異步編程利器:CompletableFuture詳解
源 / 文/
前言
最近剛好使用CompeletableFuture優(yōu)化了項目中的代碼,所以跟大家一起學(xué)習(xí)CompletableFuture。
公眾號:撿田螺的小男孩
一個例子回顧 Future
因為CompletableFuture實現(xiàn)了Future接口,我們先來回顧Future吧。
Future是Java5新加的一個接口,它提供了一種異步并行計算的功能。如果主線程需要執(zhí)行一個很耗時的計算任務(wù),我們就可以通過future把這個任務(wù)放到異步線程中執(zhí)行。主線程繼續(xù)處理其他任務(wù),處理完成后,再通過Future獲取計算結(jié)果。
來看個簡單例子吧,假設(shè)我們有兩個任務(wù)服務(wù),一個查詢用戶基本信息,一個是查詢用戶勛章信息。如下,
public class UserInfoService {
public UserInfo getUserInfo(Long userId) throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(300);//模擬調(diào)用耗時
return new UserInfo("666", "撿田螺的小男孩", 27); //一般是查數(shù)據(jù)庫,或者遠程調(diào)用返回的
}
}
public class MedalService {
public MedalInfo getMedalInfo(long userId) throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(500); //模擬調(diào)用耗時
return new MedalInfo("666", "守護勛章");
}
}
接下來,我們來演示下,在主線程中是如何使用Future來進行異步調(diào)用的。
public class FutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
UserInfoService userInfoService = new UserInfoService();
MedalService medalService = new MedalService();
long userId =666L;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//調(diào)用用戶服務(wù)獲取用戶基本信息
FutureTask<UserInfo> userInfoFutureTask = new FutureTask<>(new Callable<UserInfo>() {
@Override
public UserInfo call() throws Exception {
return userInfoService.getUserInfo(userId);
}
});
executorService.submit(userInfoFutureTask);
Thread.sleep(300); //模擬主線程其它操作耗時
FutureTask<MedalInfo> medalInfoFutureTask = new FutureTask<>(new Callable<MedalInfo>() {
@Override
public MedalInfo call() throws Exception {
return medalService.getMedalInfo(userId);
}
});
executorService.submit(medalInfoFutureTask);
UserInfo userInfo = userInfoFutureTask.get();//獲取個人信息結(jié)果
MedalInfo medalInfo = medalInfoFutureTask.get();//獲取勛章信息結(jié)果
System.out.println("總共用時" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms");
}
}
運行結(jié)果:
總共用時806ms
如果我們不使用Future進行并行異步調(diào)用,而是在主線程串行進行的話,耗時大約為300+500+300 = 1100 ms。可以發(fā)現(xiàn),future+線程池異步配合,提高了程序的執(zhí)行效率。
但是Future對于結(jié)果的獲取,不是很友好,只能通過阻塞或者輪詢的方式得到任務(wù)的結(jié)果。
Future.get() 就是阻塞調(diào)用,在線程獲取結(jié)果之前get方法會一直阻塞。 Future提供了一個isDone方法,可以在程序中輪詢這個方法查詢執(zhí)行結(jié)果。
阻塞的方式和異步編程的設(shè)計理念相違背,而輪詢的方式會耗費無謂的CPU資源。因此,JDK8設(shè)計出CompletableFuture。CompletableFuture提供了一種觀察者模式類似的機制,可以讓任務(wù)執(zhí)行完成后通知監(jiān)聽的一方。
一個例子走進CompletableFuture
我們還是基于以上Future的例子,改用CompletableFuture 來實現(xiàn)
public class FutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
UserInfoService userInfoService = new UserInfoService();
MedalService medalService = new MedalService();
long userId =666L;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//調(diào)用用戶服務(wù)獲取用戶基本信息
CompletableFuture<UserInfo> completableUserInfoFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> userInfoService.getUserInfo(userId));
Thread.sleep(300); //模擬主線程其它操作耗時
CompletableFuture<MedalInfo> completableMedalInfoFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> medalService.getMedalInfo(userId));
