第二步:GPU(0)把這個minibatch去scatter到其他GPU上,每個GPU拿到1/n的數(shù)據(jù),這就是data parallel的定義。
第三步:GPU(0)把模型也分配到其他GPU上,現(xiàn)在模型是同步的
第四步:在每個GPU上并行的做forward pass,得到每個sub-minibatch的輸出
第五步:GPU(0)把所有GPU的輸出gather到自己這里,計算loss
第六步:GPU(0)把loss scatter到其他GPU,分別進行backward pass計算梯度
第七步:GPU(0)把梯度集中起來進行reduce,計算出梯度的總和
第八步:GPU(0)用這個梯度更新自己的模型。而其他模型沒有更新,是stale版本。
我們可以看到,nn.DataParallel做了很多不必要的操作,導致其性能不佳:
第一步的時候,從page-lock memory先取數(shù)據(jù)到GPU(0),然后由GPU(0)再進行分發(fā)。為什么不能直接從page-lock memory中分發(fā)到各個GPU呢?
第五步的時候,GPU(0)拿到每個GPU的output然后計算loss,那么為什么不能每個GPU自己計算自己的loss呢?
最后一步參數(shù)的更新是在GPU(0)上進行的,此時其他GPU上的模型和GPU(0)不再同步。所以每次都需要broadcast 模型進行顯式的同步。
由于loss的計算、梯度的reduce、模型的更新都是在GPU(0)上進行,所以造成了第一個GPU的負載遠遠大于剩余其他的GPU。
02
真正使用了多進程(process),而DataParallel只是使用了多線程(thread):
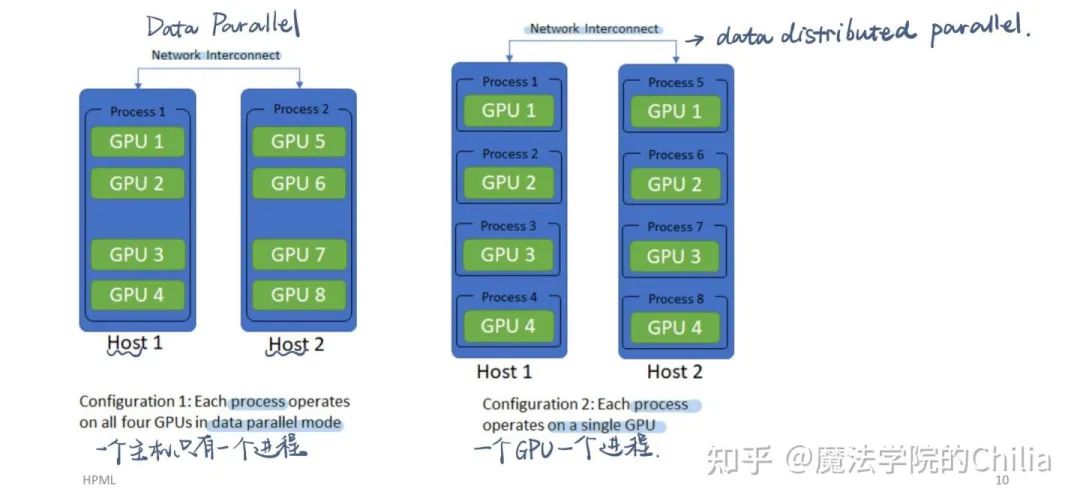
DataParallel: 一個host一個process;DistributedDataParallel: 一個GPU一個process
DistributedDataParallel是對每個GPU使用一個進程,適用于單機多卡和多機多卡的場景。它的主要工作流程如下圖所示,可以看到相比DataParallel做了很多的優(yōu)化:
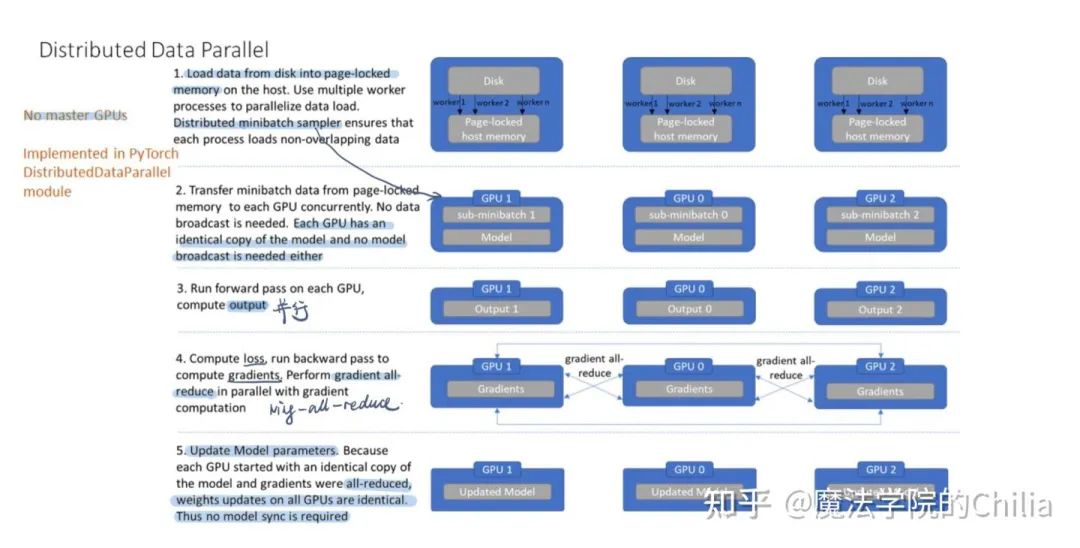
每個GPU都有一個process,分別計算在這個GPU上的loss、gradient,然后用ring-all-reduce的方式進行聚合。得到綜合的gradient之后同時更新本GPU上的模型參數(shù),所以模型一直都是同步的,不需要手動同步。
