【推薦】7個強大實用的Python機器學(xué)習(xí)庫!
點擊下方卡片,關(guān)注“新機器視覺”公眾號
重磅干貨,第一時間送達(dá)
來源:今日頭條-IT技術(shù)資源愛好者
https://www.toutiao.com/article/7179178014276698662/

Prophet 是 Facebook 開源的時間序列預(yù)測工具庫,基于 Stan 框架,可以自動檢測時間序列中的趨勢、周期性和節(jié)假日效應(yīng),并根據(jù)這些信息進(jìn)行預(yù)測。這個庫在 GitHub 上有超過 15k 星。
# Pythonforecast = m.predict(future)forecast[['ds', 'yhat', 'yhat_lower', 'yhat_upper']].tail()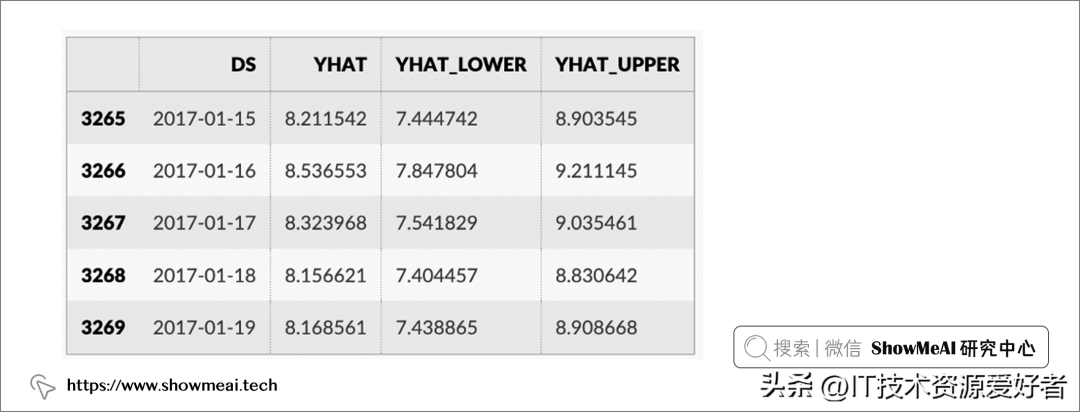
2.Deep Lake

for epoch in range(2): running_loss = 0.0 for i, data in enumerate(deeplake_loader): images, labels = data['images'], data['labels'] # zero the parameter gradients optimizer.zero_grad() # forward + backward + optimize outputs = net(images) loss = criterion(outputs, labels.reshape(-1)) loss.backward() optimizer.step() # print statistics running_loss += loss.item() if i % 100 == 99: #print every 100 mini-batches print('[%d, %5d] loss: %.3f' % (epoch + 1, i + 1, running_loss / 100)) running_loss = 0.03.Optuna

import ... # Define an objective function to be minimized.def objective(trial): # Invoke suggest methods of a Trial object to generate hyperparameters regressor_name = trial.suggest_categorical('regressor',['SVR', 'RandomForest']) if regressor_name = 'SVR': svr_c = trial.suggest_float('svr_c', 1e-10, 1e10, log=True) regressor_obj = sklearn.svm.SVR(C=svr_c) else: rf_max_depth = trial.suggest_int('rf_max_depth', 2, 332) regressor_obj = sklearn.ensemble.RandomForestRegressor(max_depth=rf_max_depth) X, y = sklearn.datasets.fetch_california_housing(return_X_y=True) X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = sklearn.model_selection.train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0) regressor_obj.fit(X_train, y_train) y_pred = regressor_obj.predict(X_val) error = sklearn.metrics.mean_squared_error(y_val, y_pred) return error # An objective value linked with the Trial object. study = optuna.create_study() # Create a neW studystudy.optimize(objective, n_trials=100) # Invoke opotimization of the objective function4.pycm

它可以計算多種常用的指標(biāo),包括準(zhǔn)確率、召回率、F1值、混淆矩陣等。此外,pycm 還提供了一些額外的功能,例如可視化混淆矩陣、評估模型性能的指標(biāo)來源差異等。pycm是一個非常實用的庫,可以幫助快速評估模型的性能。
from pycm import *y_actu = [2, 0, 2, 2, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 0, 1, 2] y_pred = [0, 0, 2, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 2, 2, 2, 2] cm = ConfusionMatrix(actual_vector=y_actu, predict_vector=y_pred) cm.classes cm.print_matrix() cm.print_normalized_matrix()5.NannyML

為數(shù)據(jù)科學(xué)家設(shè)計的 NannyML 具有易于使用的交互式可視化界面,目前支持所有表格式的用例(tabular use cases)、分類(classification)和回歸(regression)。NannyML 的核心貢獻(xiàn)者研發(fā)了多種用于估算模型性能的新算法:基于信心的性能估算(CBPE)與直接損失估算(DLE)等。NannyML 通過構(gòu)建“性能監(jiān)控+部署后數(shù)據(jù)科學(xué)”的閉環(huán),使數(shù)據(jù)科學(xué)家能夠快速理解并自動檢測靜默模型故障。通過使用 NannyML,數(shù)據(jù)科學(xué)家最終可以保持對他們部署的機器學(xué)習(xí)模型的完全可見性和信任。
import nannyml as nmlfrom IPython.display import display # Load synthetic data reference, analysis, analysis_target = nml.load_synthnetic_binary_classification_dataset()display(reference.head())display(analysis.head()) # Choose a chunker or set a chunk sizechunk size = 5000 # initialize, specify required data columns,, fit estimator and estimateestimator = nml.CBPE( y_pred_proba='y_pred_proba', y_pred='y_pred', y_true='work_home_actual', metrics=['roc_auc'], chunk_size=chunk_size, problem_type='classification_binary',)estimator = estimator.fit(reference)estimated_performance = estimator.estimate(analysis) # Show resultsfigure = estimated_performance.plot(kind='performance', metric='roc_auc', plot_reference=True)figure.show()6.ColossalAI

ColossalAI 提供了一系列預(yù)定義的模型和模型基礎(chǔ)架構(gòu),可用于快速構(gòu)建和訓(xùn)練模型。它還提供了一系列工具,用于模型評估,調(diào)優(yōu)和可視化,以確保模型的高質(zhì)量和準(zhǔn)確性。此外,ColossalAI 還支持部署模型,使其能夠通過各種不同的接口與其他系統(tǒng)集成。ColossalAI 的優(yōu)勢在于它易于使用,可以為數(shù)據(jù)科學(xué)家和機器學(xué)習(xí)工程師提供快速和有效的方法來構(gòu)建和部署高質(zhì)量的大型模型。
from colossalai.logging import get_dist_loggerfrom colossalai.trainer import Trainer, hooks # build components and initialize with colossaalai.initialize... # create a logger so that trainer can log on thhe consolelogger = get_dist_logger() # create a trainer objecttrainer = Trainer( engine=engine, logger=logger)7.emcee
import numpy as npimport emcee def log_prob(x, ivar): return -0.5 * np.sum(ivar * x ** 2) ndim, nwalkers = 5, 100 ivar = 1./np.random.rand(ndim)p0 = np.random.randn(nwalkers, ndim) sampler = emcee.EnsembleSampler(nwalkers, ndim, log_prob, args=[ivar])sampler.run_mcmc(p0, 10000)總結(jié)
本文僅做學(xué)術(shù)分享,如有侵權(quán),請聯(lián)系刪文。
