基于Yolo-V3對衛(wèi)星圖像進行儲油罐容積占用率的研究
點擊上方“小白學視覺”,選擇加"星標"或“置頂”
重磅干貨,第一時間送達



本文的所有內(nèi)容和整個代碼都可以在這個github存儲庫中找到 https://github.com/mdmub0587/Oil-Storage-Tank-s-Volume-Occupancy
目錄
問題陳述、數(shù)據(jù)集和評估指標
現(xiàn)有方法
相關(guān)研究工作
有用的博客和研究論文
我們的貢獻
探索性數(shù)據(jù)分析(EDA)
數(shù)據(jù)擴充
數(shù)據(jù)預處理、擴充和TFRecords
基于YoloV3的目標檢測
儲量估算
結(jié)果
結(jié)論
參考引用
1.問題陳述、數(shù)據(jù)集和評估指標
問題陳述:
數(shù)據(jù)集:
large_images: 這是一個文件夾,包含100個衛(wèi)星原始圖像,每個大小為4800x4800,所有圖像都以id_large.jpg格式命名。 Image_patches: Image_patches目錄包含從大圖像生成的512x512大小的子圖,每個大的圖像被分割成100個512x512大小的子圖,兩個軸上的子圖之間有37個像素的重疊,生成圖像子圖的程序以id_row_column.jpg格式命名 **labels.json:**它包含所有圖像的標簽。標簽存儲為字典列表,每個圖像對應一個字典,不包含任何浮頂罐的圖像將被標記為“skip”,邊界框標簽的格式為邊界框四個角的(x,y)坐標。 labels_coco.json: 它包含與前一個文件相同的標簽的COCO標簽格式。在這里,邊界框的格式為[x_min, y_min, width, height]. **large_image_data.csv:**它包含大型圖像文件的元數(shù)據(jù),包括每個圖像的中心坐標和海拔高度。
評估指標:
2.現(xiàn)有方法
3.相關(guān)研究工作
Estimating the Volume of Oil Tanks Based on High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images [2]:
4.有用的博客和研究論文
A Beginner’s Guide To Calculating Oil Storage Tank Occupancy With Help Of Satellite Imagery [3]:
A Gentle Introduction to Object Recognition With Deep Learning [4] :
