【深度學(xué)習(xí)】我用 PyTorch 復(fù)現(xiàn)了 LeNet-5 神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)(MNIST 手寫數(shù)據(jù)集篇)!
正文開始!
一、使用 LeNet-5 網(wǎng)絡(luò)結(jié)構(gòu)創(chuàng)建 MNIST 手寫數(shù)字識別分類器
MNIST是一個非常有名的手寫體數(shù)字識別數(shù)據(jù)集,訓(xùn)練樣本:共60000個,其中55000個用于訓(xùn)練,另外5000個用于驗證;測試樣本:共10000個。MNIST數(shù)據(jù)集每張圖片是單通道的,大小為28x28。

1.1 下載并加載數(shù)據(jù),并做出一定的預(yù)先處理
由于 MNIST 數(shù)據(jù)集圖片尺寸是 28x28 單通道的,而 LeNet-5 網(wǎng)絡(luò)輸入 Input 圖片尺寸是 32x32,因此使用 transforms.Resize 將輸入圖片尺寸調(diào)整為 32x32。
首先導(dǎo)入 PyToch 的相關(guān)算法庫:
import torchimport torch.nn as nnimport torch.nn.functional as Fimport torch.optim as optimfrom torchvision import datasets, transformsimport timefrom matplotlib import pyplot as plt
pipline_train = transforms.Compose([#隨機旋轉(zhuǎn)圖片transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),#將圖片尺寸resize到32x32transforms.Resize((32,32)),#將圖片轉(zhuǎn)化為Tensor格式transforms.ToTensor(),#正則化(當(dāng)模型出現(xiàn)過擬合的情況時,用來降低模型的復(fù)雜度)transforms.Normalize((0.1307,),(0.3081,))])pipline_test = transforms.Compose([#將圖片尺寸resize到32x32transforms.Resize((32,32)),transforms.ToTensor(),transforms.Normalize((0.1307,),(0.3081,))])#下載數(shù)據(jù)集train_set = datasets.MNIST(root="./data", train=True, download=True, transform=pipline_train)test_set = datasets.MNIST(root="./data", train=False, download=True, transform=pipline_test)#加載數(shù)據(jù)集trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_set, batch_size=32, shuffle=False)
這里要解釋一下 Pytorch MNIST 數(shù)據(jù)集標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化為什么是 transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))??
標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化(Normalization)是神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)對數(shù)據(jù)的一種經(jīng)常性操作。標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化處理指的是:樣本減去它的均值,再除以它的標(biāo)準(zhǔn)差,最終樣本將呈現(xiàn)均值為 0 方差為 1 的數(shù)據(jù)分布。
神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)模型偏愛標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化數(shù)據(jù),原因是均值為0方差為1的數(shù)據(jù)在 sigmoid、tanh 經(jīng)過激活函數(shù)后求導(dǎo)得到的導(dǎo)數(shù)很大,反之原始數(shù)據(jù)不僅分布不均(噪聲大)而且數(shù)值通常都很大(本例中數(shù)值范圍是 0~255),激活函數(shù)后求導(dǎo)得到的導(dǎo)數(shù)則接近與 0,這也被稱為梯度消失。所以說,數(shù)據(jù)的標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化有利于加快神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)的訓(xùn)練。?
除此之外,還需要保持 train_set、val_set 和 test_set 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化系數(shù)的一致性。標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化系數(shù)就是計算要用到的均值和標(biāo)準(zhǔn)差,在本例中是((0.1307,), (0.3081,)),均值是 0.1307,標(biāo)準(zhǔn)差是 0.3081,這些系數(shù)都是數(shù)據(jù)集提供方計算好的數(shù)據(jù)。不同數(shù)據(jù)集就有不同的標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化系數(shù),例如([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])就是 ImageNet dataset 的標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化系數(shù)(RGB三個通道對應(yīng)三組系數(shù)),當(dāng)需要將 Imagenet 預(yù)訓(xùn)練的參數(shù)遷移到另一神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)時,被遷移的神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)就需要使用 Imagenet的系數(shù),否則預(yù)訓(xùn)練不僅無法起到應(yīng)有的作用甚至還會幫倒忙。
1.2 搭建 LeNet-5 神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)結(jié)構(gòu),并定義前向傳播的過程
class LeNet(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(LeNet, self).__init__()self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5)self.relu = nn.ReLU()self.maxpool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)self.maxpool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16*5*5, 120)self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)def forward(self, x):x = self.conv1(x)x = self.relu(x)x = self.maxpool1(x)x = self.conv2(x)x = self.maxpool2(x)x = x.view(-1, 16*5*5)x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))x = self.fc3(x)output = F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)return output
1.3 將定義好的網(wǎng)絡(luò)結(jié)構(gòu)搭載到 GPU/CPU,并定義優(yōu)化器
#創(chuàng)建模型,部署gpudevice = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")model = LeNet().to(device)#定義優(yōu)化器optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
1.4 定義訓(xùn)練過程
def train_runner(model, device, trainloader, optimizer, epoch):#訓(xùn)練模型, 啟用 BatchNormalization 和 Dropout, 將BatchNormalization和Dropout置為Truemodel.train()total = 0correct =0.0#enumerate迭代已加載的數(shù)據(jù)集,同時獲取數(shù)據(jù)和數(shù)據(jù)下標(biāo)for i, data in enumerate(trainloader, 0):inputs, labels = data#把模型部署到device上inputs, labels = inputs.to(device), labels.to(device)#初始化梯度optimizer.zero_grad()#保存訓(xùn)練結(jié)果outputs = model(inputs)#計算損失和#多分類情況通常使用cross_entropy(交叉熵?fù)p失函數(shù)), 而對于二分類問題, 通常使用sigmodloss = F.cross_entropy(outputs, labels)#獲取最大概率的預(yù)測結(jié)果#dim=1表示返回每一行的最大值對應(yīng)的列下標(biāo)predict = outputs.argmax(dim=1)total += labels.size(0)correct += (predict == labels).sum().item()#反向傳播loss.backward()#更新參數(shù)optimizer.step()if i % 1000 == 0:#loss.item()表示當(dāng)前l(fā)oss的數(shù)值print("Train Epoch{} \t Loss: {:.6f}, accuracy: {:.6f}%".format(epoch, loss.item(), 100*(correct/total)))Loss.append(loss.item())Accuracy.append(correct/total)return loss.item(), correct/total
1.5 定義測試過程
def test_runner(model, device, testloader):#模型驗證, 必須要寫, 否則只要有輸入數(shù)據(jù), 即使不訓(xùn)練, 它也會改變權(quán)值#因為調(diào)用eval()將不啟用 BatchNormalization 和 Dropout, BatchNormalization和Dropout置為Falsemodel.eval()#統(tǒng)計模型正確率, 設(shè)置初始值correct = 0.0test_loss = 0.0total = 0#torch.no_grad將不會計算梯度, 也不會進(jìn)行反向傳播with torch.no_grad():for data, label in testloader:data, label = data.to(device), label.to(device)output = model(data)test_loss += F.cross_entropy(output, label).item()predict = output.argmax(dim=1)#計算正確數(shù)量total += label.size(0)correct += (predict == label).sum().item()#計算損失值print("test_avarage_loss: {:.6f}, accuracy: {:.6f}%".format(test_loss/total, 100*(correct/total)))
1.6 運行
LeNet-5 網(wǎng)絡(luò)模型定義好,訓(xùn)練函數(shù)、驗證函數(shù)也定義好了,就可以直接使用 MNIST 數(shù)據(jù)集進(jìn)行訓(xùn)練了。
# 調(diào)用epoch = 5Loss = []Accuracy = []for epoch in range(1, epoch+1):print("start_time",time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',time.localtime(time.time())))loss, acc = train_runner(model, device, trainloader, optimizer, epoch)Loss.append(loss)Accuracy.append(acc)test_runner(model, device, testloader)print("end_time: ",time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',time.localtime(time.time())),'\n')print('Finished Training')plt.subplot(2,1,1)plt.plot(Loss)plt.title('Loss')plt.show()plt.subplot(2,1,2)plt.plot(Accuracy)plt.title('Accuracy')plt.show()

經(jīng)歷 5 次 epoch 的 loss 和 accuracy 曲線如下:
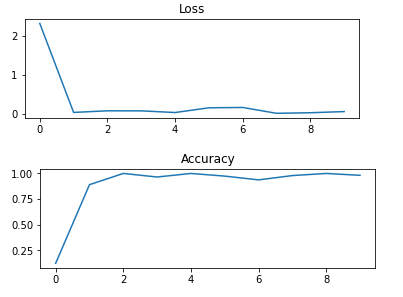
最終在 10000 張測試樣本上,average_loss降到了?0.00228,accuracy 達(dá)到了 97.72%。可以說 LeNet-5 的效果非常好!
1.7 保存模型
print(model)torch.save(model, './models/model-mnist.pth') #保存模型
LeNet-5 的模型會 print 出來,并將模型模型命令為 model-mnist.pth 保存在固定目錄下。
LeNet(
(conv1): Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(relu): ReLU()
(maxpool1): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(conv2): Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(maxpool2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(fc1): Linear(in_features=400, out_features=120, bias=True)
(fc2): Linear(in_features=120, out_features=84, bias=True)
(fc3): Linear(in_features=84, out_features=10, bias=True)
)1.8 手寫圖片的測試
下面,我們將利用剛剛訓(xùn)練的 LeNet-5 模型進(jìn)行手寫數(shù)字圖片的測試。
import cv2if __name__ == '__main__':device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')model = torch.load('./models/model-mnist.pth') #加載模型model = model.to(device)model.eval() #把模型轉(zhuǎn)為test模式#讀取要預(yù)測的圖片img = cv2.imread("./images/test_mnist.jpg")img=cv2.resize(img,dsize=(32,32),interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)plt.imshow(img,cmap="gray") # 顯示圖片plt.axis('off') # 不顯示坐標(biāo)軸plt.show()# 導(dǎo)入圖片,圖片擴展后為[1,1,32,32]trans = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(),transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))])img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)#圖片轉(zhuǎn)為灰度圖,因為mnist數(shù)據(jù)集都是灰度圖img = trans(img)img = img.to(device)????img?=?img.unsqueeze(0)??#圖片擴展多一維,因為輸入到保存的模型中是4維的[batch_size,通道,長,寬],而普通圖片只有三維,[通道,長,寬]????# 預(yù)測output = model(img)prob = F.softmax(output,dim=1) #prob是10個分類的概率print("概率:",prob)value, predicted = torch.max(output.data, 1)predict = output.argmax(dim=1)print("預(yù)測類別:",predict.item())

輸出:
概率:tensor([[2.0888e-07, 1.1599e-07, 6.1852e-05, 1.5797e-04, 1.4975e-09, 9.9977e-01,
? ? ? ? 1.9271e-06, 3.1589e-06, 1.2186e-07, 4.3405e-07]],
? ? ? grad_fn=) 預(yù)測類別:5
模型預(yù)測結(jié)果正確!
以上就是 PyTorch 構(gòu)建 LeNet-5 卷積神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)并用它來識別 MNIST 數(shù)據(jù)集的例子。全文的代碼都是可以順利運行的,建議大家自己跑一邊。
所有完整的代碼我都放在 GitHub 上,GitHub地址為:
https://github.com/RedstoneWill/ObjectDetectionLearner/tree/main/LeNet-5
也可以點擊閱讀原文進(jìn)入~
往期精彩回顧
