【W(wǎng)eb 技術(shù)】1753- 總結(jié)虛擬滾動的3種實現(xiàn)方式!

鏈接:https://juejin.cn/post/7232856799170805820
前言
工作中一直有接觸大量數(shù)據(jù)渲染的業(yè)務(wù),使用react-window多之又多,所以對虛擬列表有了些淺顯的理解。今天,我們就照著react-window的使用方式來實現(xiàn)三種虛擬列表。
-
元素固定高度的虛擬列表 -
元素不定高度的虛擬列表 -
元素動態(tài)高度的虛擬列表
虛擬列表核心原理
我們先來看一下整個虛擬列表元素的表現(xiàn)。
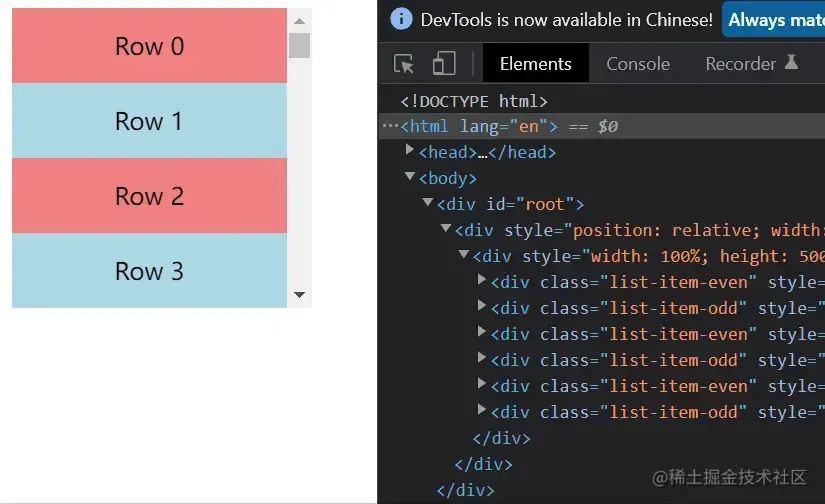
看右邊的元素個數(shù),會發(fā)現(xiàn)起初只有6個,之后無論怎么滾動,他都保持著8個元素,由此我們可以得出他的靜態(tài)原理圖是這樣的。
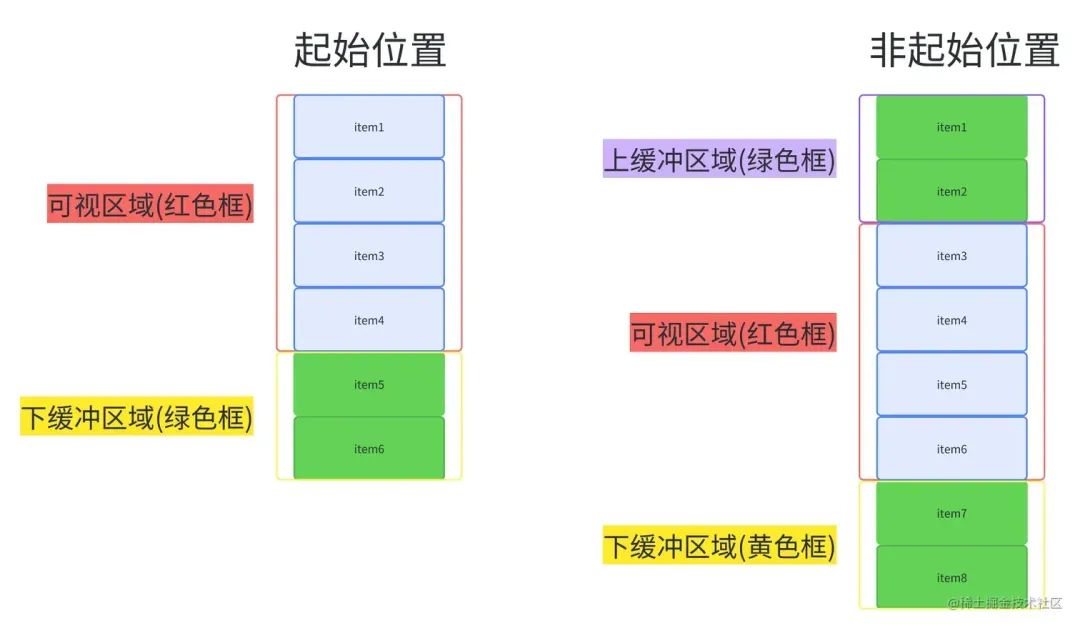
當我們進行了滾動后。
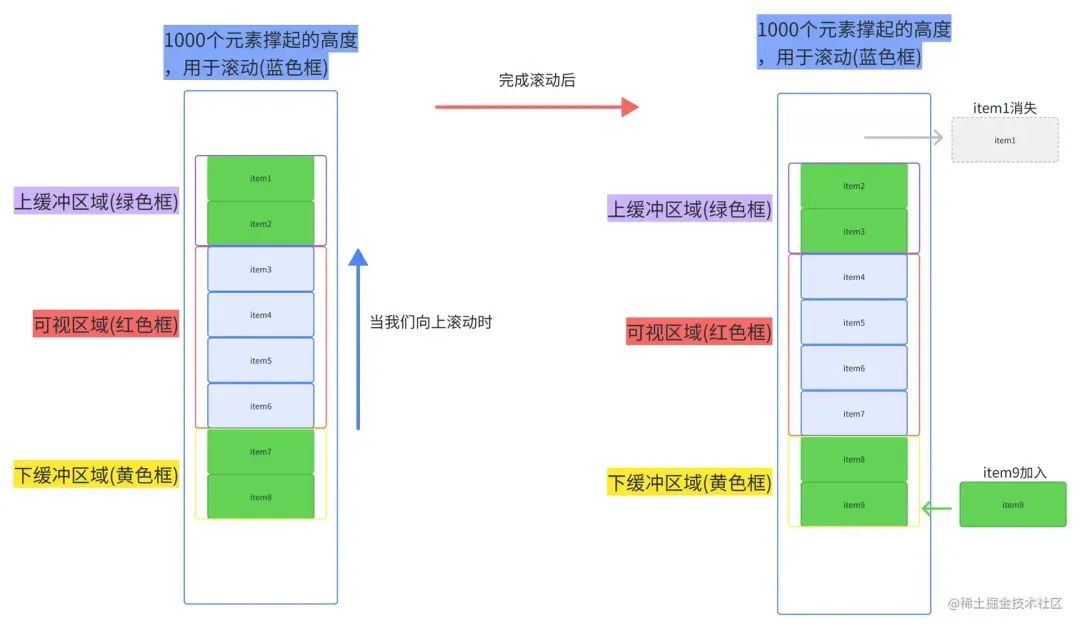
從上面兩圖我們可以總結(jié)出,整個虛擬列表劃分為三個區(qū)域,分別是上緩沖區(qū)(0/2個元素),可視區(qū)(n個元素),下緩沖區(qū)(2個元素)。當我們滾動到一個元素離開可視區(qū)范圍內(nèi)時,就去掉上緩沖區(qū)頂上的一個元素,然后再下緩沖區(qū)增加一個元素。這就是虛擬列表的核心原理了。
虛擬列表的實現(xiàn)
一、元素固定高度的虛擬列表
使用:
js
復(fù)制代碼
const Row = ({ index, style, forwardRef }) => {
return (
<div className={index % 2 ? 'list-item-odd' : 'list-item-even'} style={style} ref={forwardRef}>
{`Row ${index}`}
</div>
)
}
const App = () => {
return (
<FixedSizeList
className="list"
height={200}
width={200}
itemSize={50}
itemCount={1000}
>
{Row}
</FixedSizeList>
);
}
實現(xiàn):
(1)首先先計算出由1000個元素撐起的盒子(稱之為container)的高度,撐開盒子,讓用戶能進行滾動操作。
(2)計算出可視區(qū)的起始索引、上緩沖區(qū)的起始索引以及下緩沖區(qū)的結(jié)束索引(就像上圖滾動后,上緩沖區(qū)的起始索引為2,可視區(qū)起始索引為4,下緩沖區(qū)結(jié)束索引為9)。
(3)采用絕對定位,計算上緩沖區(qū)到下緩沖區(qū)之間的每一個元素在contianer中的top值,只有知道top值才能讓元素出現(xiàn)在可視區(qū)內(nèi)。
(4)將上緩沖區(qū)到下緩沖區(qū)的元素塞到container中。
js
復(fù)制代碼
import { useState } from 'react';
const FixedSizeList = (props) => {
const { height, width, itemSize, itemCount, children: Child } = props;
// 記錄滾動掉的高度
const [scrollOffset, setScrollOffset] = useState(0);
// 外部容器高度
const containerStyle = {
position: 'relative',
width,
height,
overflow: 'auto',
};
// 1000個元素撐起盒子的實際高度
const contentStyle = {
height: itemSize * itemCount,
width: '100%',
};
const getCurrentChildren = () => {
// 可視區(qū)起始索引
const startIndex = Math.floor(scrollOffset / itemSize);
// 上緩沖區(qū)起始索引
const finialStartIndex = Math.max(0, startIndex - 2);
// 可視區(qū)能展示的元素的最大個數(shù)