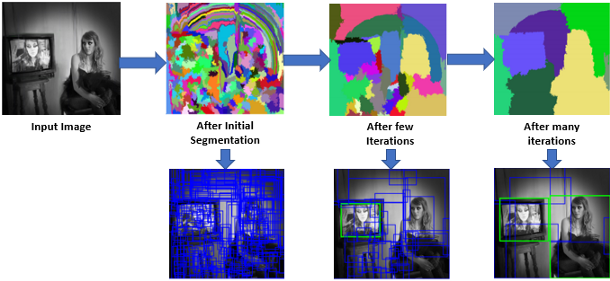
Selective Search for Object Recognition [5]:
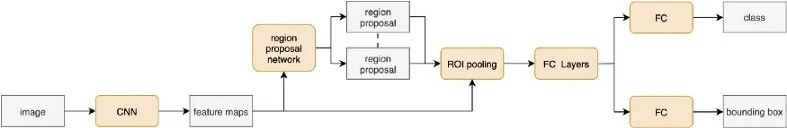
Region Proposal Network — A detailed view[6]:
Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks[7]:
Real-time Object Detection with YOLO, YOLOv2, and now YOLOv3 [8]:
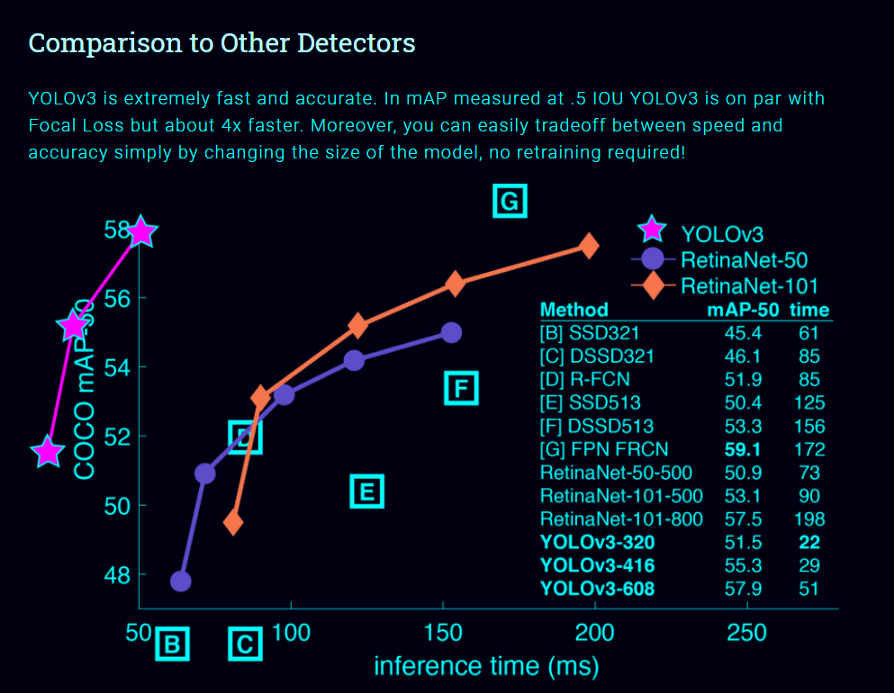
單神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)模型(即分類和定位任務(wù)都將從同一個模型中執(zhí)行):以一張照片作為輸入,直接預測每個邊界框的邊界框和類標簽,這意味著它只看一次圖像。 由于它對整個圖像而不是圖像的一部分執(zhí)行卷積,因此它產(chǎn)生的背景錯誤非常少。 YOLO學習對象的一般化表示。在對自然圖像進行訓練和藝術(shù)品測試時,YOLO的性能遠遠超過DPM和R-CNN等頂級檢測方法。由于YOLO具有高度的通用性,所以當應用于新的域或意外的輸入時,它不太可能崩潰。
如果你仔細看一下yolov2論文的標題,那就是“YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger”。yolov3比yolov2更好嗎?答案是肯定的,它更好,但不是更快更強,因為體系的復雜性增加了。 Yolov2使用了19層DarkNet架構(gòu),沒有任何殘差塊、skip連接和上采樣,因此它很難檢測到小對象,然而在Yolov3中,這些特性被添加了,并且使用了在Imagenet上訓練的53層DarkNet網(wǎng)絡(luò),除此之外,還堆積了53個卷積層,形成了106個卷積層結(jié)構(gòu)。
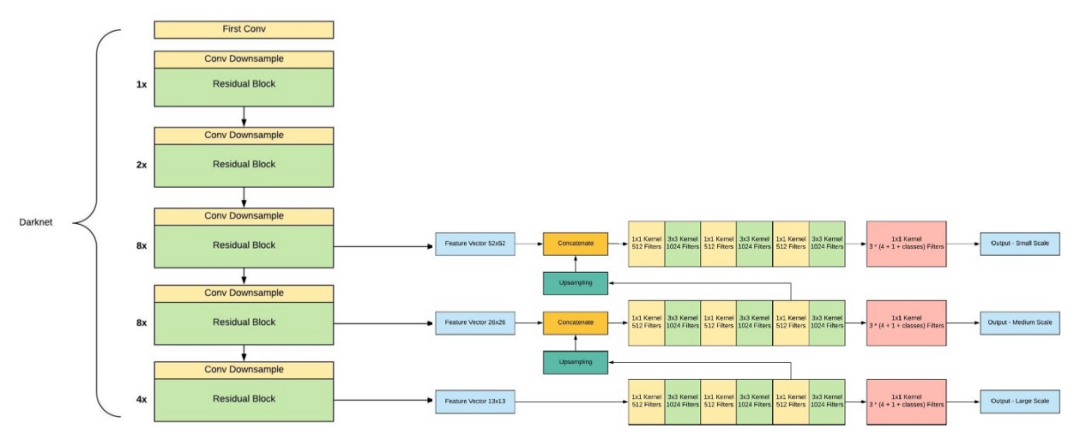
Yolov3在三種不同的尺度上進行預測,首先是大對象的13X13網(wǎng)格,其次是中等對象的26X26網(wǎng)格,最后是小對象的52X52網(wǎng)格。 YoloV3總共使用9個錨箱,每個標度3個,用K均值聚類法選出最佳錨盒。 Yolov3可以對圖像中檢測到的對象執(zhí)行多標簽分類,通過logistic回歸預測對象置信度和類預測。
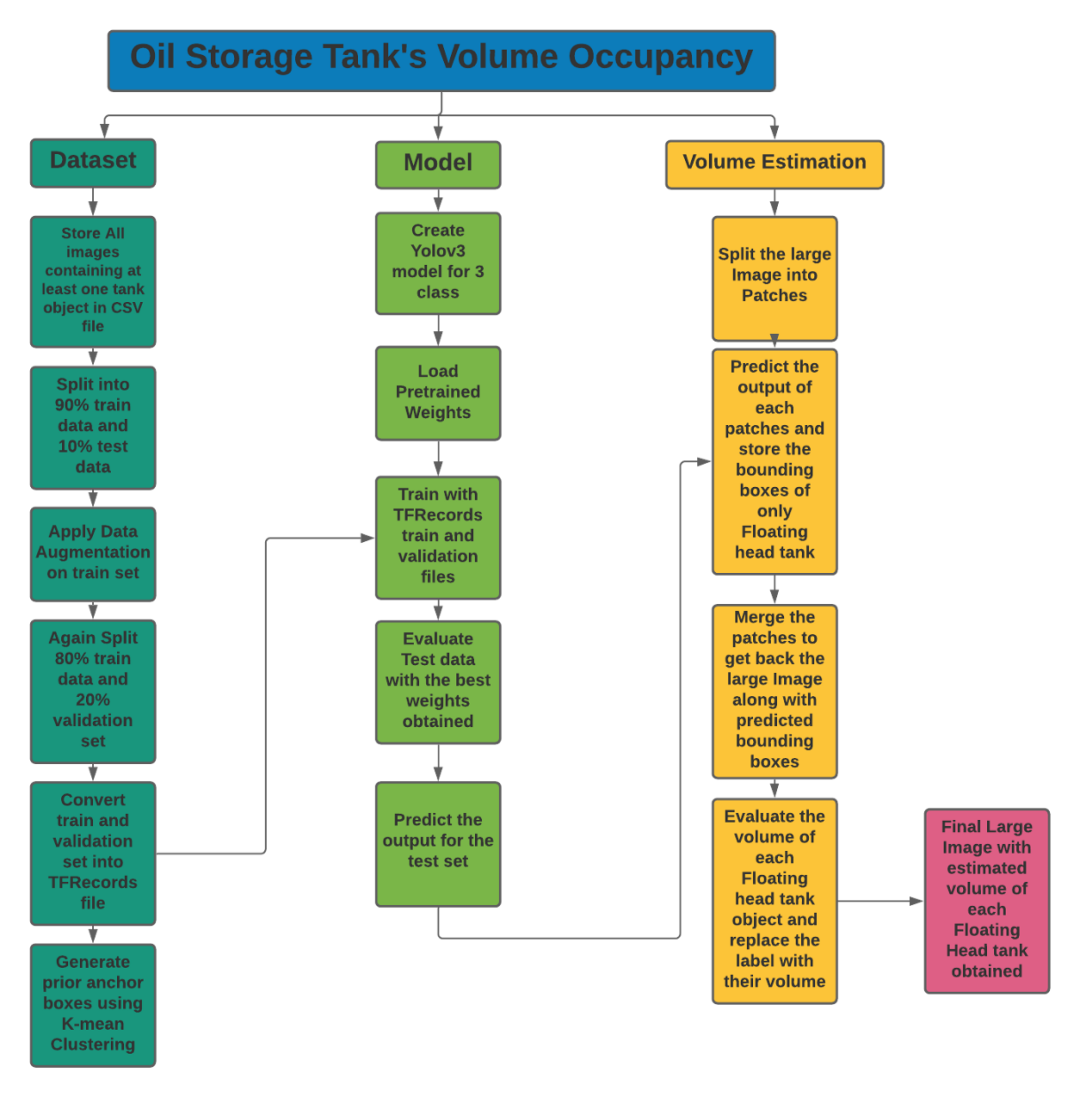
