目標(biāo)跟蹤初探之DeepSORT:源碼詳解DeepSort工作流程
作者 | 可樂 編輯 | 汽車人
原文鏈接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/90835266
最近由于工作原因,首次接觸到了目標(biāo)跟蹤任務(wù),這幾天讀了一些該領(lǐng)域的優(yōu)秀論文,真心感覺目標(biāo)跟蹤任務(wù)的難度和復(fù)雜度要比分類和目標(biāo)檢測高不少,具有更大的挑戰(zhàn)性。
如果你跟我一樣是正在學(xué)習(xí)目標(biāo)跟蹤的新手,希望本文能讓你對目標(biāo)跟蹤任務(wù)和DeepSORT算法的工作流程有個初步的了解,如果你是該領(lǐng)域的前輩,歡迎對文中的不足之處進(jìn)行指正,多多指教。
本文首先將介紹在目標(biāo)跟蹤任務(wù)中常用的匈牙利算法(Hungarian Algorithm)和卡爾曼濾波(Kalman Filter),然后介紹經(jīng)典算法DeepSORT的工作流程以及對相關(guān)源碼進(jìn)行解析。
目前主流的目標(biāo)跟蹤算法都是基于Tracking-by-Detecton策略,即基于目標(biāo)檢測的結(jié)果來進(jìn)行目標(biāo)跟蹤。DeepSORT運(yùn)用的就是這個策略,上面的視頻是DeepSORT對人群進(jìn)行跟蹤的結(jié)果,每個bbox左上角的數(shù)字是用來標(biāo)識某個人的唯一ID號。
這里就有個問題,視頻中不同時刻的同一個人,位置發(fā)生了變化,那么是如何關(guān)聯(lián)上的呢?答案就是匈牙利算法和卡爾曼濾波。
匈牙利算法可以告訴我們當(dāng)前幀的某個目標(biāo),是否與前一幀的某個目標(biāo)相同。 卡爾曼濾波可以基于目標(biāo)前一時刻的位置,來預(yù)測當(dāng)前時刻的位置,并且可以比傳感器(在目標(biāo)跟蹤中即目標(biāo)檢測器,比如Yolo等)更準(zhǔn)確的估計目標(biāo)的位置。
1匈牙利算法(Hungarian Algorithm)
首先,先介紹一下什么是分配問題(Assignment Problem):假設(shè)有N個人和N個任務(wù),每個任務(wù)可以任意分配給不同的人,已知每個人完成每個任務(wù)要花費(fèi)的代價不盡相同,那么如何分配可以使得總的代價最小。
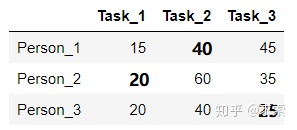
舉個例子,假設(shè)現(xiàn)在有3個任務(wù),要分別分配給3個人,每個人完成各個任務(wù)所需代價矩陣(cost matrix)如下所示(這個代價可以是金錢、時間等等):
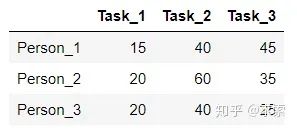
怎樣才能找到一個最優(yōu)分配,使得完成所有任務(wù)花費(fèi)的代價最小呢?