UserInfo userInfo = completableUserInfoFuture.get(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS);//獲取個人信息結(jié)果
MedalInfo medalInfo = completableMedalInfoFuture.get();//獲取勛章信息結(jié)果
System.out.println("總共用時" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms");
}
}
可以發(fā)現(xiàn),使用CompletableFuture,代碼簡潔了很多。CompletableFuture的supplyAsync方法,提供了異步執(zhí)行的功能,線程池也不用單獨創(chuàng)建了。實際上,它CompletableFuture使用了默認線程池是ForkJoinPool.commonPool。
CompletableFuture提供了幾十種方法,輔助我們的異步任務(wù)場景。這些方法包括創(chuàng)建異步任務(wù)、任務(wù)異步回調(diào)、多個任務(wù)組合處理等方面。我們一起來學(xué)習(xí)吧
CompletableFuture使用場景
創(chuàng)建異步任務(wù)
CompletableFuture創(chuàng)建異步任務(wù),一般有supplyAsync和runAsync兩個方法
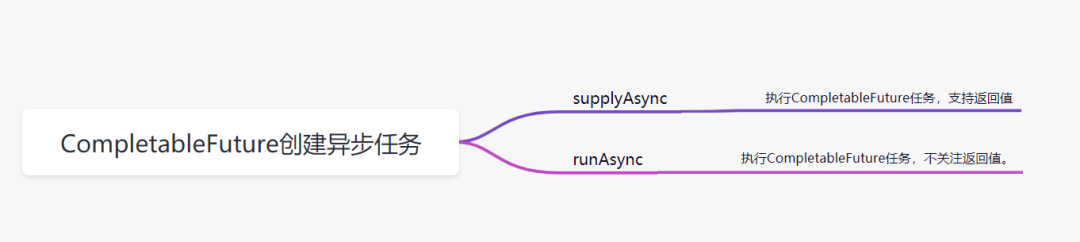
supplyAsync執(zhí)行CompletableFuture任務(wù),支持返回值 runAsync執(zhí)行CompletableFuture任務(wù),沒有返回值。
supplyAsync方法
//使用默認內(nèi)置線程池ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),根據(jù)supplier構(gòu)建執(zhí)行任務(wù)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
//自定義線程,根據(jù)supplier構(gòu)建執(zhí)行任務(wù)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
runAsync方法
//使用默認內(nèi)置線程池ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),根據(jù)runnable構(gòu)建執(zhí)行任務(wù)
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
//自定義線程,根據(jù)runnable構(gòu)建執(zhí)行任務(wù)
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
實例代碼如下:
public class FutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//可以自定義線程池
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//runAsync的使用
CompletableFuture<Void> runFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> System.out.println("run,關(guān)注公眾號:撿田螺的小男孩"), executor);
//supplyAsync的使用
CompletableFuture<String> supplyFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.print("supply,關(guān)注公眾號:撿田螺的小男孩");
return "撿田螺的小男孩"; }, executor);
//runAsync的future沒有返回值,輸出null
System.out.println(runFuture.join());
//supplyAsync的future,有返回值
System.out.println(supplyFuture.join());
executor.shutdown(); // 線程池需要關(guān)閉
}
}
//輸出
run,關(guān)注公眾號:撿田螺的小男孩
null
supply,關(guān)注公眾號:撿田螺的小男孩撿田螺的小男孩
任務(wù)異步回調(diào)

1. thenRun/thenRunAsync
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action);
CompletableFuture的thenRun方法,通俗點講就是,做完第一個任務(wù)后,再做第二個任務(wù)。某個任務(wù)執(zhí)行完成后,執(zhí)行回調(diào)方法;但是前后兩個任務(wù)沒有參數(shù)傳遞,第二個任務(wù)也沒有返回值
public class FutureThenRunTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> orgFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
()->{
System.out.println("先執(zhí)行第一個CompletableFuture方法任務(wù)");
return "撿田螺的小男孩";
}
);
CompletableFuture thenRunFuture = orgFuture.thenRun(() -> {
System.out.println("接著執(zhí)行第二個任務(wù)");
});
System.out.println(thenRunFuture.get());
}
}
//輸出
先執(zhí)行第一個CompletableFuture方法任務(wù)
接著執(zhí)行第二個任務(wù)
null
thenRun 和thenRunAsync有什么區(qū)別呢?可以看下源碼哈:
private static final Executor asyncPool = useCommonPool ?