5.我們的貢獻
儲罐檢測:
陰影提取和體積估計:
6.探索性數(shù)據(jù)分析(EDA)
探索Labels.json文件:
json_labels = json.load(open(os.path.join('data','labels.json')))
print('Number of Images: ',len(json_labels))
json_labels[25:30]
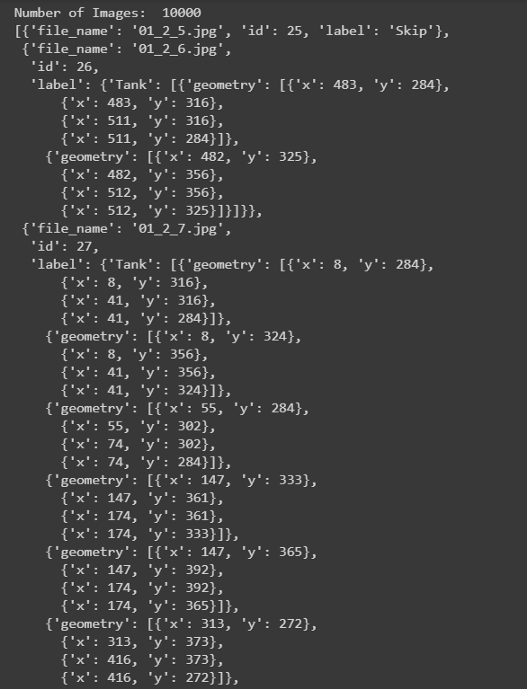
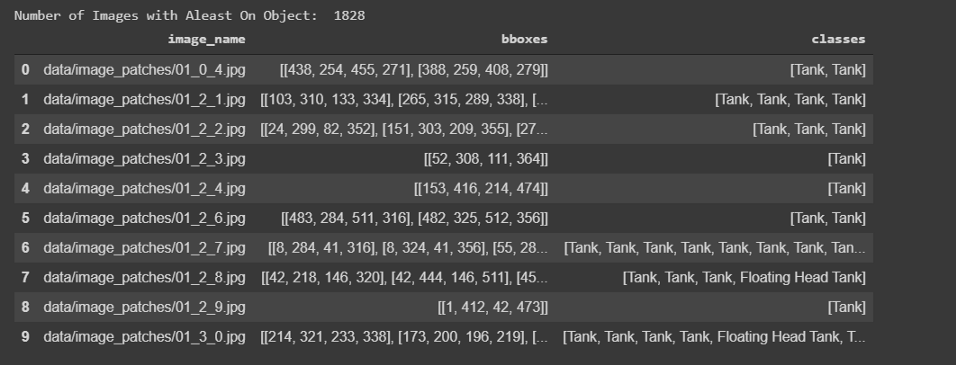
所有的標簽都存儲在字典列表中,總共有10萬張圖片。不包含任何儲罐的圖像將標記為Skip,而包含儲罐的圖像將標記為tank、tank Cluster或Floating Head tank,每個tank對象都有字典格式的四個角點的邊界框坐標。
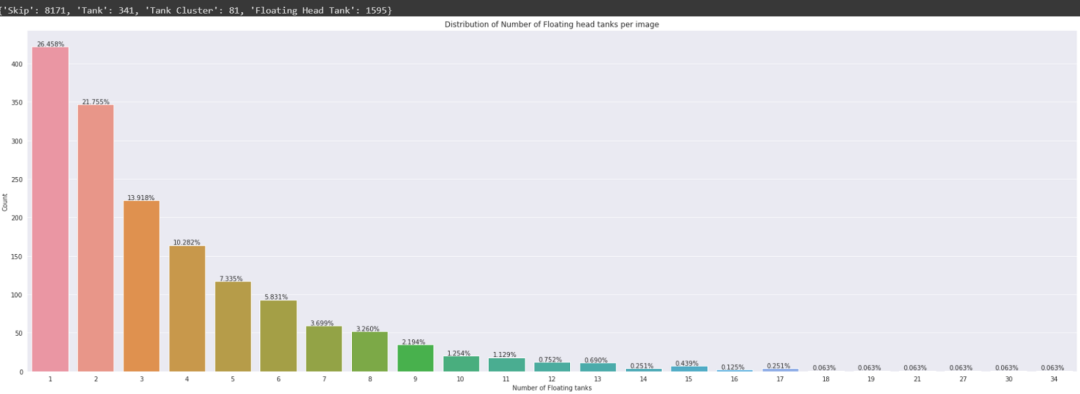
計數(shù):
探索labels_coco.json文件:
json_labels_coco = json.load(open(os.path.join('data','labels_coco.json')))
print('Number of Floating tanks: ',len(json_labels_coco['annotations']))
no_unique_img_id = set()
for ann in json_labels_coco['annotations']:
no_unique_img_id.add(ann['image_id'])
print('Number of Images that contains Floating head tank: ', len(no_unique_img_id))
json_labels_coco['annotations'][:8]
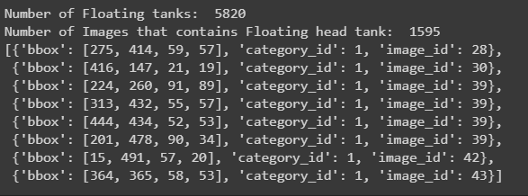
此文件僅包含浮頂罐的邊界框及其在字典格式列表中的image_id
打印邊界框:

儲油罐有三種:
Tank(T 油罐) Tank Cluster(TC 油罐組), Floating Head Tank(FHT,浮頂罐)
7.數(shù)據(jù)擴充
8.數(shù)據(jù)預處理、擴充和TFRecords
數(shù)據(jù)預處理:
def conv_bbox(box_dict):
"""
input: box_dict-> 字典中有4個角點
Function: 獲取左上方和右下方的點
