20 個實例玩轉 Java 8 Stream
回復架構師獲取資源
大家好,我是架構君,一個會寫代碼吟詩的架構師。
先貼上幾個案例,水平高超的同學可以挑戰(zhàn)一下:
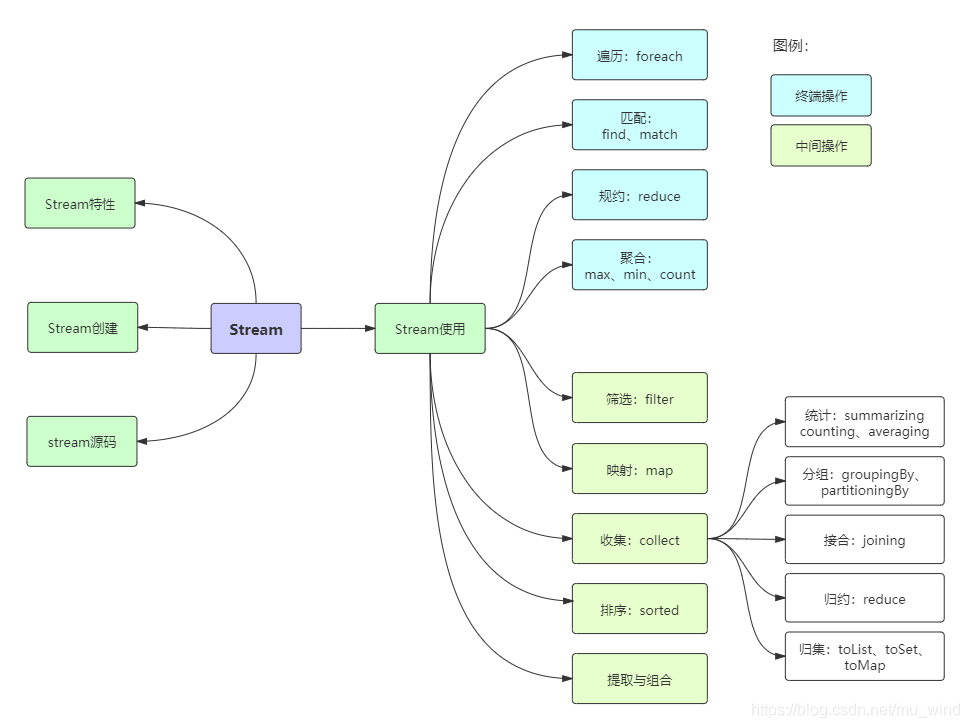
Stream,配合同版本出現(xiàn)的 Lambda ,給我們操作集合(Collection)提供了極大的便利。Stream?Stream將要處理的元素集合看作一種流,在流的過程中,借助Stream API對流中的元素進行操作,比如:篩選、排序、聚合等。Stream可以由數(shù)組或集合創(chuàng)建,對流的操作分為兩種:1. 中間操作,每次返回一個新的流,可以有多個。
2. 終端操作,每個流只能進行一次終端操作,終端操作結束后流無法再次使用。終端操作會產(chǎn)生一個新的集合或值。
Stream有幾個特性:1. stream不存儲數(shù)據(jù),而是按照特定的規(guī)則對數(shù)據(jù)進行計算,一般會輸出結果。
2. stream不會改變數(shù)據(jù)源,通常情況下會產(chǎn)生一個新的集合或一個值。
3. stream具有延遲執(zhí)行特性,只有調(diào)用終端操作時,中間操作才會執(zhí)行。
Stream可以通過集合數(shù)組創(chuàng)建。java.util.Collection.stream() 方法用集合創(chuàng)建流List list?= Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c");
// 創(chuàng)建一個順序流
Stream stream = list.stream();
// 創(chuàng)建一個并行流
Stream parallelStream = list.parallelStream(); java.util.Arrays.stream(T[] array)方法用數(shù)組創(chuàng)建流int[] array={1,3,5,6,8};
IntStream stream = Arrays.stream(array);Stream的靜態(tài)方法:of()、iterate()、generate()Stream stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);
Stream stream2 = Stream.iterate(0, (x) -> x + 3).limit(4);
stream2.forEach(System.out::println);
Stream stream3 = Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(3);
stream3.forEach(System.out::println); 0 3 6 9
0.6796156909271994
0.1914314208854283
0.8116932592396652
stream和parallelStream的簡單區(qū)分: stream是順序流,由主線程按順序對流執(zhí)行操作,而parallelStream是并行流,內(nèi)部以多線程并行執(zhí)行的方式對流進行操作,但前提是流中的數(shù)據(jù)處理沒有順序要求。例如篩選集合中的奇數(shù),兩者的處理不同之處: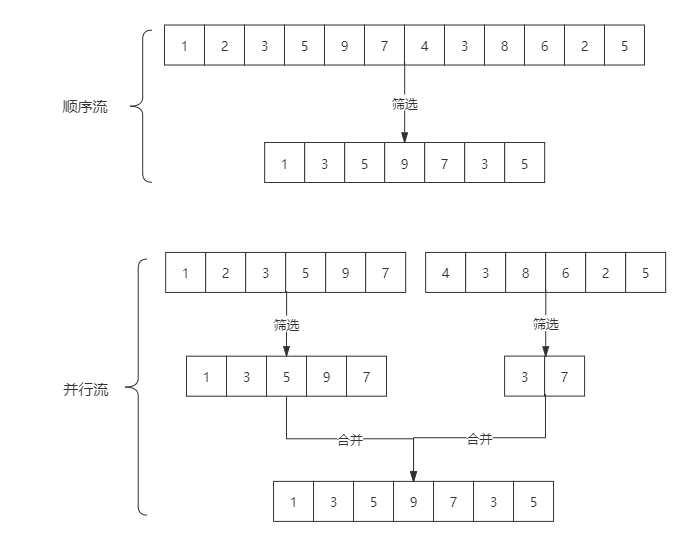
如果流中的數(shù)據(jù)量足夠大,并行流可以加快處速度。除了直接創(chuàng)建并行流,還可以通過parallel()把順序流轉換成并行流:
Optional findFirst = list.stream().parallel().filter(x->x>6).findFirst(); 在使用stream之前,先理解一個概念:Optional 。
Optional類是一個可以為null的容器對象。如果值存在則isPresent()方法會返回true,調(diào)用get()方法會返回該對象。
更詳細說明請見:菜鳥教程Java 8 Optional類

案例使用的員工類
List personList = new?ArrayList();
personList.add(new?Person("Tom", 8900, "male", "New York"));
personList.add(new?Person("Jack", 7000, "male", "Washington"));
personList.add(new?Person("Lily", 7800, "female", "Washington"));
personList.add(new?Person("Anni", 8200, "female", "New York"));
personList.add(new?Person("Owen", 9500, "male", "New York"));
personList.add(new?Person("Alisa", 7900, "female", "New York"));
class?Person?{
??private?String name; // 姓名
??private?int?salary; // 薪資
??private?int?age; // 年齡
??private?String sex; //性別
??private?String area; // 地區(qū)
??// 構造方法
??public?Person(String name, int?salary, int?age,String sex,String area) {
