一文搞定 Spring Bean 的創(chuàng)建全過程!
作者 | x1aoda1
1.1 Spring測試環(huán)境搭建
Spring模塊概覽,綠色是模塊,Spring中八大模塊,黑色表示該模塊包含的jar包(組件)。例如我們想要用IOC容器,也就是綠色的CoreContainer,我們需要導(dǎo)入Beans,Core,Context,SpEL(spring-expression)四個包。
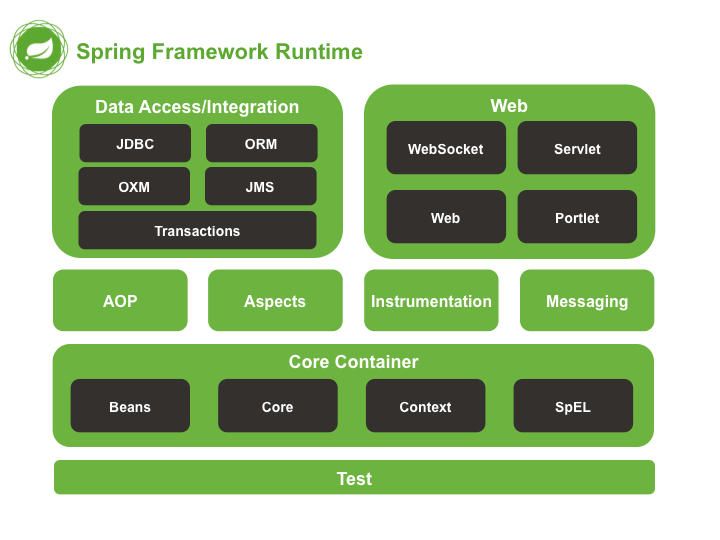
Spring模塊概覽
Test:測試相關(guān) Core Container:IOC容器 AOP:面向切面編程 Aspects:切面 Instrumenttation:跟JDK關(guān)聯(lián),一般不用 Messaging:消息服務(wù),一般不用 Data Access/Integration:數(shù)據(jù)訪問與集成(JDBC訪問,Transaction事務(wù),ORM對象關(guān)系映射,OXM和XML映射一般不用,JMS為Java消息服務(wù)Java-message-service一般不用) Web:Web服務(wù)(WebSocket網(wǎng)絡(luò)通信協(xié)議,Servlet, Web,Portlet一般不用)
最偷懶的方式,是直接導(dǎo)入Spring-Framework。但是可能導(dǎo)入不必要的包,導(dǎo)致項(xiàng)目打包后比較大
由于Spring-Content中的ApplicationContent是整個IOC的入口。我們導(dǎo)入Spring-context包即可
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-context -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
我們導(dǎo)入spring-content后,默認(rèn)會導(dǎo)入該組件的依賴jar,spring-content底層的依賴可以看到,實(shí)際上我們是導(dǎo)入了Core Container模塊:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>5.2.3.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>5.2.3.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>5.2.3.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-expression</artifactId>
<version>5.2.3.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
新建Spring配置文件spring.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--注冊一個對象,spring回自動創(chuàng)建這個對象-->
<!--
一個bean標(biāo)簽就表示一個對象
id:這個對象的唯一標(biāo)識
class:注冊對象的完全限定名
-->
<bean id="hello" class="com.xiaodai.service.Hello">
<!--使用property標(biāo)簽給對象的屬性賦值
name:表示屬性的名稱
value:表示屬性的值
-->
<property name="id" value="1"></property>
<property name="name" value="zhangsan"></property>
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
編寫測試類:
import com.xiaodai.service.Hello;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
Hello hello = applicationContext.getBean("hello", Hello.class);
System.out.println(hello.getName());
}
}
1.2 Debug容器創(chuàng)建過程
從測試類的new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml")開始debug,進(jìn)入ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,可以看到:
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
// 設(shè)置配置文件路徑
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
// 核心步驟
refresh();
}
}
加載配置文件后,進(jìn)入refresh()方法,該方法是容器初始化的核心步驟。該方法包含十三個方法:
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
/**