匈牙利算法(又叫KM算法)就是用來解決分配問題的一種方法,它基于定理:
如果代價矩陣的某一行或某一列同時加上或減去某個數(shù),則這個新的代價矩陣的最優(yōu)分配仍然是原代價矩陣的最優(yōu)分配。
算法步驟(假設(shè)矩陣為NxN方陣):
對于矩陣的每一行,減去其中最小的元素 對于矩陣的每一列,減去其中最小的元素 用最少的水平線或垂直線覆蓋矩陣中所有的0 如果線的數(shù)量等于N,則找到了最優(yōu)分配,算法結(jié)束,否則進(jìn)入步驟5 找到?jīng)]有被任何線覆蓋的最小元素,每個沒被線覆蓋的行減去這個元素,每個被線覆蓋的列加上這個元素,返回步驟3
繼續(xù)拿上面的例子做演示:
step1 每一行最小的元素分別為15、20、20,減去得到:
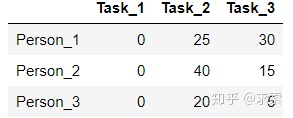
step2 每一列最小的元素分別為0、20、5,減去得到:
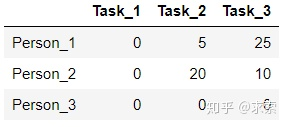
step3 用最少的水平線或垂直線覆蓋所有的0,得到:

step4 線的數(shù)量為2,小于3,進(jìn)入下一步;
step5 現(xiàn)在沒被覆蓋的最小元素是5,沒被覆蓋的行(第一和第二行)減去5,得到:
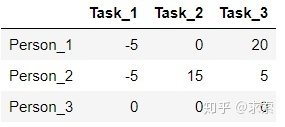
被覆蓋的列(第一列)加上5,得到:
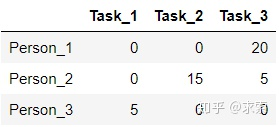
跳轉(zhuǎn)到step3,用最少的水平線或垂直線覆蓋所有的0,得到:
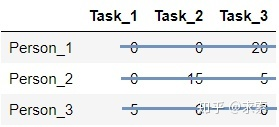
step4:線的數(shù)量為3,滿足條件,算法結(jié)束。顯然,將任務(wù)2分配給第1個人、任務(wù)1分配給第2個人、任務(wù)3分配給第3個人時,總的代價最小(0+0+0=0):
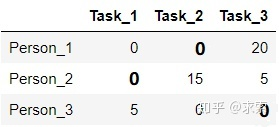
所以原矩陣的最小總代價為(40+20+25=85):
sklearn里的linear_assignment()函數(shù)以及scipy里的linear_sum_assignment()函數(shù)都實現(xiàn)了匈牙利算法,兩者的返回值的形式不同:
import numpy as np
from sklearn.utils.linear_assignment_ import linear_assignment
from scipy.optimize import linear_sum_assignment
cost_matrix = np.array([
[15,40,45],
[20,60,35],
[20,40,25]
])
matches = linear_assignment(cost_matrix)
print('sklearn API result:\n', matches)
matches = linear_sum_assignment(cost_matrix)
print('scipy API result:\n', matches)
"""Outputs
sklearn API result:
[[0 1]
[1 0]
[2 2]]
scipy API result:
(array([0, 1, 2], dtype=int64), array([1, 0, 2], dtype=int64))
"""
在DeepSORT中,匈牙利算法用來將前一幀中的跟蹤框tracks與當(dāng)前幀中的檢測框detections進(jìn)行關(guān)聯(lián),通過外觀信息(appearance information)和馬氏距離(Mahalanobis distance),或者IOU來計算代價矩陣。
源碼解讀:
# linear_assignment.py
def min_cost_matching(distance_metric, max_distance, tracks, detections,
track_indices=None, detection_indices=None):
...