????this.name = name;
????this.salary = salary;
????this.age = age;
????this.sex = sex;
????this.area = area;
??}
??// 省略了get和set,請自行添加
} 3.1 遍歷/匹配(foreach/find/match)
Stream也是支持類似集合的遍歷和匹配元素的,只是Stream中的元素是以Optional類型存在的。Stream的遍歷、匹配非常簡單。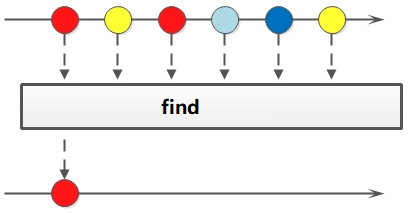
// import已省略,請自行添加,后面代碼亦是
public?class?StreamTest?{
??public?static?void main(String[] args) {
????????List list?= Arrays.asList(7, 6, 9, 3, 8, 2, 1);
????????// 遍歷輸出符合條件的元素
????????list.stream().filter(x -> x > 6).forEach(System.out::println);
????????// 匹配第一個
????????Optional findFirst = list.stream().filter(x -> x > 6).findFirst();
????????// 匹配任意(適用于并行流)
????????Optional findAny = list.parallelStream().filter(x -> x > 6).findAny();
????????// 是否包含符合特定條件的元素
????????boolean anyMatch = list.stream().anyMatch(x -> x < 6);
????????System.out.println("匹配第一個值:"?+ findFirst.get());
????????System.out.println("匹配任意一個值:"?+ findAny.get());
????????System.out.println("是否存在大于6的值:"?+ anyMatch);
????}
} 3.2 篩選(filter)
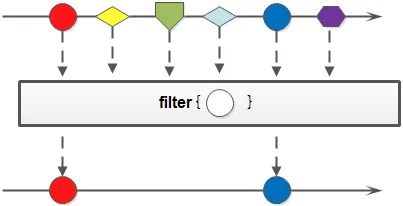
Integer集合中大于7的元素,并打印出來public?class?StreamTest?{
??public?static?void main(String[] args) {
????List list?= Arrays.asList(6, 7, 3, 8, 1, 2, 9);
????Stream stream = list.stream();
????stream.filter(x -> x > 7).forEach(System.out::println);
??}
} 8 9
collect(收集),后文有詳細介紹。public?class?StreamTest?{
??public?static?void main(String[] args) {
????List personList = new?ArrayList();
????personList.add(new?Person("Tom", 8900, 23, "male", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Jack", 7000, 25, "male", "Washington"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Lily", 7800, 21, "female", "Washington"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Anni", 8200, 24, "female", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Owen", 9500, 25, "male", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Alisa", 7900, 26, "female", "New York"));
????List fiterList = personList.stream().filter(x -> x.getSalary() > 8000).map(Person::getName)
????????.collect(Collectors.toList());
????System.out.print("高于8000的員工姓名:"?+ fiterList);
??}
} 高于8000的員工姓名:[Tom, Anni, Owen]
3.3 聚合(max/min/count)
max、min、count這些字眼你一定不陌生,沒錯,在mysql中我們常用它們進行數(shù)據(jù)統(tǒng)計。Java stream中也引入了這些概念和用法,極大地方便了我們對集合、數(shù)組的數(shù)據(jù)統(tǒng)計工作。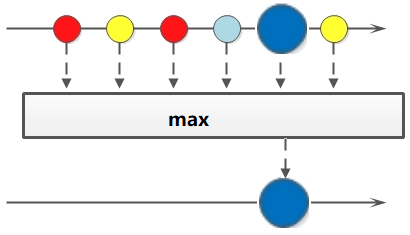
String集合中最長的元素。public?class?StreamTest?{
??public?static?void main(String[] args) {
????List list?= Arrays.asList("adnm", "admmt", "pot", "xbangd", "weoujgsd");
