前端應(yīng)該掌握的編譯基礎(chǔ)(基于 babel)
- 作者:陳大魚(yú)頭
- github: KRISACHAN
開(kāi)發(fā)息息相關(guān)
雖然 Babel 團(tuán)隊(duì)在各種哭窮,但是 Babel 始終是我們前端在開(kāi)發(fā)中不可或缺的重要工具。 雖然我們只是 API 調(diào)用工,但是多了解一些總是會(huì)有好處的嘛 ??????
什么是編譯器?
編譯器(compiler)是一種計(jì)算機(jī)程序,它會(huì)將某種編程語(yǔ)言寫(xiě)成的源代碼(原始語(yǔ)言)轉(zhuǎn)換成另一種編程語(yǔ)言(目標(biāo)語(yǔ)言)。
源代碼(source code)→ 預(yù)處理器(preprocessor)→ 編譯器(compiler)→ 匯編程序(assembler)→ 目標(biāo)代碼(object code)→ 鏈接器(linker)→ 可執(zhí)行文件(executables),最后打包好的文件就可以給電腦去判讀運(yùn)行了。
什么是解釋器?
解釋器(英語(yǔ):interpreter),是一種計(jì)算機(jī)程序,能夠把解釋型語(yǔ)言解釋執(zhí)行。解釋器就像一位“中間人”。解釋器邊解釋邊執(zhí)行,因此依賴于解釋器的程序運(yùn)行速度比較緩慢。解釋器的好處是它不需要重新編譯整個(gè)程序,從而減輕了每次程序更新后編譯的負(fù)擔(dān)。相對(duì)的編譯器一次性將所有源代碼編譯成二進(jìn)制文件,執(zhí)行時(shí)無(wú)需依賴編譯器或其他額外的程序。
跟編譯器的區(qū)別就是一個(gè)是邊編譯邊執(zhí)行,一個(gè)是編譯完才執(zhí)行。
高級(jí)語(yǔ)言編譯器步驟
- 輸入源程序字符流
- 詞法分析
- 語(yǔ)法分析
- 語(yǔ)義分析
- 中間代碼生成
- 機(jī)器無(wú)關(guān)代碼優(yōu)化
- 代碼生成
- 機(jī)器相關(guān)代碼優(yōu)化
- 目標(biāo)代碼生成
V8 編譯 JS 代碼的過(guò)程
- 生成抽象語(yǔ)法樹(shù)(AST)和執(zhí)行上下文
- 第一階段是分詞(tokenize),又稱為詞法分析
- 第二階段是解析(parse),又稱為語(yǔ)法分析
- 生成字節(jié)碼
- 字節(jié)碼就是介于 AST 和機(jī)器碼之間的一種代碼。但是與特定類型的機(jī)器碼無(wú)關(guān),字節(jié)碼需要通過(guò)解釋器將其轉(zhuǎn)換為機(jī)器碼后才能執(zhí)行。
- 執(zhí)行代碼
JS 執(zhí)行代碼的過(guò)程
- 執(zhí)行全局代碼時(shí),創(chuàng)建全局上下文
- 調(diào)用函數(shù)時(shí),創(chuàng)建函數(shù)上下文
- 使用 eval 函數(shù)時(shí),創(chuàng)建 eval 上下文
- 執(zhí)行局部代碼時(shí),創(chuàng)建局部上下文
關(guān)于 Babel
Babel ,又名 Babel.js。 是一個(gè)用于 web 開(kāi)發(fā),且自由開(kāi)源的 JavaScript 編譯器、轉(zhuǎn)譯器。
Babel 的編譯流程:
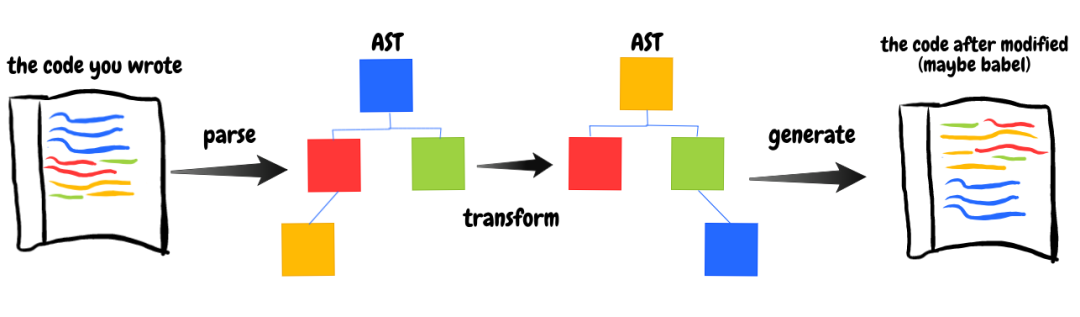
圖片來(lái)源:透過(guò)製作 Babel-plugin 初訪 AST
Parse
Babel 的第一步就是將源碼轉(zhuǎn)換為抽象語(yǔ)法樹(shù)(AST)
const?babel?=?require('@babel/core');
const?{?parseAsync?}?=?babel;
const?parseCode?=?async?(code?=?'',?options?=?{})?=>?{
??const?res?=?await?parseAsync(code,?options);
};
parseCode(`
??const?a?=?1;
`)
可通過(guò) https://astexplorer.net/ 在線查看具體結(jié)果
這一步會(huì)將收集到的的代碼,通過(guò) 詞法分析(Lexical analysis) 跟 語(yǔ)法分析(Parsing) 兩個(gè)階段將代碼轉(zhuǎn)換成 AST
詞法分析(Lexical analysis)
詞法分析會(huì)將代碼轉(zhuǎn)為 token ,可以理解為是對(duì)每個(gè)不可分割單詞元的描述,例如 const 就會(huì)轉(zhuǎn)換成下面這樣:
Token?{
????type:?
????????TokenType?{
????????label:?'const',
????????keyword:?'const',
????????beforeExpr:?false,
????????startsExpr:?false,
????????rightAssociative:?false,
????????isLoop:?false,
????????isAssign:?false,
????????prefix:?false,
????????postfix:?false,
????????binop:?null,
????????updateContext:?null
????},
????value:?'const',
????start:?5,
????end:?10,