const numVisible = Math.ceil(height / itemSize);
// 下緩沖區(qū)結(jié)束索引
const endIndex = Math.min(itemCount - 1, startIndex + numVisible + 2);
const items = [];
// 根據(jù)上面計算的索引值,不斷添加元素給container
for (let i = finialStartIndex; i < endIndex; i++) {
const itemStyle = {
position: 'absolute',
height: itemSize,
width: '100%',
// 計算每個元素在container中的top值
top: itemSize * i,
};
items.push(
<Child key={i} index={i} style={itemStyle} />
);
}
return items;
}
// 當觸發(fā)滾動就重新計算
const scrollHandle = (event) => {
const { scrollTop } = event.currentTarget;
setScrollOffset(scrollTop);
}
return (
<div style={containerStyle} onScroll={scrollHandle}>
<div style={contentStyle}>
{getCurrentChildren()}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default FixedSizeList;
結(jié)果

二、元素不定高度的虛擬列表
使用:
js
復(fù)制代碼
const rowSizes = new Array(1000).fill(true).map(() => 25 + Math.round(Math.random() * 55))
const getItemSize = (index) => rowSizes[index];
const Row = ({ index, style }) => {
return (
<div className={index % 2 ? 'list-item-odd' : 'list-item-even'} style={style} >
Row {index}
</div>
)
}
const App = () => {
return (
<VariableSizeList
className="list"
height={200}
width={200}
itemSize={getItemSize}
itemCount={1000}
>
{Row}
</VariableSizeList>
);
}
從代碼可以看出,Row每一個高度都是隨機的,就不能像第一種虛擬列表那樣簡單得通過itemSize * index計算出top值了。
思路
難點一:
由于每個元素高度不一,我們起先無法直接計算出container的總高度。
難點二:
每個元素高度不一,每個元素的top值不能通過itemSize * index直接計算出top值。
難點三:
每個元素高度不一,不能直接通過scrollOffset / itemSize計算出已被滾動掉的元素的個數(shù),很難獲取到可視區(qū)的起始索引。
難點一的解決方案
可以通過遍歷所有的Row計算出總高度,但我認為計算出精確總高度的必要性不大,同時也為了兼容第三種虛擬列表,我們不去計算精確的總高度。現(xiàn)在我們回到出發(fā)點,思考container的高度的作用是什么?其實就是為了足夠大,讓用戶能進行滾動操作,那我們可以自己假設(shè)每一個元素的高度,在乘上個數(shù),弄出一個假的但足夠高的container讓用戶去觸發(fā)滾動事件。當然這種方案會帶來一些小bug(這個bug的影響大,我認為是可以忽略的)。
難點二和難點三的解決方案
其實難點二和難點三本質(zhì)都一樣,元素高度不一,導(dǎo)致不知道被滾動掉了多少元素,只要知道被滾動掉的元素的個數(shù),top值和索引都迎刃而解。
我們可以采用這種解決方案,那就是每次只計算需要上緩沖區(qū)到下緩沖區(qū)之間的元素,并記錄他們,并且記錄下最底下的那個元素的索引,當用戶進行滾動時,如果我們是向上滾動,就可以直接從已經(jīng)計算好的記錄里取,如果向下滾動,我們根據(jù)上一次記錄的最大的索引的那個元素不斷累加新元素的高度,直到它大于已經(jīng)滾動掉的高度,此時的索引值就是可視區(qū)的起始索引了,這個起始索引所對應(yīng)的top就是累加的高度。