????Optional max = list.stream().max(Comparator.comparing(String::length));
????System.out.println("最長的字符串:"?+ max.get());
??}
} 最長的字符串:weoujgsd
Integer集合中的最大值。public?class?StreamTest?{
??public?static?void?main(String[] args)?{
????List list?= Arrays.asList(7, 6, 9, 4, 11, 6);
????// 自然排序
????Optional max = list.stream().max(Integer::compareTo);
????// 自定義排序
????Optional max2 = list.stream().max(new?Comparator() {
??????@Override
??????public?int?compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
????????return?o1.compareTo(o2);
??????}
????});
????System.out.println("自然排序的最大值:"?+ max.get());
????System.out.println("自定義排序的最大值:"?+ max2.get());
??}
} 自然排序的最大值:11
自定義排序的最大值:11
public?class?StreamTest?{
??public?static?void main(String[] args) {
????List personList = new?ArrayList();
????personList.add(new?Person("Tom", 8900, 23, "male", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Jack", 7000, 25, "male", "Washington"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Lily", 7800, 21, "female", "Washington"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Anni", 8200, 24, "female", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Owen", 9500, 25, "male", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Alisa", 7900, 26, "female", "New York"));
????Optional max = personList.stream().max(Comparator.comparingInt(Person::getSalary));
????System.out.println("員工工資最大值:"?+ max.get().getSalary());
??}
} 員工工資最大值:9500
Integer集合中大于6的元素的個數(shù)。import?java.util.Arrays;
import?java.util.List;
public?class?StreamTest?{
??public?static?void?main(String[] args)?{
????List list?= Arrays.asList(7, 6, 4, 8, 2, 11, 9);
????long?count = list.stream().filter(x -> x > 6).count();
????System.out.println("list中大于6的元素個數(shù):"?+ count);
??}
} list中大于6的元素個數(shù):4
3.4 映射(map/flatMap)
map和flatMap:map:接收一個函數(shù)作為參數(shù),該函數(shù)會被應用到每個元素上,并將其映射成一個新的元素。flatMap:接收一個函數(shù)作為參數(shù),將流中的每個值都換成另一個流,然后把所有流連接成一個流。
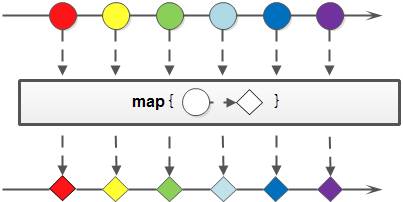

public?class?StreamTest?{
??public?static?void main(String[] args) {
????String[] strArr = { "abcd", "bcdd", "defde", "fTr"?};
????List strList = Arrays.stream(strArr).map(String::toUpperCase).collect(Collectors.toList());
????List intList = Arrays.asList(1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11);
????List intListNew = intList.stream().map(x -> x + 3).collect(Collectors.toList());
????System.out.println("每個元素大寫:"?+ strList);
????System.out.println("每個元素+3:"?+ intListNew);
??}
} 每個元素大寫:[ABCD, BCDD, DEFDE, FTR]
