服務(wù)注冊(cè)發(fā)現(xiàn)之服務(wù)注冊(cè)中心設(shè)計(jì)原理與Golang實(shí)現(xiàn)
內(nèi)容提要
通過本文您將 get 如下知識(shí):
微服務(wù)為什么引入服務(wù)注冊(cè)發(fā)現(xiàn) 服務(wù)注冊(cè)中心設(shè)計(jì)原理
Golang 代碼實(shí)現(xiàn)服務(wù)注冊(cè)中心
為什么引入服務(wù)注冊(cè)發(fā)現(xiàn)
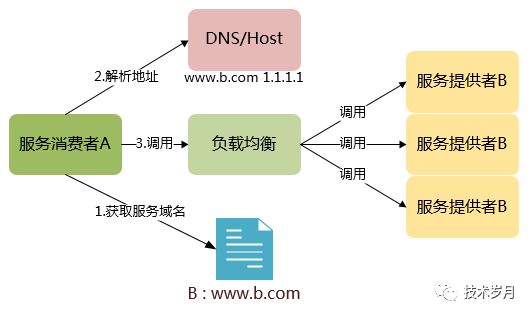
(服務(wù)域名配置模式)
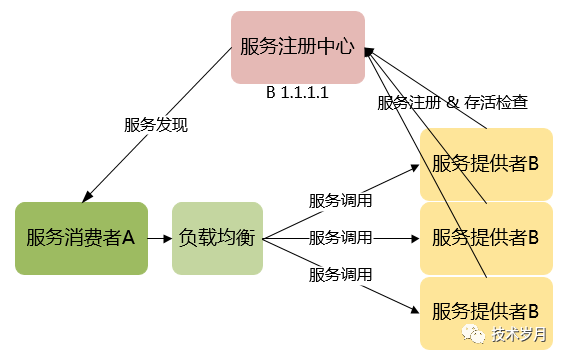
(服務(wù)注冊(cè)發(fā)現(xiàn)模式)
注冊(cè)中心實(shí)現(xiàn)原理
設(shè)計(jì)思想
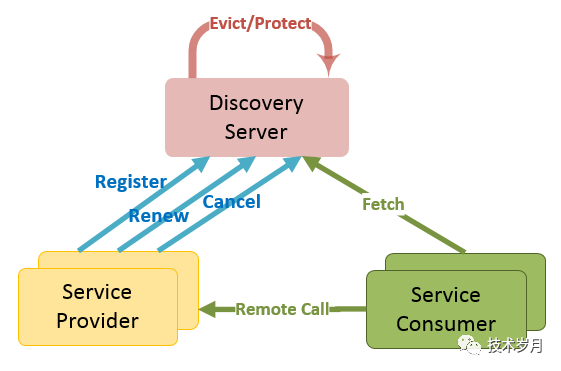
首先進(jìn)行功能需求分析,作為服務(wù)注冊(cè)中心,要實(shí)現(xiàn)如下基本功能:
服務(wù)注冊(cè):接受來自服務(wù)提交的注冊(cè)信息,并保存起來 服務(wù)下線:接受服務(wù)的主動(dòng)下線請(qǐng)求,并將服務(wù)從注冊(cè)信息表中刪除
服務(wù)獲取:調(diào)用方從注冊(cè)中心拉取服務(wù)信息
服務(wù)續(xù)約:服務(wù)健康檢查,服務(wù)通過心跳保持(主動(dòng)續(xù)約)告知注冊(cè)中心服務(wù)可用
服務(wù)剔除:注冊(cè)中心將長(zhǎng)時(shí)間不續(xù)約的服務(wù)實(shí)例從注冊(cè)信息表中刪除
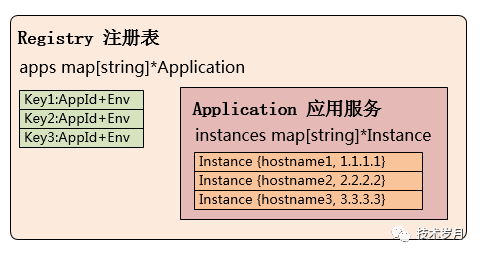
構(gòu)造注冊(cè)表
type Registry struct {
apps map[string]*Application
lock sync.RWMutex
}apps 記錄應(yīng)用服務(wù) Application 的信息,使用 map 結(jié)構(gòu),key 為應(yīng)用服務(wù)的唯一標(biāo)識(shí),值為應(yīng)用服務(wù)結(jié)構(gòu)類型 lock 讀寫鎖,保障并發(fā)讀寫安全
type Application struct {
appid string
instances map[string]*Instance
latestTimestamp int64
lock sync.RWMutex
}
appid 記錄應(yīng)用服務(wù)唯一標(biāo)識(shí) lock 讀寫鎖,保障并發(fā)讀寫安全
latestTimestamp 記錄更新時(shí)間
instances 記錄服務(wù)實(shí)例 Instance 的信息,使用 map 結(jié)構(gòu),key 為實(shí)例的 hostname (唯一標(biāo)識(shí)),值為實(shí)例結(jié)構(gòu)類型
type Instance struct {
Env string `json:"env"`
AppId string `json:"appid"`
Hostname string `json:"hostname"`
Addrs []string `json:"addrs"`
Version string `json:"version"`
Status uint32 `json:"status"`
RegTimestamp int64 `json:"reg_timestamp"`
UpTimestamp int64 `json:"up_timestamp"`
RenewTimestamp int64 `json:"renew_timestamp"`
DirtyTimestamp int64 `json:"dirty_timestamp"`
LatestTimestamp int64 `json:"latest_timestamp"`
}
Env 服務(wù)環(huán)境標(biāo)識(shí),如 online、dev、test AppId 應(yīng)用服務(wù)的唯一標(biāo)識(shí)
Hostname 服務(wù)實(shí)例的唯一標(biāo)識(shí)
Addrs 服務(wù)實(shí)例的地址,可以是 http 或 rpc 地址,多個(gè)地址可以維護(hù)數(shù)組
Version 服務(wù)實(shí)例版本
Status 服務(wù)實(shí)例狀態(tài),用于控制上下線
xxTimestamp 依次記錄服務(wù)實(shí)例注冊(cè)時(shí)間戳,上線時(shí)間戳,最近續(xù)約時(shí)間戳,臟時(shí)間戳(后面解釋),最后更新時(shí)間戳
服務(wù)注冊(cè)
功能目標(biāo):接受來自服務(wù)提交的注冊(cè)信息,并保存到注冊(cè)表中。先初始化注冊(cè)表 NewRegistry() ,根據(jù)提交信息構(gòu)建實(shí)例 NewInstance(),然后進(jìn)行注冊(cè)寫入。
