【機器學(xué)習(xí)】在機器學(xué)習(xí)中處理大量數(shù)據(jù)!
知乎 | https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/357361005
之前系統(tǒng)梳理過大數(shù)據(jù)概念和基礎(chǔ)知識(可點擊),本文基于PySpark在機器學(xué)習(xí)實踐中的用法,希望對大數(shù)據(jù)學(xué)習(xí)的同學(xué)起到拋磚引玉的作用。(當(dāng)數(shù)據(jù)集較小時,用Pandas足夠,當(dāng)數(shù)據(jù)量較大時,就需要利用分布式數(shù)據(jù)處理工具,Spark很適用)
1.PySpark簡介
Apache Spark是一個閃電般快速的實時處理框架。它進行內(nèi)存計算以實時分析數(shù)據(jù)。由于Apache Hadoop MapReduce僅執(zhí)行批處理并且缺乏實時處理功能,因此它開始出現(xiàn)。因此,引入了Apache Spark,因為它可以實時執(zhí)行流處理,也可以處理批處理。
Apache Spark是Scala語言實現(xiàn)的一個計算框架。為了支持Python語言使用Spark,Apache Spark社區(qū)開發(fā)了一個工具PySpark。我們可以通過Python語言操作RDDs
RDD簡介
RDD (Resiliennt Distributed Datasets)
?RDD = 彈性 + 分布式 Datasets
1)分布式,好處是讓數(shù)據(jù)在不同工作節(jié)點并行存儲,并行計算
2)彈性,指的節(jié)點存儲時,既可以使用內(nèi)存,也可以使用外存
?RDD還有個特性是延遲計算,也就是一個完整的RDD運行任務(wù)分成兩部分:Transformation和Action
Spark RDD的特性:
分布式:可以分布在多臺機器上進行并行處理 彈性:計算過程中內(nèi)存不夠時,它會和磁盤進行數(shù)據(jù)交換 基于內(nèi)存:可以全部或部分緩存在內(nèi)存中 只讀:不能修改,只能通過轉(zhuǎn)換操作生成新的 RDD
2.Pandas和PySpark對比
可以參考這位作者的,詳細(xì)的介紹了pyspark與pandas之間的區(qū)別:
https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//blog.csdn.net/suzyu12345/article/details/79673483
3.PySpark實戰(zhàn)小練
數(shù)據(jù)集:從1994年人口普查數(shù)據(jù)庫中提取。(后臺回復(fù)“210323”可獲取)
TO DO:預(yù)測一個人新收入是否會超過5萬美金
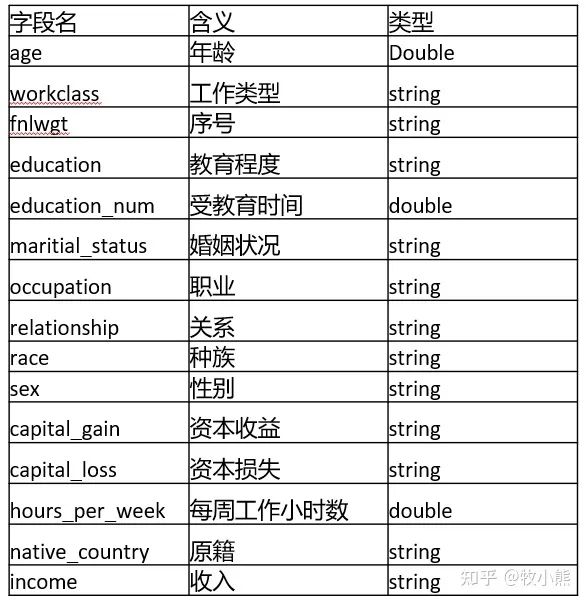
參數(shù)說明:
創(chuàng)建SparkSession
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
spark=SparkSession.builder.appName('adult').getOrCreate()
讀取數(shù)據(jù)
df = spark.read.csv('adult.csv', inferSchema = True, header=True) #讀取csv文件
df.show(3) #用來顯示前3行
注意:pyspark必須創(chuàng)建SparkSession才能像類似于pandas一樣操作數(shù)據(jù)集
我們看看數(shù)據(jù)集:
cols = df.columns #和pandas一樣看列名
df.printSchema()
root
|-- age: integer (nullable = true)
|-- workclass: string (nullable = true)
|-- fnlwgt: integer (nullable = true)
|-- education: string (nullable = true)
|-- education-num: integer (nullable = true)
|-- marital-status: string (nullable = true)
|-- occupation: string (nullable = true)
|-- relationship: string (nullable = true)
|-- race: string (nullable = true)
|-- sex: string (nullable = true)
|-- capital-gain: integer (nullable = true)
|-- capital-loss: integer (nullable = true)
|-- hours-per-week: integer (nullable = true)
|-- native-country: string (nullable = true)
|-- income: string (nullable = true)
#找到所有的string類型的變量
#dtypes用來看數(shù)據(jù)變量類型
cat_features = [item[0] for item in df.dtypes if item[1]=='string']
# 需要刪除 income列,否則標(biāo)簽泄露
cat_features.remove('income')
#找到所有數(shù)字變量
num_features = [item[0] for item in df.dtypes if item[1]!='string']
對于類別變量我們需要進行編碼,在pyspark中提供了StringIndexer, OneHotEncoder, VectorAssembler特征編碼模式:
from pyspark.ml import Pipeline
from pyspark.ml.feature import StringIndexer, OneHotEncoder, VectorAssembler