每個元素+3:[4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14]
public?class?StreamTest?{
??public?static?void?main(String[] args) {
????List personList = new?ArrayList();
????personList.add(new?Person("Tom", 8900, 23, "male", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Jack", 7000, 25, "male", "Washington"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Lily", 7800, 21, "female", "Washington"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Anni", 8200, 24, "female", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Owen", 9500, 25, "male", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Alisa", 7900, 26, "female", "New York"));
????// 不改變原來員工集合的方式
????List personListNew = personList.stream().map(person -> {
??????Person personNew = new?Person(person.getName(), 0, 0, null, null);
??????personNew.setSalary(person.getSalary() + 10000);
??????return?personNew;
????}).collect(Collectors.toList());
????System.out.println("一次改動前:"?+ personList.get(0).getName() + "-->"?+ personList.get(0).getSalary());
????System.out.println("一次改動后:"?+ personListNew.get(0).getName() + "-->"?+ personListNew.get(0).getSalary());
????// 改變原來員工集合的方式
????List personListNew2 = personList.stream().map(person -> {
??????person.setSalary(person.getSalary() + 10000);
??????return?person;
????}).collect(Collectors.toList());
????System.out.println("二次改動前:"?+ personList.get(0).getName() + "-->"?+ personListNew.get(0).getSalary());
????System.out.println("二次改動后:"?+ personListNew2.get(0).getName() + "-->"?+ personListNew.get(0).getSalary());
??}
} 一次改動前:Tom–>8900
一次改動后:Tom–>18900
二次改動前:Tom–>18900
二次改動后:Tom–>18900
public?class?StreamTest?{
??public?static?void main(String[] args) {
????List list?= Arrays.asList("m,k,l,a", "1,3,5,7");
????List listNew = list.stream().flatMap(s -> {
??????// 將每個元素轉換成一個stream
??????String[] split = s.split(",");
??????Stream s2 = Arrays.stream(split);
??????return?s2;
????}).collect(Collectors.toList());
????System.out.println("處理前的集合:"?+ list);
????System.out.println("處理后的集合:"?+ listNew);
??}
} 處理前的集合:[m-k-l-a, 1-3-5]
處理后的集合:[m, k, l, a, 1, 3, 5]
3.5 歸約(reduce)

Integer集合的元素之和、乘積和最大值。public?class?StreamTest?{
??public?static?void main(String[] args) {
????List list?= Arrays.asList(1, 3, 2, 8, 11, 4);
????// 求和方式1
????Optional sum = list.stream().reduce((x, y) -> x + y);
????// 求和方式2
????Optional sum2 = list.stream().reduce(Integer::sum);
????// 求和方式3
????Integer sum3 = list.stream().reduce(0, Integer::sum);
????