* 準(zhǔn)備刷新,做一些最基本的準(zhǔn)備化工作
**/
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
/**
* 獲得一個刷新的bean容器,實(shí)質(zhì)就是獲取工廠。
* 加載xml等配置文件,用該文件產(chǎn)生的BeanDefinition來創(chuàng)建一個工廠
**/
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
/**
* 準(zhǔn)備bean工廠
**/
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 后置增強(qiáng),方便擴(kuò)展
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 實(shí)例化并且執(zhí)行BeanFactoryPostProcessors
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 實(shí)例化并且注冊所有的BeanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 國際化設(shè)置,一般用不到
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 初始化應(yīng)用程序的多波器和廣播器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 空方法,預(yù)留給子類做擴(kuò)展
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 注冊監(jiān)聽器
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 工作中常用,面試常問。實(shí)例化所有非懶加載的實(shí)例對象
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// 完成刷新
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
1.3 AbstractApplicationContext的refresh()包含的13個方法分析
結(jié)合概覽圖一個一個方法分析:
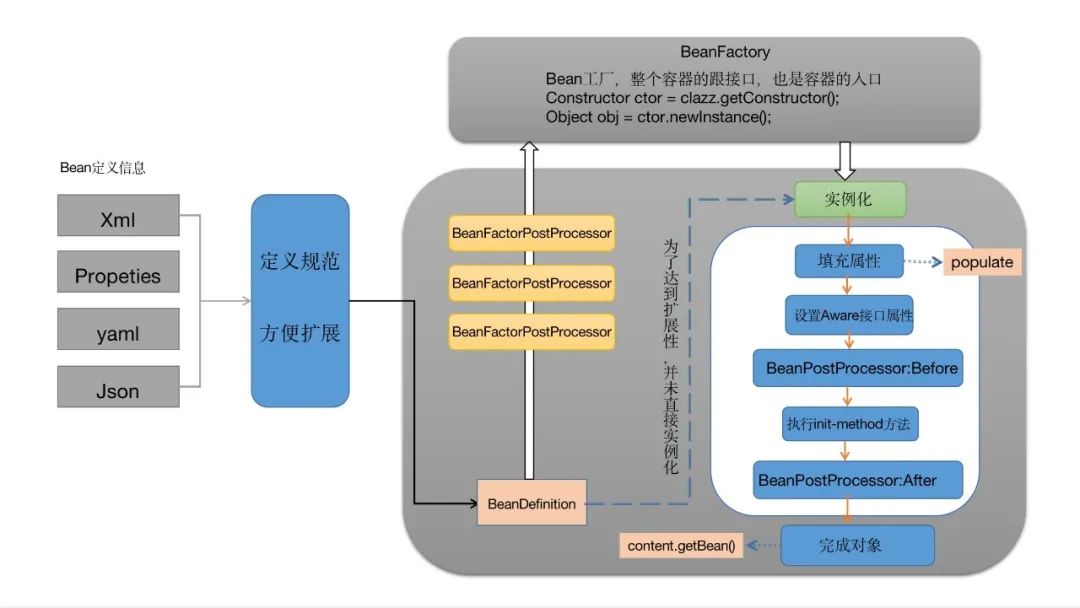
Bean工廠實(shí)例化Bean概覽圖
方法1:prepareRefresh() => 準(zhǔn)備工作
準(zhǔn)備刷新,做一些最基本的準(zhǔn)備化工作
protected void prepareRefresh() {
// Switch to active.
// 設(shè)置開始時間
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 關(guān)閉狀態(tài)設(shè)置為false
this.closed.set(false);
// 活躍狀態(tài)設(shè)置為true
this.active.set(true);
// 打印日志
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Refreshing " + this);
}
else {
logger.debug("Refreshing " + getDisplayName());
}
}
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment.
// 初始化屬性資源
initPropertySources();
// Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable:
// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
// 獲取環(huán)境信息,驗(yàn)證屬性信息
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
// Store pre-refresh
// 存儲預(yù)刷新的一些應(yīng)用信息的監(jiān)聽器
ApplicationListeners...
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) {
this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.applicationListeners);
}
else {
// Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state.
this.applicationListeners.clear();
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);
}
// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
// to be published once the multicaster is available...