output: tuple(ymin, xmin, ymax, xmax)
"""
xs = np.array(list(set([i['x'] for i in box_dict])))
ys = np.array(list(set([i['y'] for i in box_dict])))
x_min = xs.min()
x_max = xs.max()
y_min = ys.min()
y_max = ys.max()
return y_min, x_min, y_max, x_max
# 訓練和測試劃分
df_train, df_test= model_selection.train_test_split(
df, #CSV文件注釋
test_size=0.1,
random_state=42,
shuffle=True,
)
df_train.shape, df_test.shape
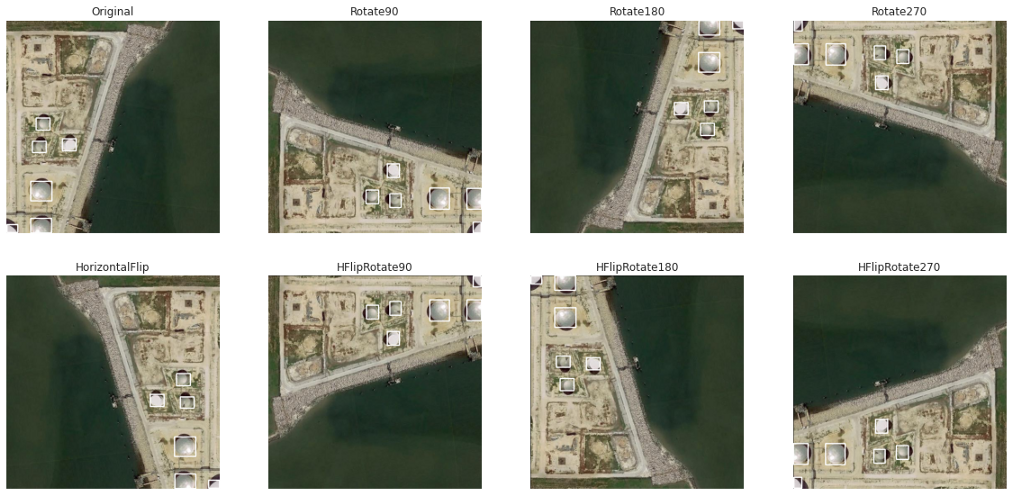
數(shù)據(jù)擴充:
水平翻轉(zhuǎn) 旋轉(zhuǎn)90度 旋轉(zhuǎn)180度 旋轉(zhuǎn)270度 水平翻轉(zhuǎn)和90度旋轉(zhuǎn) 水平翻轉(zhuǎn)和180度旋轉(zhuǎn) 水平翻轉(zhuǎn)和270度旋轉(zhuǎn)

TFRecords:
9.基于YoloV3的目標檢測
訓練:
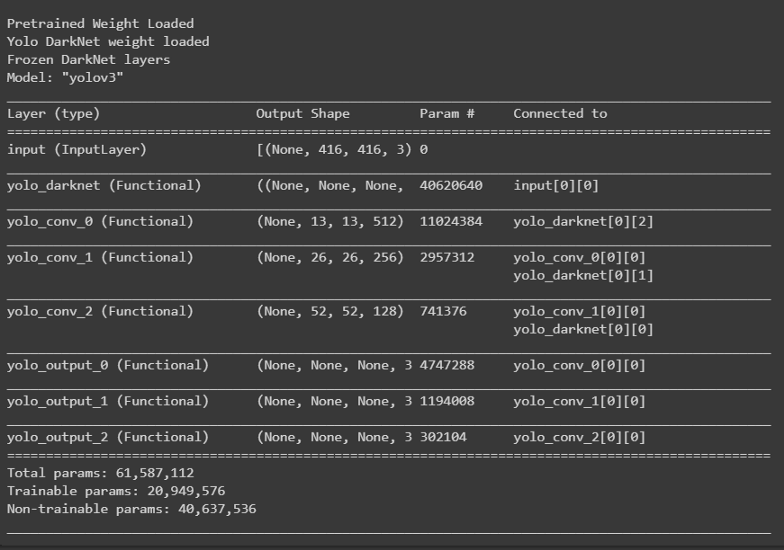
def create_model():
tf.keras.backend.clear_session()
pret_model = YoloV3(size, channels, classes=80)
load_darknet_weights(pret_model, 'Pretrained_Model/yolov3.weights')
print('\nPretrained Weight Loaded')
model = YoloV3(size, channels, classes=3)
model.get_layer('yolo_darknet').set_weights(
pret_model.get_layer('yolo_darknet').get_weights())
print('Yolo DarkNet weight loaded')
freeze_all(model.get_layer('yolo_darknet'))
print('Frozen DarkNet layers')
return model
model = create_model()
model.summary()