????// 求乘積
????Optional product = list.stream().reduce((x, y) -> x * y);
????// 求最大值方式1
????Optional max = list.stream().reduce((x, y) -> x > y ? x : y);
????// 求最大值寫法2
????Integer max2 = list.stream().reduce(1, Integer::max);
????System.out.println("list求和:"?+ sum.get() + ","?+ sum2.get() + ","?+ sum3);
????System.out.println("list求積:"?+ product.get());
????System.out.println("list求和:"?+ max.get() + ","?+ max2);
??}
} list求和:29,29,29
list求積:2112
list求和:11,11
public class?StreamTest?{
??public static void main(String[] args) {
????List personList = new?ArrayList();
????personList.add(new?Person("Tom", 8900, 23, "male", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Jack", 7000, 25, "male", "Washington"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Lily", 7800, 21, "female", "Washington"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Anni", 8200, 24, "female", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Owen", 9500, 25, "male", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Alisa", 7900, 26, "female", "New York"));
????//?求工資之和方式1:
????Optional sumSalary = personList.stream().map(Person::getSalary).reduce(Integer::sum);
????//?求工資之和方式2:
????Integer sumSalary2 = personList.stream().reduce(0, (sum, p)?->?sum += p.getSalary(),
????????(sum1, sum2)?->?sum1 + sum2);
????//?求工資之和方式3:
????Integer sumSalary3 = personList.stream().reduce(0, (sum, p)?->?sum += p.getSalary(), Integer::sum);
????//?求最高工資方式1:
????Integer maxSalary = personList.stream().reduce(0, (max, p)?->?max > p.getSalary() ? max : p.getSalary(),
????????Integer::max);
????//?求最高工資方式2:
????Integer maxSalary2 = personList.stream().reduce(0, (max, p)?->?max > p.getSalary() ? max : p.getSalary(),
????????(max1, max2)?->?max1 > max2 ? max1 : max2);
????System.out.println("工資之和:"?+ sumSalary.get() + ","?+ sumSalary2 + ","?+ sumSalary3);
????System.out.println("最高工資:"?+ maxSalary + ","?+ maxSalary2);
??}
} 工資之和:49300,49300,49300
最高工資:9500,9500
3.6 收集(collect)
collect,收集,可以說是內(nèi)容最繁多、功能最豐富的部分了。從字面上去理解,就是把一個流收集起來,最終可以是收集成一個值也可以收集成一個新的集合。collect主要依賴java.util.stream.Collectors類內(nèi)置的靜態(tài)方法。
3.6.1 歸集(toList/toSet/toMap)
toList、toSet和toMap比較常用,另外還有toCollection、toConcurrentMap等復雜一些的用法。toList、toSet和toMap:public?class?StreamTest?{
??public?static?void?main(String[] args)?{
????List list?= Arrays.asList(1, 6, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 6, 20);
????List listNew = list.stream().filter(x -> x % 2?== 0).collect(Collectors.toList());
????Set set?= list.stream().filter(x -> x % 2?== 0).collect(Collectors.toSet());
????List personList = new?ArrayList();
????personList.add(new?Person("Tom", 8900, 23, "male", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Jack", 7000, 25, "male", "Washington"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Lily", 7800, 21, "female", "Washington"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Anni", 8200, 24, "female", "New York"));
????
????Map map?= personList.stream().filter(p -> p.getSalary() > 8000)
????????.collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getName, p -> p));
????System.out.println("toList:"?+ listNew);
????System.out.println("toSet:"?+ set);
????System.out.println("toMap:"?+ map);
??}
} toList:[6, 4, 6, 6, 20]
toSet:[4, 20, 6]
toMap:{Tom=mutest.Person@5fd0d5ae, Anni=mutest.Person@2d98a335}
3.6.2 統(tǒng)計(count/averaging)
Collectors提供了一系列用于數(shù)據(jù)統(tǒng)計的靜態(tài)方法:計數(shù): count平均值: averagingInt、averagingLong、averagingDouble最值: maxBy、minBy求和: summingInt、summingLong、summingDouble統(tǒng)計以上所有: summarizingInt、summarizingLong、summarizingDouble
public?class?StreamTest?{
??public?static?void main(String[] args) {
????List personList = new?ArrayList();
????personList.add(new?Person("Tom", 8900, 23, "male", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Jack", 7000, 25, "male", "Washington"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Lily", 7800, 21, "female", "Washington"));
