有趣的對抗生成網(wǎng)絡(luò)(六)二次元頭像生成
關(guān)于對抗生成網(wǎng)絡(luò)的概念,前面已經(jīng)說了不少了,話不多說,直接開整!
我們的數(shù)據(jù)集如下(共2.1w+張圖片,回復(fù)“動漫人臉”即可獲取下載鏈接):
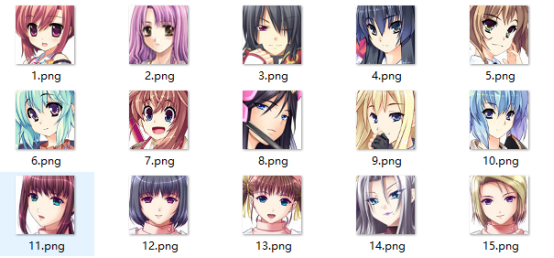
數(shù)據(jù)加載
DataSets
接著,我們加載這些二次元頭像,然后進(jìn)行數(shù)據(jù)處理,新建一個dcgan.py文件寫入如下代碼:
主要的作用是把圖片加載進(jìn)內(nèi)存,內(nèi)存比較小的同學(xué)可以將它改寫成生成器的方式。
import tensorflow.keras as kerasfrom tensorflow.keras import layersimport numpy as npimport osimport cv2from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import imageimport mathfrom PIL import Imageanime_path = './amine'# 導(dǎo)入數(shù)據(jù)集x_train = []for i in os.listdir(anime_path):image_path = os.path.join(anime_path, i)img = cv2.imread(image_path)img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)x_train.append(img)# 數(shù)據(jù)集處理x_train = np.array(x_train)x_train = x_train.reshape(-1, 64, 64, 3)print(x_train.shape)
模型搭建
Model
接著,我們搭建網(wǎng)絡(luò)模型,我們知道,生成對抗網(wǎng)絡(luò)是由2個模型相互對抗得到的,所以在這里我們需要搭建2個網(wǎng)絡(luò),分別是生成網(wǎng)絡(luò)和判別網(wǎng)絡(luò):
?
生成網(wǎng)絡(luò)的結(jié)構(gòu)大體如下,我們可以看到,生成網(wǎng)絡(luò)的輸入是一個長度為100的噪聲,接著與一個4*4*1024的特征向量做全連接,然后使用反卷積一步一步進(jìn)行上采樣,最后得到一張64*64*3的圖片:
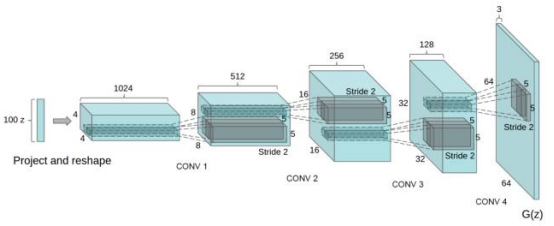
我們對這個網(wǎng)絡(luò)進(jìn)行稍微的修改,代碼如下
# 定義網(wǎng)絡(luò)參數(shù)latent_dim = 64 # 輸入生成網(wǎng)絡(luò)的噪聲height = 64width = 64channels = 3generator_input = keras.Input(shape=(latent_dim,))# 首先,將輸入轉(zhuǎn)換為16 x 16 x 256通道的feature mapx = layers.Dense(256 * 16 * 16)(generator_input)x = layers.LeakyReLU()(x)x = layers.Reshape((16, 16, 256))(x)# 然后,添加卷積層x = layers.Conv2D(128, 5, padding='same')(x)x = layers.LeakyReLU()(x)# 上采樣至 32 x 32x = layers.Conv2DTranspose(128, 5, strides=2, padding='same')(x)x = layers.LeakyReLU()(x)# 上采樣至 64 x 64x = layers.Conv2DTranspose(128, 5, strides=2, padding='same')(x)x = layers.LeakyReLU()(x)# 添加更多的卷積層x = layers.Conv2D(64, 5, padding='same')(x)x = layers.LeakyReLU()(x)# 生成一個 64 x 64 1-channel 的feature mapx = layers.Conv2D(channels, 7, activation='tanh', padding='same')(x)generator = keras.models.Model(generator_input, x)generator.summary()
接著,我們搭建判別網(wǎng)絡(luò),判別網(wǎng)絡(luò)其實和普通的圖片分類網(wǎng)絡(luò)沒什么區(qū)別,輸入是一張64*64*3的圖片,經(jīng)過一系列的卷積和下采樣,最終得到分類結(jié)果。
判別網(wǎng)絡(luò)代碼如下:
discriminator_input = layers.Input(shape=(height, width, channels))x = layers.Conv2D(256, 3)(discriminator_input)x = layers.LeakyReLU()(x)x = layers.Conv2D(256, 3, strides=2)(x)x = layers.LeakyReLU()(x)x = layers.Conv2D(128, 3, strides=2)(x)x = layers.LeakyReLU()(x)x = layers.Conv2D(128, 3, strides=2)(x)x = layers.LeakyReLU()(x)x = layers.Flatten()(x)# 重要的技巧(添加一個dropout層)x = layers.Dropout(0.3)(x)# 分類層x = layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')(x)discriminator = keras.models.Model(discriminator_input, x)keras.utils.plot_model(discriminator, 'dis.png', show_shapes=True)discriminator.summary()
我們對比以上兩個網(wǎng)絡(luò),會發(fā)現(xiàn)一個有趣的問題,這兩個網(wǎng)絡(luò)其實是相反的,生成網(wǎng)絡(luò)是給定一組噪聲,通過上采樣生成一張圖片,而判別網(wǎng)絡(luò)是給定一張圖片,通過下采樣生成概率。
?
接著我們編譯判別器網(wǎng)絡(luò),并設(shè)置判別器為不訓(xùn)練狀態(tài),然后組裝GAN網(wǎng)絡(luò):
optimizer = keras.optimizers.Adam(0.0002, 0.5)# 編譯判斷器網(wǎng)絡(luò)discriminator_optimizer = keras.optimizers.RMSprop(lr=8e-4, clipvalue=1.0, decay=1e-8)discriminator.compile(optimizer=optimizer, loss='binary_crossentropy')# 設(shè)置判別器為不訓(xùn)練(單獨交替迭代訓(xùn)練)discriminator.trainable = False# 組裝GAN網(wǎng)絡(luò)gan_input = keras.Input(shape=(latent_dim,))gan_output = discriminator(generator(gan_input))gan = keras.models.Model(gan_input, gan_output)gan_optimizer = keras.optimizers.Adam(lr=4e-4, clipvalue=1.0, decay=1e-8)gan.compile(optimizer=optimizer, loss='binary_crossentropy')
GAN網(wǎng)絡(luò)的運作流程如下:1.輸入一個長度為100的噪聲,通過生成網(wǎng)絡(luò)生成一張圖片。2.將生成網(wǎng)絡(luò)生成的圖片送入判別網(wǎng)絡(luò)中,得到判別結(jié)果。3.在這個過程中,需要平衡生成器與判別器,所以將判別網(wǎng)絡(luò)設(shè)置為不訓(xùn)練狀態(tài)。網(wǎng)絡(luò)形如:
開始訓(xùn)練
Train
完成了這些,其實我們就可以開始訓(xùn)練函數(shù)的編寫了,但是為了后面更好地觀看生成的圖片,我們再寫一個組合圖片的函數(shù)
# 將一個批次的圖片合成一張圖片def combine_images(generated_images):''':param generated_images: 一個批次的圖片:return: 圖片'''num = generated_images.shape[0] # 圖片的數(shù)量(-1, 64, 64, 3)width = int(math.sqrt(num)) # 新創(chuàng)建圖片的寬度height = int(math.ceil(float(num) / width))shape = generated_images.shape[1:3]# 生成一張純黑色圖片image = np.zeros((height * shape[0], width * shape[1], 3),dtype=generated_images.dtype)# 循環(huán)每張圖片,并將圖片內(nèi)的像素點填充到生成的黑色圖片中for index, img in enumerate(generated_images):i = int(index / width)j = index % width# 分別填充3個通道image[i * shape[0]:(i+1) * shape[0], j * shape[1]:(j+1) * shape[1], 0] = \img[:, :, 0]image[i * shape[0]:(i+1) * shape[0], j * shape[1]:(j+1) * shape[1], 1] = \img[:, :, 1]image[i * shape[0]:(i+1) * shape[0], j * shape[1]:(j+1) * shape[1], 2] = \img[:, :, 2]return image
接著定義訓(xùn)練參數(shù):
