一文讀懂Spring中的AOP機制

點擊上方老周聊架構關注我
一、前言
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Documentedpublic @interface PrintLog {}
public class PrintLogAspect {(value = "@annotation(com.riemann.core.annotation.PrintLog)")public Object handlerPrintLog(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {String clazzName = joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName();String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();Map<String, Object> nameAndArgs = getFieldsName(this.getClass(), clazzName, methodName, args);log.info("Enter class[{}] method[{}] params[{}]", clazzName, methodName, nameAndArgs);Object object = null;try {object = joinPoint.proceed();} catch (Throwable throwable) {log.error("Process class[{}] method[{}] error", clazzName, methodName, throwable);}log.info("End class[{}] method[{}]", clazzName, methodName);return object;}private Map<String, Object> getFieldsName(Class clazz, String clazzName, String methodName, Object[] args) throws NotFoundException {Map<String, Object > map = new HashMap<>();ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();ClassClassPath classPath = new ClassClassPath(clazz);pool.insertClassPath(classPath);CtClass cc = pool.get(clazzName);CtMethod cm = cc.getDeclaredMethod(methodName);MethodInfo methodInfo = cm.getMethodInfo();CodeAttribute codeAttribute = methodInfo.getCodeAttribute();LocalVariableAttribute attr = (LocalVariableAttribute) codeAttribute.getAttribute(LocalVariableAttribute.tag);if (attr == null) {// exception}int pos = Modifier.isStatic(cm.getModifiers()) ? 0 : 1;for (int i = 0; i < cm.getParameterTypes().length; i++) {map.put( attr.variableName(i + pos), args[i]);}return map;}}
public class Controller {public String findUserNameById( int id) {// 模擬根據(jù)id查詢用戶名String userName = "公眾號【老周聊架構】";return userName;}}
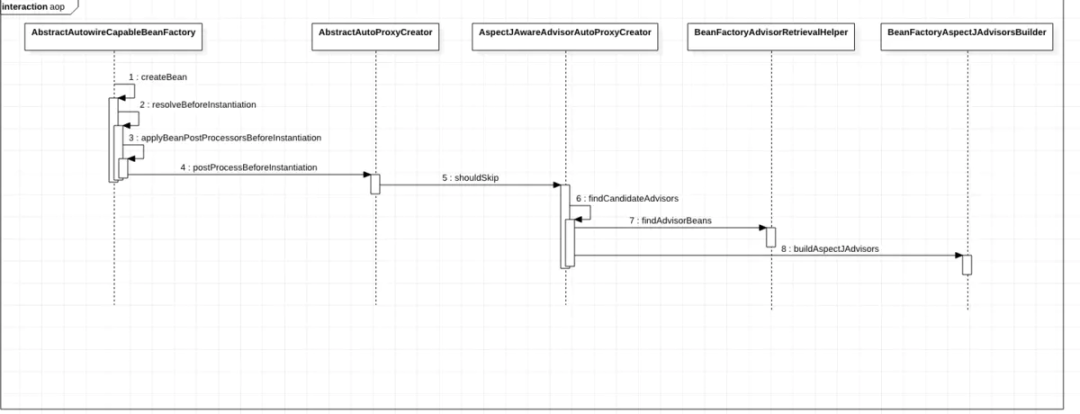
二、Spring中的AOP機制
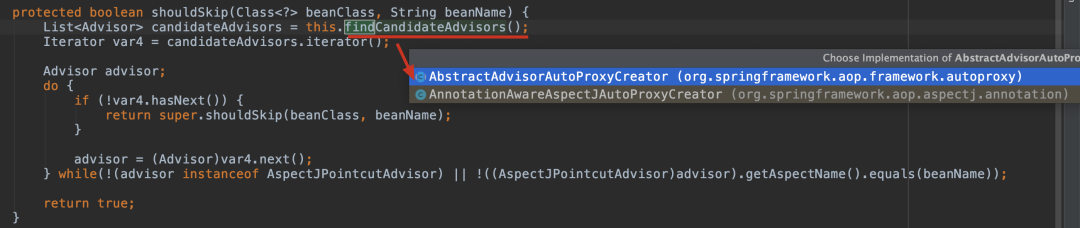
public List<Advisor> findAdvisorBeans() {String[] advisorNames = this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames;if (advisorNames == null) {advisorNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(this.beanFactory, Advisor.class, true, false);this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames = advisorNames;}if (advisorNames.length == 0) {return new ArrayList();} else {List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList();String[] var3 = advisorNames;int var4 = advisorNames.length;for(int var5 = 0; var5 < var4; ++var5) {String name = var3[var5];if (this.isEligibleBean(name)) {if (this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(name)) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Skipping currently created advisor '" + name + "'");}} else {try {// 核心方法advisors.add(this.beanFactory.getBean(name, Advisor.class));} catch (BeanCreationException var11) {Throwable rootCause = var11.getMostSpecificCause();if (rootCause instanceof BeanCurrentlyInCreationException) {BeanCreationException bce = (BeanCreationException)rootCause;String bceBeanName = bce.getBeanName();if (bceBeanName != null && this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(bceBeanName)) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Skipping advisor '" + name + "' with dependency on currently created bean: " + var11.getMessage());}continue;}}throw var11;}}}}return advisors;}}
advisors.add(this.beanFactory.getBean(name, Advisor.class));public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() {List<String> aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;if (aspectNames == null) {synchronized(this) {aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;if (aspectNames == null) {List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList();List<String> aspectNames = new ArrayList();// 找到所有的類(因為是Object所以基本上就是所有被spring管理的類)String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);String[] var18 = beanNames;int var19 = beanNames.length;for(int var7 = 0; var7 < var19; ++var7) {String beanName = var18[var7];// 是否是Aspect(比如含有@Aspect注解)if (this.isEligibleBean(beanName)) {Class<?> beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName);if (beanType != null && this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) {aspectNames.add(beanName);AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) {MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);// 生成AdvisorList<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);} else {this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);}advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);} else {if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName + "' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton");}MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));}}}}this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames;return advisors;}}}if (aspectNames.isEmpty()) {return Collections.emptyList();} else {List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList();Iterator var3 = aspectNames.iterator();while(var3.hasNext()) {String aspectName = (String)var3.next();List<Advisor> cachedAdvisors = (List)this.advisorsCache.get(aspectName);if (cachedAdvisors != null) {advisors.addAll(cachedAdvisors);} else {MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = (MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory)this.aspectFactoryCache.get(aspectName);advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));}}return advisors;}}
找到所有被 spring 管理的類(父類是 Object 的類)
如果類含有 @Aspect 注解,調(diào)用 advisorFactory.getAdvisors 方法生成對應的 advisor
返回advisors
org.springframework.aop.aspectj.annotation.ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory#getAdvisorspublic List<Advisor> getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory) {Class<?> aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName();this.validate(aspectClass);MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory = new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory);List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList();Iterator var6 = this.getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass).iterator();// 遍歷所有沒有 @Pointcut 注解的方法while(var6.hasNext()) {Method method = (Method)var6.next();Advisor advisor = this.getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, advisors.size(), aspectName);if (advisor != null) {advisors.add(advisor);}}if (!advisors.isEmpty() && lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) {Advisor instantiationAdvisor = new ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory.SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor(lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory);advisors.add(0, instantiationAdvisor);}Field[] var12 = aspectClass.getDeclaredFields();int var13 = var12.length;for(int var14 = 0; var14 < var13; ++var14) {Field field = var12[var14];Advisor advisor = this.getDeclareParentsAdvisor(field);if (advisor != null) {advisors.add(advisor);}}return advisors;}
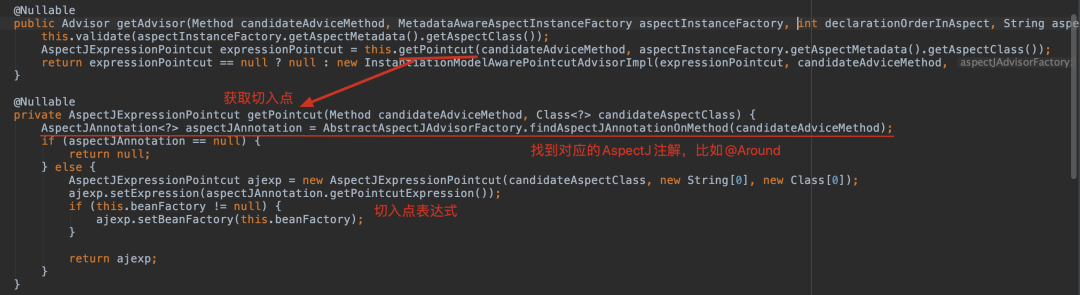
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) {this.validate(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = this.getPointcut(candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());return expressionPointcut == null ? null : new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod, this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);}
private Advice instantiateAdvice(AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut) {Advice advice = this.aspectJAdvisorFactory.getAdvice(this.aspectJAdviceMethod, pointcut, this.aspectInstanceFactory, this.declarationOrder, this.aspectName);return advice != null ? advice : EMPTY_ADVICE;}
public Advice getAdvice(Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {Class<?> candidateAspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();this.validate(candidateAspectClass);AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation = AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {return null;} else if (!this.isAspect(candidateAspectClass)) {throw new AopConfigException("Advice must be declared inside an aspect type: Offending method '" + candidateAdviceMethod + "' in class [" + candidateAspectClass.getName() + "]");} else {if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {this.logger.debug("Found AspectJ method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);}Object springAdvice;switch(aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType()) {case AtPointcut:if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {this.logger.debug("Processing pointcut '" + candidateAdviceMethod.getName() + "'");}return null;case AtAround:springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);break;case AtBefore:springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);break;case AtAfter:springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);break;case AtAfterReturning:springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning)aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning())) {((AbstractAspectJAdvice)springAdvice).setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning());}break;case AtAfterThrowing:springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing)aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing())) {((AbstractAspectJAdvice)springAdvice).setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing());}break;default:throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Unsupported advice type on method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);}((AbstractAspectJAdvice)springAdvice).setAspectName(aspectName);((AbstractAspectJAdvice)springAdvice).setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrder);String[] argNames = this.parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod);if (argNames != null) {((AbstractAspectJAdvice)springAdvice).setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames);}((AbstractAspectJAdvice)springAdvice).calculateArgumentBindings();return (Advice)springAdvice;}}
