實(shí)操教程|詳細(xì)記錄solov2的ncnn實(shí)現(xiàn)和優(yōu)化

極市導(dǎo)讀
由于目前solo系列在GitHub中沒有轉(zhuǎn)ncnn的項(xiàng)目,作者詳細(xì)記錄了自己solov2的ncnn實(shí)現(xiàn)以及后處理后處理優(yōu)化的一些策略,給需要的人一點(diǎn)借鑒。附有代碼地址。 >>加入極市CV技術(shù)交流群,走在計(jì)算機(jī)視覺的最前沿
SOLOV2簡(jiǎn)介
solo大家都知道,核心思想是:將分割問題轉(zhuǎn)化為位置分類問題,從而做到不需要anchor,不需要normalization,不需要bounding box detections的實(shí)例分割。
https://github.com/Epiphqny/SOLOv2
緣由
目前solo系列在github中沒有轉(zhuǎn)ncnn的項(xiàng)目
solov2的思想比較簡(jiǎn)單明了,但是轉(zhuǎn)ncnn還是需要很多比較復(fù)雜操作,想在用ncnn實(shí)現(xiàn)更加了解solov2內(nèi)部的算法流程,也熟悉ncnn的一些其他op操作
文字有很多干貨:param手動(dòng)修改、動(dòng)態(tài)op、加速技巧等等
1 、torch導(dǎo)出onnx
在導(dǎo)出onnx之前有幾部操作:
修改split_feats: onnx不支持F.interpolate() 中 scale_factor < 1 ;因此對(duì)split_feats做了修改為nn.Maxpool 卷積,后面轉(zhuǎn)ncnn手動(dòng)修改;
def split_feats(self, feats):return [self.maxpool(feats[0]),# F.interpolate(feats[0],scale_factor=0.5,mode='bilinear'),feats[1],feats[2],feats[3],F.interpolate(feats[4], size=feats[3].shape[-2:], mode='bilinear')]
添加輸入?yún)?shù):
添加onnx參數(shù),金生coord改為手動(dòng)輸入
def forward(self, feats, eval=False,onnx=False):if onnx:feats,p3_input,p4_input,p5_input = featsnew_feats = self.split_feats(feats)featmap_sizes = [featmap.size()[-2:] for featmap in new_feats]if onnx:new_feats[0] = [new_feats[0],p3_input]new_feats[1] = [new_feats[1],p3_input]new_feats[2] = [new_feats[2],p4_input]new_feats[3] = [new_feats[3],p5_input]new_feats[4] = [new_feats[4],p5_input]
實(shí)現(xiàn)轉(zhuǎn)換代碼
實(shí)現(xiàn)轉(zhuǎn)換代碼,并onnxsim優(yōu)化,這里需要注意的是輸入盡量小一點(diǎn),因?yàn)閟olo的四個(gè)輸出頭的size比較小(40,36,24,16,12),輸入較大時(shí)會(huì)使F.interpolate() 中 scale_factor < 1 ,input_size = 256時(shí)fpn最后一層上采樣的scale_factor剛好可以等于2(256%64=0)
from torch import nnimport torchfrom mmcv import Configfrom mmdet.models.builder import build_backbone,build_head,build_neckclass SOLOV2(nn.Module):def __init__(self,confg):super(SOLOV2,self).__init__()self.cfg = Config.fromfile(confg)self.cfg = self.cfg["model"]self.backbone = build_backbone(self.cfg["backbone"])self.neck = build_neck(self.cfg["neck"])self.bbox_head = build_head(self.cfg["bbox_head"])def forward(self,x,p3_input,p4_input,p5_input):x = self.backbone(x)x = self.neck(x)feature_pred,kernel_pred,cate_pred = self.bbox_head([x,p3_input,p4_input,p5_input],eval=True,onnx=True)return feature_pred,kernel_pred,cate_predcfg = "./configs/solov2/solov2_r101_3x.py"pretrained = "./weights/solov2.pth"#net = SOLOV2(cfg)state_dict = torch.load(pretrained, map_location=lambda storage, loc: storage)["state_dict"]res = net.load_state_dict(state_dict,strict=False)net.eval()input_size = 256dummy_input1 = torch.randn(1, 3, input_size, input_size)dummy_input2 = torch.randn(1, 2, input_size//8, input_size//8)dummy_input3 = torch.randn(1, 2, input_size//16, input_size//16)dummy_input4 = torch.randn(1, 2, input_size//32, input_size//32)input_names = ["input","p3_input","p4_input","p5_input"]output_names = ["feature_pred","kernel_pred1","kernel_pred2","kernel_pred3","kernel_pred4","kernel_pred5","cate_pred1","cate_pred2","cate_pred3","cate_pred4","cate_pred5" ]save_name = "./onnx/solov2.onnx"# torch.onnx.export(model, (dummy_input1, dummy_input2, dummy_input3), "C3AE.onnx", verbose=True, input_names=input_names, output_names=output_names)torch.onnx.export(net, (dummy_input1,dummy_input2,dummy_input3,dummy_input4),save_name , verbose=False, input_names=input_names,output_names=output_names)import osos.system("python -m onnxsim {0} {0}".format(save_name))
2、onnx轉(zhuǎn)ncnn
onnx2ncnn
./onnx2ncnn solov2.onnx solov2.param solov2.bin
ncnn 參數(shù)手工優(yōu)化
將之前轉(zhuǎn)onnx時(shí)的maxpool改為上采樣操作:
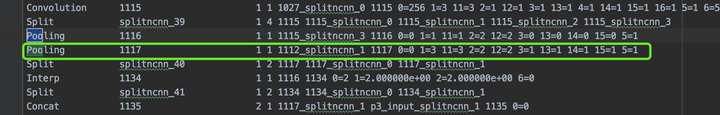
改為
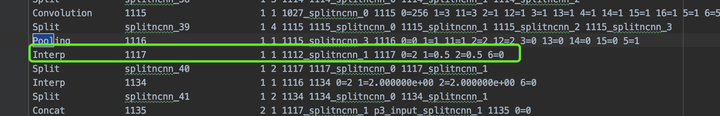
2、將所有的kernel_pred和cate_pred之前的Interp參數(shù)改為對(duì)用的w和h:

改為
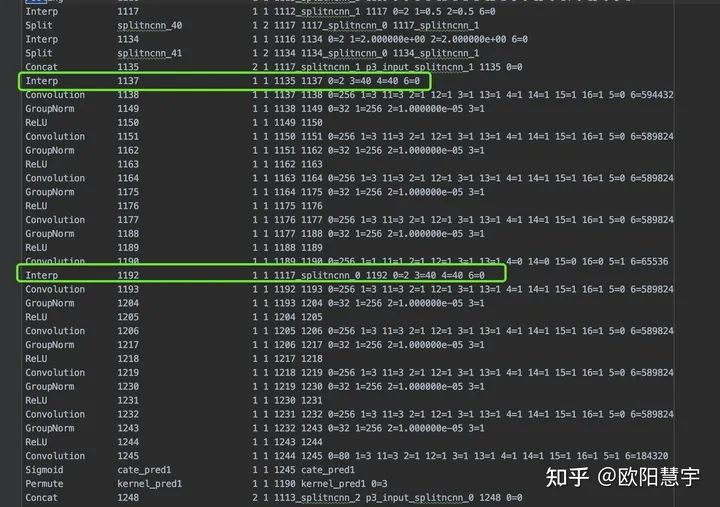
對(duì)應(yīng)40尺寸的改好了,后面32、24、26、12也是類似的;
3、ncnn推理實(shí)現(xiàn)
coord輸入實(shí)現(xiàn)
對(duì)比torch半的coord實(shí)現(xiàn):
x_range = torch.linspace(-1, 1, kernel_feat.shape[-1], device=kernel_feat.device)y_range = torch.linspace(-1, 1, kernel_feat.shape[-2], device=kernel_feat.device)x = torch.meshgrid(y_range, x_range)y = y.expand([kernel_feat.shape[0], 1, -1, -1])x = x.expand([kernel_feat.shape[0], 1, -1, -1])coord_feat = torch.cat([x, y], 1)
因?yàn)閷?duì)應(yīng)stride只有8、16、32,因此ncnn需要生成3個(gè)對(duì)應(yīng)尺寸的Mat:
size_t elemsize = sizeof(float);ncnn::Mat x_p3;ncnn::Mat x_p4;ncnn::Mat x_p5;// coord convint pw = int(target_w / 8);int ph = int(target_h / 8);x_p3.create(pw, ph, 2, elemsize);float step_h = 2.f / (ph - 1);float step_w = 2.f / (pw - 1);for (int h = 0; h < ph; h++) {for (int w = 0; w < pw; w++) {x_p3.channel(0)[h * pw + w] = -1.f + step_w * (float) w;x_p3.channel(1)[h * pw + w] = -1.f + step_h * (float) h;}}pw = int(target_w / 16);ph = int(target_h / 16);x_p4.create(pw, ph, 2, elemsize);step_h = 2.f / (ph - 1);step_w = 2.f / (pw - 1);for (int h = 0; h < ph; h++) {for (int w = 0; w < pw; w++) {x_p4.channel(0)[h * pw + w] = -1.f + step_w * (float) w;x_p4.channel(1)[h * pw + w] = -1.f + step_h * (float) h;}}pw = int(target_w / 32);ph = int(target_h / 32);x_p5.create(pw, ph, 2, elemsize);step_h = 2.f / (ph - 1);step_w = 2.f / (pw - 1);for (int h = 0; h < ph; h++) {for (int w = 0; w < pw; w++) {x_p5.channel(0)[h * pw + w] = -1.f + step_w * (float) w;x_p5.channel(1)[h * pw + w] = -1.f + step_h * (float) h;}}
將其作為輸入:
ncnn::Extractor ex = solov2.create_extractor();ex.input("input", in);ex.input("p3_input", x_p3);ex.input("p4_input", x_p4);ex.input("p5_input", x_p5);
抽取feature_pred、kernerl_pred、cate_pred特征:
ncnn::Mat feature_pred, cate_pred1, cate_pred2, cate_pred3, cate_pred4, cate_pred5, kernel_pred1, kernel_pred2, kernel_pred3, kernel_pred4, kernel_pred5;ex.extract("cate_pred1", cate_pred1);ex.extract("cate_pred2", cate_pred2);ex.extract("cate_pred3", cate_pred3);ex.extract("cate_pred4", cate_pred4);ex.extract("cate_pred5", cate_pred5);ex.extract("kernel_pred1", kernel_pred1);ex.extract("kernel_pred2", kernel_pred2);ex.extract("kernel_pred3", kernel_pred3);ex.extract("kernel_pred4", kernel_pred4);ex.extract("kernel_pred5", kernel_pred5);ex.extract("feature_pred", feature_pred);
生成分割mask圖
前面已經(jīng)有了kernel_pred和feature_pred,接下來(lái)就是生成mask圖,這就用到了low-level op api<這里說(shuō)一句ncnn真靈活,誰(shuí)用誰(shuí)知道>,目的是實(shí)現(xiàn)torch中的動(dòng)態(tài)conv2d,對(duì)應(yīng)torch實(shí)現(xiàn)為:
ins_i = F.conv2d(feature_pred, kernel, groups=N).view(N, self.seg_num_grids[i] ** 2, h, w)ncnn的low-level op api使用wiki:
https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/wiki創(chuàng)建ncnn::Option
ncnn::Option opt;opt.num_threads = num_threads;opt.use_fp16_storage = false;opt.use_packing_layout = false;
實(shí)現(xiàn)分割的預(yù)測(cè)功能函數(shù)
static void ins_decode(const ncnn::Mat &kernel_pred, const ncnn::Mat &feature_pred, ncnn::Mat *ins_pred, int c_in, int c_out,ncnn::Option &opt) {ncnn::Layer *op = ncnn::create_layer("Convolution");ncnn::ParamDict pd;pd.set(0, c_out);pd.set(1, 1);pd.set(6, c_in * c_out);op->load_param(pd);ncnn::Mat weights[1];weights[0].create(c_in * c_out);float *kernel_pred_data = (float *) kernel_pred.data;for (int i = 0; i < c_in * c_out; i++) {weights[0][i] = kernel_pred_data[i];}op->load_model(ncnn::ModelBinFromMatArray(weights));op->create_pipeline(opt);ncnn::Mat temp_ins;op->forward(feature_pred, temp_ins, opt);*ins_pred = temp_ins;op->destroy_pipeline(opt);delete op;}