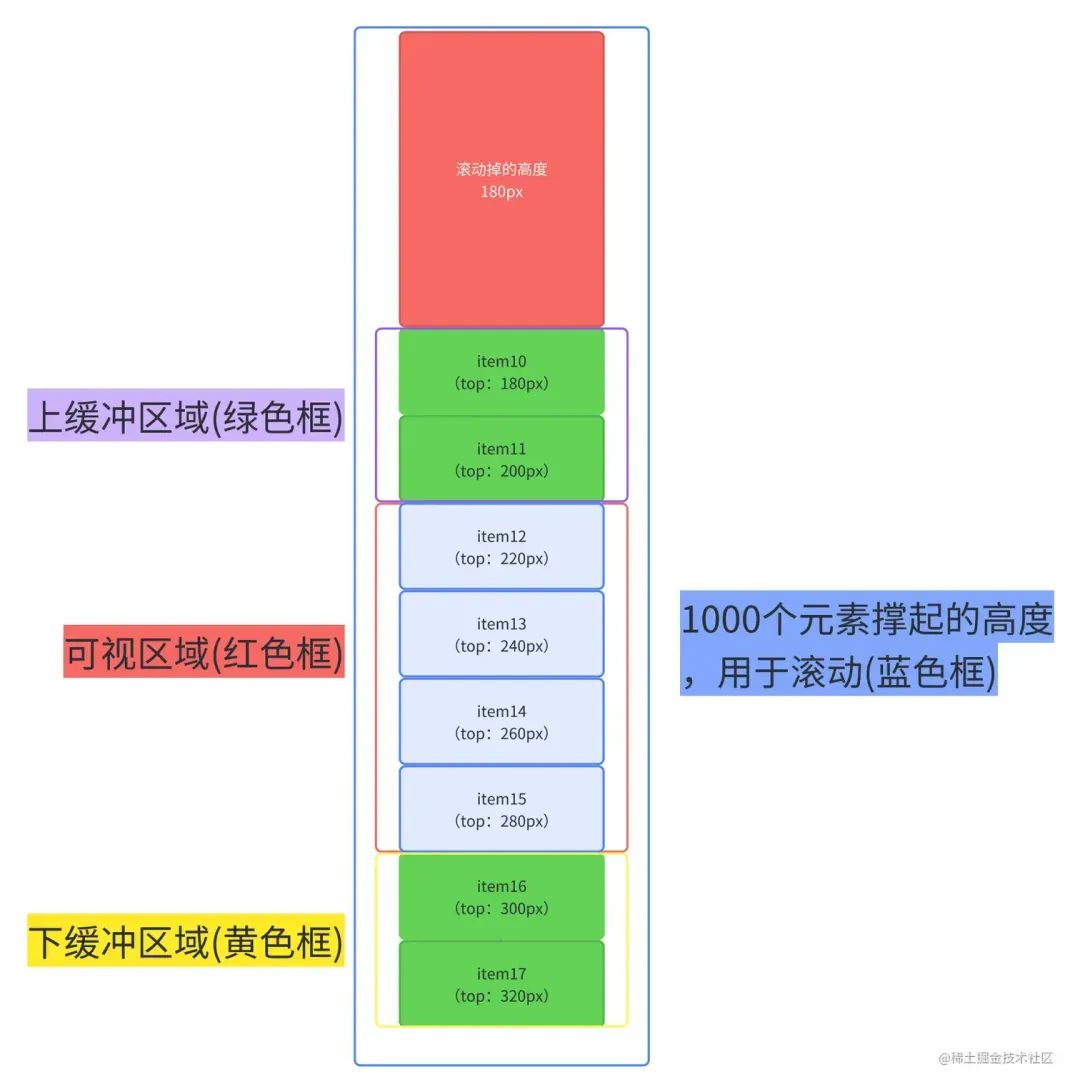
文字看起來生硬拗口,我們可以看下面這張圖。
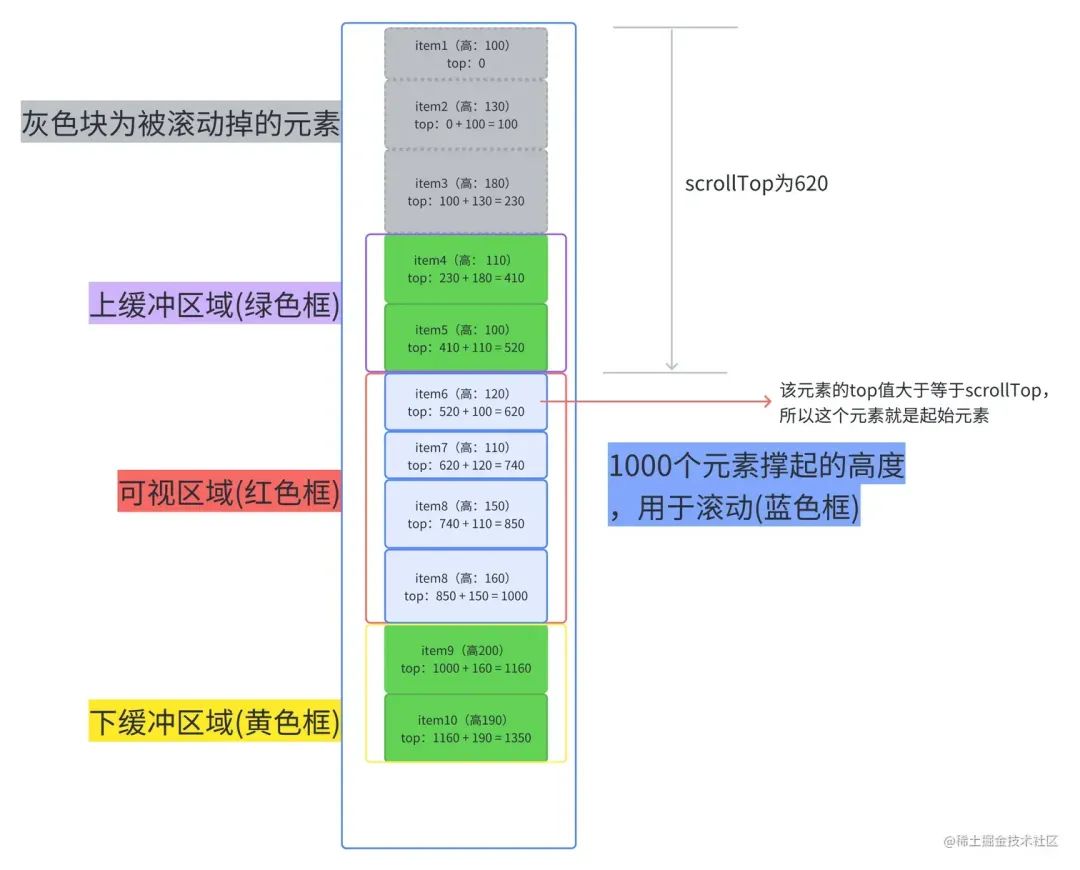
每一個元素的top值都能通過上一個元素的top值 + 上一個元素的height計算出來。
舉個例子,假設(shè)我們需要知道item14的top值
(1)我們先在記錄里找有沒有item13的數(shù)據(jù),如果有,我們就拿item13.top + item13.heighht得到item14的top。
(2)如果記錄中(由上圖得知我們只記錄了item1-item10的數(shù)據(jù))沒有,我們就拿到記錄中最后一個元素的數(shù)據(jù)(item10)進行累加,先計算并記錄item11的,再計算并記錄item12的,再計算并記錄item13的,最后就是item14的了。
實現(xiàn)
js
復(fù)制代碼
import { useState } from 'react';
// 元數(shù)據(jù)
const measuredData = {
measuredDataMap: {},
LastMeasuredItemIndex: -1,
};
const estimatedHeight = (defaultEstimatedItemSize = 50, itemCount) => {
let measuredHeight = 0;
const { measuredDataMap, LastMeasuredItemIndex } = measuredData;
// 計算已經(jīng)獲取過真實高度的項的高度之和
if (LastMeasuredItemIndex >= 0) {
const lastMeasuredItem = measuredDataMap[LastMeasuredItemIndex];
measuredHeight = lastMeasuredItem.offset + lastMeasuredItem.size;
}
// 未計算過真實高度的項數(shù)
const unMeasuredItemsCount = itemCount - measuredData.LastMeasuredItemIndex - 1;
// 預(yù)測總高度
const totalEstimatedHeight = measuredHeight + unMeasuredItemsCount * defaultEstimatedItemSize;
return totalEstimatedHeight;
}
const getItemMetaData = (props, index) => {
const { itemSize } = props;
const { measuredDataMap, LastMeasuredItemIndex } = measuredData;
// 如果當前索引比已記錄的索引要大,說明要計算當前索引的項的size和offset
if (index > LastMeasuredItemIndex) {
let offset = 0;
// 計算當前能計算出來的最大offset值
if (LastMeasuredItemIndex >= 0) {
const lastMeasuredItem = measuredDataMap[LastMeasuredItemIndex];
offset += lastMeasuredItem.offset + lastMeasuredItem.size;
}
// 計算直到index為止,所有未計算過的項
for (let i = LastMeasuredItemIndex + 1; i <= index; i++) {
const currentItemSize = itemSize(i);
measuredDataMap[i] = { size: currentItemSize, offset };
offset += currentItemSize;
}
// 更新已計算的項的索引值
measuredData.LastMeasuredItemIndex = index;
}
return measuredDataMap[index];
};