DistributedDataParallel is proven to be significantly faster than torch.nn.DataParallel for single-node multi-GPU data parallel training.
調(diào)用過程:
(1)初始化:sync the processes
#初始化使用nccl后端torch.distributed.init_process_group(backend="nccl")
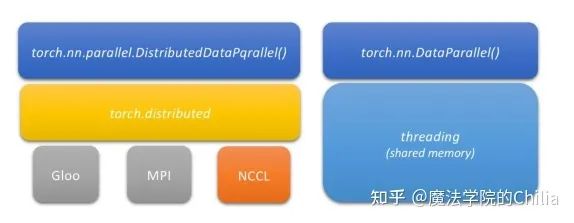
Gloo(用于CPU)和NCCL(用于GPU)都是用于多個node之間通信的庫。從下面的圖中我們可以看到,torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel是依賴于torch.distributed的,而torch.distributed提供的是多機通信的一些原語。它依賴于Gloo/NCCL/MPI backend。
而torch.nn.DataParallel根本就是虛假的分布式!因為它只能使用于單個node,而且是單進程(single process)的,它的并行化全部依賴于線程(thread)。
(2)使用DistributedSampler
多gpu訓練是,我們希望同一時刻在每個gpu上的數(shù)據(jù)是不一樣的,這樣相當于batch size擴大了N倍,因此起到了加速訓練的作用。DistributedSampler用于把鎖頁內(nèi)存的一個minibatch再進行切分,分配到不同的GPU進程中去。要保證這樣的劃分是沒有overlap的。
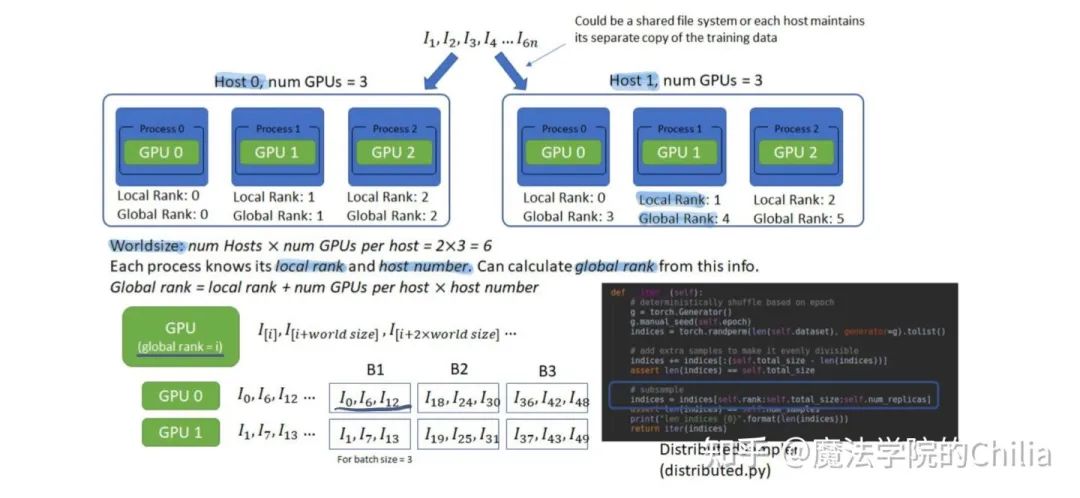
每個進程都知道自己的local rank 和 host number,就可以推算出自己的global rank, 然后獲得自己應有的那一份sub-minibatch數(shù)據(jù),保證每個進程拿到的數(shù)據(jù)沒有重疊。
03
dist.broadcast(tensor,src,group): 對于group中的所有GPU編號,把tensor從src GPU分發(fā)到其他的GPU process中
dist.reduce(tensor,dst,op,group): Applies op to all tensor in group and store the result in dst.