func NewRegistry() *Registry {
registry := &Registry{
apps: make(map[string]*Application),
}
return registry
}
func NewInstance(req *RequestRegister) *Instance {
now := time.Now().UnixNano()
instance := &Instance{
Env: req.Env,
AppId: req.AppId,
Hostname: req.Hostname,
Addrs: req.Addrs,
Version: req.Version,
Status: req.Status,
RegTimestamp: now,
UpTimestamp: now,
RenewTimestamp: now,
DirtyTimestamp: now,
LatestTimestamp: now,
}
return instance
}
r := NewRegistry()
instance := NewInstance(&req)
r.Register(instance, req.LatestTimestamp)
注冊(cè)時(shí),先從 apps 中查找是否已注冊(cè)過,根據(jù)唯一標(biāo)識(shí) key = appid + env 確定。如果沒有注冊(cè)過,先新建應(yīng)用 app,然后將 instance 加入到 app 中,最后 app 放入注冊(cè)表中。這里分別使用了讀鎖和寫鎖,保障數(shù)據(jù)安全同時(shí),盡量減少鎖時(shí)間和鎖搶占影響。
func (r *Registry) Register(instance *Instance, latestTimestamp int64) (*Application, *errcode.Error) {
key := getKey(instance.AppId, instance.Env)
r.lock.RLock()
app, ok := r.apps[key]
r.lock.RUnlock()
if !ok { //new app
app = NewApplication(instance.AppId)
}
//add instance
_, isNew := app.AddInstance(instance, latestTimestamp)
if isNew { //todo }
//add into registry apps
r.lock.Lock()
r.apps[key] = app
r.lock.Unlock()
return app, nil
}
新建應(yīng)用服務(wù) app,初始化 instances
func NewApplication(appid string) *Application {
return &Application{
appid: appid,
instances: make(map[string]*Instance),
}
}
將服務(wù)主機(jī)實(shí)例 instance 加入應(yīng)用 app 中,注意判斷是否已存在,存在根據(jù)臟時(shí)間戳 DirtyTimestamp 比對(duì),是否進(jìn)行替換,添加實(shí)例信息,更新最新時(shí)間 latestTimestamp ,并返回實(shí)例。
func (app *Application) AddInstance(in *Instance, latestTimestamp int64) (*Instance, bool) {
app.lock.Lock()
defer app.lock.Unlock()
appIns, ok := app.instances[in.Hostname]
if ok { //exist
in.UpTimestamp = appIns.UpTimestamp
//dirtytimestamp
if in.DirtyTimestamp < appIns.DirtyTimestamp {
log.Println("register exist dirty timestamp")
in = appIns
}
}
//add or update instances
app.instances[in.Hostname] = in
app.upLatestTimestamp(latestTimestamp)
returnIns := new(Instance)
*returnIns = *in
return returnIns, !ok
}
返回 !ok (isNew)表明,本次服務(wù)注冊(cè)時(shí),實(shí)例為新增還是替換,用來維護(hù)服務(wù)健康信息(后面會(huì)再次提到)。
var req = &model.RequestRegister{AppId: "com.xx.testapp", Hostname: "myhost", Addrs: []string{"http://testapp.xx.com/myhost"}, Status: 1}