const getStartIndex = (props, scrollOffset) => {
let index = 0;
while (true) {
const currentOffset = getItemMetaData(props, index).offset;
if (currentOffset >= scrollOffset) return index;
index++
}
}
const getEndIndex = (props, startIndex) => {
const { height } = props;
// 獲取可視區(qū)內(nèi)開始的項
const startItem = getItemMetaData(props, startIndex);
// 可視區(qū)內(nèi)最大的offset值
const maxOffset = startItem.offset + height;
// 開始項的下一項的offset,之后不斷累加此offset,知道等于或超過最大offset,就是找到結(jié)束索引了
let offset = startItem.offset + startItem.size;
// 結(jié)束索引
let endIndex = startIndex;
// 累加offset
while (offset <= maxOffset) {
endIndex++;
const currentItem = getItemMetaData(props, endIndex);
offset += currentItem.size;
}
return endIndex;
};
const getRangeToRender = (props, scrollOffset) => {
const { itemCount } = props;
const startIndex = getStartIndex(props, scrollOffset);
const endIndex = getEndIndex(props, startIndex);
return [
Math.max(0, startIndex - 2),
Math.min(itemCount - 1, endIndex + 2),
startIndex,
endIndex,
];
};
const VariableSizeList = (props) => {
const { height, width, itemCount, itemEstimatedSize, children: Child } = props;
const [scrollOffset, setScrollOffset] = useState(0);
const containerStyle = {
position: 'relative',
width,
height,
overflow: 'auto',
willChange: 'transform'
};
const contentStyle = {
height: estimatedHeight(itemEstimatedSize, itemCount),
width: '100%',
};
const getCurrentChildren = () => {
const [startIndex, endIndex, originStartIndex, originEndIndex] = getRangeToRender(props, scrollOffset)
const items = [];
for (let i = startIndex; i < endIndex; i++) {
const item = getItemMetaData(props, i);
const itemStyle = {
position: 'absolute',
height: item.size,
width: '100%',
top: item.offset,
};
items.push(
<Child key={i} index={i} style={itemStyle} />
);
}
return items;
}
const scrollHandle = (event) => {
const { scrollTop } = event.currentTarget;
setScrollOffset(scrollTop);
}
return (
<div style={containerStyle} onScroll={scrollHandle}>