# 計算代價矩陣
cost_matrix = distance_metric(tracks, detections, track_indices, detection_indices)
cost_matrix[cost_matrix > max_distance] = max_distance + 1e-5
# 執(zhí)行匈牙利算法,得到匹配成功的索引對,行索引為tracks的索引,列索引為detections的索引
row_indices, col_indices = linear_assignment(cost_matrix)
matches, unmatched_tracks, unmatched_detections = [], [], []
# 找出未匹配的detections
for col, detection_idx in enumerate(detection_indices):
if col not in col_indices:
unmatched_detections.append(detection_idx)
# 找出未匹配的tracks
for row, track_idx in enumerate(track_indices):
if row not in row_indices:
unmatched_tracks.append(track_idx)
# 遍歷匹配的(track, detection)索引對
for row, col in zip(row_indices, col_indices):
track_idx = track_indices[row]
detection_idx = detection_indices[col]
# 如果相應(yīng)的cost大于閾值max_distance,也視為未匹配成功
if cost_matrix[row, col] > max_distance:
unmatched_tracks.append(track_idx)
unmatched_detections.append(detection_idx)
else:
matches.append((track_idx, detection_idx))
return matches, unmatched_tracks, unmatched_detections
2卡爾曼濾波(Kalman Filter)
卡爾曼濾波被廣泛應(yīng)用于無人機(jī)、自動駕駛、衛(wèi)星導(dǎo)航等領(lǐng)域,簡單來說,其作用就是基于傳感器的測量值來更新預(yù)測值,以達(dá)到更精確的估計。
假設(shè)我們要跟蹤小車的位置變化,如下圖所示,藍(lán)色的分布是卡爾曼濾波預(yù)測值,棕色的分布是傳感器的測量值,灰色的分布就是預(yù)測值基于測量值更新后的最優(yōu)估計。
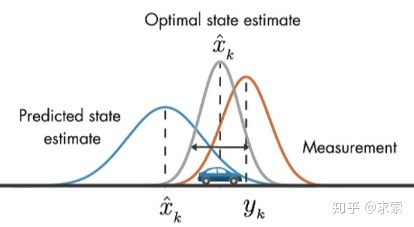
在目標(biāo)跟蹤中,需要估計track的以下兩個狀態(tài):
均值(Mean):表示目標(biāo)的位置信息,由bbox的中心坐標(biāo) (cx, cy),寬高比r,高h(yuǎn),以及各自的速度變化值組成,由8維向量表示為 x = [cx, cy, r, h, vx, vy, vr, vh],各個速度值初始化為0。 協(xié)方差(Covariance ):表示目標(biāo)位置信息的不確定性,由8x8的對角矩陣表示,矩陣中數(shù)字越大則表明不確定性越大,可以以任意值初始化。
卡爾曼濾波分為兩個階段:(1) 預(yù)測track在下一時刻的位置,(2) 基于detection來更新預(yù)測的位置。
下面將介紹這兩個階段用到的計算公式。(這里不涉及公式的原理推導(dǎo),因為我也不清楚原理(?_?) ,只是說明一下各個公式的作用)
預(yù)測
基于track在t-1時刻的狀態(tài)來預(yù)測其在t時刻的狀態(tài)。
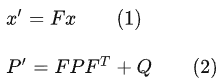
在公式1中,x為track在t-1時刻的均值,F(xiàn)稱為狀態(tài)轉(zhuǎn)移矩陣,該公式預(yù)測t時刻的x':
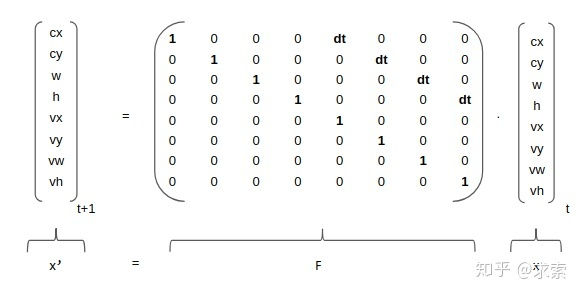
矩陣F中的dt是當(dāng)前幀和前一幀之間的差,將等號右邊的矩陣乘法展開,可以得到cx'=cx+dt*vx,cy'=cy+dt*vy...,所以這里的卡爾曼濾波是一個勻速模型(Constant Velocity Model)。
在公式2中,P為track在t-1時刻的協(xié)方差,Q為系統(tǒng)的噪聲矩陣,代表整個系統(tǒng)的可靠程度,一般初始化為很小的值,該公式預(yù)測t時刻的P'。
源碼解讀:
# kalman_filter.py
def predict(self, mean, covariance):
"""Run Kalman filter prediction step.
Parameters
----------
mean: ndarray, the 8 dimensional mean vector of the object state at the previous time step.
covariance: ndarray, the 8x8 dimensional covariance matrix of the object state at the previous time step.