將每個(gè)kernel_pre轉(zhuǎn)換為分割圖:
ncnn::Mat ins_pred1, ins_pred2, ins_pred3, ins_pred4, ins_pred5;int c_in = feature_pred.c;ins_decode(kernel_pred1, feature_pred, &ins_pred1, c_in, 40 * 40,opt);ins_decode(kernel_pred2, feature_pred, &ins_pred2, c_in, 36 * 36,opt);ins_decode(kernel_pred3, feature_pred, &ins_pred3, c_in, 24 * 24,opt);ins_decode(kernel_pred4, feature_pred, &ins_pred4, c_in, 16 * 16,opt);ins_decode(kernel_pred5, feature_pred, &ins_pred5, c_in, 12 * 12,opt);
后處理
有了這一切后就是后處理啦,貼代碼:
功能函數(shù)
void generate_res(ncnn::Mat &cate_pred, ncnn::Mat &ins_pred, std::vector <std::vector<Object>> &objects, float cate_thresh,float conf_thresh, int img_w, int img_h, int num_class, float stride) {int w = cate_pred.w;int h = cate_pred.h;int w_ins = ins_pred.w;int h_ins = ins_pred.h;for (int q = 0; q < num_class; q++) {const float *cate_ptr = cate_pred.channel(q);for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < w; j++) {int index = i * w + j;float cate_socre = cate_ptr[index];if (cate_socre < cate_thresh) {continue;}const float *ins_ptr = ins_pred.channel(index);cv::Mat mask(h_ins, w_ins, CV_32FC1);float sum_mask = 0.f;int count_mask = 0;{mask = cv::Scalar(0.f);float *mp = (float *) mask.data;for (int m = 0; m < w_ins * h_ins; m++) {float mask_score = sigmoid(ins_ptr[m]);if (mask_score > 0.5) {mp[m] += mask_score;sum_mask += mask_score;count_mask++;}}}if (count_mask < stride) {continue;}float mask_score = sum_mask / (float(count_mask) + 1e-6);// float socre = mask_score * cate_socre;float socre = mask_score * cate_socre;if (socre < conf_thresh) {continue;}cv::Mat mask2;cv::resize(mask, mask2, cv::Size(img_w, img_h));Object obj;obj.mask = cv::Mat(img_h, img_w, CV_8UC1);float sum_mask_y = 0.f;float sum_mask_x = 0.f;int area = 0;{obj.mask = cv::Scalar(0);for (int y = 0; y < img_h; y++) {const float *mp2 = mask2.ptr<const float>(y);uchar *bmp = obj.mask.ptr<uchar>(y);for (int x = 0; x < img_w; x++) {if (mp2[x] > 0.5f) {bmp[x] = 255;sum_mask_y += (float) y;sum_mask_x += (float) x;area++;} else bmp[x] = 0;}}}obj.cx = int(sum_mask_x / area);obj.cy = int(sum_mask_y / area);obj.label = q + 1;obj.prob = socre;objects[q].push_back(obj);}}}}
每個(gè)head的解碼:
std::vector <std::vector<Object>> class_candidates;class_candidates.resize(num_class);generate_res(cate_pred1,ins_pred1,class_candidates,cate_thresh,confidence_thresh,img_w,img_h,num_class,8.f);generate_res(cate_pred2,ins_pred2,class_candidates,cate_thresh,confidence_thresh,img_w,img_h,num_class,8.f);generate_res(cate_pred3,ins_pred3,class_candidates,cate_thresh,confidence_thresh,img_w,img_h,num_class,16.f);generate_res(cate_pred4,ins_pred4,class_candidates,cate_thresh,confidence_thresh,img_w,img_h,num_class,32.f);generate_res(cate_pred5,ins_pred5,class_candidates,cate_thresh,confidence_thresh,img_w,img_h,num_class,32.f);
最后就是nms了,nms實(shí)現(xiàn)的比較低效:
objects.clear();for (int i = 0; i < (int) class_candidates.size(); i++) {std::vector <Object> &candidates = class_candidates[i];qsort_descent_inplace(candidates);std::vector<int> picked;nms_sorted_segs(candidates, picked, nms_threshold,img_w,img_h);for (int j = 0; j < (int) picked.size(); j++) {int z = picked[j];objects.push_back(candidates[z]);}}qsort_descent_inplace(objects);
至此,已經(jīng)基本完成了所有工作啦:來(lái)預(yù)測(cè)一張圖看看:
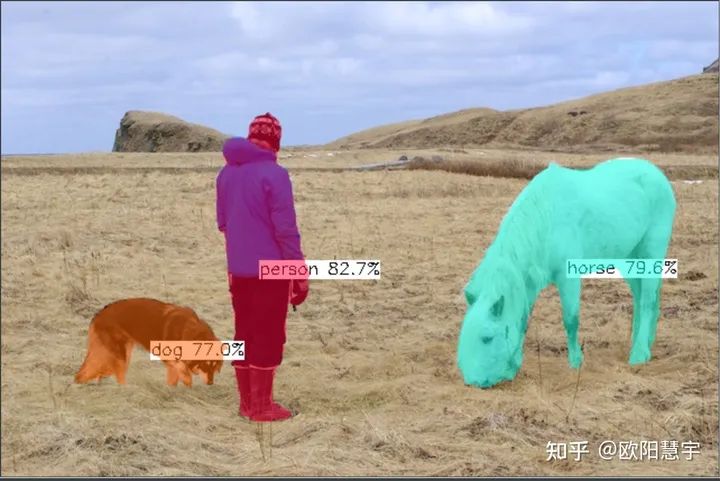

可以看出來(lái)結(jié)果還是非常好的QAQ
速度優(yōu)化
重中之重來(lái)啦,本人針對(duì)SOLO的特點(diǎn)做了一處優(yōu)化,就是kernel_pred的部分,在kernel_pred1部分輸出特征圖為256x40x40,轉(zhuǎn)換為cond2d的核就為1600x256,1600的通道在stride=4的特征圖上耗時(shí)巨大,那怎么來(lái)優(yōu)化呢。
SOLO預(yù)測(cè)的cate_pred1分支預(yù)測(cè)了40x40=1600個(gè)網(wǎng)格,但并不是所有網(wǎng)格都是需要的,只有大于預(yù)值得才需要,那么在kernel_pred1的輸出部分僅僅只需要cate_pred1大于閾值對(duì)應(yīng)的核就好,基于這個(gè)思想就能減少非常多的通道,進(jìn)而減少計(jì)算量。
話不多說(shuō),具體這樣實(shí)現(xiàn):
首先獲取cate_pred大于閾值的index:
功能函數(shù)為:
static void kernel_pick(const ncnn::Mat &cate_pred, std::vector<int> &picked, int num_class, float cate_thresh){int w = cate_pred.w;int h = cate_pred.h;for (int q = 0; q < num_class; q++) {const float *cate_ptr = cate_pred.channel(q);for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < w; j++) {int index = i * w + j;float cate_score = cate_ptr[index];if (cate_score < cate_thresh) {continue;}else picked.push_back(index);}}}}
獲取每個(gè)cate_pred分支的index結(jié)果:
std::vector<int> kernel_picked1, kernel_picked2, kernel_picked3, kernel_picked4, kernel_picked5;kernel_pick(cate_pred1, kernel_picked1, num_class, cate_thresh);kernel_pick(cate_pred2, kernel_picked2, num_class, cate_thresh);kernel_pick(cate_pred3, kernel_picked3, num_class, cate_thresh);kernel_pick(cate_pred4, kernel_picked4, num_class, cate_thresh);kernel_pick(cate_pred5, kernel_picked5, num_class, cate_thresh);
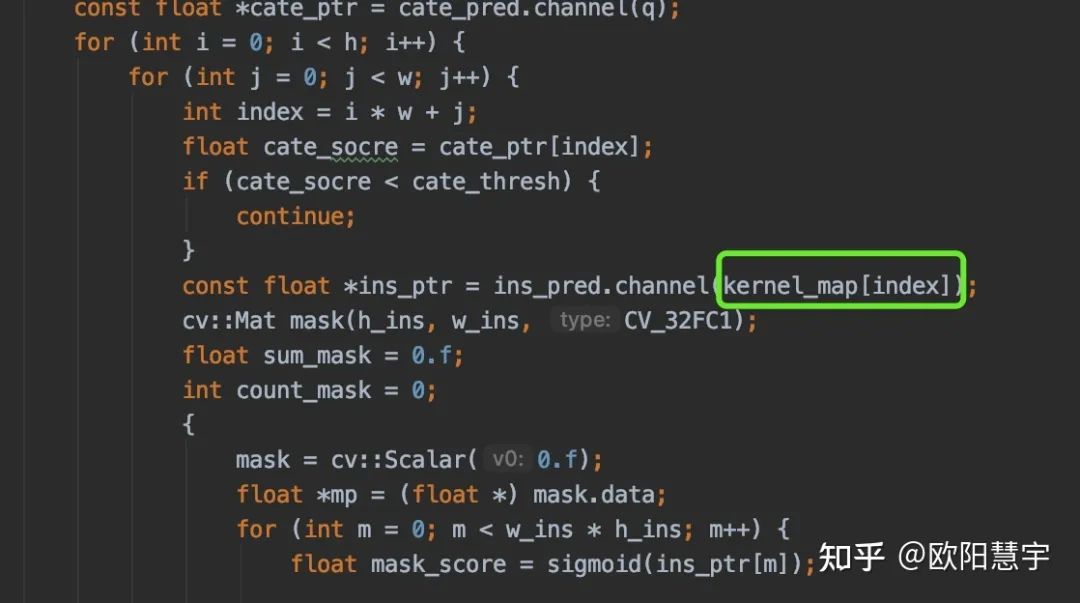
在ins_decode功能函數(shù)中加入map,來(lái)保存index和ins_pred的通道索引的映射關(guān)系