<div style={contentStyle}>
{getCurrentChildren()}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default VariableSizeList;
難點的地方都給了注釋,如果一遍看不懂的話,可以去調(diào)試調(diào)試。
以上代碼主要寫了個思路和功能,其實優(yōu)化點是很多的,這里給出兩個顯而易見的優(yōu)化點。
-
緩存每一個已經(jīng)計算完成的item的樣式,這樣回滾的時候不用重新計算樣式。 -
getStartIndex可以通過二分法去優(yōu)化。
結(jié)果
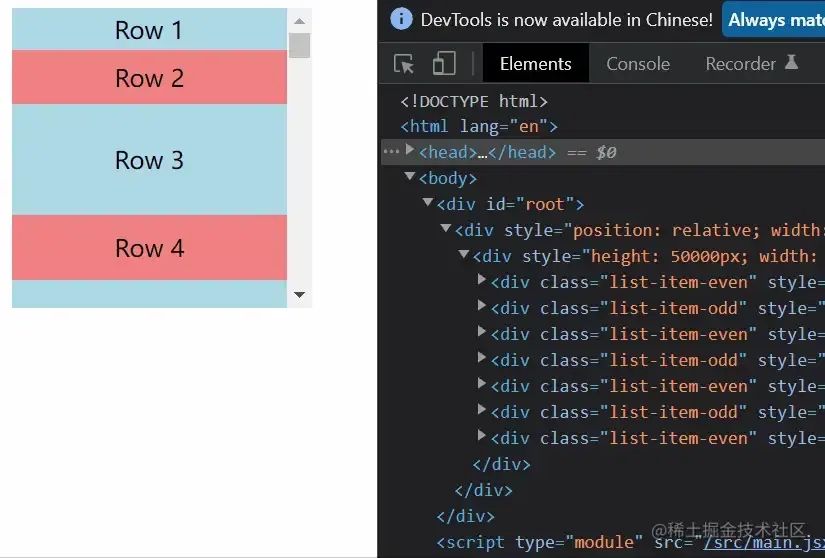
結(jié)果還是挺滿意的了,這里提一下上文提到的小bug,那就是在向下拉動滾動條時,鼠標和滾動條時脫節(jié)的。
元素動態(tài)高度的虛擬列表
最后這一種虛擬列表其實就是基于第二種來實現(xiàn)的,只不過增加監(jiān)聽元素高度變化事件,在某個元素發(fā)生變化的時候重新計算各種數(shù)據(jù)。
使用
js
復(fù)制代碼
const items = [];
const itemCount = 1000;
for (let i = 0; i < itemCount; i++) {
const height = (30 + Math.floor(Math.random() * 30));
const style = {
height,
width: '100%',
}
items.push(
<div className={i % 2 ? 'list-item-odd' : 'list-item-even'} style={style}>Row {i}</div>
)
}
const Row = ({ index }) => items[index];
const App = () => {
// 注意:這里我沒有把itemSize傳過去
return (
<VariableSizeList
className="list"
height={200}
width={200}
itemCount={itemCount}
isDynamic
>
{Row}
</VariableSizeList>
);
}
從上面代碼可以看出,我們沒將itemSize傳過去,虛擬列表是不知道每一個元素的高度的,只有在渲染的時候執(zhí)行了Row才知道。
實現(xiàn)
在上面那種虛擬列表進行改動
js
復(fù)制代碼
// 修改getCurrentChildren函數(shù)
const getCurrentChildren = () => {
const [startIndex, endIndex] = getRangeToRender(props, scrollOffset)
const items = [];
for (let i = startIndex; i <= endIndex; i++) {
const item = getItemMetaData(props, i);
const itemStyle = {
position: 'absolute',
height: item.size,
width: '100%',
top: item.offset,
};
items.push(
<ListItem key={i} index={i} style={itemStyle} ComponentType={Child} onSizeChange={sizeChangeHandle} />
);
}
return items;
}
// 增加sizeChangeHandle
const sizeChangeHandle = (index, domNode) => {
const height = domNode.offsetHeight;
const { measuredDataMap, lastMeasuredItemIndex } = measuredData;
const itemMetaData = measuredDataMap[index];
itemMetaData.size = height;
let offset = 0;
for (let i = 0; i <= lastMeasuredItemIndex; i++) {
const itemMetaData = measuredDataMap[i];
