Java8異步利器:CompletableFuture全網(wǎng)最全使用教程
閱讀本文大概需要 11 分鐘。
來自:blog.csdn.net/zsx_xiaoxin/article/details/123898171
CompletableFuture是jdk8的新特性。CompletableFuture實現(xiàn)了CompletionStage接口和Future接口,前者是對后者的一個擴展,增加了異步會點、流式處理、多個Future組合處理的能力,使Java在處理多任務的協(xié)同工作時更加順暢便利。一、創(chuàng)建異步任務
1. supplyAsync
supplyAsync是創(chuàng)建帶有返回值的異步任務。它有如下兩個方法,一個是使用默認線程池(ForkJoinPool.commonPool())的方法,一個是帶有自定義線程池的重載方法// 帶返回值異步請求,默認線程池
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
// 帶返回值的異步請求,可以自定義線程池
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
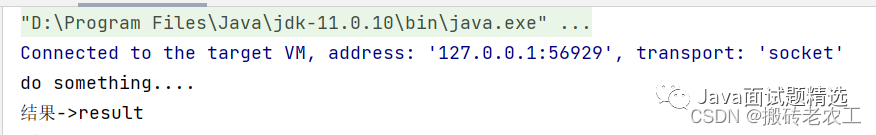
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("do something....");
return "result";
});
//等待任務執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("結果->" + cf.get());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 自定義線程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("do something....");
return "result";
}, executorService);
//等待子任務執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("結果->" + cf.get());
}
2. runAsync
ForkJoinPool.commonPool())的方法,一個是帶有自定義線程池的重載方法// 不帶返回值的異步請求,默認線程池
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
// 不帶返回值的異步請求,可以自定義線程池
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
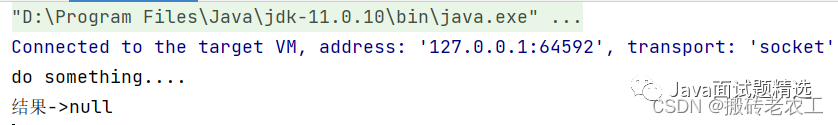
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Void> cf = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("do something....");
});
//等待任務執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("結果->" + cf.get());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 自定義線程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuture<Void> cf = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("do something....");
}, executorService);
//等待任務執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("結果->" + cf.get());
}
3.獲取任務結果的方法
// 如果完成則返回結果,否則就拋出具體的異常
public T get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException
// 最大時間等待返回結果,否則就拋出具體異常
public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException
// 完成時返回結果值,否則拋出unchecked異常。為了更好地符合通用函數(shù)形式的使用,如果完成此 CompletableFuture所涉及的計算引發(fā)異常,則此方法將引發(fā)unchecked異常并將底層異常作為其原因
public T join()
// 如果完成則返回結果值(或拋出任何遇到的異常),否則返回給定的 valueIfAbsent。
public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent)
// 如果任務沒有完成,返回的值設置為給定值
public boolean complete(T value)