// 創(chuàng)建一些監(jiān)聽器事件的集合
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
總結(jié):1.設(shè)置啟動事件 2.設(shè)置關(guān)閉活躍的狀態(tài) 3.獲取環(huán)境對象并設(shè)置屬性值 4.設(shè)置監(jiān)聽器以及需要發(fā)布事件的集合。
重要的點(diǎn):
獲取環(huán)境信息,驗(yàn)證屬性信息,getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties(); 存儲預(yù)刷新的一些應(yīng)用信息的監(jiān)聽器,在Spring中是空實(shí)現(xiàn),但是SpringBoot中,是有具體的值的
方法2:obtainFreshBeanFactory() => 獲得一個刷新的bean容器
獲得一個刷新的bean容器,實(shí)質(zhì)就是獲取工廠。創(chuàng)建容器對象DefaultListableBeanFactory;加載xml配置文件的屬性到當(dāng)前的工廠中,最重要的就是BeanDefinition
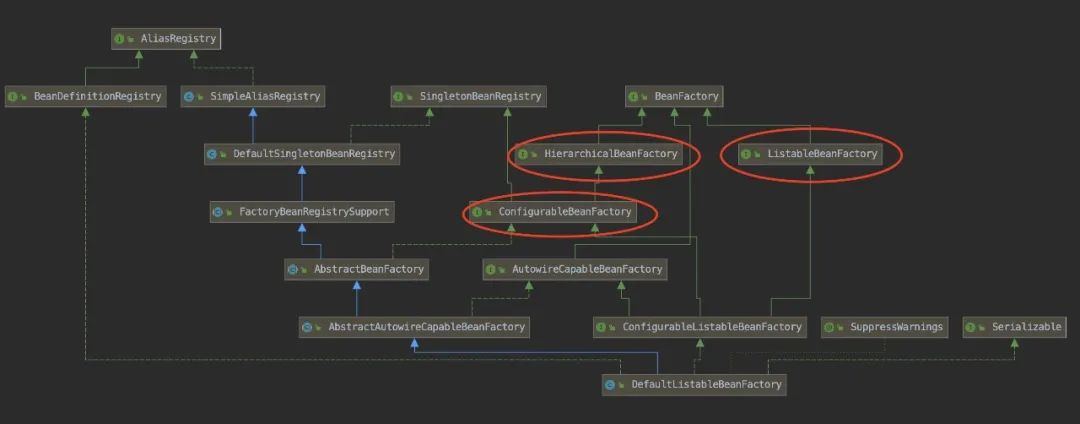
Bean工廠實(shí)例繼承關(guān)系圖
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext:
// 只要進(jìn)到這個方法,那么我們創(chuàng)建的一定是一個新的工廠
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
// 如果存在先銷毀,后關(guān)閉
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
// 創(chuàng)建bean工廠,這里使用的就是DefaultListableBeanFactory。此時創(chuàng)建的工廠里面的屬性值都是默認(rèn)值
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
// 序列化id
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
// 設(shè)置一些屬性值
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 加載bean的定義屬性值。該方法有很多重載,非常復(fù)雜,核心是do操作
// 完成配置文件或者配置類文件的加載
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
方法3:prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory) => 準(zhǔn)備(初始化)Bean工廠
為方法2拿到的工廠,設(shè)置某些具體的值
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
// 為bean工廠設(shè)置類加載器
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
// 設(shè)置SPEL解析器
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
// 添加一個BeanPostProcessor
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
// 忽略對應(yīng)接口的實(shí)現(xiàn)
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
// 注冊一些依賴
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as
// ApplicationListeners添加一個BeanPostProcessor增強(qiáng)器
ApplicationListeners.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Register default environment beans.
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}
方法4:postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory) => 后置增強(qiáng)Bean(擴(kuò)展實(shí)現(xiàn))
空方法,方便擴(kuò)展
方法5:invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory) => 執(zhí)行BFPP
實(shí)例化并且執(zhí)行BeanFactoryPostProcessors
/**
* Instantiate and invoke all registered BeanFactoryPostProcessor beans,
* respecting explicit order if given.
* <p>Must be called before singleton instantiation.
* 單例對象之前一定調(diào)用,因?yàn)閱卫齜ean創(chuàng)建后就只有一份
*/
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
方法6:registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory) => 注冊BPP
實(shí)例化并且注冊所有的BeanPostProcessor。實(shí)例化Bean之前的準(zhǔn)備工作
/**
* Instantiate and register all BeanPostProcessor beans,
* respecting explicit order if given.
* <p>Must be called before any instantiation of application beans.