static void ins_decode(const ncnn::Mat &kernel_pred, const ncnn::Mat &feature_pred, std::vector<int> &kernel_picked,std::map<int, int> &kernel_map, ncnn::Mat *ins_pred, int c_in,ncnn::Option &opt) {std::set<int> kernel_pick_set;kernel_pick_set.insert(kernel_picked.begin(), kernel_picked.end());int c_out = kernel_pick_set.size();if (c_out > 0) {ncnn::Layer *op = ncnn::create_layer("Convolution");ncnn::ParamDict pd;pd.set(0, c_out);pd.set(1, 1);pd.set(6, c_in * c_out);op->load_param(pd);ncnn::Mat weights[1];weights[0].create(c_in * c_out);float *kernel_pred_data = (float *) kernel_pred.data;std::set<int>::iterator pick_c;int count_c = 0;for (pick_c = kernel_pick_set.begin(); pick_c != kernel_pick_set.end(); pick_c++){kernel_map[*pick_c] = count_c;for (int j = 0; j < c_in; j++) {weights[0][count_c * c_in + j] = kernel_pred_data[c_in * (*pick_c) + j];}count_c++;}op->load_model(ncnn::ModelBinFromMatArray(weights));op->create_pipeline(opt);ncnn::Mat temp_ins;op->forward(feature_pred, temp_ins, opt);*ins_pred = temp_ins;op->destroy_pipeline(opt);delete op;}}
這樣后面generate_res里面通過(guò)map來(lái)獲取ins_pred的特征:
速度對(duì)比
先來(lái)打印一下ins_pred的通道
std::cout << ins_pred1.h << "," << ins_pred1.w << "," << ins_pred1.c << std::endl;std::cout << ins_pred2.h << "," << ins_pred2.w << "," << ins_pred2.c << std::endl;std::cout << ins_pred3.h << "," << ins_pred3.w << "," << ins_pred3.c << std::endl;std::cout << ins_pred4.h << "," << ins_pred4.w << "," << ins_pred4.c << std::endl;std::cout << ins_pred5.h << "," << ins_pred5.w << "," << ins_pred5.c << std::endl;
沒做通道篩選之前:

做了通道篩選后:
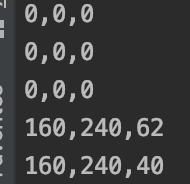
從1600+1296+576+256+144 = 3872 -> 62+40 = 102 ,對(duì)于stride=4的特征圖這計(jì)算量減少了許多,如果在cate_pred的輸出做maxpool的nms,通道數(shù)還會(huì)減少幾倍。
resnet_r101的backbone下,耗時(shí)6825.4ms ->5226.95ms(backbone太厚了,本人訓(xùn)練一個(gè)mbv2版本,已經(jīng)上傳百度云,700ms左右的樣子,14年老mac cpu單線程)
總結(jié)
實(shí)踐下如何在ncnn上使用動(dòng)態(tài)op和corrd_conv,以及后處理后處理優(yōu)化的一些策略,給需要的人一點(diǎn)借鑒。
項(xiàng)目地址
https://github.com/DayBreak-u/SOLOV2_ncnn
推薦閱讀
2020-11-07
2020-03-26

2021-04-14


# CV技術(shù)社群邀請(qǐng)函 #
備注:姓名-學(xué)校/公司-研究方向-城市(如:小極-北大-目標(biāo)檢測(cè)-深圳)
即可申請(qǐng)加入極市目標(biāo)檢測(cè)/圖像分割/工業(yè)檢測(cè)/人臉/醫(yī)學(xué)影像/3D/SLAM/自動(dòng)駕駛/超分辨率/姿態(tài)估計(jì)/ReID/GAN/圖像增強(qiáng)/OCR/視頻理解等技術(shù)交流群
每月大咖直播分享、真實(shí)項(xiàng)目需求對(duì)接、求職內(nèi)推、算法競(jìng)賽、干貨資訊匯總、與 10000+來(lái)自港科大、北大、清華、中科院、CMU、騰訊、百度等名校名企視覺開發(fā)者互動(dòng)交流~