// 如果任務沒有完成,就拋出給定異常
public boolean completeExceptionally(Throwable ex)
二、異步回調處理
1.thenApply和thenApplyAsync
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.thenApplyAsync((result) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
result += 2;
return result;
});
//等待任務1執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf1結果->" + cf1.get());
//等待任務2執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf2結果->" + cf2.get());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.thenApply((result) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
result += 2;
return result;
});
//等待任務1執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf1結果->" + cf1.get());
//等待任務2執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf2結果->" + cf2.get());
}
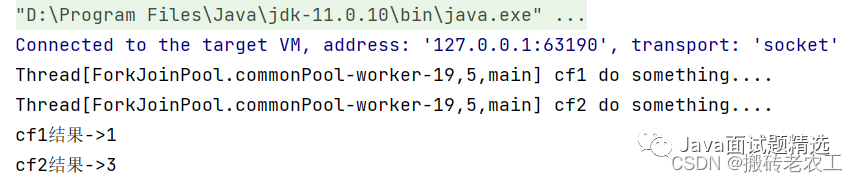
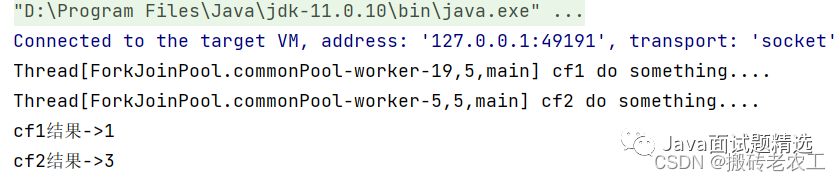
thenApplyAsync在子任務中是另起一個線程執(zhí)行任務,并且thenApplyAsync可以自定義線程池,默認的使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()線程池。2.thenAccept和thenAcceptAsync
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> cf2 = cf1.thenAccept((result) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
});
//等待任務1執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf1結果->" + cf1.get());
//等待任務2執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf2結果->" + cf2.get());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> cf2 = cf1.thenAcceptAsync((result) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
});
//等待任務1執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf1結果->" + cf1.get());
//等待任務2執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf2結果->" + cf2.get());
}

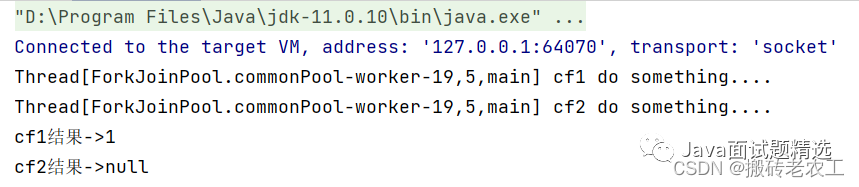
thenAccep和thenAccepAsync區(qū)別在于,使用thenAccep方法時子任務與父任務使用的是同一個線程,而thenAccepAsync在子任務中可能是另起一個線程執(zhí)行任務,并且thenAccepAsync可以自定義線程池,默認的使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()線程池。3.thenRun和thenRunAsync
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> cf2 = cf1.thenRun(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
});
//等待任務1執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf1結果->" + cf1.get());
//等待任務2執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf2結果->" + cf2.get());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> cf2 = cf1.thenRunAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
});