itemMetaData.offset = offset;
offset += itemMetaData.size;
}
setState({});
}
js
復(fù)制代碼
// 增加一個ListItem組件
class ListItem extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.domRef = React.createRef();
this.resizeObserver = null;
}
componentDidMount() {
if (this.domRef.current) {
const domNode = this.domRef.current.firstChild;
const { index, onSizeChange } = this.props;
this.resizeObserver = new ResizeObserver(() => {
onSizeChange(index, domNode);
});
this.resizeObserver.observe(domNode);
}
}
componentWillUnmount() {
if (this.resizeObserver && this.domRef.current.firstChild) {
this.resizeObserver.unobserve(this.domRef.current.firstChild);
}
}
render() {
const { index, style, ComponentType } = this.props;
return (
<div style={style} ref={this.domRef}>
<ComponentType index={index} />
</div>
)
}
}
完整代碼
js
復(fù)制代碼
import React, { useState } from 'react';
// 元數(shù)據(jù)
const measuredData = {
measuredDataMap: {},
lastMeasuredItemIndex: -1,
};
const estimatedHeight = (defaultEstimatedItemSize = 50, itemCount) => {
let measuredHeight = 0;
const { measuredDataMap, lastMeasuredItemIndex } = measuredData;
// 計算已經(jīng)獲取過真實高度的項的高度之和
if (lastMeasuredItemIndex >= 0) {
const lastMeasuredItem = measuredDataMap[lastMeasuredItemIndex];
measuredHeight = lastMeasuredItem.offset + lastMeasuredItem.size;
}
// 未計算過真實高度的項數(shù)
const unMeasuredItemsCount = itemCount - measuredData.lastMeasuredItemIndex - 1;
// 預(yù)測總高度
const totalEstimatedHeight = measuredHeight + unMeasuredItemsCount * defaultEstimatedItemSize;
return totalEstimatedHeight;
}
const getItemMetaData = (props, index) => {
const { itemSize } = props;
const { measuredDataMap, lastMeasuredItemIndex } = measuredData;
// 如果當前索引比已記錄的索引要大,說明要計算當前索引的項的size和offset
if (index > lastMeasuredItemIndex) {
let offset = 0;
// 計算當前能計算出來的最大offset值
if (lastMeasuredItemIndex > 0) {
const lastMeasuredItem = measuredDataMap[lastMeasuredItemIndex];
offset += lastMeasuredItem.offset + lastMeasuredItem.size;