func TestRegister(t *testing.T) {
r := model.NewRegistry()
instance := model.NewInstance(req)
app, _ := r.Register(instance, req.LatestTimestamp)
t.Log(app)
}

服務(wù)發(fā)現(xiàn)
功能目標(biāo):查找已注冊(cè)的服務(wù)獲取信息,可以指定條件查找,也可以全量查找。這里以指定過濾條件 appid 、env 和 status 為例。
r := model.NewRegistry()
fetchData, err := r.Fetch(req.Env, req.AppId, req.Status, 0)
根據(jù) appid 和 env 組合成 key,然后從注冊(cè)表的 apps 中獲取應(yīng)用 app,然后通過 app 獲取服務(wù)實(shí)例 GetInstance()
func (r *Registry) Fetch(env, appid string, status uint32, latestTime int64) (*FetchData, *errcode.Error) {
app, ok := r.getApplication(appid, env)
if !ok {
return nil, errcode.NotFound
}
return app.GetInstance(status, latestTime)
}
func (r *Registry) getApplication(appid, env string) (*Application, bool) {
key := getKey(appid, env)
r.lock.RLock()
app, ok := r.apps[key]
r.lock.RUnlock()
return app, ok
}
根據(jù) app 獲取所有應(yīng)用實(shí)例,并用 status 過濾,這里對(duì)返回結(jié)果 instances 中的 Addr 進(jìn)行了拷貝返回一個(gè)新的切片。
func (app *Application) GetInstance(status uint32, latestTime int64) (*FetchData, *errcode.Error) {
app.lock.RLock()
defer app.lock.RUnlock()
if latestTime >= app.latestTimestamp {
return nil, errcode.NotModified
}
fetchData := FetchData{
Instances: make([]*Instance, 0),
LatestTimestamp: app.latestTimestamp,
}
var exists bool
for _, instance := range app.instances {
if status&instance.Status > 0 {
exists = true
newInstance := copyInstance(instance)
fetchData.Instances = append(fetchData.Instances, newInstance)
}
}
if !exists {
return nil, errcode.NotFound
}
return &fetchData, nil
}
//deep copy
func copyInstance(src *Instance) *Instance {
dst := new(Instance)
*dst = *src
//copy addrs
dst.Addrs = make([]string, len(src.Addrs))
for i, addr := range src.Addrs {
dst.Addrs[i] = addr
}
return dst
}
編寫測(cè)試用例,先注冊(cè)再獲取,看到可以正常獲取到信息。

服務(wù)下線
功能目標(biāo):接受服務(wù)的下線請(qǐng)求,并將服務(wù)從注冊(cè)信息列表中刪除。通過傳入 env, appid, hostname 三要素信息進(jìn)行對(duì)應(yīng)服務(wù)實(shí)例的取消。
r := model.NewRegistry()
r.Cancel(req.Env, req.AppId, req.Hostname, 0)根據(jù) appid 和 env 找到對(duì)象的 app,然后刪除 app 中對(duì)應(yīng)的 hostname。如果 hostname 后 app.instances 為空,那么將 app 從注冊(cè)表中清除。
func (r *Registry) Cancel(env, appid, hostname string, latestTimestamp int64) (*Instance, *errcode.Error) {
log.Println("action cancel...")