ForkJoinPool.commonPool() : new ThreadPerTaskExecutor();
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action) {
return uniRunStage(null, action);
}
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action) {
return uniRunStage(asyncPool, action);
}
如果你執(zhí)行第一個任務(wù)的時候,傳入了一個自定義線程池:
調(diào)用thenRun方法執(zhí)行第二個任務(wù)時,則第二個任務(wù)和第一個任務(wù)是共用同一個線程池。 調(diào)用thenRunAsync執(zhí)行第二個任務(wù)時,則第一個任務(wù)使用的是你自己傳入的線程池,第二個任務(wù)使用的是ForkJoin線程池
TIPS: 后面介紹的thenAccept和thenAcceptAsync,thenApply和thenApplyAsync等,它們之間的區(qū)別也是這個哈。
2.thenAccept/thenAcceptAsync
CompletableFuture的thenAccept方法表示,第一個任務(wù)執(zhí)行完成后,執(zhí)行第二個回調(diào)方法任務(wù),會將該任務(wù)的執(zhí)行結(jié)果,作為入?yún)ⅲ瑐鬟f到回調(diào)方法中,但是回調(diào)方法是沒有返回值的。
public class FutureThenAcceptTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> orgFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
()->{
System.out.println("原始CompletableFuture方法任務(wù)");
return "撿田螺的小男孩";
}
);
CompletableFuture thenAcceptFuture = orgFuture.thenAccept((a) -> {
if ("撿田螺的小男孩".equals(a)) {
System.out.println("關(guān)注了");
}
System.out.println("先考慮考慮");
});
System.out.println(thenAcceptFuture.get());
}
}
3. thenApply/thenApplyAsync
CompletableFuture的thenApply方法表示,第一個任務(wù)執(zhí)行完成后,執(zhí)行第二個回調(diào)方法任務(wù),會將該任務(wù)的執(zhí)行結(jié)果,作為入?yún)ⅲ瑐鬟f到回調(diào)方法中,并且回調(diào)方法是有返回值的。
public class FutureThenApplyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> orgFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
()->{
System.out.println("原始CompletableFuture方法任務(wù)");
return "撿田螺的小男孩";
}
);
CompletableFuture<String> thenApplyFuture = orgFuture.thenApply((a) -> {
if ("撿田螺的小男孩".equals(a)) {
return "關(guān)注了";
}
return "先考慮考慮";
});
System.out.println(thenApplyFuture.get());
}
}
//輸出
原始CompletableFuture方法任務(wù)
關(guān)注了
4. exceptionally
CompletableFuture的exceptionally方法表示,某個任務(wù)執(zhí)行異常時,執(zhí)行的回調(diào)方法;并且有拋出異常作為參數(shù),傳遞到回調(diào)方法。
public class FutureExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> orgFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
()->{
System.out.println("當(dāng)前線程名稱:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
throw new RuntimeException();
}
);
CompletableFuture<String> exceptionFuture = orgFuture.exceptionally((e) -> {
e.printStackTrace();
return "你的程序異常啦";
});
System.out.println(exceptionFuture.get());
}
}
//輸出
當(dāng)前線程名稱:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1
java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.RuntimeException
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.encodeThrowable(CompletableFuture.java:273)
