MySQL 老有賊慢 SQL ,怎么優(yōu)化?
閱讀本文大概需要 8 分鐘。
來自:my.oschina.net/liughDevelop/blog/1788148
一、導(dǎo)致SQL執(zhí)行慢的原因
二、分析原因時(shí),一定要找切入點(diǎn)
三、什么是索引?
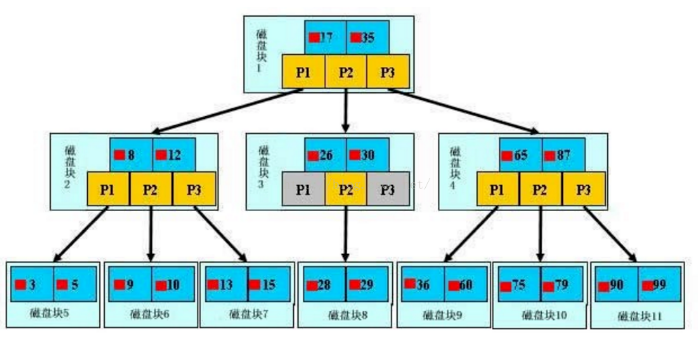
四、Explain分析
CREATE TABLE `user_info` (
`id` BIGINT(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`age` INT(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `name_index` (`name`)
)ENGINE = InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8;
INSERT INTO user_info (name, age) VALUES ('xys', 20);
INSERT INTO user_info (name, age) VALUES ('a', 21);
INSERT INTO user_info (name, age) VALUES ('b', 23);
INSERT INTO user_info (name, age) VALUES ('c', 50);
INSERT INTO user_info (name, age) VALUES ('d', 15);
INSERT INTO user_info (name, age) VALUES ('e', 20);
INSERT INTO user_info (name, age) VALUES ('f', 21);
INSERT INTO user_info (name, age) VALUES ('g', 23);
INSERT INTO user_info (name, age) VALUES ('h', 50);
INSERT INTO user_info (name, age) VALUES ('i', 15);
CREATE TABLE `order_info` (
`id` BIGINT(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_id` BIGINT(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`product_name` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`productor` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `user_product_detail_index` (`user_id`, `product_name`, `productor`)
)ENGINE = InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8;
INSERT INTO order_info (user_id, product_name, productor) VALUES (1, 'p1', 'WHH');
INSERT INTO order_info (user_id, product_name, productor) VALUES (1, 'p2', 'WL');
INSERT INTO order_info (user_id, product_name, productor) VALUES (1, 'p1', 'DX');
INSERT INTO order_info (user_id, product_name, productor) VALUES (2, 'p1', 'WHH');
INSERT INTO order_info (user_id, product_name, productor) VALUES (2, 'p5', 'WL');
INSERT INTO order_info (user_id, product_name, productor) VALUES (3, 'p3', 'MA');
INSERT INTO order_info (user_id, product_name, productor) VALUES (4, 'p1', 'WHH');
INSERT INTO order_info (user_id, product_name, productor) VALUES (6, 'p1', 'WHH');
INSERT INTO order_info (user_id, product_name, productor) VALUES (9, 'p8', 'TE');
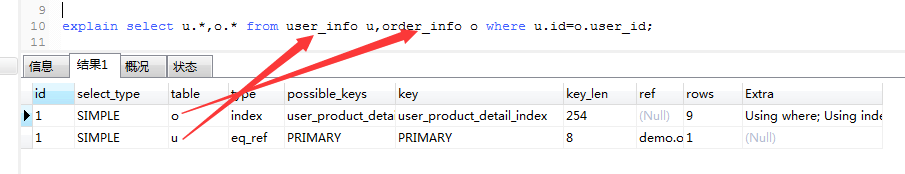
1.id
--id相同,執(zhí)行順序由上而下
explain select u.*,o.* from user_info u,order_info o where u.id=o.user_id;
--id不同,值越大越先被執(zhí)行
explain select * from user_info where id=(select user_id from order_info where product_name ='p8');
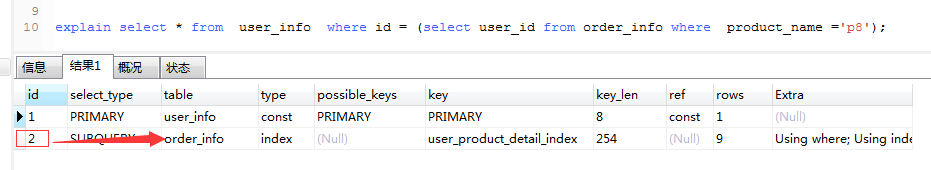
2.select_type
SIMPLE:?表示此查詢不包含 UNION 查詢或子查詢
PRIMARY:?表示此查詢是最外層的查詢
SUBQUERY:?子查詢中的第一個(gè) SELECT
UNION:?表示此查詢是 UNION 的第二或隨后的查詢
DEPENDENT UNION:UNION 中的第二個(gè)或后面的查詢語句, 取決于外面的查詢
UNION RESULT, UNION 的結(jié)果
DEPENDENT SUBQUERY: 子查詢中的第一個(gè) SELECT, 取決于外面的查詢. 即子查詢依賴于外層查詢的結(jié)果.