tf.keras.backend.clear_session()
epochs = 100
learning_rate=1e-3
optimizer = get_optimizer(
optim_type = 'adam',
learning_rate=1e-3,
decay_type='cosine',
decay_steps=10*600
)
loss = [YoloLoss(yolo_anchors[mask], classes=3) for mask in yolo_anchor_masks]
model = create_model()
model.compile(optimizer=optimizer, loss=loss)
# Tensorbaord
! rm -rf ./logs/
logdir = os.path.join("logs", datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S"))
%tensorboard --logdir $logdir
tensorboard_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.TensorBoard(logdir, histogram_freq=1)
callbacks = [
EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', min_delta=0, patience=15, verbose=1),
ModelCheckpoint('Weights/Best_weight.hdf5', verbose=1, save_best_only=True),
tensorboard_callback,
]
history = model.fit(train_dataset,
epochs=epochs,
callbacks=callbacks,
validation_data=valid_dataset)
model.save('Weights/Last_weight.hdf5')
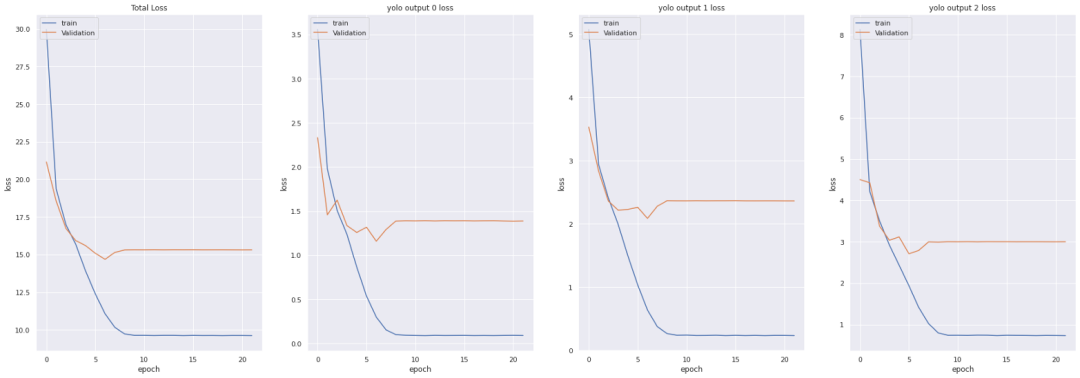
YOLO損失函數(shù):
中心(x,y) 的MSE損失. 邊界框的寬度和高度的均方誤差(MSE) 邊界框的二元交叉熵得分與無目標得分 邊界框多類預測的二元交叉熵或稀疏范疇交叉熵
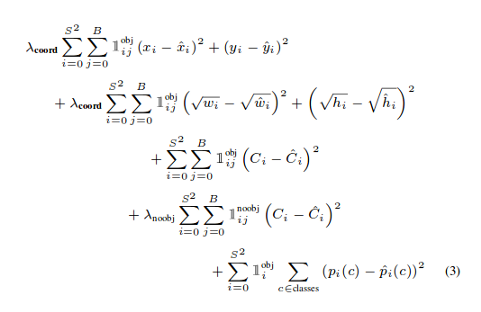
def YoloLoss(anchors, classes=3, ignore_thresh=0.5):