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.completeThrowable(CompletableFuture.java:280)
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture$AsyncSupply.run(CompletableFuture.java:1592)
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture$AsyncSupply.exec(CompletableFuture.java:1582)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask.doExec(ForkJoinTask.java:289)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool$WorkQueue.runTask(ForkJoinPool.java:1056)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.runWorker(ForkJoinPool.java:1692)
at java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinWorkerThread.run(ForkJoinWorkerThread.java:157)
Caused by: java.lang.RuntimeException
at cn.eovie.future.FutureWhenTest.lambda$main$0(FutureWhenTest.java:13)
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture$AsyncSupply.run(CompletableFuture.java:1590)
... 5 more
你的程序異常啦
5. whenComplete方法
CompletableFuture的whenComplete方法表示,某個任務(wù)執(zhí)行完成后,執(zhí)行的回調(diào)方法,無返回值;并且whenComplete方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是上個任務(wù)的結(jié)果。
public class FutureWhenTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> orgFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
()->{
System.out.println("當(dāng)前線程名稱:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "撿田螺的小男孩";
}
);
CompletableFuture<String> rstFuture = orgFuture.whenComplete((a, throwable) -> {
System.out.println("當(dāng)前線程名稱:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("上個任務(wù)執(zhí)行完啦,還把" + a + "傳過來");
if ("撿田螺的小男孩".equals(a)) {
System.out.println("666");
}
System.out.println("233333");
});
System.out.println(rstFuture.get());
}
}
//輸出
當(dāng)前線程名稱:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1
當(dāng)前線程名稱:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1
上個任務(wù)執(zhí)行完啦,還把撿田螺的小男孩傳過來
666
233333
撿田螺的小男孩
6. handle方法
CompletableFuture的handle方法表示,某個任務(wù)執(zhí)行完成后,執(zhí)行回調(diào)方法,并且是有返回值的;并且handle方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是回調(diào)方法執(zhí)行的結(jié)果。
public class FutureHandlerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> orgFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
()->{
System.out.println("當(dāng)前線程名稱:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "撿田螺的小男孩";
}
);
CompletableFuture<String> rstFuture = orgFuture.handle((a, throwable) -> {
System.out.println("上個任務(wù)執(zhí)行完啦,還把" + a + "傳過來");
if ("撿田螺的小男孩".equals(a)) {
System.out.println("666");
return "關(guān)注了";
}
System.out.println("233333");
return null;
});
System.out.println(rstFuture.get());
}
}
//輸出
當(dāng)前線程名稱:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1