dist.all_reduce(tensor,op,group): Same as reduce, but the result is stored in all processes.
dist.scatter(tensor,src,scatter_list,group): copy the ith tensor scatter_list[i] to the ith process.
dist.gather(tensor, dst, gather_list, group): copy tensor from all processes in group in dst
dist.all_gather(tensor_list,tensor,group): copy tensor from all processes to tensor_list, on all processes.
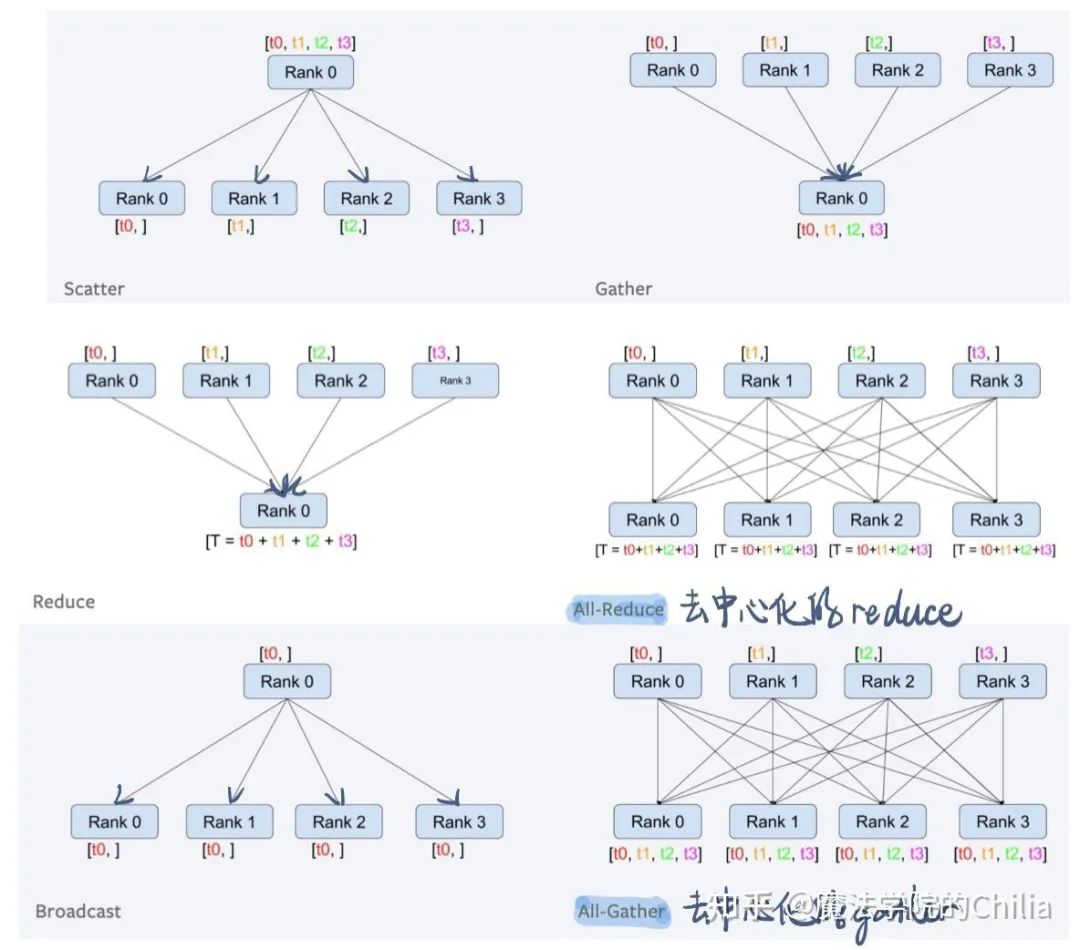
下面我們來看一個例子:
import torchimport argparsefrom torch import distributed as distprint(torch.cuda.device_count()) # 打印gpu數(shù)量torch.distributed.init_process_group(backend="nccl") # 并行訓練初始化,'nccl'模式print('world_size', torch.distributed.get_world_size()) # 打印當前進程數(shù)# 下面這個參數(shù)需要加上,torch內(nèi)部調(diào)用多進程時,會使用該參數(shù),對每個gpu進程而言,其local_rank都是不同的;parser.add_argument('--local_rank', default=-1, type=int)args = parser.parse_args()torch.cuda.set_device(args.local_rank) # 設置gpu編號為local_rank;此句也可能看出local_rank的值是什么'''多卡訓練加載數(shù)據(jù):注意shuffle與sampler是沖突的,并行訓練需要設置sampler,此時務必# 要把shuffle設為False。但是這里shuffle=False并不意味著數(shù)據(jù)就不會亂序了,而是亂序的方式交給# sampler來控制,實質(zhì)上數(shù)據(jù)仍是亂序的。'''train_sampler = torch.utils.data.distributed.DistributedSampler(My_Dataset)dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(ds,batch_size=batch_size,shuffle=False,num_workers=16,pin_memory=True, ##鎖頁內(nèi)存drop_last=True,sampler=self.train_sampler)'''多卡訓練的模型設置:'''def average_gradients(model): ##每個gpu上的梯度求平均size = float(dist.get_world_size())for param in model.parameters:dist.all_reduce(param.grad.data,op = dist.reduce_op.SUM)param.grad.data /= sizeMy_model = My_model.cuda(args.local_rank) # 將模型拷貝到每個gpu上.