????// 求總數(shù)
????Long count = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.counting());
????// 求平均工資
????Double average = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(Person::getSalary));
????// 求最高工資
????Optional max = personList.stream().map(Person::getSalary).collect(Collectors.maxBy(Integer::compare));
????// 求工資之和
????Integer sum = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.summingInt(Person::getSalary));
????// 一次性統(tǒng)計所有信息
????DoubleSummaryStatistics collect = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingDouble(Person::getSalary));
????System.out.println("員工總數(shù):"?+ count);
????System.out.println("員工平均工資:"?+ average);
????System.out.println("員工工資總和:"?+ sum);
????System.out.println("員工工資所有統(tǒng)計:"?+ collect);
??}
} 員工總數(shù):3
員工平均工資:7900.0
員工工資總和:23700
員工工資所有統(tǒng)計:DoubleSummaryStatistics{count=3, sum=23700.000000,min=7000.000000, average=7900.000000, max=8900.000000}
3.6.3 分組(partitioningBy/groupingBy)
分區(qū):將 stream按條件分為兩個Map,比如員工按薪資是否高于8000分為兩部分。分組:將集合分為多個Map,比如員工按性別分組。有單級分組和多級分組。
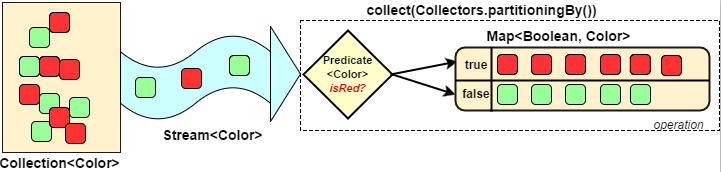
public class?StreamTest?{
??public static?void?main(String[] args) {
????List personList = new?ArrayList();
????personList.add(new?Person("Tom", 8900, "male", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Jack", 7000, "male", "Washington"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Lily", 7800, "female", "Washington"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Anni", 8200, "female", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Owen", 9500, "male", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Alisa", 7900, "female", "New York"));
????// 將員工按薪資是否高于8000分組
????????Map<Boolean, List> part = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(x -> x.getSalary() > 8000));
????????// 將員工按性別分組
????????Map<String, List> group = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getSex));
????????// 將員工先按性別分組,再按地區(qū)分組
????????Map<String, Map<String, List>> group2 = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getSex, Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getArea)));
????????System.out.println("員工按薪資是否大于8000分組情況:"?+ part);
????????System.out.println("員工按性別分組情況:"?+ group);
????????System.out.println("員工按性別、地區(qū):"?+ group2);
??}
} 員工按薪資是否大于8000分組情況:{false=[mutest.Person@2d98a335, mutest.Person@16b98e56, mutest.Person@7ef20235], true=[mutest.Person@27d6c5e0, mutest.Person@4f3f5b24, mutest.Person@15aeb7ab]}
員工按性別分組情況:{female=[mutest.Person@16b98e56, mutest.Person@4f3f5b24, mutest.Person@7ef20235], male=[mutest.Person@27d6c5e0, mutest.Person@2d98a335, mutest.Person@15aeb7ab]}
員工按性別、地區(qū):{female={New York=[mutest.Person@4f3f5b24, mutest.Person@7ef20235], Washington=[mutest.Person@16b98e56]}, male={New York=[mutest.Person@27d6c5e0, mutest.Person@15aeb7ab], Washington=[mutest.Person@2d98a335]}}3.6.4 接合(joining)
joining可以將stream中的元素用特定的連接符(沒有的話,則直接連接)連接成一個字符串。public?class?StreamTest?{
??public?static?void?main(String[] args) {
????List personList = new?ArrayList();
????personList.add(new?Person("Tom", 8900, 23, "male", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Jack", 7000, 25, "male", "Washington"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Lily", 7800, 21, "female", "Washington"));
????String names = personList.stream().map(p -> p.getName()).collect(Collectors.joining(","));
????System.out.println("所有員工的姓名:"?+ names);
????List list = Arrays.asList("A", "B", "C");
????String string?= list.stream().collect(Collectors.joining("-"));
????System.out.println("拼接后的字符串:"?+ string);
??}
} 所有員工的姓名:Tom,Jack,Lily
拼接后的字符串:A-B-C
3.6.5 歸約(reducing)
Collectors類提供的reducing方法,相比于stream本身的reduce方法,增加了對自定義歸約的支持。public?class?StreamTest?{