上個任務(wù)執(zhí)行完啦,還把撿田螺的小男孩傳過來
666
關(guān)注了
多個任務(wù)組合處理
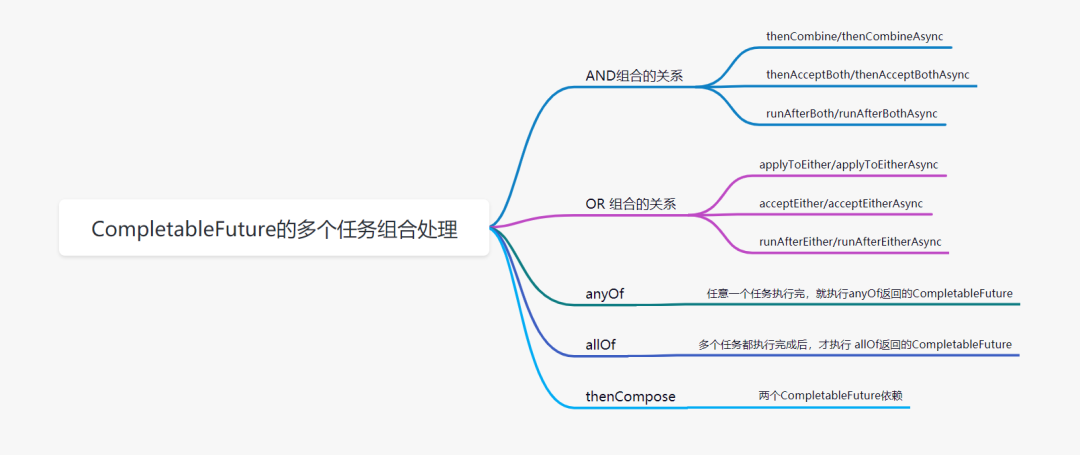
AND組合關(guān)系

thenCombine / thenAcceptBoth / runAfterBoth都表示:將兩個CompletableFuture組合起來,只有這兩個都正常執(zhí)行完了,才會執(zhí)行某個任務(wù)。
區(qū)別在于:
thenCombine:會將兩個任務(wù)的執(zhí)行結(jié)果作為方法入?yún)ⅲ瑐鬟f到指定方法中,且有返回值 thenAcceptBoth: 會將兩個任務(wù)的執(zhí)行結(jié)果作為方法入?yún)ⅲ瑐鬟f到指定方法中,且無返回值 runAfterBoth 不會把執(zhí)行結(jié)果當(dāng)做方法入?yún)?/strong>,且沒有返回值。
public class ThenCombineTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
CompletableFuture<String> first = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("第一個異步任務(wù)");
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture
//第二個異步任務(wù)
.supplyAsync(() -> "第二個異步任務(wù)", executor)
// (w, s) -> System.out.println(s) 是第三個任務(wù)
.thenCombineAsync(first, (s, w) -> {
System.out.println(w);
System.out.println(s);
return "兩個異步任務(wù)的組合";
}, executor);
System.out.println(future.join());
executor.shutdown();
}
}
//輸出
第一個異步任務(wù)
第二個異步任務(wù)
兩個異步任務(wù)的組合
OR 組合的關(guān)系

applyToEither / acceptEither / runAfterEither 都表示:將兩個CompletableFuture組合起來,只要其中一個執(zhí)行完了,就會執(zhí)行某個任務(wù)。
區(qū)別在于:
applyToEither:會將已經(jīng)執(zhí)行完成的任務(wù),作為方法入?yún)ⅲ瑐鬟f到指定方法中,且有返回值 acceptEither: 會將已經(jīng)執(zhí)行完成的任務(wù),作為方法入?yún)ⅲ瑐鬟f到指定方法中,且無返回值 runAfterEither:不會把執(zhí)行結(jié)果當(dāng)做方法入?yún)ⅲ覜]有返回值。
public class AcceptEitherTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//第一個異步任務(wù),休眠2秒,保證它執(zhí)行晚點
CompletableFuture<String> first = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try{
Thread.sleep(2000L);
System.out.println("執(zhí)行完第一個異步任務(wù)");}
catch (Exception e){
return "第一個任務(wù)異常";
}
return "第一個異步任務(wù)";
});
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture
//第二個異步任務(wù)
.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("執(zhí)行完第二個任務(wù)");
return "第二個任務(wù)";}
, executor)
//第三個任務(wù)
.acceptEitherAsync(first, System.out::println, executor);
executor.shutdown();
}
}
//輸出
執(zhí)行完第二個任務(wù)
第二個任務(wù)
AllOf
所有任務(wù)都執(zhí)行完成后,才執(zhí)行 allOf返回的CompletableFuture。如果任意一個任務(wù)異常,allOf的CompletableFuture,執(zhí)行g(shù)et方法,會拋出異常
public class allOfFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Void> a = CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
System.out.println("我執(zhí)行完了");
});
CompletableFuture<Void> b = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("我也執(zhí)行完了");
});
CompletableFuture<Void> allOfFuture = CompletableFuture.allOf(a, b).whenComplete((m,k)->{
System.out.println("finish");
});
}
}
//輸出
我執(zhí)行完了
我也執(zhí)行完了
finish
AnyOf
任意一個任務(wù)執(zhí)行完,就執(zhí)行anyOf返回的CompletableFuture。如果執(zhí)行的任務(wù)異常,anyOf的CompletableFuture,執(zhí)行g(shù)et方法,會拋出異常