stages = []
for col in cat_features:
# 字符串轉(zhuǎn)成索引
string_index = StringIndexer(inputCol = col, outputCol = col + 'Index')
# 轉(zhuǎn)換為OneHot編碼
encoder = OneHotEncoder(inputCols=[string_index.getOutputCol()], outputCols=[col + "_one_hot"])
# 將每個字段的轉(zhuǎn)換方式 放到stages中
stages += [string_index, encoder]
# 將income轉(zhuǎn)換為索引
label_string_index = StringIndexer(inputCol = 'income', outputCol = 'label')
# 添加到stages中
stages += [label_string_index]
# 類別變量 + 數(shù)值變量
assembler_cols = [c + "_one_hot" for c in cat_features] + num_features
assembler = VectorAssembler(inputCols=assembler_cols, outputCol="features")
stages += [assembler]
# 使用pipeline完成數(shù)據(jù)處理
pipeline = Pipeline(stages=stages)
pipeline_model = pipeline.fit(df)
df = pipeline_model.transform(df)
selected_cols = ["label", "features"] + cols
df = df.select(selected_cols)
因為pyspark顯示的數(shù)據(jù)比較像Mysql 那樣不方便觀看,因此我們轉(zhuǎn)成pandas:
import pandas as pd
pd.DataFrame(df.take(20), columns = df.columns)

通過pandas發(fā)現(xiàn),好像還有較多字符串變量,難道特征編碼失敗了?
原來是使用VectorAssembler直接將特征轉(zhuǎn)成了features這一列,pyspark做ML時 需要特征編碼好了并做成向量列,
到這里,數(shù)據(jù)的特征工程就做好了。
分割數(shù)據(jù)集 測試集
train, test = df.randomSplit([0.7, 0.3], seed=2021)
print(train.count())
print(test.count())
22795
9766
可以看到,訓(xùn)練集和測試集安裝7:3的比例分割了,接下來就是構(gòu)建模型進行訓(xùn)練。
邏輯回歸
from pyspark.ml.classification import LogisticRegression
# 創(chuàng)建模型
lr = LogisticRegression(featuresCol = 'features', labelCol = 'label',maxIter=10)
lr_model = lr.fit(train)
可以看到ML的用法和sklearn非常的像,因此使用起來也是相當(dāng)?shù)姆奖恪?/p>
#結(jié)果預(yù)測
predictions = lr_model.transform(test)
看看predictions的結(jié)構(gòu)
predictions.printSchema()
root
|-- label: double (nullable = false)
|-- features: vector (nullable = true)
|-- age: integer (nullable = true)
|-- workclass: string (nullable = true)
|-- fnlwgt: integer (nullable = true)
|-- education: string (nullable = true)
|-- education-num: integer (nullable = true)
|-- marital-status: string (nullable = true)
|-- occupation: string (nullable = true)
|-- relationship: string (nullable = true)
|-- race: string (nullable = true)
|-- sex: string (nullable = true)
|-- capital-gain: integer (nullable = true)
|-- capital-loss: integer (nullable = true)
|-- hours-per-week: integer (nullable = true)
|-- native-country: string (nullable = true)
|-- income: string (nullable = true)
|-- rawPrediction: vector (nullable = true)
|-- probability: vector (nullable = true)
|-- prediction: double (nullable = false)
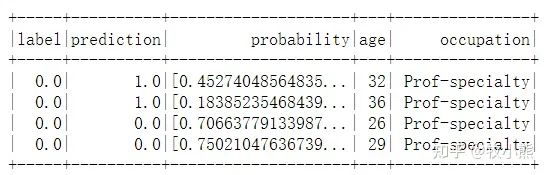
抽取需要的信息
selected = predictions.select("label", "prediction", "probability", "age", "occupation")
display(selected)
selected.show(4)
技術(shù)AUC值
from pyspark.ml.evaluation import BinaryClassificationEvaluator
