c#異步編程-線程
c#異步編程-線程
近期會(huì)分享自己學(xué)習(xí)c#異步編程系列的文章,如果能幫助大家希望多多關(guān)注文章末尾的微信公眾號(hào)和知乎三連。各位舉手之勞是對我更新技術(shù)文章最大的支持。
1.線程
線程是一個(gè)可執(zhí)行的路徑,它可以獨(dú)立于其他線程執(zhí)行。
每個(gè)線程都在操作系統(tǒng)的進(jìn)程內(nèi)執(zhí)行,而操作系統(tǒng)進(jìn)程提供了程序運(yùn)行的獨(dú)立環(huán)境。
單線程應(yīng)用,在進(jìn)程的獨(dú)立環(huán)境里只跑一個(gè)線程,所以該線程擁有獨(dú)占權(quán)。
多線程應(yīng)用,單個(gè)進(jìn)程中會(huì)跑多個(gè)線程,他們會(huì)共享當(dāng)前的執(zhí)行環(huán)境(內(nèi)存)等。
進(jìn)程和線程的對應(yīng)關(guān)系,一個(gè)進(jìn)程可以擁有多個(gè)線程,多個(gè)線程只能屬于一個(gè)進(jìn)程。例如:一個(gè)非常耗時(shí)的操作(讀數(shù)據(jù)庫、復(fù)雜耗時(shí)的計(jì)算),如果只用主線程執(zhí)行UI線程會(huì)“假死”專業(yè)術(shù)語叫線程阻塞。這時(shí)候的解決辦法就是單獨(dú)開一個(gè)線程去執(zhí)行這個(gè)耗時(shí)操作。這個(gè)時(shí)候處理的數(shù)據(jù)就可被稱作是共享狀態(tài)。
示例代碼如下:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread t = new Thread(PrintValue);
t.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("main thread.");
}
}
static void PrintValue()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("thread t.");
}
}
效果:
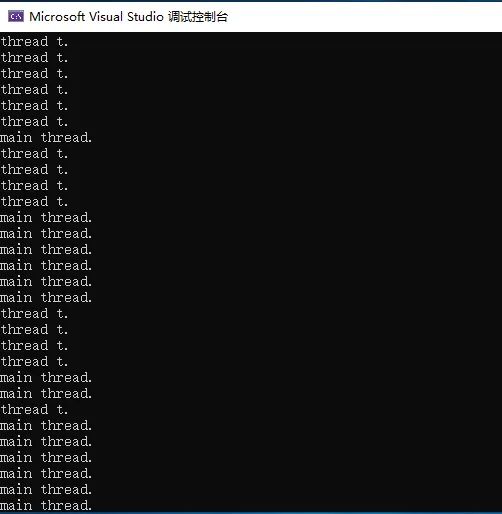
在單核計(jì)算機(jī)上,操作系統(tǒng)必須為每個(gè)線程分派“時(shí)間片”(在windows中通常為20毫秒)來模擬并發(fā),從而導(dǎo)致重復(fù)的"main thread."和"thread t."輸出。
在多核或多處理計(jì)算機(jī)上,這兩個(gè)線程可以真正的并行執(zhí)行(也可能受到計(jì)算機(jī)上其他活動(dòng)進(jìn)程的競爭)。
線程搶占:A線程的執(zhí)行與另外一個(gè)線程上代碼的執(zhí)行交織的那一刻。可被成為線程搶占。
線程屬性:
線程一旦開始執(zhí)行,isAlive就是True,線程結(jié)束就編程false。
線程結(jié)束的條件就是:線程構(gòu)造函數(shù)傳入的委托結(jié)束了執(zhí)行。
線程一旦結(jié)束,就無法再重啟,因?yàn)榫€程需要執(zhí)行的代碼執(zhí)行完成之后會(huì)自動(dòng)銷毀。
每個(gè)線程都有Name屬性,通常用于調(diào)試。每個(gè)線程的Name只能設(shè)置一次,以后更改會(huì)拋出異常。
靜態(tài)的Thread.CurrentThread屬性,會(huì)返回當(dāng)前執(zhí)行的線程。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread.CurrentThread.Name = "Main_Thread";
Thread t = new Thread(PrintValue);
t.Name = "T_Thread";
t.Start();
Console.WriteLine(Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("main thread.");
}
}
static void PrintValue()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("thread t.");
}
}
2.Thread.Join 和 Thread.Sleep
Join();
調(diào)用Join方法,就可以等待另一個(gè)線程結(jié)束。也叫阻塞線程
示例代碼如下:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region Join and Sleep
Thread t = new Thread(PrintValue);
t.Start();
t.Join();//等待PrintValue執(zhí)行完成
Console.WriteLine("End.");
#endregion
}
static void PrintValue()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("thread t.");
}
}
調(diào)用join的時(shí)候,可以設(shè)置一個(gè)超時(shí),用毫秒或者TimeSpan都可以。
如果返回true,那就是線程結(jié)束;如果超時(shí),則返回false。
static Thread t1, t2;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
t1 = new Thread(ThreadTest);
t1.Name = "t1";
t1.Start();
t2 = new Thread(ThreadTest);
t2.Name = "t2";
t2.Start();
}
private static void ThreadTest()
{
Console.WriteLine("Current thread:{0}",Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