*/
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this);
}
方法7:initMessageSource() => 國際化設(shè)置
方法8:initApplicationEventMulticaster() => 初始化應(yīng)用程序的多波器和廣播器
也屬于準(zhǔn)備工作
方法9:onRefresh() => 預(yù)留給子類做擴(kuò)展
空方法
方法10:registerListeners() => 注冊監(jiān)聽器
也屬于準(zhǔn)備工作
/**
* Add beans that implement ApplicationListener as listeners.
* Doesn't affect other listeners, which can be added without being beans.
*/
protected void registerListeners() {
// Register statically specified listeners first.
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
}
// Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...
Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (earlyEventsToProcess != null) {
for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
}
}
}
方法11:finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory) => 實(shí)例化所有單例對象
面試常問,工作常用。過程比較復(fù)雜
/**
* Finish the initialization of this context's bean factory,
* initializing all remaining singleton beans.
*/
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Initialize conversion service for this context.
/**
* 把類型轉(zhuǎn)化操作,設(shè)置到當(dāng)前的beanFactory里面去
**/
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// Register a default embedded value resolver if no bean post-processor
// (such as a PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before:
// at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values.
/**
* 判斷當(dāng)前的beanFactory有沒有內(nèi)置的值處理器
**/
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal));
}
// Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early.
/**
* 織入Aware
**/
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
// 設(shè)置類加載器
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.
/**
* 凍結(jié):某些bean不需要進(jìn)行修改操作了,放入
**/
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
/**
* 實(shí)例化所有非懶加載的實(shí)例對象(重要)
**/
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
實(shí)例化所有非懶加載的實(shí)例對象方法:
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
/**
* 拿到所有注冊bean的名稱
**/
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
// 循環(huán)去創(chuàng)建我們需要的單例對象
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 拿到bean的定義信息,就是我們在xml配置文件里面指定的一些屬性
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
// 是否是抽象的,是否是單例的,是否是懶加載的
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
// 判斷當(dāng)前類是否實(shí)現(xiàn)了factoryBean接口。一般沒實(shí)現(xiàn),直接進(jìn)入下面的getBean
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Boolean>)
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
// 通過beanName。拿到bean
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}
重要方法:
getMergedLocalBeanDefinition
/**
* Return a merged RootBeanDefinition, traversing the parent bean definition
* if the specified bean corresponds to a child bean definition.
* @param beanName the name of the bean to retrieve the merged definition for
* @return a (potentially merged) RootBeanDefinition for the given bean
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of an invalid bean definition
*/
// 返回一個合并好的RootBeanDefinition。整合子類和父類
protected RootBeanDefinition getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws BeansException {
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
RootBeanDefinition mbd = this.mergedBeanDefinitions.get(beanName);
if (mbd != null && !mbd.stale) {
return mbd;
}
return getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName, getBeanDefinition(beanName));
}
getBean() => doGetBean()
/**
* Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean.
* @param name the name of the bean to retrieve
* @param requiredType the required type of the bean to retrieve
* @param args arguments to use when creating a bean instance using explicit arguments
* (only applied when creating a new instance as opposed to retrieving an existing one)
* @param typeCheckOnly whether the instance is obtained for a type check,
* not for actual use
* @return an instance of the bean
* @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected <T> T doGetBean(final String name, @Nullable final Class<T> requiredType,
@Nullable final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException {
// 獲取beanName
final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
// 單例檢查,如果一級,二級,三級緩存中存在該Bean,直接獲取到了
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.trace("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
}
else {
logger.trace("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
// 如果是單例對象的話,嘗試解決循環(huán)依賴問題
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
// 獲取父類容器
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) {
return ((AbstractBeanFactory) parentBeanFactory).doGetBean(
nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly);
}
else if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else if (requiredType != null) {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
else {
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup);
}
}
// 標(biāo)志位。如果不是類型檢查,表示要創(chuàng)建bean,此處在集合中做一個記錄
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
try {
// 獲取beanDefinition
final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
// 檢測beanDefinition
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
// 檢查當(dāng)前的bean是否有其他依賴的bean
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
// 如果有依賴的bean,我們要先遞歸解決其他依賴的bean
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
getBean(dep);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
}
// Create bean instance.
// 是否是單例的
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else {
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " +
"defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
try {
T convertedBean = getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
if (convertedBean == null) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
return convertedBean;
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
return (T) bean;
}
getSingleton
/**
* Return the (raw) singleton object registered under the given name,
* creating and registering a new one if none registered yet.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param singletonFactory the ObjectFactory to lazily create the singleton
* with, if necessary
* @return the registered singleton object
*/
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
if (this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction) {
throw new BeanCreationNotAllowedException(beanName,
"Singleton bean creation not allowed while singletons of this factory are in destruction " +
"(Do not request a bean from a BeanFactory in a destroy method implementation!)");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating shared instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
beforeSingletonCreation(beanName);
boolean newSingleton = false;
boolean recordSuppressedExceptions = (this.suppressedExceptions == null);
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
try {
// 實(shí)際上就是調(diào)用了CreateBean
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
newSingleton = true;
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// Has the singleton object implicitly appeared in the meantime ->
// if yes, proceed with it since the exception indicates that state.
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
throw ex;
}
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
for (Exception suppressedException : this.suppressedExceptions) {
ex.addRelatedCause(suppressedException);
}
}
throw ex;
}
finally {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = null;
}
afterSingletonCreation(beanName);
}
if (newSingleton) {
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
}
doCreateBean => 通過上方法的singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();進(jìn)入的
/**
* Actually create the specified bean. Pre-creation processing has already happened
* at this point, e.g. checking {@code postProcessBeforeInstantiation} callbacks.
* <p>Differentiates between default bean instantiation, use of a
* factory method, and autowiring a constructor.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param args explicit arguments to use for constructor or factory method invocation
* @return a new instance of the bean
* @throws BeanCreationException if the bean could not be created
* @see #instantiateBean
* @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod
* @see #autowireConstructor
*/
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
/**
* 核心的創(chuàng)建實(shí)例化Bean的過程
**/
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
/**
* 解決循環(huán)依賴。使用三級緩存
**/
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
/**
* 填充屬性,上文的實(shí)例化只是默認(rèn)屬性值。填充屬性是初始化的第一步,第二步是執(zhí)行init方法
**/
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
/**
* 執(zhí)行init方法
**/
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
/**
* 需要銷毀的時候,銷毀的鉤子函數(shù)
**/
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
面試題:為甚么循環(huán)依賴的解決要使用三級緩存?
createBeanInstance => 核心的創(chuàng)建和實(shí)例化bean的過程,由doCreateBean調(diào)用
大量的反射出現(xiàn)在該方法中,用來創(chuàng)建對象
/**
* Create a new instance for the specified bean, using an appropriate instantiation strategy:
* factory method, constructor autowiring, or simple instantiation.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @param args explicit arguments to use for constructor or factory method invocation
* @return a BeanWrapper for the new instance
* @see #obtainFromSupplier
* @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod
* @see #autowireConstructor
* @see #instantiateBean
*/
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
Class<?> beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName());
}
Supplier<?> instanceSupplier = mbd.getInstanceSupplier();
if (instanceSupplier != null) {
return obtainFromSupplier(instanceSupplier, beanName);
}
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// Shortcut when re-creating the same bean...
boolean resolved = false;
boolean autowireNecessary = false;
if (args == null) {
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) {
resolved = true;
autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved;
}
}
}
if (resolved) {
if (autowireNecessary) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null);
}
else {
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
}
// Candidate constructors for autowiring?
// 構(gòu)造器
Constructor<?>[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args);
}
// Preferred constructors for default construction?
ctors = mbd.getPreferredConstructors();
if (ctors != null) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, null);
}
// No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor.
/**
* 默認(rèn)無參構(gòu)造
**/
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
instantiateBean(beanName, mbd) => 默認(rèn)無參構(gòu)造
/**
* Instantiate the given bean using its default constructor.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @return a BeanWrapper for the new instance
*/
protected BeanWrapper instantiateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
try {
Object beanInstance;
final BeanFactory parent = this;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
beanInstance = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () ->
// 實(shí)例化只會分配內(nèi)存空間,設(shè)置默認(rèn)值
getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent),
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
beanInstance = getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent);
}
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(beanInstance);
initBeanWrapper(bw);
return bw;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
}
instantiate
@Override
public Object instantiate(RootBeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String beanName, BeanFactory owner) {
// Don't override the class with CGLIB if no overrides.