Returns
-------
(ndarray, ndarray), the mean vector and covariance matrix of the predicted state.
Unobserved velocities are initialized to 0 mean.
"""
std_pos = [
self._std_weight_position * mean[3],
self._std_weight_position * mean[3],
1e-2,
self._std_weight_position * mean[3]]
std_vel = [
self._std_weight_velocity * mean[3],
self._std_weight_velocity * mean[3],
1e-5,
self._std_weight_velocity * mean[3]]
motion_cov = np.diag(np.square(np.r_[std_pos, std_vel])) # 初始化噪聲矩陣Q
mean = np.dot(self._motion_mat, mean) # x' = Fx
covariance = np.linalg.multi_dot((self._motion_mat, covariance, self._motion_mat.T)) + motion_cov # P' = FPF(T) + Q
return mean, covariance
更新
基于t時刻檢測到的detection,校正與其關(guān)聯(lián)的track的狀態(tài),得到一個更精確的結(jié)果。
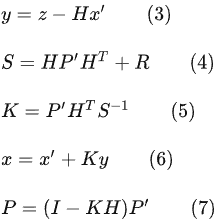
在公式3中,z為detection的均值向量,不包含速度變化值,即z=[cx, cy, r, h],H稱為測量矩陣,它將track的均值向量x'映射到檢測空間,該公式計算detection和track的均值誤差;
在公式4中,R為檢測器的噪聲矩陣,它是一個4x4的對角矩陣,對角線上的值分別為中心點(diǎn)兩個坐標(biāo)以及寬高的噪聲,以任意值初始化,一般設(shè)置寬高的噪聲大于中心點(diǎn)的噪聲,該公式先將協(xié)方差矩陣P'映射到檢測空間,然后再加上噪聲矩陣R;
公式5計算卡爾曼增益K,卡爾曼增益用于估計誤差的重要程度;
公式6和公式7得到更新后的均值向量x和協(xié)方差矩陣P。
源碼解讀:
# kalman_filter.py
def project(self, mean, covariance):
"""Project state distribution to measurement space.
Parameters
----------
mean: ndarray, the state's mean vector (8 dimensional array).
covariance: ndarray, the state's covariance matrix (8x8 dimensional).
Returns
-------
(ndarray, ndarray), the projected mean and covariance matrix of the given state estimate.
"""
std = [self._std_weight_position * mean[3],
self._std_weight_position * mean[3],
1e-1,
self._std_weight_position * mean[3]]
innovation_cov = np.diag(np.square(std)) # 初始化噪聲矩陣R
mean = np.dot(self._update_mat, mean) # 將均值向量映射到檢測空間,即Hx'
covariance = np.linalg.multi_dot((
self._update_mat, covariance, self._update_mat.T)) # 將協(xié)方差矩陣映射到檢測空間,即HP'H^T
return mean, covariance + innovation_cov
def update(self, mean, covariance, measurement):
"""Run Kalman filter correction step.
Parameters
----------
mean: ndarra, the predicted state's mean vector (8 dimensional).
covariance: ndarray, the state's covariance matrix (8x8 dimensional).
measurement: ndarray, the 4 dimensional measurement vector (x, y, a, h), where (x, y) is the
center position, a the aspect ratio, and h the height of the bounding box.
Returns
-------
(ndarray, ndarray), the measurement-corrected state distribution.