//find app
app, ok := r.getApplication(appid, env)
if !ok {
return nil, errcode.NotFound
}
instance, ok, insLen := app.Cancel(hostname, latestTimestamp)
if !ok {
return nil, errcode.NotFound
}
//if instances is empty, delete app from apps
if insLen == 0 {
r.lock.Lock()
delete(r.apps, getKey(appid, env))
r.lock.Unlock()
}
return instance, nil
}
func (app *Application) Cancel(hostname string, latestTimestamp int64) (*Instance, bool, int) {
newInstance := new(Instance)
app.lock.Lock()
defer app.lock.Unlock()
appIn, ok := app.instances[hostname]
if !ok {
return nil, ok, 0
}
//delete hostname
delete(app.instances, hostname)
appIn.LatestTimestamp = latestTimestamp
app.upLatestTimestamp(latestTimestamp)
*newInstance = *appIn
return newInstance, true, len(app.instances)
}
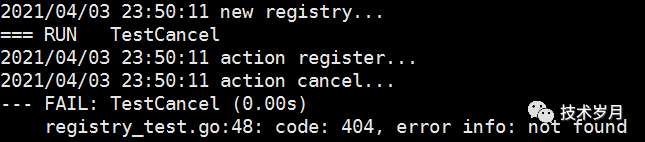
編寫測(cè)試用例先注冊(cè),再取消,然后獲取信息,發(fā)現(xiàn) 404 not found。
服務(wù)續(xù)約
功能目標(biāo):實(shí)現(xiàn)服務(wù)的健康檢查機(jī)制,服務(wù)注冊(cè)后,如果沒有取消,那么就應(yīng)該在注冊(cè)表中,可以隨時(shí)查到,如果某個(gè)服務(wù)實(shí)例掛了,能否自動(dòng)的從注冊(cè)表中刪除,保障注冊(cè)表中的服務(wù)實(shí)例都是正常的。
通常有兩種方式做法:注冊(cè)中心(服務(wù)端)主動(dòng)探活,通過請(qǐng)求指定接口得到正常響應(yīng)來確認(rèn);服務(wù)實(shí)例(客戶端)主動(dòng)上報(bào),調(diào)用續(xù)約接口進(jìn)行續(xù)約,續(xù)約設(shè)有時(shí)效 TTL (time to live)。兩種方式各有優(yōu)缺點(diǎn),大家可以思考一下,不同的注冊(cè)中心也采用了不同的方式,這里選型第二種方案。
r := model.NewRegistry()
r.Renew(req.Env, req.AppId, req.Hostname)根據(jù) appid 和 env 找到對(duì)象的 app,再根據(jù) hostname 找到對(duì)應(yīng)主機(jī)實(shí)例,更新其 RenewTimestamp 為當(dāng)前時(shí)間。
func (r *Registry) Renew(env, appid, hostname string) (*Instance, *errcode.Error) {
app, ok := r.getApplication(appid, env)
if !ok {
return nil, errcode.NotFound
}
in, ok := app.Renew(hostname)
if !ok {
return nil, errcode.NotFound
}
return in, nil
}
func (app *Application) Renew(hostname string) (*Instance, bool) {
app.lock.Lock()
defer app.lock.Unlock()
appIn, ok := app.instances[hostname]
if !ok {
return nil, ok
}
appIn.RenewTimestamp = time.Now().UnixNano()
return copyInstance(appIn), true
} 服務(wù)剔除
功能目標(biāo):既然有服務(wù)定期續(xù)約,那么對(duì)應(yīng)的如果服務(wù)沒有續(xù)約呢?服務(wù)如果下線可以使用 Cancel 進(jìn)行取消,但如果服務(wù)因?yàn)榫W(wǎng)絡(luò)故障或掛了導(dǎo)致不能提供服務(wù),那么可以通過檢查它是否按時(shí)續(xù)約來判斷,把 TTL 達(dá)到閾值的服務(wù)實(shí)例剔除(Cancel),實(shí)現(xiàn)服務(wù)的被動(dòng)下線。
func NewRegistry() *Registry {
++ go r.evictTask()
}
func (r *Registry) evictTask() {
ticker := time.Tick(configs.CheckEvictInterval)
for {
select {
case <-ticker:
r.evict()
}
}
}
遍歷注冊(cè)表的所有 apps,然后再遍歷其中的 instances,如果當(dāng)前時(shí)間減去實(shí)例上一次續(xù)約時(shí)間 instance.RenewTimestamp 達(dá)到閾值(默認(rèn) 90 秒),那么將其加入過期隊(duì)列中。這里并沒有直接將過期隊(duì)列所有實(shí)例都取消,考慮 GC 以及 本地時(shí)間漂移的因素,設(shè)定了一個(gè)剔除的上限 evictionLimit,隨機(jī)剔除一些過期實(shí)例。
func (r *Registry) evict() {
now := time.Now().UnixNano()
var expiredInstances []*Instance
apps := r.getAllApplications()
var registryLen int
for _, app := range apps {