}
// 計算直到index為止,所有未計算過的項
for (let i = lastMeasuredItemIndex + 1; i <= index; i++) {
const currentItemSize = itemSize ? itemSize(i) : 50;
measuredDataMap[i] = { size: currentItemSize, offset };
offset += currentItemSize;
}
// 更新已計算的項的索引值
measuredData.lastMeasuredItemIndex = index;
}
return measuredDataMap[index];
};
const getStartIndex = (props, scrollOffset) => {
let index = 0;
while (true) {
const currentOffset = getItemMetaData(props, index).offset;
if (currentOffset >= scrollOffset) return index;
index++
}
}
const getEndIndex = (props, startIndex) => {
const { height } = props;
// 獲取可視區(qū)內(nèi)開始的項
const startItem = getItemMetaData(props, startIndex);
// 可視區(qū)內(nèi)最大的offset值
const maxOffset = startItem.offset + height;
// 開始項的下一項的offset,之后不斷累加此offset,知道等于或超過最大offset,就是找到結(jié)束索引了
let offset = startItem.offset + startItem.size;
// 結(jié)束索引
let endIndex = startIndex;
// 累加offset
while (offset <= maxOffset) {
endIndex++;
const currentItem = getItemMetaData(props, endIndex);
offset += currentItem.size;
}
return endIndex;
};
const getRangeToRender = (props, scrollOffset) => {
const { itemCount } = props;
const startIndex = getStartIndex(props, scrollOffset);
const endIndex = getEndIndex(props, startIndex);
return [
Math.max(0, startIndex - 2),
Math.min(itemCount - 1, endIndex + 2),
startIndex,
endIndex,
];
};
class ListItem extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.domRef = React.createRef();
this.resizeObserver = null;
}
componentDidMount() {
if (this.domRef.current) {
const domNode = this.domRef.current.firstChild;
const { index, onSizeChange } = this.props;
this.resizeObserver = new ResizeObserver(() => {
onSizeChange(index, domNode);
});
this.resizeObserver.observe(domNode);
}
}
componentWillUnmount() {
if (this.resizeObserver && this.domRef.current.firstChild) {
this.resizeObserver.unobserve(this.domRef.current.firstChild);
}
}
render() {
const { index, style, ComponentType } = this.props;