def yolo_loss(y_true, y_pred):
# 1. 轉(zhuǎn)換所有預測輸出
# y_pred: (batch_size, grid, grid, anchors, (x, y, w, h, obj, ...cls))
pred_box, pred_obj, pred_class, pred_xywh = yolo_boxes(
y_pred, anchors, classes)
# predicted (tx, ty, tw, th)
pred_xy = pred_xywh[..., 0:2] #x,y of last channel
pred_wh = pred_xywh[..., 2:4] #w,h of last channel
# 2. 轉(zhuǎn)換所有真實輸出
# y_true: (batch_size, grid, grid, anchors, (x1, y1, x2, y2, obj, cls))
true_box, true_obj, true_class_idx = tf.split(
y_true, (4, 1, 1), axis=-1)
#轉(zhuǎn)換 x1, y1, x2, y2 to x, y, w, h
# x,y = (x2 - x1)/2, (y2-y1)/2
# w, h = (x2- x1), (y2 - y1)
true_xy = (true_box[..., 0:2] + true_box[..., 2:4]) / 2
true_wh = true_box[..., 2:4] - true_box[..., 0:2]
# 小的box要更高權(quán)重
#shape-> (batch_size, grid, grid, anchors)
box_loss_scale = 2 - true_wh[..., 0] * true_wh[..., 1]
# 3. 對pred box進行反向
# 把 (bx, by, bw, bh) 變?yōu)?nbsp;(tx, ty, tw, th)
grid_size = tf.shape(y_true)[1]
grid = tf.meshgrid(tf.range(grid_size), tf.range(grid_size))
grid = tf.expand_dims(tf.stack(grid, axis=-1), axis=2)
true_xy = true_xy * tf.cast(grid_size, tf.float32) - tf.cast(grid, tf.float32)
true_wh = tf.math.log(true_wh / anchors)