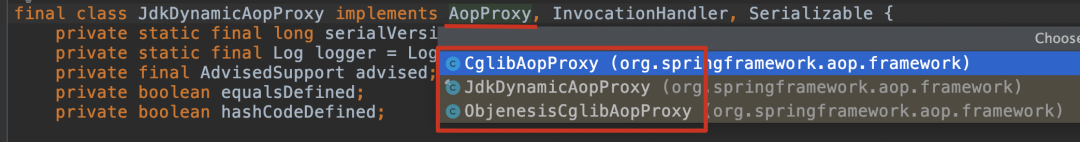
public interface AopProxy {Object getProxy();Object getProxy( ClassLoader var1);}
public Object getProxy( ClassLoader classLoader) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());}Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised, true);this.findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces);return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this);}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {Object oldProxy = null;boolean setProxyContext = false;TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;Object target = null;Object retVal;try {// equals 方法if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {Boolean var18 = this.equals(args[0]);return var18;}// hashCode方法if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {Integer var17 = this.hashCode();return var17;}// 如果是 DecoratingProxy類if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) {Class var16 = AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised);return var16;}// 實現(xiàn)了Advised接口if (this.advised.opaque || !method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() || !method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {// ThreadLocal里記錄下當前被代理的對象oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);setProxyContext = true;}target = targetSource.getTarget();Class<?> targetClass = target != null ? target.getClass() : null;// 核心方法,獲取當前方法的攔截器List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);if (chain.isEmpty()) {Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);} else {MethodInvocation invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);// 調(diào)用這些攔截器及方法retVal = invocation.proceed();}Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();if (retVal != null && retVal == target && returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) && !RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {retVal = proxy;} else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) {throw new AopInvocationException("Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method);}Object var12 = retVal;return var12;}retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);} finally {if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {targetSource.releaseTarget(target);}if (setProxyContext) {AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);}}return retVal;}
hashCode、equals方法單獨處理
根據(jù)當前方法等,生成所需的方法攔截器
調(diào)用方法及攔截器
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {return this.invokeJoinpoint(); // ①} else {// ②Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice = this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm = (InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher)interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;Class<?> targetClass = this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass();return dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments) ? dm.interceptor.invoke(this) : this.proceed();} else {// ③return ((MethodInterceptor)interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);}}}
會根據(jù)我們之前生成的各個 Advisor 對應的切入點,判斷下當前的方法是否滿足該切入點。如果滿足,將其適配為 MethodInterceptor 接口并返回。
核心調(diào)用邏輯,就是取出一個個攔截器,先判斷下方法是否滿足攔截器條件,如果滿足就調(diào)用。
三、總結
spring 在創(chuàng)建一個類之前,會看下有沒有配置 AOP(可能是xml、可能是注解),如果有的話,會把配置給轉(zhuǎn)換成一個個 advisor,然后緩存起來(這樣后面需要生成代理類時候,就可以直接使用了)。
如果有繼續(xù)看它的 PointCut 對應的規(guī)則,只要在創(chuàng)建 bean 的時候符合這個 PointCut 規(guī)則的,就用動態(tài)代理(JDK Proxy、CGLib)的方式創(chuàng)建代理對象作為 bean 放到容器中。
當我們從 bean 容器中獲取代理對象 bean 并調(diào)用它的方法的時候,因為這個bean是通過代理的方式創(chuàng)建的,所以必然會走org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy.DynamicAdvisedInterceptor#intercept() 方法,而這個方法也必然會執(zhí)行org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation#proceed() 這個方法,而這個方法就會根據(jù)上面說的執(zhí)行過程依次執(zhí)行不同的 MethodInterceptor 子類對象的 invoke() 方法,這個方法會根據(jù)元數(shù)據(jù)信息通過反射的方式調(diào)用代理對象對應的真正的對象的方法,例如我上面創(chuàng)建的 PrintLogAspect 這個類的被 @Around 標注的方法。
歡迎大家關注我的公眾號【老周聊架構】,Java后端主流技術棧的原理、源碼分析、架構以及各種互聯(lián)網(wǎng)高并發(fā)、高性能、高可用的解決方案。
喜歡的話,點贊、再看、分享三連。

點個在看你最好看