registryLen += app.GetInstanceLen()
allInstances := app.GetAllInstances()
for _, instance := range allInstances {
if now-instance.RenewTimestamp > int64(configs.InstanceExpireDuration) {
expiredInstances = append(expiredInstances, instance)
}
}
}
evictionLimit := registryLen - int(float64(registryLen)*configs.SelfProtectThreshold)
expiredLen := len(expiredInstances)
if expiredLen > evictionLimit {
expiredLen = evictionLimit
}
if expiredLen == 0 {
return
}
for i := 0; i < expiredLen; i++ {
j := i + rand.Intn(len(expiredInstances)-i)
expiredInstances[i], expiredInstances[j] = expiredInstances[j], expiredInstances[i]
expiredInstance := expiredInstances[i]
r.Cancel(expiredInstance.Env, expiredInstance.AppId, expiredInstance.Hostname, now)
}
}
剔除過期時(shí),采用了 Knuth-Shuffle 算法,也叫公平洗牌算法來實(shí)現(xiàn)隨機(jī)剔除。當(dāng)然如果 expiredLen <= evictionLimit,隨機(jī)剔除的意義不大,如果前者大于后者,隨機(jī)剔除能最大程度保障,剔除的實(shí)例均勻分散到所有應(yīng)用實(shí)例中,降低某服務(wù)被全部清空的風(fēng)險(xiǎn)。公平洗牌算法實(shí)現(xiàn)也比較簡(jiǎn)單,循環(huán)遍歷過期列表,將當(dāng)前數(shù)與特定隨機(jī)數(shù)交換,和我們打牌時(shí)兩兩交換洗牌過程類似,它實(shí)現(xiàn)了 O(n) 的時(shí)間復(fù)雜度,由 Knuth 發(fā)明。
自我保護(hù)
功能目標(biāo):既然服務(wù)會(huì)定期剔除超時(shí)未續(xù)約的服務(wù),那么假設(shè)一種情況,網(wǎng)絡(luò)一段時(shí)間發(fā)生了異常,所有服務(wù)都沒成功續(xù)約,這時(shí)注冊(cè)中心是否將所有服務(wù)全部剔除?當(dāng)然不行!所以,我們需要一個(gè)自我保護(hù)的機(jī)制防止此類事情的發(fā)生。
type Guard struct {
renewCount int64
lastRenewCount int64
needRenewCount int64
threshold int64
lock sync.RWMutex
}renewCount 記錄所有服務(wù)續(xù)約次數(shù),每執(zhí)行一次 renew 加 1 lastRenewCount 記錄上一次檢查周期(默認(rèn) 60 秒)服務(wù)續(xù)約統(tǒng)計(jì)次數(shù)
needRenewCount 記錄一個(gè)周期總計(jì)需要的續(xù)約數(shù),按一次續(xù)約 30 秒,一周期 60 秒,一個(gè)實(shí)例就需要 2 次,所以服務(wù)注冊(cè)時(shí) + 2,服務(wù)取消時(shí) - 2
threshold 通過 needRenewCount 和閾值比例 (0.85)確定觸發(fā)自我保護(hù)的值
func (gd *Guard) incrNeed() {
gd.lock.Lock()
defer gd.lock.Unlock()
gd.needRenewCount += int64(configs.CheckEvictInterval / configs.RenewInterval)
gd.threshold = int64(float64(gd.needRenewCount) * configs.SelfProtectThreshold)
}
func (gd *Guard) decrNeed() {
gd.lock.Lock()
defer gd.lock.Unlock()
gd.needRenewCount -= int64(configs.CheckEvictInterval / configs.RenewInterval)
gd.threshold = int64(float64(gd.needRenewCount) * configs.SelfProtectThreshold)
}
func (gd *Guard) setNeed(count int64) {
gd.lock.Lock()
defer gd.lock.Unlock()
gd.needRenewCount = count * int64(configs.CheckEvictInterval/configs.RenewInterval)
gd.threshold = int64(float64(gd.needRenewCount) * configs.SelfProtectThreshold)
}
func (gd *Guard) incrCount() {
atomic.AddInt64(&gd.renewCount, 1)
}
type Registry struct {
++ gd *Guard
}
func NewRegistry() *Registry {
r := &Registry{
++ gd: new(Guard),
}
}
func (r *Registry) Register(...) {
if isNew {
++ r.gd.incrNeed()
}
}
func (r *Registry) Cancel(...) {
++ r.gd.decrNeed()
}
func (r *Registry) Renew(...) {
++ r.gd.incrCount()
}
在服務(wù)剔除前進(jìn)行上一周期計(jì)數(shù)統(tǒng)計(jì),并判斷是否達(dá)到自我保護(hù)開啟狀態(tài)。