??public?static?void main(String[] args) {
????List personList = new?ArrayList();
????personList.add(new?Person("Tom", 8900, 23, "male", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Jack", 7000, 25, "male", "Washington"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Lily", 7800, 21, "female", "Washington"));
????// 每個員工減去起征點后的薪資之和(這個例子并不嚴謹,但一時沒想到好的例子)
????Integer sum = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.reducing(0, Person::getSalary, (i, j) -> (i + j - 5000)));
????System.out.println("員工扣稅薪資總和:"?+ sum);
????// stream的reduce
????Optional sum2 = personList.stream().map(Person::getSalary).reduce(Integer::sum);
????System.out.println("員工薪資總和:"?+ sum2.get());
??}
} 員工扣稅薪資總和:8700
員工薪資總和:23700
3.7 排序(sorted)
sorted():自然排序,流中元素需實現(xiàn)Comparable接口 sorted(Comparator com):Comparator排序器自定義排序
public?class?StreamTest?{
??public?static?void main(String[] args) {
????List personList = new?ArrayList();
????personList.add(new?Person("Sherry", 9000, 24, "female", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Tom", 8900, 22, "male", "Washington"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Jack", 9000, 25, "male", "Washington"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Lily", 8800, 26, "male", "New York"));
????personList.add(new?Person("Alisa", 9000, 26, "female", "New York"));
????// 按工資升序排序(自然排序)
????List newList = personList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getSalary)).map(Person::getName)
????????.collect(Collectors.toList());
????// 按工資倒序排序
????List newList2 = personList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getSalary).reversed())
????????.map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());
????// 先按工資再按年齡升序排序
????List newList3 = personList.stream()
????????.sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getSalary).thenComparing(Person::getAge)).map(Person::getName)
????????.collect(Collectors.toList());
????// 先按工資再按年齡自定義排序(降序)
????List newList4 = personList.stream().sorted((p1, p2) -> {
??????if?(p1.getSalary() == p2.getSalary()) {
????????return?p2.getAge() - p1.getAge();
??????} else?{
????????return?p2.getSalary() - p1.getSalary();
??????}
????}).map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());
????System.out.println("按工資升序排序:"?+ newList);
????System.out.println("按工資降序排序:"?+ newList2);
????System.out.println("先按工資再按年齡升序排序:"?+ newList3);
????System.out.println("先按工資再按年齡自定義降序排序:"?+ newList4);
??}
} 按工資升序排序:[Lily, Tom, Sherry, Jack, Alisa]
按工資降序排序:[Sherry, Jack, Alisa, Tom, Lily]
先按工資再按年齡升序排序:[Lily, Tom, Sherry, Jack, Alisa]
先按工資再按年齡自定義降序排序:[Alisa, Jack, Sherry, Tom, Lily]
3.8 提取/組合
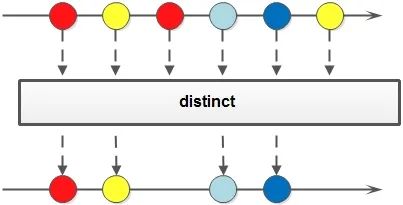

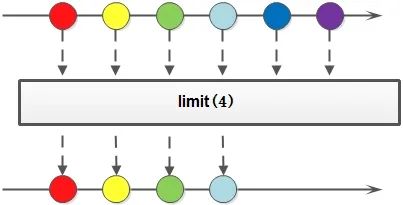
public?class?StreamTest {
??public?static?void?main(String[] args) {
????String[] arr1 = { "a", "b", "c", "d"?};
????String[] arr2 = { "d", "e", "f", "g"?};
????Stream<String> stream1 = Stream.of(arr1);
????Stream<String> stream2 = Stream.of(arr2);
????// concat:合并兩個流 distinct:去重
????List<String> newList = Stream.concat(stream1, stream2).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
????// limit:限制從流中獲得前n個數(shù)據(jù)
????List collect = Stream.iterate(1, x -> x + 2).limit(10).collect(Collectors.toList());
????// skip:跳過前n個數(shù)據(jù)
????List collect2 = Stream.iterate(1, x -> x + 2).skip(1).limit(5).collect(Collectors.toList());
????System.out.println("流合并:"?+ newList);
????System.out.println("limit:"?+ collect);
????System.out.println("skip:"?+ collect2);
??}
} 流合并:[a, b, c, d, e, f, g]
limit:[1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19]
skip:[3, 5, 7, 9, 11]
文章來源:https://blog.csdn.net/mu_wind/article/details/109516995
這些年小編給你分享過的干貨
2.優(yōu)質(zhì)ERP系統(tǒng)帶進銷存財務生產(chǎn)功能(附源碼)
3.優(yōu)質(zhì)SpringBoot帶工作流管理項目(附源碼)
5.SBoot+Vue外賣系統(tǒng)前后端都有(附源碼)

轉發(fā)在看就是最大的支持??
評論
圖片
表情