true_wh = tf.where(tf.logical_or(tf.math.is_inf(true_wh),
tf.math.is_nan(true_wh)),
tf.zeros_like(true_wh), true_wh)
# 4. 計算所有掩碼
#從張量的形狀中去除尺寸為1的維度。
#obj_mask: (batch_size, grid, grid, anchors)
obj_mask = tf.squeeze(true_obj, -1)
#當iou超過臨界值時,忽略假正例
#best_iou: (batch_size, grid, grid, anchors)
best_iou = tf.map_fn(
lambda x: tf.reduce_max(broadcast_iou(x[0], tf.boolean_mask(
x[1], tf.cast(x[2], tf.bool))), axis=-1),
(pred_box, true_box, obj_mask),
tf.float32)
ignore_mask = tf.cast(best_iou < ignore_thresh, tf.float32)
# 5.計算所有損失
xy_loss = obj_mask * box_loss_scale * \
tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(true_xy - pred_xy), axis=-1)
wh_loss = obj_mask * box_loss_scale * \
tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(true_wh - pred_wh), axis=-1)
obj_loss = binary_crossentropy(true_obj, pred_obj)
obj_loss = obj_mask * obj_loss + \
(1 - obj_mask) * ignore_mask * obj_loss
#TODO:使用binary_crossentropy代替
class_loss = obj_mask * sparse_categorical_crossentropy(
true_class_idx, pred_class)
# 6. 在(batch, gridx, gridy, anchors)求和得到 => (batch, 1)
xy_loss = tf.reduce_sum(xy_loss, axis=(1, 2, 3))
wh_loss = tf.reduce_sum(wh_loss, axis=(1, 2, 3))
obj_loss = tf.reduce_sum(obj_loss, axis=(1, 2, 3))
class_loss = tf.reduce_sum(class_loss, axis=(1, 2, 3))
return xy_loss + wh_loss + obj_loss + class_loss
return yolo_loss
get_mAP(model, 'data/test.csv')

get_mAP(model, 'data/train.csv')
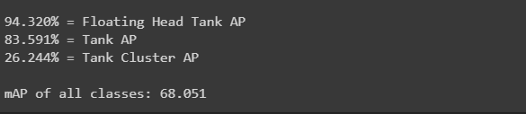
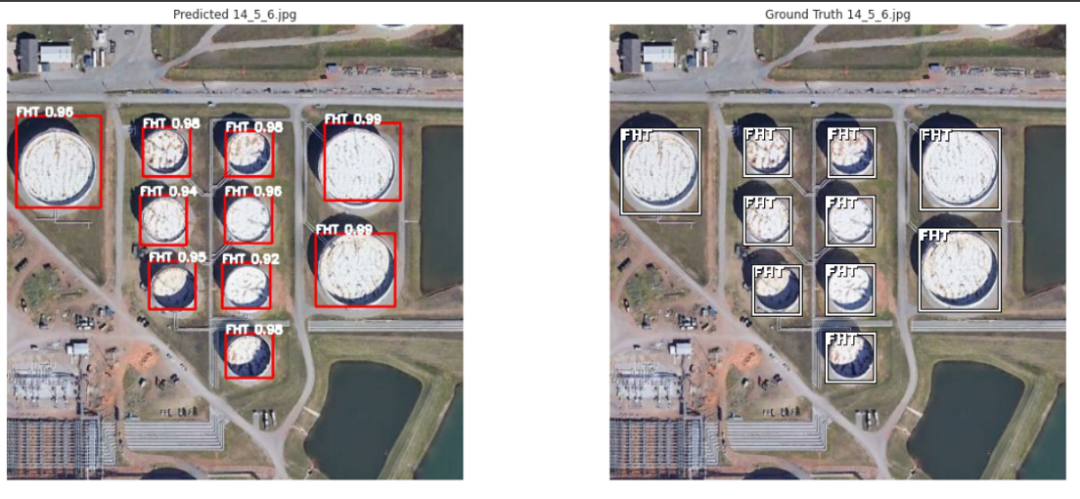
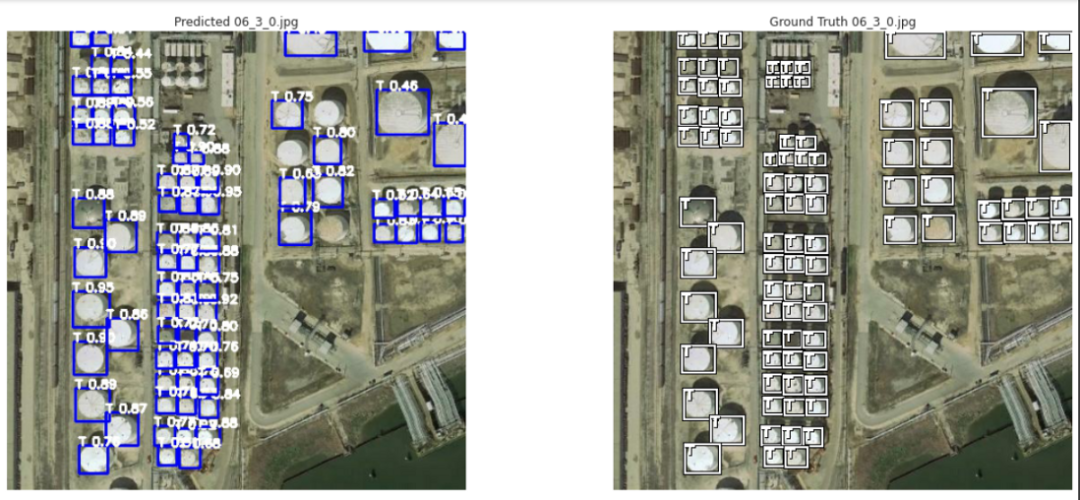
10.儲量估算

11.結(jié)果
12.結(jié)論
只需有限的圖像就可以得到相當好的結(jié)果。 數(shù)據(jù)增強工作得很到位。 在本例中,與RetinaNet模型的現(xiàn)有方法相比,yolov3表現(xiàn)得很好。
好消息!
小白學視覺知識星球
開始面向外開放啦??????
下載1:OpenCV-Contrib擴展模塊中文版教程 在「小白學視覺」公眾號后臺回復:擴展模塊中文教程,即可下載全網(wǎng)第一份OpenCV擴展模塊教程中文版,涵蓋擴展模塊安裝、SFM算法、立體視覺、目標跟蹤、生物視覺、超分辨率處理等二十多章內(nèi)容。 下載2:Python視覺實戰(zhàn)項目52講 在「小白學視覺」公眾號后臺回復:Python視覺實戰(zhàn)項目,即可下載包括圖像分割、口罩檢測、車道線檢測、車輛計數(shù)、添加眼線、車牌識別、字符識別、情緒檢測、文本內(nèi)容提取、面部識別等31個視覺實戰(zhàn)項目,助力快速學校計算機視覺。 下載3:OpenCV實戰(zhàn)項目20講 在「小白學視覺」公眾號后臺回復:OpenCV實戰(zhàn)項目20講,即可下載含有20個基于OpenCV實現(xiàn)20個實戰(zhàn)項目,實現(xiàn)OpenCV學習進階。 交流群
歡迎加入公眾號讀者群一起和同行交流,目前有SLAM、三維視覺、傳感器、自動駕駛、計算攝影、檢測、分割、識別、醫(yī)學影像、GAN、算法競賽等微信群(以后會逐漸細分),請掃描下面微信號加群,備注:”昵稱+學校/公司+研究方向“,例如:”張三 + 上海交大 + 視覺SLAM“。請按照格式備注,否則不予通過。添加成功后會根據(jù)研究方向邀請進入相關(guān)微信群。請勿在群內(nèi)發(fā)送廣告,否則會請出群,謝謝理解~
評論
圖片
表情