//等待任務1執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf1結果->" + cf1.get());
//等待任務2執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf2結果->" + cf2.get());
}
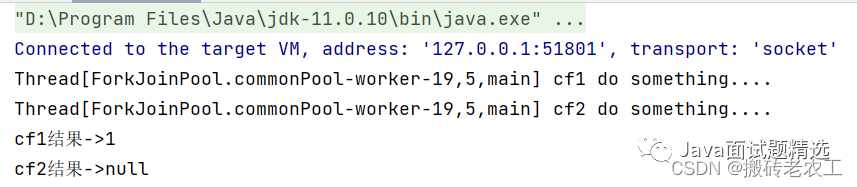
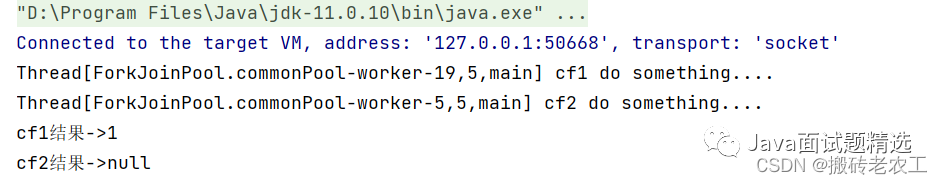
thenRunAsync區(qū)別在于,使用thenRun方法時子任務與父任務使用的是同一個線程,而thenRunAsync在子任務中可能是另起一個線程執(zhí)行任務,并且thenRunAsync可以自定義線程池,默認的使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()線程池。4.whenComplete和whenCompleteAsync
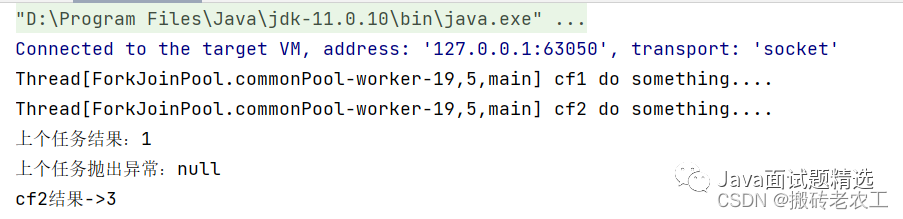
whenComplete是當某個任務執(zhí)行完成后執(zhí)行的回調方法,會將執(zhí)行結果或者執(zhí)行期間拋出的異常傳遞給回調方法,如果是正常執(zhí)行則異常為null,回調方法對應的CompletableFuture的result和該任務一致,如果該任務正常執(zhí)行,則get方法返回執(zhí)行結果,如果是執(zhí)行異常,則get方法拋出異常。public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
int a = 1/0;
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.whenComplete((result, e) -> {
System.out.println("上個任務結果:" + result);
System.out.println("上個任務拋出異常:" + e);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
});
// //等待任務1執(zhí)行完成
// System.out.println("cf1結果->" + cf1.get());
// //等待任務2執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf2結果->" + cf2.get());
}
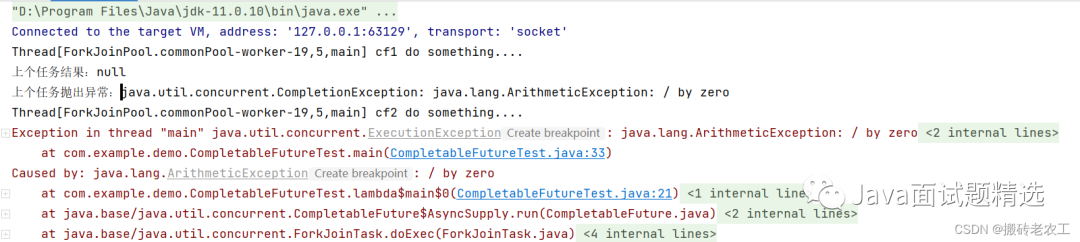
whenCompleteAsync和whenComplete區(qū)別也是whenCompleteAsync可能會另起一個線程執(zhí)行任務,并且thenRunAsync可以自定義線程池,默認的使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()線程池。5.handle和handleAsync
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
// int a = 1/0;
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.handle((result, e) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
System.out.println("上個任務結果:" + result);
System.out.println("上個任務拋出異常:" + e);
return result+2;
});
//等待任務2執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf2結果->" + cf2.get());
}
三、多任務組合處理
1.thenCombine、thenAcceptBoth 和runAfterBoth
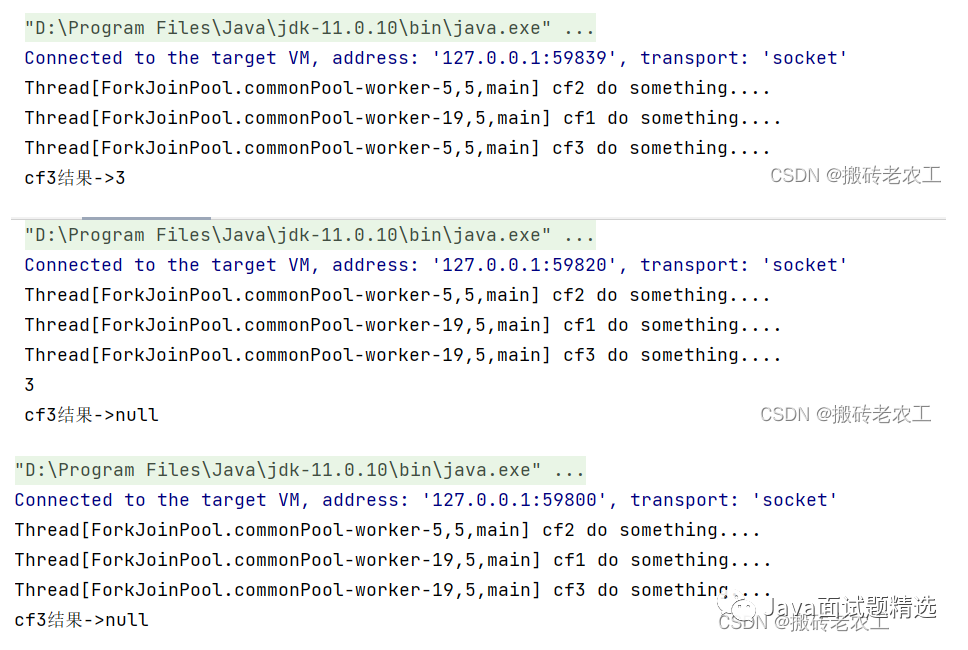
CompletableFuture組合起來處理,只有兩個任務都正常完成時,才進行下階段任務。thenCombine會將兩個任務的執(zhí)行結果作為所提供函數(shù)的參數(shù),且該方法有返回值;thenAcceptBoth同樣將兩個任務的執(zhí)行結果作為方法入?yún)ⅲ菬o返回值;runAfterBoth沒有入?yún)ⅲ矝]有返回值。注意兩個任務中只要有一個執(zhí)行異常,則將該異常信息作為指定任務的執(zhí)行結果。public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
return 2;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf3 = cf1.thenCombine(cf2, (a, b) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf3 do something....");
return a + b;
});