DERIVED:衍生,表示導(dǎo)出表的SELECT(FROM子句的子查詢)
3.table
explain select tt.* from (select u.* from user_info u,order_info o where u.id=o.user_id and u.id=1) tt
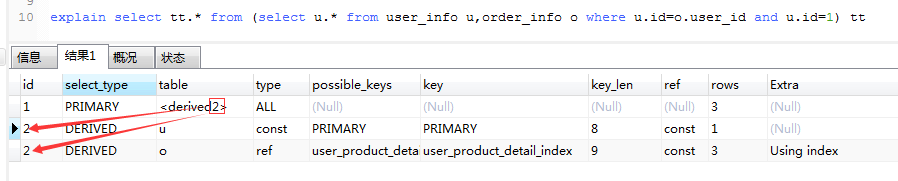
4.type
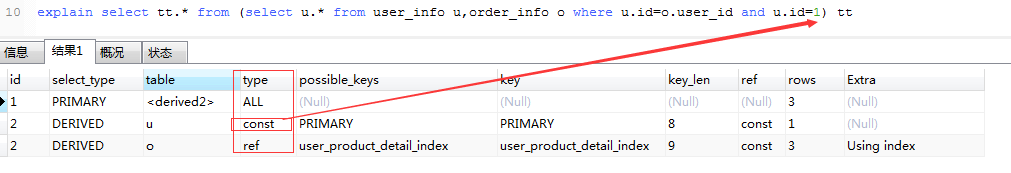
type 常用的取值有:
system: 表中只有一條數(shù)據(jù),?這個(gè)類型是特殊的 const 類型。
const: 針對(duì)主鍵或唯一索引的等值查詢掃描,最多只返回一行數(shù)據(jù)。const 查詢速度非常快, 因?yàn)樗鼉H僅讀取一次即可。例如下面的這個(gè)查詢,它使用了主鍵索引,因此 type 就是 const 類型的:explain select * from user_info where id = 2;
eq_ref: 此類型通常出現(xiàn)在多表的 join 查詢,表示對(duì)于前表的每一個(gè)結(jié)果,都只能匹配到后表的一行結(jié)果。并且查詢的比較操作通常是 =,查詢效率較高。例如:explain select * from user_info, order_info where user_info.id = order_info.user_id;
ref: 此類型通常出現(xiàn)在多表的 join 查詢,針對(duì)于非唯一或非主鍵索引,或者是使用了 最左前綴 規(guī)則索引的查詢。例如下面這個(gè)例子中, 就使用到了 ref 類型的查詢:explain select * from user_info, order_info where user_info.id = order_info.user_id AND order_info.user_id = 5
range: 表示使用索引范圍查詢,通過索引字段范圍獲取表中部分?jǐn)?shù)據(jù)記錄。這個(gè)類型通常出現(xiàn)在 =, <>, >, >=, <, <=, IS NULL, <=>, BETWEEN, IN() 操作中。例如下面的例子就是一個(gè)范圍查詢:explain select * from user_info ?where id between 2 and 8;
index: 表示全索引掃描(full index scan),和 ALL 類型類似,只不過 ALL 類型是全表掃描,而 index 類型則僅僅掃描所有的索引, 而不掃描數(shù)據(jù)。index 類型通常出現(xiàn)在:所要查詢的數(shù)據(jù)直接在索引樹中就可以獲取到, 而不需要掃描數(shù)據(jù)。當(dāng)是這種情況時(shí),Extra 字段 會(huì)顯示 Using index。