"""
# 將mean和covariance映射到檢測空間,得到Hx'和S
projected_mean, projected_cov = self.project(mean, covariance)
# 矩陣分解(這一步?jīng)]看懂)
chol_factor, lower = scipy.linalg.cho_factor(projected_cov, lower=True, check_finite=False)
# 計算卡爾曼增益K(這一步?jīng)]看明白是如何對應(yīng)上公式5的,求線代大佬指教)
kalman_gain = scipy.linalg.cho_solve(
(chol_factor, lower), np.dot(covariance, self._update_mat.T).T,
check_finite=False).T
# z - Hx'
innovation = measurement - projected_mean
# x = x' + Ky
new_mean = mean + np.dot(innovation, kalman_gain.T)
# P = (I - KH)P'
new_covariance = covariance - np.linalg.multi_dot((kalman_gain, projected_cov, kalman_gain.T))
return new_mean, new_covariance
3DeepSort工作流程
DeepSORT對每一幀的處理流程如下:
檢測器得到bbox → 生成detections → 卡爾曼濾波預(yù)測→ 使用匈牙利算法將預(yù)測后的tracks和當(dāng)前幀中的detecions進(jìn)行匹配(級聯(lián)匹配和IOU匹配) → 卡爾曼濾波更新
Frame 0:檢測器檢測到了3個detections,當(dāng)前沒有任何tracks,將這3個detections初始化為tracks Frame 1:檢測器又檢測到了3個detections,對于Frame 0中的tracks,先進(jìn)行預(yù)測得到新的tracks,然后使用匈牙利算法將新的tracks與detections進(jìn)行匹配,得到(track, detection)匹配對,最后用每對中的detection更新對應(yīng)的track
檢測
使用Yolo作為檢測器,檢測當(dāng)前幀中的bbox:
# demo_yolo3_deepsort.py
def detect(self):
while self.vdo.grab():
...
bbox_xcycwh, cls_conf, cls_ids = self.yolo3(im) # 檢測到的bbox[cx,cy,w,h],置信度,類別id
if bbox_xcycwh is not None:
# 篩選出人的類別
mask = cls_ids == 0
bbox_xcycwh = bbox_xcycwh[mask]
bbox_xcycwh[:, 3:] *= 1.2
cls_conf = cls_conf[mask]
...
生成detections
將檢測到的bbox轉(zhuǎn)換成detections:
# deep_sort.py
def update(self, bbox_xywh, confidences, ori_img):
self.height, self.width = ori_img.shape[:2]
# 提取每個bbox的feature
features = self._get_features(bbox_xywh, ori_img)
# [cx,cy,w,h] -> [x1,y1,w,h]
bbox_tlwh = self._xywh_to_tlwh(bbox_xywh)
# 過濾掉置信度小于self.min_confidence的bbox,生成detections
detections = [Detection(bbox_tlwh[i], conf, features[i]) for i,conf in enumerate(confidences) if conf > self.min_confidence]
# NMS (這里self.nms_max_overlap的值為1,即保留了所有的detections)
boxes = np.array([d.tlwh for d in detections])
scores = np.array([d.confidence for d in detections])
indices = non_max_suppression(boxes, self.nms_max_overlap, scores)
detections = [detections[i] for i in indices]
...
卡爾曼濾波預(yù)測階段
使用卡爾曼濾波預(yù)測前一幀中的tracks在當(dāng)前幀的狀態(tài):
# track.py
def predict(self, kf):
"""Propagate the state distribution to the current time step using a
Kalman filter prediction step.
Parameters
----------
kf: The Kalman filter.