return (
<div style={style} ref={this.domRef}>
<ComponentType index={index} />
</div>
)
}
}
const VariableSizeList = (props) => {
const { height, width, itemCount, itemEstimatedSize, children: Child } = props;
const [scrollOffset, setScrollOffset] = useState(0);
const [, setState] = useState({});
const containerStyle = {
position: 'relative',
width,
height,
overflow: 'auto',
willChange: 'transform'
};
const contentStyle = {
height: estimatedHeight(itemEstimatedSize, itemCount),
width: '100%',
};
const sizeChangeHandle = (index, domNode) => {
const height = domNode.offsetHeight;
const { measuredDataMap, lastMeasuredItemIndex } = measuredData;
const itemMetaData = measuredDataMap[index];
itemMetaData.size = height;
let offset = 0;
for (let i = 0; i <= lastMeasuredItemIndex; i++) {
const itemMetaData = measuredDataMap[i];
itemMetaData.offset = offset;
offset += itemMetaData.size;
}
setState({});
}
const getCurrentChildren = () => {
const [startIndex, endIndex] = getRangeToRender(props, scrollOffset)
const items = [];
for (let i = startIndex; i <= endIndex; i++) {
const item = getItemMetaData(props, i);
const itemStyle = {
position: 'absolute',
height: item.size,
width: '100%',
top: item.offset,
};
items.push(
<ListItem key={i} index={i} style={itemStyle} ComponentType={Child} onSizeChange={sizeChangeHandle} />
);
}
return items;
}
const scrollHandle = (event) => {
const { scrollTop } = event.currentTarget;
setScrollOffset(scrollTop);
}
return (
<div style={containerStyle} onScroll={scrollHandle}>
<div style={contentStyle}>
{getCurrentChildren()}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default VariableSizeList;
結(jié)果
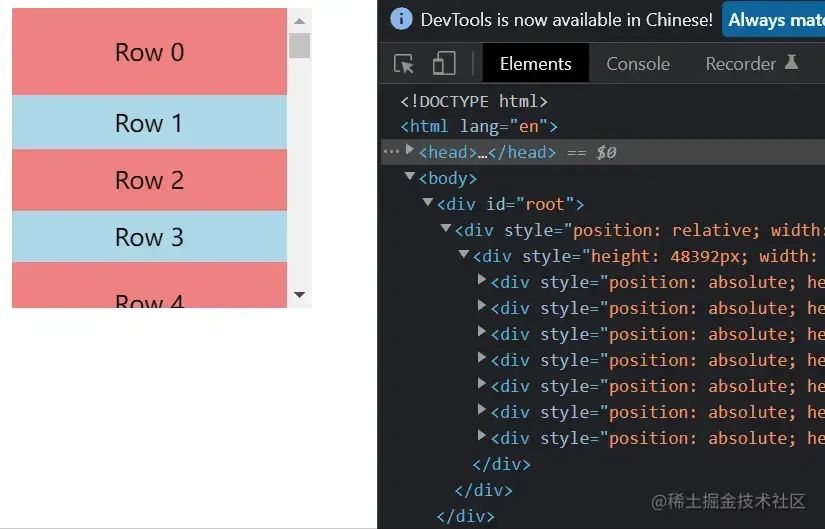
結(jié)尾
react-window只有前兩種虛擬列表,最后一種虛擬列表是在別的虛擬列表庫中有,借鑒了一下各路大佬的思路實現(xiàn)的,總得來說三種虛擬列表雖然表現(xiàn)和實現(xiàn)都不同,但只要掌握了核心原理,手擼出來虛擬列表還是手到擒來的。
最后,希望這篇文章能幫助到各位讀者。同時也非常歡迎各位大佬對上面的各種實現(xiàn)提出建議,也希望各位大佬對于第二種虛擬列表提出更多的優(yōu)化點。
往期回顧 # # # # # # # 回復(fù)“加群”,一起學習進步