# 歸一化x_train = x_train.astype('float32') / 255.iterations = 50000batch_size = 16start = 0save_dir = './save'
然后使用for循環(huán)開始訓(xùn)練,在每一個批次的訓(xùn)練中,我們需要生成隨機點送入生成器生成假圖像,然后將假圖像和真圖像進(jìn)行比較,并組合標(biāo)簽,然后單獨訓(xùn)練判別器,接著訓(xùn)練GAN網(wǎng)絡(luò),這時候判別器的權(quán)重被凍結(jié)。最后我們每隔一定的周期保存好模型與生成的圖片,便于觀察生成器的效果
for step in range(iterations):# 在潛在空間中抽樣隨機點random_latent_vectors = np.random.normal(size=(batch_size, latent_dim))# print(random_latent_vecotors.shape)# 將隨機抽樣點解碼為假圖像generated_images = generator.predict(random_latent_vectors)# 將假圖像與真實圖像進(jìn)行比較stop = start + batch_sizereal_images = x_train[start: stop]combined_images = np.concatenate([generated_images, real_images])# 組裝區(qū)別真假圖像的標(biāo)簽(真全為1 假全為0)labels = np.concatenate([np.ones((batch_size, 1)),np.zeros((batch_size, 1))])# 重要的技巧,在標(biāo)簽上添加隨機噪聲labels += 0.05 * np.random.random(labels.shape)# 訓(xùn)練鑒別器(discrimitor)d_loss = discriminator.train_on_batch(combined_images, labels)# 在潛在空間中采樣隨機點random_latent_vectors = np.random.normal(size=(batch_size, latent_dim))# 匯集標(biāo)有“所有真實圖像”的標(biāo)簽misleading_targets = np.zeros((batch_size, 1))# 訓(xùn)練生成器(generator) (通過gan模型,鑒別器(discrimitor)權(quán)值被凍結(jié))a_loss = gan.train_on_batch(random_latent_vectors, misleading_targets)start += batch_sizeif start > len(x_train) - batch_size:start = 0if step % 500 == 0:gan.save('gan.h5')generator.save('generator.h5')print('step: %s, d_loss: %s, a_loss: %s' % (step, d_loss, a_loss))# 保存生成的圖像img = combine_images(generated_images) # 組合圖片img = image.array_to_img(img * 255., scale=False)img.save(save_dir + '/anime_' + str(step) + '.png')
最后,我們就可以右鍵運行程序了,GAN訓(xùn)練的時候需要大量的時間,所以要耐心等待!放幾張圖片感受一下:

測試
Test
在上面的訓(xùn)練中,我們一邊訓(xùn)練一邊保存了模型的權(quán)重,在使用的時候,我們只需要加載保存后的生成網(wǎng)絡(luò)的權(quán)重即可進(jìn)行測試:
import tensorflow.keras as kimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import image#加載模型model=k.models.load_model('generator.h5')model.summary()#生成0~1的隨機噪聲random_latent_vectors = np.random.uniform(0,1,size=(1, 64))print(random_latent_vectors)#*255random_latent_vectors=random_latent_vectors*255.#轉(zhuǎn)換成unit8格式random_latent_vectors.astype('uint8')plt.axis('off')plt.imshow(random_latent_vectors)#放入模型中預(yù)測generated_images = model.predict(random_latent_vectors)#數(shù)組轉(zhuǎn)圖片格式img = image.array_to_img(generated_images[0]* 255., scale=False)plt.imshow(img)
運行結(jié)果如下:

掃二維碼|關(guān)注我們
微信號|深度學(xué)習(xí)從入門到放棄
長按關(guān)注|永不迷路