if (!bd.hasMethodOverrides()) {
Constructor<?> constructorToUse;
synchronized (bd.constructorArgumentLock) {
constructorToUse = (Constructor<?>) bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod;
if (constructorToUse == null) {
final Class<?> clazz = bd.getBeanClass();
if (clazz.isInterface()) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "Specified class is an interface");
}
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
constructorToUse = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedExceptionAction<Constructor<?>>) clazz::getDeclaredConstructor);
}
else {
constructorToUse = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor();
}
bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod = constructorToUse;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "No default constructor found", ex);
}
}
}
return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructorToUse);
}
else {
// Must generate CGLIB subclass.
return instantiateWithMethodInjection(bd, beanName, owner);
}
}
BeanUtils.instantiateClass => 通過構(gòu)造器反射創(chuàng)建bean
/**
* Convenience method to instantiate a class using the given constructor.
* <p>Note that this method tries to set the constructor accessible if given a
* non-accessible (that is, non-public) constructor, and supports Kotlin classes
* with optional parameters and default values.
* @param ctor the constructor to instantiate
* @param args the constructor arguments to apply (use {@code null} for an unspecified
* parameter, Kotlin optional parameters and Java primitive types are supported)
* @return the new instance
* @throws BeanInstantiationException if the bean cannot be instantiated
* @see Constructor#newInstance
*/
public static <T> T instantiateClass(Constructor<T> ctor, Object... args) throws BeanInstantiationException {
Assert.notNull(ctor, "Constructor must not be null");
try {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(ctor);
if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinReflectPresent() && KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(ctor.getDeclaringClass())) {
return KotlinDelegate.instantiateClass(ctor, args);
}
else {
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = ctor.getParameterTypes();
Assert.isTrue(args.length <= parameterTypes.length, "Can't specify more arguments than constructor parameters");
Object[] argsWithDefaultValues = new Object[args.length];
for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length; i++) {
if (args[i] == null) {
Class<?> parameterType = parameterTypes[i];
argsWithDefaultValues[i] = (parameterType.isPrimitive() ? DEFAULT_TYPE_VALUES.get(parameterType) : null);
}
else {
argsWithDefaultValues[i] = args[i];
}
}
return ctor.newInstance(argsWithDefaultValues);
}
}
catch (InstantiationException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Is it an abstract class?", ex);
}
catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Is the constructor accessible?", ex);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Illegal arguments for constructor", ex);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Constructor threw exception", ex.getTargetException());
}
}
方法12:finishRefresh() => 完成刷新
/**
* Finish the refresh of this context, invoking the LifecycleProcessor's
* onRefresh() method and publishing the
* {@link org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent}.
*/
protected void finishRefresh() {
// Clear context-level resource caches (such as ASM metadata from scanning).
//
clearResourceCaches();
// Initialize lifecycle processor for this context.
initLifecycleProcessor();
// Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
// Publish the final event.
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
// Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);
}
方法13:resetCommonCaches() => 緩存重置
/**
* Reset Spring's common reflection metadata caches, in particular the
* {@link ReflectionUtils}, {@link AnnotationUtils}, {@link ResolvableType}
* and {@link CachedIntrospectionResults} caches.
* @since 4.2
* @see ReflectionUtils#clearCache()
* @see AnnotationUtils#clearCache()
* @see ResolvableType#clearCache()
* @see CachedIntrospectionResults#clearClassLoader(ClassLoader)
*/
protected void resetCommonCaches() {
ReflectionUtils.clearCache();
AnnotationUtils.clearCache();
ResolvableType.clearCache();
CachedIntrospectionResults.clearClassLoader(getClassLoader());
}
最后回顧整個流程概覽圖:


往 期 推 薦 1、Intellij IDEA這樣 配置注釋模板,讓你瞬間高出一個逼格! 2、吊炸天的 Docker 圖形化工具 Portainer,必須推薦給你! 3、最牛逼的 Java 日志框架,性能無敵,橫掃所有對手! 4、把Redis當(dāng)作隊列來用,真的合適嗎? 5、驚呆了,Spring Boot居然這么耗內(nèi)存!你知道嗎? 6、全網(wǎng)最全 Java 日志框架適配方案!還有誰不會? 7、Spring中毒太深,離開Spring我居然連最基本的接口都不會寫了

點(diǎn)分享

點(diǎn)收藏

點(diǎn)點(diǎn)贊

點(diǎn)在看