func (gd *Guard) storeLastCount() {
atomic.StoreInt64(&gd.lastRenewCount, atomic.SwapInt64(&gd.needRenewCount, 0))
}
func (gd *Guard) selfProtectStatus() bool {
return atomic.LoadInt64(&gd.lastRenewCount) < atomic.LoadInt64(&gd.threshold)
}
func (r *Registry) evictTask() {
case <-ticker:
++ r.gd.storeLastCount()
r.evict()
}
}
func (r *Registry) evict() {
delta := now - instance.RenewTimestamp
++ if !protectStatus && delta > int64(configs.InstanceExpireDuration) ||
delta > int64(configs.InstanceMaxExpireDuration) {
expiredInstances = append(expiredInstances, instance)
}
}
func (r *Registry) evictTask() {
resetTicker := time.Tick(configs.ResetGuardNeedCountInterval)
for {
select {
case <-resetTicker:
var count int64
for _, app := range r.getAllApplications() {
count += int64(app.GetInstanceLen())
}
r.gd.setNeed(count)
}
}
} 注冊(cè)中心對(duì)外提供服務(wù)
目前注冊(cè)中心基本功能已實(shí)現(xiàn),需要對(duì)外提供服務(wù)了,我們采用 gin 來實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè) web 服務(wù),接受 http 請(qǐng)求進(jìn)行服務(wù)的注冊(cè)、查找、續(xù)約、下線操作,這樣保障注冊(cè)中心可以方便的接受來自任何語(yǔ)言客戶端請(qǐng)求。
func main() {
//init config
c := flag.String("c", "", "config file path")
flag.Parse()
config, err := configs.LoadConfig(*c)
if err != nil {
log.Println("load config error:", err)
return
}
//global discovery
global.Discovery = model.NewDiscovery(config)
//init router and start server
router := api.InitRouter()
srv := &http.Server{
Addr: config.HttpServer,
Handler: router,
}
go func() {
if err := srv.ListenAndServe(); err != nil && err != http.ErrServerClosed {
log.Fatalf("listen:%s\n", err)
}
}()
}
增加一個(gè) discovery 結(jié)構(gòu),并開啟一個(gè)全局變量 global.Discovery ,該結(jié)構(gòu)中維護(hù)注冊(cè)表 Registry,然后就可以根據(jù)注冊(cè)表實(shí)現(xiàn)各種操作了。
type Discovery struct {
config *configs.GlobalConfig
protected bool
Registry *Registry
}
func NewDiscovery(config *configs.GlobalConfig) *Discovery {
dis := &Discovery{
protected: false,
config: config,
Registry: NewRegistry(), //init registry
}
return dis
}
//init discovery
var Discovery *model.Discovery
router.POST("api/register", handler.RegisterHandler)
func RegisterHandler(c *gin.Context) {
var req model.RequestRegister
if e := c.ShouldBindJSON(&req); e != nil {
err := errcode.ParamError
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"code": err.Code(),
"message": err.Error(),
})
return
}
//bind instance
instance := model.NewInstance(&req)
if instance.Status == 0 || instance.Status > 2 {
err := errcode.ParamError
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"code": err.Code(),
"message": err.Error(),
})
return
}
//dirtytime
if req.DirtyTimestamp > 0 {
instance.DirtyTimestamp = req.DirtyTimestamp
}
global.Discovery.Registry.Register(instance, req.LatestTimestamp)
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"code": 200,
"message": "",
"data": "",
})
}
func main() {
//...