直接.cuda()也行,因為多進程時每個進程的device號是不一樣的My_model = torch.nn.SyncBatchNorm.convert_sync_batchnorm(My_model) # 設置多個gpu的BN同步My_model = torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel(My_model,device_ids=[args.local_rank],output_device=args.local_rank,find_unused_parameters=False,broadcast_buffers=False)'''開始多卡訓練:'''for epoch in range(200):train_sampler.set_epoch(epoch) # 這句莫忘,否則相當于沒有shuffle數(shù)據(jù)My_model.train()for idx, sample in enumerate(dataloader):inputs, targets = sample[0].cuda(local_rank, non_blocking=True), sample[1].cuda(local_rank, non_blocking=True)opt.zero_grad()output = My_model(inputs)loss = My_loss(output, targets)loss.backward()average_gradient(My_model) ##計算梯度的平均opt.step() ##根據(jù)梯度更新模型'''多卡測試(evaluation):'''if local_rank == 0:My_model.eval()with torch.no_grad():acc = My_eval(My_model)torch.save(My_model.module.state_dict(), model_save_path)dist.barrier() # 這一句作用是:所有進程(gpu)上的代碼都執(zhí)行到這,才會執(zhí)行該句下面的代碼'''其它代碼'''
在分布式的GPU上進行SGD,每個GPU在計算完梯度之后,需要把不同GPU上的梯度進行all-reduce,即計算所有GPU上梯度的平均值:dist.all_reduce(param.grad.data, op=dist.reduce_op.SUM), 意為我們對每個模型參數(shù)的梯度進行all_reduce, 采用求和的形式計算all_reduce.
最后一步,運行上述代碼的方式(8卡為例):
python3 -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=8 DDP.py
參考資料:
熊勒個貓:和nn.DataParallel說再見
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/95700549
格子不太方:pytorch 并行訓練之DistributedDataParallel(代碼樣例和解釋)
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/350301395
Columbia University COMS 6998: Deep Learning System 課件
猜您喜歡:
 戳我,查看GAN的系列專輯~!
戳我,查看GAN的系列專輯~!附下載 |《TensorFlow 2.0 深度學習算法實戰(zhàn)》
《基于深度神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡的少樣本學習綜述》