if (Thread.CurrentThread.Name == "t1" && t2.ThreadState != ThreadState.Unstarted)
{
if (t2.Join(1000))
{
Console.WriteLine("t2 join 2000ms.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("the time out.");
}
}
Thread.Sleep(4000);
Console.WriteLine("thread 1:{0}", t1.ThreadState);
Console.WriteLine("thread 2:{0}", t2.ThreadState);
}
效果:

Sleep()
Thread.Sleep()方法會(huì)暫停當(dāng)前的線程,并等一段時(shí)間。期間是不占用cpu資源的。
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 10000; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine("i");
}
Thread.Sleep(4000);
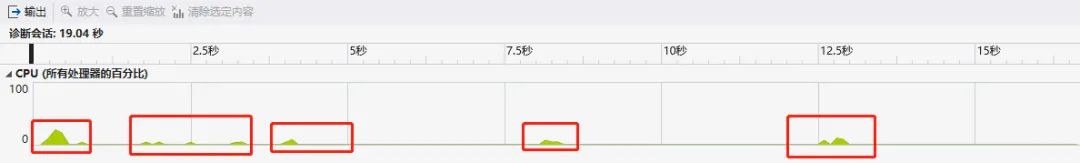
}驗(yàn)證:在每次i循環(huán)的時(shí)候會(huì)占用CPU輸出10000次,然后休息4秒再繼續(xù)循環(huán)。這時(shí)候分析圖如下:
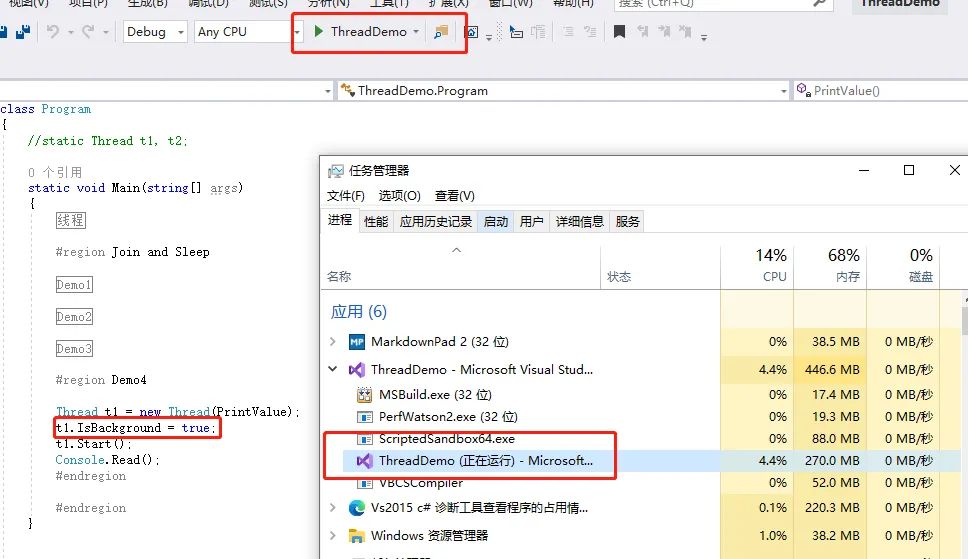
3.前臺(tái)線程和后臺(tái)線程
前臺(tái)線程:
該線程在沒有執(zhí)行完成函數(shù)代碼時(shí),在程序關(guān)閉時(shí)是不會(huì)退出進(jìn)程的。
Thread t1 = new Thread(PrintValue);
t1.IsBackground = true;
t1.Start();
static void PrintValue()
{
while (true)
{
Console.WriteLine("thread t.");
}
}
效果:
后臺(tái)線程:
該線程不管有沒有執(zhí)行完成函數(shù)代碼,都會(huì)直接退出進(jìn)程。
Thread t1 = new Thread(PrintValue);
t1.IsBackground = false;
t1.Start();
static void PrintValue()
{
while (true)
{
Console.WriteLine("thread t.");
}
}
4.線程優(yōu)先級(jí)
線程優(yōu)先級(jí)決定了相對于操作系統(tǒng)中其他活躍線程所占的執(zhí)行時(shí)間,提升指定線程優(yōu)先級(jí)如果該線程處理任務(wù)比較重則會(huì)降低其他線程優(yōu)先級(jí)會(huì)導(dǎo)致其他搶占不到CPU處理時(shí)間片,。
Thread t1 = new Thread(() => { Console.ReadLine(); });
t1.Priority = ThreadPriority.Highest;
t1.Start();
ThreadPriority枚舉如下:
//
// 摘要:
// Specifies the scheduling priority of a System.Threading.Thread.
public enum ThreadPriority
{
//
// 摘要:
// The System.Threading.Thread can be scheduled after threads with any other priority.
Lowest = 0,
//
// 摘要:
// The System.Threading.Thread can be scheduled after threads with Normal priority
// and before those with Lowest priority.
BelowNormal = 1,
//
// 摘要:
// The System.Threading.Thread can be scheduled after threads with AboveNormal priority
// and before those with BelowNormal priority. Threads have Normal priority by default.
Normal = 2,
//
// 摘要:
// The System.Threading.Thread can be scheduled after threads with Highest priority
// and before those with Normal priority.
AboveNormal = 3,
//
// 摘要:
// The System.Threading.Thread can be scheduled before threads with any other priority.
Highest = 4
}
如果想讓某線程的優(yōu)先級(jí)比其他進(jìn)程中的線程高,那么就必須提升進(jìn)程的優(yōu)先級(jí)。
使用system.Diagnostics下的Process類。
using(Process p = Process.GetCurrentProcess()) p.PriorityClass = ProcessPriorityClass.High;
這可以很好的用于只做少量工作且需要較低延遲的非UI進(jìn)程。
對于需要大量計(jì)算的程序(wpf、winfrom等),提高進(jìn)程優(yōu)先級(jí)可能會(huì)降低其他進(jìn)程搶占不到CPU處理時(shí)間片,從而降低整個(gè)計(jì)算機(jī)的速度。