# 模型評估,通過原始數(shù)據(jù) rawPrediction計算AUC
evaluator = BinaryClassificationEvaluator(rawPredictionCol="rawPrediction")
print('AUC:', evaluator.evaluate(predictions))
AUC:0.9062153434371653
進行網(wǎng)格調(diào)參
from pyspark.ml.tuning import ParamGridBuilder, CrossValidator
# 創(chuàng)建網(wǎng)絡(luò)參數(shù),用于交叉驗證
param_grid = (ParamGridBuilder()
.addGrid(lr.regParam, [0.01, 0.5, 2.0])
.addGrid(lr.elasticNetParam, [0.0, 0.5, 1.0])
.addGrid(lr.maxIter, [1, 5, 10])
.build())
# 五折交叉驗證,設(shè)置模型,網(wǎng)格參數(shù),驗證方法,折數(shù)
cv = CrossValidator(estimator=lr, estimatorParamMaps=param_grid, evaluator=evaluator, numFolds=5)
# 交叉驗證運行
cv_model = cv.fit(train)
# 對于測試數(shù)據(jù),使用五折交叉驗證
predictions = cv_model.transform(test)
print('AUC:', evaluator.evaluate(predictions))
AUC:0.9054096433333642
決策樹模型
from pyspark.ml.classification import DecisionTreeClassifier
# 創(chuàng)建決策樹模型
dt = DecisionTreeClassifier(featuresCol = 'features', labelCol = 'label', maxDepth = 3)
dt_model = dt.fit(train)
#查看決策樹結(jié)構(gòu)
print(dt_model._call_java('toDebugString'))
DecisionTreeClassificationModel: uid=DecisionTreeClassifier_4bd113e9a3c2, depth=3, numNodes=11, numClasses=2, numFeatures=100
If (feature 23 in {0.0})
If (feature 97 <= 7792.0)
Predict: 0.0
Else (feature 97 > 7792.0)
If (feature 94 <= 19.5)
Predict: 0.0
Else (feature 94 > 19.5)
Predict: 1.0
Else (feature 23 not in {0.0})
If (feature 96 <= 12.5)
If (feature 97 <= 3368.0)
Predict: 0.0
Else (feature 97 > 3368.0)
Predict: 1.0
Else (feature 96 > 12.5)
Predict: 1.0
predictions = dt_model.transform(test)
predictions.printSchema()
root
|-- label: double (nullable = false)
|-- features: vector (nullable = true)
|-- age: integer (nullable = true)
|-- workclass: string (nullable = true)
|-- fnlwgt: integer (nullable = true)
|-- education: string (nullable = true)
|-- education-num: integer (nullable = true)
|-- marital-status: string (nullable = true)
|-- occupation: string (nullable = true)
|-- relationship: string (nullable = true)
|-- race: string (nullable = true)
|-- sex: string (nullable = true)
|-- capital-gain: integer (nullable = true)
|-- capital-loss: integer (nullable = true)
|-- hours-per-week: integer (nullable = true)
|-- native-country: string (nullable = true)
|-- income: string (nullable = true)
|-- rawPrediction: vector (nullable = true)
|-- probability: vector (nullable = true)
|-- prediction: double (nullable = false)
#計算AUC值
from pyspark.ml.evaluation import BinaryClassificationEvaluator
evaluator = BinaryClassificationEvaluator()
evaluator.evaluate(predictions)
0.7455098804457034
網(wǎng)格搜參數(shù)
from pyspark.ml.tuning import ParamGridBuilder, CrossValidator
param_grid = (ParamGridBuilder()
.addGrid(dt.maxDepth, [1, 2, 6, 10])