????loc:?
????SourceLocation?{
????????start:?Position?{?line:?2,?column:?4?},
????????end:?Position?{?line:?2,?column:?9?},
????????filename:?undefined,
????????identifierName:?undefined
????}
}
type 就是 對(duì) token 的描述,如果想要查看 bebal 生成的 token,我們可以在 options 里寫(xiě)入:
parserOpts:?{
??tokens:?true
}
關(guān)于 @babel/parser ?更多配置,可查看:https://babeljs.io/docs/en/babel-parser#options
語(yǔ)法分析(Parsing)
語(yǔ)法分析則是將上述的 token 轉(zhuǎn)換成對(duì)應(yīng)的 ast 結(jié)構(gòu)
所以我們就可以看到這樣的一段樹(shù)狀結(jié)構(gòu)(過(guò)濾部分信息)
{
????"type":?"VariableDeclaration",
????"start":?0,
????"end":?14,
????"loc":?{
????????"start":?{
????????????"line":?1,
????????????"column":?0
????????},
????????"end":?{
????????????"line":?1,
????????????"column":?14
????????}
????},
????"declarations":?[
????????{
????????????"type":?"VariableDeclarator",
????????????"start":?6,
????????????"end":?13,
????????????"loc":?{
????????????????"start":?{
????????????????????"line":?1,
????????????????????"column":?6
????????????????},
????????????????"end":?{
????????????????????"line":?1,
????????????????????"column":?13
????????????????}
????????????},
????????????"id":?{
????????????????"type":?"Identifier",
????????????????"start":?6,
????????????????"end":?9,
????????????????"loc":?{
????????????????????"start":?{
????????????????????????"line":?1,
????????????????????????"column":?6
????????????????????},
????????????????????"end":?{
????????????????????????"line":?1,
????????????????????????"column":?9
????????????????????},
????????????????????"identifierName":?"abc"
????????????????},
????????????????"name":?"abc"
????????????},
????????????"init":?{
????????????????"type":?"NumericLiteral",
????????????????"start":?12,
????????????????"end":?13,
????????????????"loc":?{
????????????????????"start":?{
????????????????????????"line":?1,
????????????????????????"column":?12
????????????????????},
????????????????????"end":?{
????????????????????????"line":?1,
????????????????????????"column":?13
????????????????????}
????????????????},
????????????????"extra":?{
????????????????????"rawValue":?1,
????????????????????"raw":?"1"
????????????????},
????????????????"value":?1
????????????}
????????}
????],
????"kind":?"const"
}
這樣與 type 同級(jí)的結(jié)構(gòu)就叫 ?節(jié)點(diǎn)(Node) , loc ,start ,end 則是位置信息
Transform
Babel 的第二步就是遍歷 AST,并調(diào)用 transform 以訪問(wèn)者模式進(jìn)行修改
export?default?function?(babel)?{
??const?{?types:?t?}?=?babel;
??
??return?{
????name:?"ast-transform",?//?not?required
????visitor:?{
??????Identifier(path)?{
????????path.node.name?=?path.node.name.split('').reverse().join('');
??????}
????}
??};
}
通過(guò)執(zhí)行上述的 transform ,我們可以有:
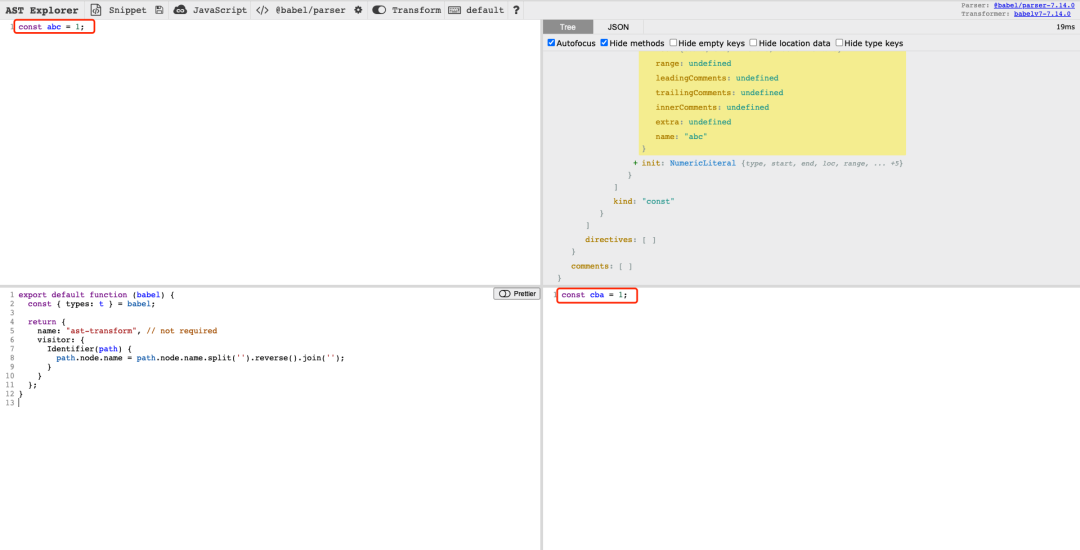
上述功能也可通過(guò) https://astexplorer.net/ 在線查看
Generate
Babel 的第三步就是把轉(zhuǎn)換后的 AST 打印成目標(biāo)代碼,并生成 sourcemap
開(kāi)發(fā)一個(gè) babel 插件
前置知識(shí) - 訪問(wèn)者模式
訪問(wèn)者模式: 在訪問(wèn)者模式(Visitor Pattern)中,我們使用了一個(gè)訪問(wèn)者類,它改變了元素類的執(zhí)行算法。通過(guò)這種方式,元素的執(zhí)行算法可以隨著訪問(wèn)者改變而改變。這種類型的設(shè)計(jì)模式屬于行為型模式。根據(jù)模式,元素對(duì)象已接受訪問(wèn)者對(duì)象,這樣訪問(wèn)者對(duì)象就可以處理元素對(duì)象上的操作。
知道你們不想看文字描述,所以直接上代碼!
class?漢堡包?{
????accept(fatBoyVisitor)?{
????????fatBoyVisitor.visit(this);
????}
};
class?薯?xiàng)l?{
????accept(fatBoyVisitor)?{
????????fatBoyVisitor.visit(this);
????}
};
class?炸雞?{
????accept(fatBoyVisitor)?{
????????fatBoyVisitor.visit(this);
????}
};
class?FatBoy?{
????constructor(foods)?{
????????this.foods?=?foods;
????}
????accept(fatBoyFoodVisitor)?{
????????this.foods.forEach(food?=>?{
????????????food.accept(fatBoyFoodVisitor);
????????});
????}
};
class?FatBoyFoodVisitor?{
????visit(food)?{
????????console.log(`肥宅吃了${food.constructor.name}`);
????}
};
const?fatBoy?=?new?FatBoy([new?漢堡包(),?new?薯?xiàng)l(),?new?炸雞()]);
fatBoy.accept(new?FatBoyFoodVisitor());
最終輸出結(jié)果是:
肥宅吃了漢堡包
肥宅吃了薯?xiàng)l
肥宅吃了炸雞
babel-plugin-transform-object-assign 源碼
import?{?declare?}?from?"@babel/helper-plugin-utils";
export?default?declare(api?=>?{
??api.assertVersion(7);
??return?{
????name:?"transform-object-assign",
????visitor:?{
??????CallExpression:?function(path,?file)?{
????????if?(path.get("callee").matchesPattern("Object.assign"))?{
??????????path.node.callee?=?file.addHelper("extends");
????????}
??????},
????},
??};
});
上面的就是 babel-plugin-transform-object-assign 的源碼。
- declare:是一個(gè)用于簡(jiǎn)化創(chuàng)建 transformer 的工具函數(shù)
- assertVersion:檢查當(dāng)前 babel 的大版本
- name:當(dāng)前插件的名字
- visitor:對(duì)外提供修改內(nèi)容的訪問(wèn)者
- CallExpression:函數(shù)調(diào)用的
type,每一句代碼都會(huì)生成對(duì)應(yīng)的type,例如最上面的函數(shù)名abc則對(duì)應(yīng)的是一個(gè)Identifier類型,如果需要修改某一個(gè)type的代碼,則在里面創(chuàng)建對(duì)應(yīng)的type訪問(wèn)者進(jìn)行修改即可。
具體生成的代碼如下:
//?input
const?a?=?Object.assign({?a:?1?},?{?b:?2?});
//?output
"use?strict";
function?_extends()?{?_extends?=?Object.assign?||?function?(target)?{?for?(var?i?=?1;?i?arguments.length;?i++)?{?var?source?=?arguments[i];?for?(var?key?in?source)?{?if?(Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(source,?key))?{?target[key]?=?source[key];?}?}?}?return?target;?};?return?_extends.apply(this,?arguments);?}
const?a?=?_extends({
??a:?1
},?{
??b:?2
});
Babel 插件實(shí)戰(zhàn) - 清除 console 源碼
先上代碼:
const?babel?=?require('@babel/core');
const?get?=?require('lodash/get');
const?eq?=?require('lodash/eq');
const?{?transformAsync?}?=?babel;
const?removeConsole?=?rootPath?=>?({
????visitor:?{
????????ExpressionStatement:?path?=>?{
????????????const?name?=?get(path,?'node.expression.callee.object.name');
????????????const?CONSOLE_PREFIX?=?'console';
????????????if?(!eq(name,?CONSOLE_PREFIX))?{
????????????????return;
????????????};
????????????path.remove();
????????},
????}
});
const?transformCode?=?async?(code?=?'')?=>?{
????const?res?=?await?transformAsync(code,?{
????????plugins:?[
????????????removeConsole,
????????],
????});
????console.log(res.code);
};
transformCode(`
????const?a?=?10;
????console.group('嚶嚶嚶');
????console.log(a);
????console.groupEnd();
`);
輸出結(jié)果:
const?a?=?10;
上面的功能就是我們?cè)诼暶髡Z(yǔ)句類型 ExpressionStatement 中實(shí)現(xiàn)的。
node.expression 對(duì)應(yīng)的是當(dāng)前類型里的子表達(dá)式,在這個(gè)場(chǎng)景里,它的 type === 'CallExpression'。
callee 對(duì)應(yīng)的就是一個(gè)調(diào)用函數(shù)類型,在這個(gè)場(chǎng)景里,它的 type === 'MemberExpression'。
object 對(duì)應(yīng)的就是當(dāng)前調(diào)用函數(shù)的前置對(duì)象,它的 type === 'Identifier',name 則是 console。
所以我們的實(shí)現(xiàn)就很簡(jiǎn)單了,只要 name === 'console' ,我們就可以通過(guò)內(nèi)部暴露的 remove 方法直接刪除當(dāng)前代碼。
Babel 插件實(shí)戰(zhàn) - 新的語(yǔ)法
眾所周知,JS 不能這么寫(xiě)
#?python
arr?=?[1,?2,?3]
print(arr[-1])?#?3
print(arr[len(arr)?-?1])?#?3
但是我們可以用魔法打敗魔法
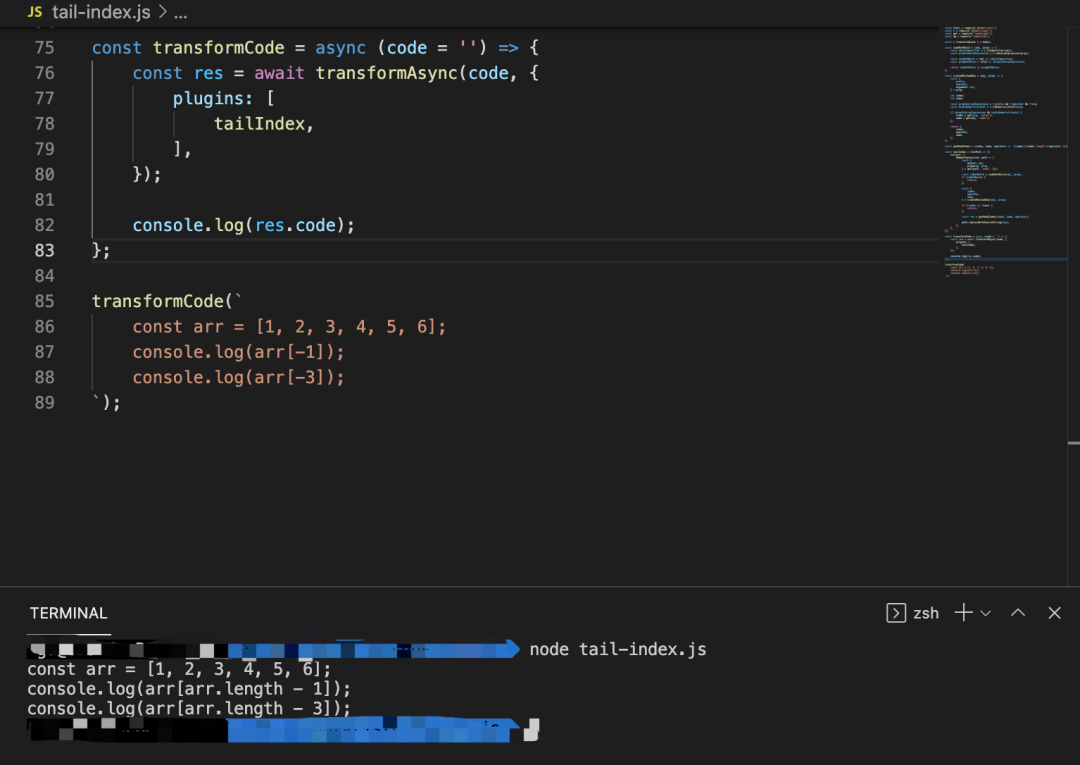
作為一個(gè)兇起來(lái)連自己都可以編譯的語(yǔ)言,這有多難呢~
具體實(shí)現(xiàn)如下:
const?babel?=?require('@babel/core');
const?get?=?require('lodash/get');
const?tailIndex?=?rootPath?=>?({
????visitor:?{
????????MemberExpression:?path?=>?{
????????????const?{
????????????????object:?obj,
????????????????property:?prop,
????????????}?=?get(path,?'node',?{});
????????????const?isNotMatch?=?codeNotMatch(obj,?prop);
????????????if?(isNotMatch)?{
????????????????return;
????????????};
????????????const?{
????????????????index,
????????????????operator,
????????????????name,
????????????}?=?createMatchedKeys(obj,?prop);
????????????if?(!index?||?!name)?{
????????????????return;
????????????};
????????????const?res?=?genHeadIndex(index,?name,?operator);
????????????path.replaceWithSourceString(res);
????????},
????},
});
MemberExpression 就是當(dāng)前要處理的語(yǔ)句類型。
codeNotMatch 是我們自己實(shí)現(xiàn)的函數(shù),用于判斷 node.object 跟 node.property 是否合法,具體實(shí)現(xiàn)如下:
const?t?=?require('@babel/types');
const?codeNotMatch?=?(obj,?prop)?=>?{
????const?objIsIdentifier?=?t.isIdentifier(obj);