"""
self.mean, self.covariance = kf.predict(self.mean, self.covariance) # 預(yù)測
self.age += 1 # 該track自出現(xiàn)以來的總幀數(shù)加1
self.time_since_update += 1 # 該track自最近一次更新以來的總幀數(shù)加1
匹配
首先對基于外觀信息的馬氏距離計算tracks和detections的代價矩陣,然后相繼進(jìn)行級聯(lián)匹配和IOU匹配,最后得到當(dāng)前幀的所有匹配對、未匹配的tracks以及未匹配的detections:
# tracker.py
def _match(self, detections):
def gated_metric(racks, dets, track_indices, detection_indices):
"""
基于外觀信息和馬氏距離,計算卡爾曼濾波預(yù)測的tracks和當(dāng)前時刻檢測到的detections的代價矩陣
"""
features = np.array([dets[i].feature for i in detection_indices])
targets = np.array([tracks[i].track_id for i in track_indices]
# 基于外觀信息,計算tracks和detections的余弦距離代價矩陣
cost_matrix = self.metric.distance(features, targets)
# 基于馬氏距離,過濾掉代價矩陣中一些不合適的項 (將其設(shè)置為一個較大的值)
cost_matrix = linear_assignment.gate_cost_matrix(self.kf, cost_matrix, tracks,
dets, track_indices, detection_indices)
return cost_matrix
# 區(qū)分開confirmed tracks和unconfirmed tracks
confirmed_tracks = [i for i, t in enumerate(self.tracks) if t.is_confirmed()]
unconfirmed_tracks = [i for i, t in enumerate(self.tracks) if not t.is_confirmed()]
# 對confirmd tracks進(jìn)行級聯(lián)匹配
matches_a, unmatched_tracks_a, unmatched_detections = \
linear_assignment.matching_cascade(
gated_metric, self.metric.matching_threshold, self.max_age,
self.tracks, detections, confirmed_tracks)
# 對級聯(lián)匹配中未匹配的tracks和unconfirmed tracks中time_since_update為1的tracks進(jìn)行IOU匹配
iou_track_candidates = unconfirmed_tracks + [k for k in unmatched_tracks_a if
self.tracks[k].time_since_update == 1]
unmatched_tracks_a = [k for k in unmatched_tracks_a if
self.tracks[k].time_since_update != 1]
matches_b, unmatched_tracks_b, unmatched_detections = \
linear_assignment.min_cost_matching(
iou_matching.iou_cost, self.max_iou_distance, self.tracks,
detections, iou_track_candidates, unmatched_detections)
# 整合所有的匹配對和未匹配的tracks
matches = matches_a + matches_b
unmatched_tracks = list(set(unmatched_tracks_a + unmatched_tracks_b))
return matches, unmatched_tracks, unmatched_detections
# 級聯(lián)匹配源碼 linear_assignment.py
def matching_cascade(distance_metric, max_distance, cascade_depth, tracks, detections,
track_indices=None, detection_indices=None):
...
unmatched_detections = detection_indice
matches = []
# 由小到大依次對每個level的tracks做匹配
for level in range(cascade_depth):
# 如果沒有detections,退出循環(huán)
if len(unmatched_detections) == 0:
break
# 當(dāng)前l(fā)evel的所有tracks索引
track_indices_l = [k for k in track_indices if
tracks[k].time_since_update == 1 + level]
# 如果當(dāng)前l(fā)evel沒有track,繼續(xù)
if len(track_indices_l) == 0:
continue
# 匈牙利匹配
matches_l, _, unmatched_detections = min_cost_matching(distance_metric, max_distance, tracks, detections,
track_indices_l, unmatched_detections)
matches += matches_l
unmatched_tracks = list(set(track_indices) - set(k for k, _ in matches))
return matches, unmatched_tracks, unmatched_detections
卡爾曼濾波更新階段
對于每個匹配成功的track,用其對應(yīng)的detection進(jìn)行更新,并處理未匹配tracks和detections:
def update(self, detections):
"""Perform measurement update and track management.
Parameters
----------
detections: List[deep_sort.detection.Detection]
A list of detections at the current time step.
"""
# 得到匹配對、未匹配的tracks、未匹配的dectections
matches, unmatched_tracks, unmatched_detections = self._match(detections)
# 對于每個匹配成功的track,用其對應(yīng)的detection進(jìn)行更新
for track_idx, detection_idx in matches:
self.tracks[track_idx].update(self.kf, detections[detection_idx])
# 對于未匹配的成功的track,將其標(biāo)記為丟失
for track_idx in unmatched_tracks:
self.tracks[track_idx].mark_missed()
# 對于未匹配成功的detection,初始化為新的track
for detection_idx in unmatched_detections:
self._initiate_track(detections[detection_idx])
...
4參考
[1] SIMPLE ONLINE AND REALTIME TRACKING WITH A DEEP ASSOCIATION METRIC
[2] https://github.com/ZQPei/deep_sort_pytorch
[3] https://towardsdatascience.com/computer-vision-for-tracking-8220759eee85
分享
收藏
點(diǎn)贊
在看