ALL: 表示全表掃描,這個(gè)類型的查詢是性能最差的查詢之一。通常來說, 我們的查詢不應(yīng)該出現(xiàn) ALL 類型的查詢,因?yàn)檫@樣的查詢?cè)跀?shù)據(jù)量大的情況下,對(duì)數(shù)據(jù)庫的性能是巨大的災(zāi)難。如一個(gè)查詢是 ALL 類型查詢, 那么一般來說可以對(duì)相應(yīng)的字段添加索引來避免。
ALL < index < range ~ index_merge < ref < eq_ref < const < system
5.possible_keys
6.key
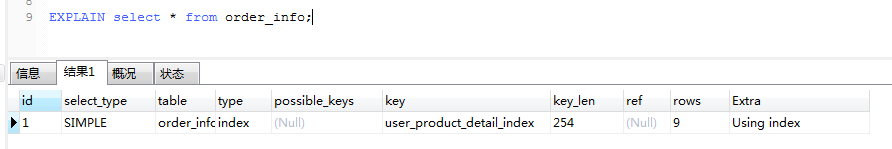
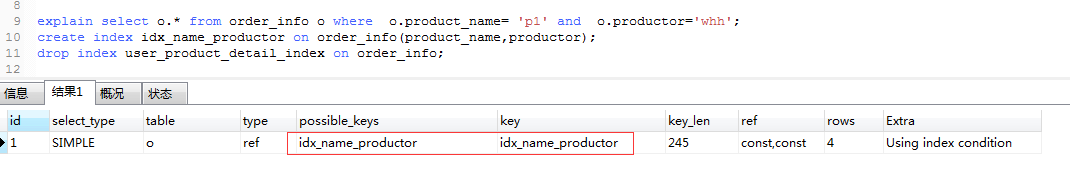
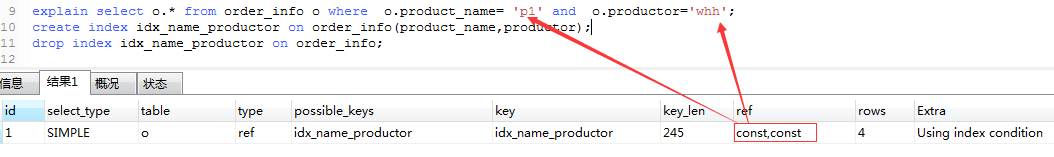
explain select o.* from order_info o where o.product_name= 'p1' and o.productor='whh';
create index idx_name_productor on order_info(productor);
drop index idx_name_productor on order_info;
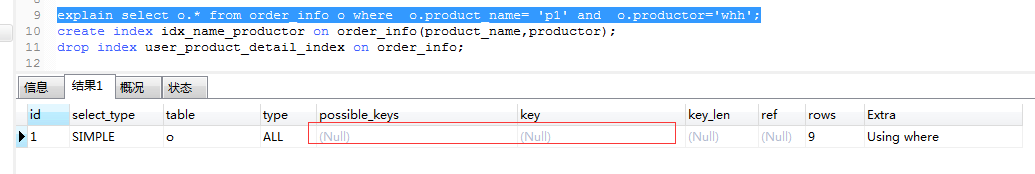
7.key_len
8.ref
9.rows
10.extra
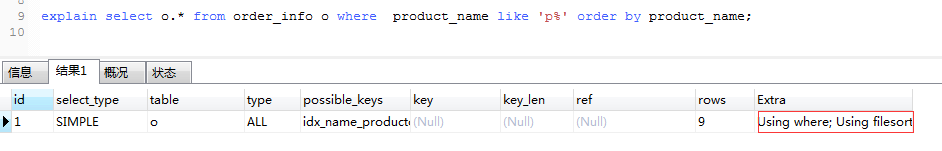
using filesort :表示 mysql 需額外的排序操作,不能通過索引順序達(dá)到排序效果。一般有 using filesort都建議優(yōu)化去掉,因?yàn)檫@樣的查詢 cpu 資源消耗大。
using index:覆蓋索引掃描,表示查詢?cè)谒饕龢渲芯涂刹檎宜钄?shù)據(jù),不用掃描表數(shù)據(jù)文件,往往說明性能不錯(cuò)。
using temporary:查詢有使用臨時(shí)表, 一般出現(xiàn)于排序, 分組和多表 join 的情況, 查詢效率不高,建議優(yōu)化。
using where :表名使用了where過濾。
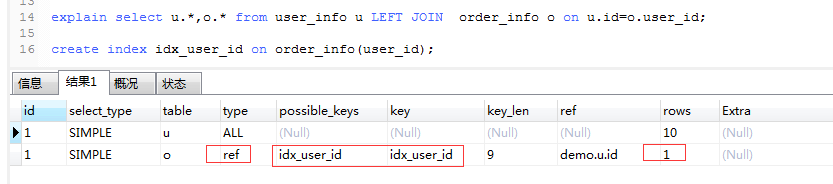
五、優(yōu)化案例
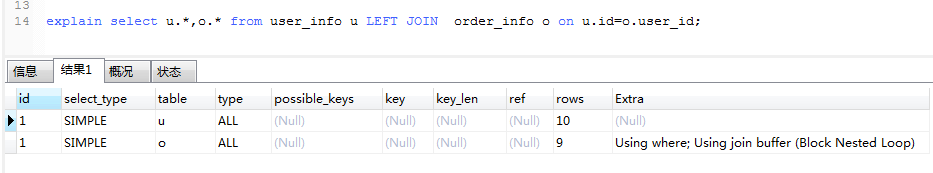
explain select u.*,o.* from user_info u LEFT JOIN order_info o on u.id=o.user_id;
六、是否需要?jiǎng)?chuàng)建索引?? ?

別忘記點(diǎn)個(gè)在看,咱們下篇見!
慢一點(diǎn)才能更快
推薦閱讀:
微信掃描二維碼,關(guān)注我的公眾號(hào)
朕已閱?