//graceful restart
quit := make(chan os.Signal)
signal.Notify(quit, syscall.SIGINT, syscall.SIGTERM, syscall.SIGHUP, syscall.SIGQUIT)
<-quit
log.Println("shutdown discovery server...")
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 5*time.Second)
defer cancel()
if err := srv.Shutdown(ctx); err != nil {
log.Fatal("server shutdown error:", err)
}
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
log.Println("timeout of 5 seconds")
}
log.Println("server exiting")
}
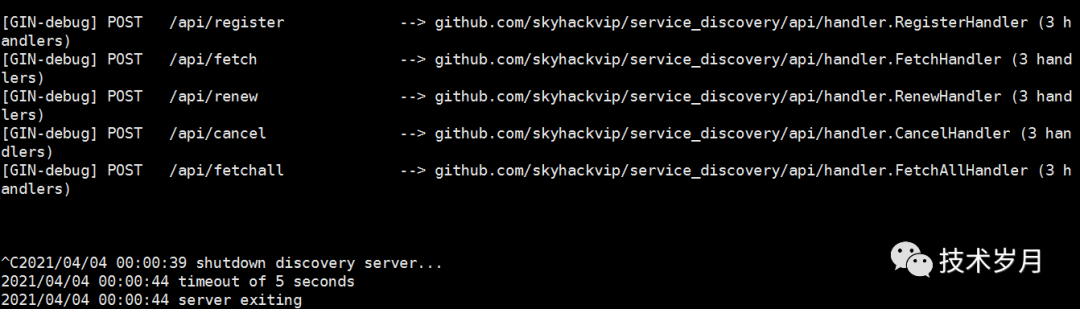
實(shí)現(xiàn)效果如圖所示:
工程實(shí)踐
使用 go module 管理依賴的三方包 (gin 和 yaml)
api 存放 http 服務(wù)路由以及對(duì)應(yīng)處理函數(shù)
cmd 存放編譯入口 main 文件
configs 存放全局配置和全局常量
global 存放全局結(jié)構(gòu)變量
model 存放注冊(cè)表結(jié)構(gòu)模型及主要邏輯

總結(jié)與問題
注冊(cè)中心功能實(shí)現(xiàn)
至此,一個(gè)單機(jī)版的注冊(cè)中心就可以工作了,但生產(chǎn)環(huán)境單點(diǎn)肯定是不能容忍的,因此有必要實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)注冊(cè)中心集群。那么是否部署多個(gè)注冊(cè)中心實(shí)例就可以了,當(dāng)然 .... 不行!這只能保障有多個(gè)注冊(cè)中心節(jié)點(diǎn),而每個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)中維護(hù)自己的注冊(cè)表,那么就需要進(jìn)行注冊(cè)表數(shù)據(jù)同步。多節(jié)點(diǎn)數(shù)據(jù)同步又會(huì)涉及著名的一致性問題,這時(shí) Paxos、Raft、ZAB、Gossip 等算法名詞涌現(xiàn),而我們將使用 P2P(Peer to Peer)對(duì)等網(wǎng)絡(luò)協(xié)議來實(shí)現(xiàn)。關(guān)于集群設(shè)計(jì)與實(shí)現(xiàn)我們將在后續(xù)文章中展開。
感謝您的閱讀,歡迎大家點(diǎn)贊、分享