public class AnyOfFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Void> a = CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
try {
Thread.sleep(3000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("我執(zhí)行完了");
});
CompletableFuture<Void> b = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("我也執(zhí)行完了");
});
CompletableFuture<Object> anyOfFuture = CompletableFuture.anyOf(a, b).whenComplete((m,k)->{
System.out.println("finish");
// return "撿田螺的小男孩";
});
anyOfFuture.join();
}
}
//輸出
我也執(zhí)行完了
finish
thenCompose
thenCompose方法會在某個任務(wù)執(zhí)行完成后,將該任務(wù)的執(zhí)行結(jié)果,作為方法入?yún)?去執(zhí)行指定的方法。該方法會返回一個新的CompletableFuture實例
如果該CompletableFuture實例的result不為null,則返回一個基于該result新的CompletableFuture實例; 如果該CompletableFuture實例為null,然后就執(zhí)行這個新任務(wù)
public class ThenComposeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> f = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("第一個任務(wù)");
//第二個異步任務(wù)
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> "第二個任務(wù)", executor)
.thenComposeAsync(data -> {
System.out.println(data); return f; //使用第一個任務(wù)作為返回
}, executor);
System.out.println(future.join());
executor.shutdown();
}
}
//輸出
第二個任務(wù)
第一個任務(wù)
CompletableFuture使用有哪些注意點
CompletableFuture 使我們的異步編程更加便利的、代碼更加優(yōu)雅的同時,我們也要關(guān)注下它,使用的一些注意點。

1. Future需要獲取返回值,才能獲取異常信息
ExecutorService executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 5L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10));
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int a = 0;
int b = 666;
int c = b / a;
return true;
},executorService).thenAccept(System.out::println);
//如果不加 get()方法這一行,看不到異常信息
//future.get();
Future需要獲取返回值,才能獲取到異常信息。如果不加 get()/join()方法,看不到異常信息。小伙伴們使用的時候,注意一下哈,考慮是否加try...catch...或者使用exceptionally方法。
2. CompletableFuture的get()方法是阻塞的。
CompletableFuture的get()方法是阻塞的,如果使用它來獲取異步調(diào)用的返回值,需要添加超時時間~
//反例
CompletableFuture.get();
//正例
CompletableFuture.get(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
3. 默認線程池的注意點
CompletableFuture代碼中又使用了默認的線程池,處理的線程個數(shù)是電腦CPU核數(shù)-1。在大量請求過來的時候,處理邏輯復(fù)雜的話,響應(yīng)會很慢。一般建議使用自定義線程池,優(yōu)化線程池配置參數(shù)。
4. 自定義線程池時,注意飽和策略
CompletableFuture的get()方法是阻塞的,我們一般建議使用future.get(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)。并且一般建議使用自定義線程池。
但是如果線程池拒絕策略是DiscardPolicy或者DiscardOldestPolicy,當(dāng)線程池飽和時,會直接丟棄任務(wù),不會拋棄異常。因此建議,CompletableFuture線程池策略最好使用AbortPolicy,然后耗時的異步線程,做好線程池隔離哈。

好文推薦


字節(jié)跳動P0級事故:實習(xí)生刪除GB以下所有模型,差點沒上頭條......

Reddit高贊熱貼:一位程序員醉酒吐真言

某女產(chǎn)品經(jīng)理吐槽:男朋友家里出450萬做婚房首付,自己想出40萬加上名字,男朋友卻不同意!網(wǎng)友:心機女!
一鍵三連「分享」、「點贊」和「在看」
技術(shù)干貨與你天天見~