System.out.println("cf3結果->" + cf3.get());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
return 2;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> cf3 = cf1.thenAcceptBoth(cf2, (a, b) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf3 do something....");
System.out.println(a + b);
});
System.out.println("cf3結果->" + cf3.get());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
return 2;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> cf3 = cf1.runAfterBoth(cf2, () -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf3 do something....");
});
System.out.println("cf3結果->" + cf3.get());
}
2.applyToEither、acceptEither和runAfterEither
CompletableFuture組合起來處理,當有一個任務正常完成時,就會進行下階段任務。applyToEither會將已經完成任務的執(zhí)行結果作為所提供函數(shù)的參數(shù),且該方法有返回值;acceptEither同樣將已經完成任務的執(zhí)行結果作為方法入?yún)ⅲ菬o返回值;runAfterEither沒有入?yún)ⅲ矝]有返回值。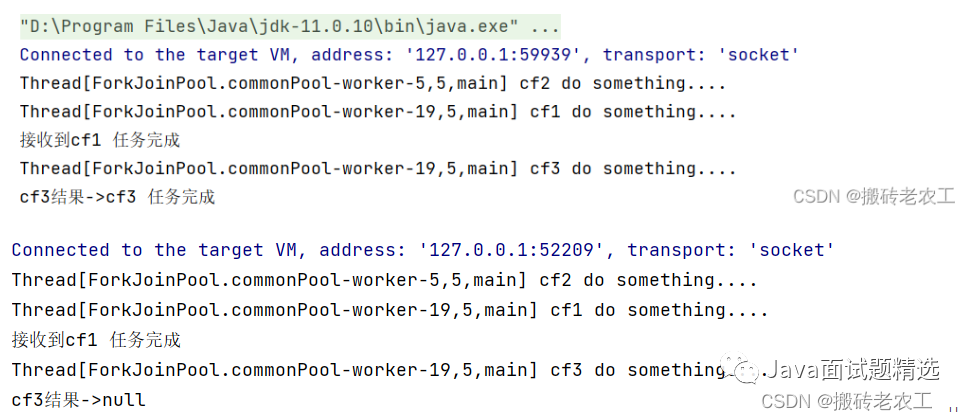
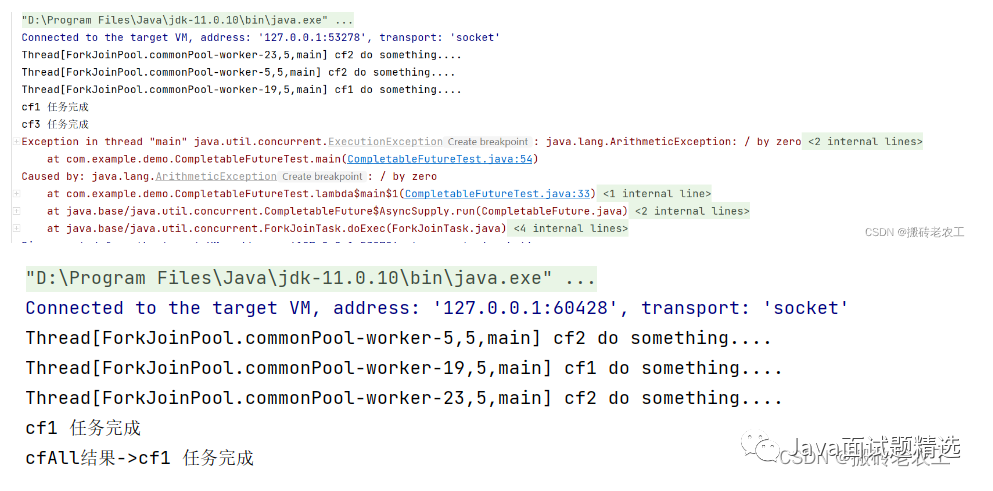
acceptEither和runAfterEither類似,acceptEither會將cf1任務的結果作為cf3任務的入?yún)ⅲ玞f3任務完成時并無返回值;runAfterEither不會將cf1任務的結果作為cf3任務的入?yún)ⅲ菦]有任務入?yún)ⅲ瑘?zhí)行完自己的任務后也并無返回值。3.allOf / anyOf
CompletableFuture執(zhí)行get方法時會拋出異常,如果都是正常執(zhí)行,則get返回null。CompletableFuture執(zhí)行get方法時會拋出異常,如果都是正常執(zhí)行,則get返回執(zhí)行完成任務的結果。public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf1 任務完成");
return "cf1 任務完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
int a = 1/0;
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf2 任務完成");
return "cf2 任務完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> cf3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf3 任務完成");
return "cf3 任務完成";
});
CompletableFuture<Void> cfAll = CompletableFuture.allOf(cf1, cf2, cf3);
System.out.println("cfAll結果->" + cfAll.get());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf1 任務完成");
return "cf1 任務完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf2 任務完成");
return "cf2 任務完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> cf3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf3 任務完成");
return "cf3 任務完成";
});
CompletableFuture<Object> cfAll = CompletableFuture.anyOf(cf1, cf2, cf3);
System.out.println("cfAll結果->" + cfAll.get());
}
推薦閱讀:
阿里技術面:每天100w次登陸請求, 8G 內存該如何設置JVM參數(shù)?
互聯(lián)網(wǎng)初中高級大廠面試題(9個G) 內容包含Java基礎、JavaWeb、MySQL性能優(yōu)化、JVM、鎖、百萬并發(fā)、消息隊列、高性能緩存、反射、Spring全家桶原理、微服務、Zookeeper......等技術棧!
?戳閱讀原文領取! 朕已閱