????const?propIsUnaryExpression?=?t.isUnaryExpression(prop);
????const?objNotMatch?=?!obj?||?!objIsIdentifier;
????const?propNotMatch?=?!prop?||?!propIsUnaryExpression;
????return?objNotMatch?||?propNotMatch;
};
這里的 require('@babel/types') 是 babel 的一個(gè)工具包,這里面我們運(yùn)用了它的語(yǔ)句判斷能力。這種 isXXX 的大體實(shí)現(xiàn)如下:
function?isIdentifier(node,?opts)?{
??if?(!node)?return?false;
??const?nodeType?=?node.type;
??if?(nodeType?===?具體類型)?{
????if?(typeof?opts?===?"undefined")?{
??????return?true;
????}?else?{
??????return?shallowEqual(node,?opts);
????}
??}
??return?false;
}
上面的 shallowEqual 實(shí)現(xiàn)如下:
function?shallowEqual(actual,?expected)?{
??const?keys?=?Object.keys(expected);
??for?(const?key?of?keys)?{
????if?(actual[key]?!==?expected[key])?{
??????return?false;
????}
??}
??return?true;
}
createMatchedKeys 用于創(chuàng)建最終匹配的字符,即需要將 -1 改為 .length - 1 的形式,所以具體實(shí)現(xiàn)如下:
const?createMatchedKeys?=?(obj,?prop)?=>?{
????const?{
????????prefix,
????????operator,
????????argument:?arg
????}?=?prop;
????let?index;
????let?name;
????const?propIsArrayExpression?=?!!prefix?&&?!!operator?&&?!!arg;
????const?argIsNumericLiteral?=?t.isNumericLiteral(arg);
????if?(propIsArrayExpression?&&?argIsNumericLiteral)?{
????????index?=?get(arg,?'value');
????????name?=?get(obj,?'name');
????};
????return?{
????????index,
????????operator,
????????name,
????};
};
這里面一路判斷,匹配即可。
所以當(dāng)我們拿到下標(biāo) ,操作符 跟 數(shù)組名 之后,直接組合成最終要生成的代碼即可,即有:
const?genHeadIndex?=?(index,?name,?operator)?=>?`${name}[${name}.length?${operator}?${index}]`;
最后我們直接替換源碼即可,怎么替換呢,babel 有通過(guò)訪問(wèn)者模式返回 replaceWithSourceString 方法進(jìn)行硬編碼替換。。。
替換的邏輯就是先通過(guò) ?babel.parse ?將要替換的代碼生成 ast,然后從 loc 到具體的 node 進(jìn)行替換。
一個(gè)新語(yǔ)法,就這么完成啦~
參考資料
- 透過(guò)製作 Babel-plugin 初訪 AST
- 詞法分析(Lexical analysis)
- 語(yǔ)法分析(Parsing)
- https://babeljs.io/docs/en/babel-parser#options
- https://astexplorer.net/
- https://github.com/babel/babel
- https://github.com/babel/minify
- 『1W7字中高級(jí)前端面試必知必會(huì)』終極版
- Babel 插件手冊(cè)
往期推薦
聊聊 Typescript 中的 extends 關(guān)鍵字
React 全局狀態(tài)管理的 3 種底層機(jī)制
WebSocket 基礎(chǔ)與應(yīng)用系列(一)—— 抓個(gè) WebSocket 的包
深入對(duì)比 eslint 插件 和 babel 插件的異同點(diǎn)
六個(gè)問(wèn)題讓你更懂 React Fiber,了解框架底層渲染邏輯
點(diǎn)擊下方“技術(shù)漫談”,選擇“設(shè)為星標(biāo)”第一時(shí)間關(guān)注技術(shù)干貨!