.addGrid(dt.maxBins, [20, 40, 80])
.build())
# 設(shè)置五折交叉驗證
cv = CrossValidator(estimator=dt, estimatorParamMaps=param_grid, evaluator=evaluator, numFolds=5)
# 運行cv
cv_model = cv.fit(train)
# 查看最優(yōu)模型
print("numNodes = ", cv_model.bestModel.numNodes)
print("depth = ", cv_model.bestModel.depth)
numNodes = 429
depth = 10
# 使用五折交叉驗證進行預(yù)測
predictions = cv_model.transform(test)
evaluator.evaluate(predictions)
0.7850384321616918
隨機森林
from pyspark.ml.classification import RandomForestClassifier
# 隨機森林
rf = RandomForestClassifier(featuresCol = 'features', labelCol = 'label')
rf_model = rf.fit(train)
predictions = rf_model.transform(test)
predictions.printSchema()
selected = predictions.select("label", "prediction", "probability", "age", "occupation")
display(selected)
evaluator = BinaryClassificationEvaluator()
evaluator.evaluate(predictions)
0.8932162982538805
一樣的方法
param_grid = (ParamGridBuilder()
.addGrid(rf.maxDepth, [3, 5, 7])
.addGrid(rf.maxBins, [20, 50])
.addGrid(rf.numTrees, [5, 10])
.build())
cv = CrossValidator(estimator=rf, estimatorParamMaps=param_grid, evaluator=evaluator, numFolds=5)
# 運行CV(大約6分鐘)
cv_model = cv.fit(train)
predictions = cv_model.transform(test)
evaluator.evaluate(predictions)
0.8948376797236669
查看模型的結(jié)構(gòu)和特征重要性
best_model
RandomForestClassificationModel: uid=RandomForestClassifier_15bbbdd6642a, numTrees=10, numClasses=2, numFeatures=100
best_model.featureImportances
太長了省略
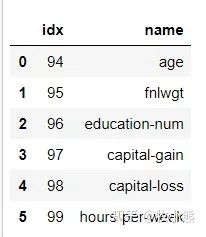
df.schema['features'].metadata
temp = df.schema["features"].metadata["ml_attr"]["attrs"]
df_importance = pd.DataFrame(columns=['idx', 'name'])
for attr in temp['numeric']:
temp_df = {}
temp_df['idx'] = attr['idx']
temp_df['name'] = attr['name']
#print(temp_df)
df_importance = df_importance.append(temp_df, ignore_index=True)
#print(attr['idx'], attr['name'])
#print(attr)
#break
df_importance
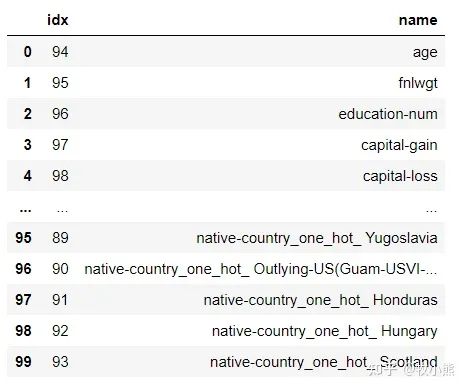
for attr in temp['binary']:
temp_df = {}
temp_df['idx'] = attr['idx']
temp_df['name'] = attr['name']
df_importance = df_importance.append(temp_df, ignore_index=True)
df_importance
對特征重要性進行可視化
df_temp = pd.DataFrame(best_model.featureImportances.toArray())
df_temp.columns = ['feature_importance']
df_importance = df_importance.merge(df_temp, left_index=True, right_index=True)
df_importance.sort_values(by=['feature_importance'], ascending=False, inplace=True)
df_importance

4.小結(jié)
本節(jié)選用了一個常規(guī)的數(shù)據(jù)集,需要通過UCI提供的數(shù)據(jù)預(yù)測個人收入是否會大于5萬,本節(jié)用PySpark對數(shù)據(jù)進行了讀取,特征的編碼以及特征的構(gòu)建,并分別使用了邏輯回歸、決策樹以及隨機森林算法展示數(shù)據(jù)預(yù)測的過程。
spark通過封裝成pyspark后使用難度降低了很多,而且pyspark的ML包提供了基本的機器學(xué)習(xí)模型,可以直接使用,模型的使用方法和sklearn比較相似,因此學(xué)習(xí)成本較低。
往期精彩回顧
本站qq群851320808,加入微信群請掃碼:
