函數(shù)節(jié)流(Throttle)和防抖(Debounce)解析及其OC實現(xiàn)

Throttle和Debounce是什么
Throttle本是機械領(lǐng)域的概念,英文解釋為:
A valve that regulates the supply of fuel to the engine.
中文翻譯成節(jié)流器,用以調(diào)節(jié)發(fā)動機燃料供應(yīng)的閥門。在計算機領(lǐng)域,同樣也引入了Throttle和Debounce概念,這兩種技術(shù)都可用來降低函數(shù)調(diào)用頻率,相似又有區(qū)別。對于連續(xù)調(diào)用的函數(shù),尤其是觸發(fā)頻率密集、目標(biāo)函數(shù)涉及大量計算時,恰當(dāng)使用Throttle和Debounce可以有效提升性能及系統(tǒng)穩(wěn)定性。
對于JS前端開發(fā)人員,由于無法控制DOM事件觸發(fā)頻率,在給DOM綁定事件的時候,常常需要進行Throttle或者Debounce來防止事件調(diào)用過于頻繁。而對于iOS開發(fā)者來說,也許會覺得這兩個術(shù)語很陌生,不過你很可能在不經(jīng)意間已經(jīng)用到了,只是沒想過會有專門的抽象概念。舉個常見的例子,對于UITableView,頻繁觸發(fā)reloadData函數(shù)可能會引起畫面閃動、卡頓,數(shù)據(jù)源動態(tài)變化時甚至?xí)?dǎo)致崩潰,一些開發(fā)者可能會想方設(shè)法減少對reload函數(shù)的調(diào)用,不過對于復(fù)雜的UITableView視圖可能會顯得捉襟見肘,因為reloadData很可能“無處不在”,甚至?xí)豢缥募{(diào)用,此時就可以考慮對reloadData函數(shù)本身做下降頻處理。
下面通過概念定義及示例來詳細解析對比下Throttle和Debounce,先看下二者在JS的Lodash庫中的解釋:
Throttle
Throttle enforces a maximum number of times a function can be called over time. For example, "execute this function at most once every 100 ms."
即,Throttle使得函數(shù)在規(guī)定時間間隔內(nèi)(如100 ms),最多只能調(diào)用一次。
Debounce
Debounce enforces that a function not be called again until a certain amount of time has passed without it being called. For example, "execute this function only if 100 ms have passed without it being called."
即,Debounce可以將小于規(guī)定時間間隔(如100 ms)內(nèi)的函數(shù)調(diào)用,歸并成一次函數(shù)調(diào)用。
對于Debounce的理解,可以想象一下電梯的例子。你在電梯中,門快要關(guān)了,突然又有人要進來,電梯此時會再次打開門,直到短時間內(nèi)沒有人再進為止。雖然電梯上行下行的時間延遲了,但是優(yōu)化了整體資源配置。
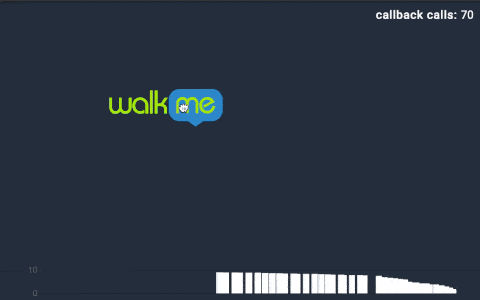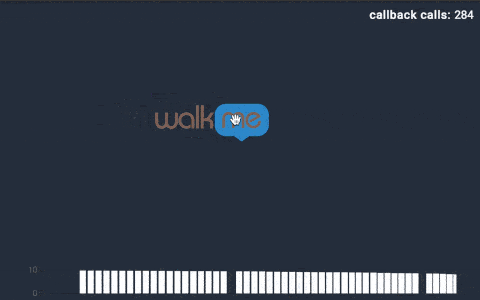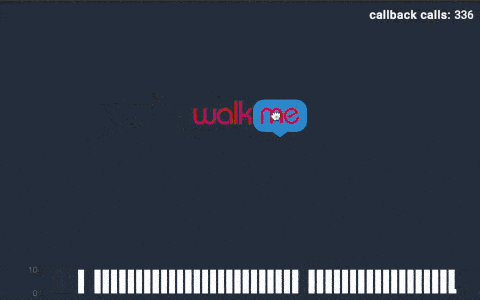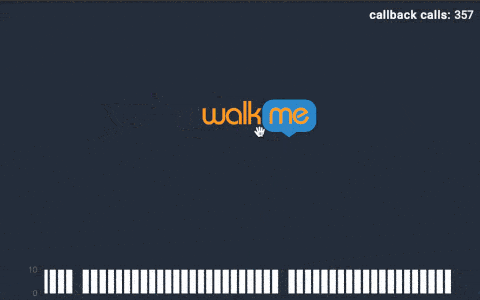
我們再以拖拽手勢回調(diào)的動圖展示為例,來直觀感受下Throttle和Debounce的區(qū)別。每次“walk me”圖標(biāo)拖拽時,會產(chǎn)生一次回調(diào)。在動圖的右上角,可以看到回調(diào)函數(shù)實際調(diào)用的次數(shù)。
概念演示
1)正常回調(diào):
2)Throttle(Leading)模式下的回調(diào):

3)Debounce(Trailing)模式下的回調(diào):

應(yīng)用場景
以下是幾個典型的Throttle和Debounce應(yīng)用場景。
防止按鈕重復(fù)點擊
為了防止用戶重復(fù)快速點擊,導(dǎo)致冗余的網(wǎng)絡(luò)請求、動畫跳轉(zhuǎn)等不必要的損耗,可以使用Throttle的Leading模式,只響應(yīng)指定時間間隔內(nèi)的第一次點擊。
滾動拖拽等密集事件
可以在UIScrollView的滾動回調(diào)didScroll函數(shù)里打日志觀察下,調(diào)用頻率相當(dāng)高,幾乎每移動1個像素都可能產(chǎn)生一次回調(diào),如果回調(diào)函數(shù)的計算量偏大很可能會導(dǎo)致卡頓,此種情況下就可以考慮使用Throttle降頻。
文本輸入自動完成
假如想要實現(xiàn),在用戶輸入時實時展示搜索結(jié)果,常規(guī)的做法是用戶每改變一個字符,就觸發(fā)一次搜索,但此時用戶很可能還沒有輸入完成,造成資源浪費。此時就可以使用Debounce的Trailing模式,在字符改變之后的一段時間內(nèi),用戶沒有繼續(xù)輸入時,再觸發(fā)搜索動作,從而有效節(jié)省網(wǎng)絡(luò)請求次數(shù)。
數(shù)據(jù)同步
以用戶埋點日志上傳為例,沒必要在用戶每操作一次后就觸發(fā)一次網(wǎng)絡(luò)請求,此時就可以使用Debounce的Traling模式,在記錄用戶開始操作之后,且一段時間內(nèi)不再操作時,再把日志merge之后上傳至服務(wù)端。其他類似的場景,比如客戶端與服務(wù)端版本同步,也可以采取這種策略。
在系統(tǒng)層面,或者一些知名的開源庫里,也經(jīng)常可以看到Throttle或者Debounce的身影。
GCD Background Queue
Items dispatched to the queue run at background priority; the queue is scheduled for execution after all high priority queues have been scheduled and the system runs items on a thread whose priority is set for background status. Such a thread has the lowest priority and any disk I/O is throttled to minimize the impact on the system. 在dispatch的Background Queue優(yōu)先級下,系統(tǒng)會自動將磁盤I/O操作進行Throttle,來降低對系統(tǒng)資源的耗費。
ASIHttpRequest及AFNetworking
- (void)handleNetworkEvent:(CFStreamEventType)type
{
//...
[self performThrottling];
//...
}
- (void)throttleBandwidthWithPacketSize:(NSUInteger)numberOfBytes
delay:(NSTimeInterval)delay;
在弱網(wǎng)環(huán)境下, 一個Packet一次傳輸失敗的概率會升高,由于TCP是有序且可靠的,前一個Packet不被ack的情況下,后面的Packet就要等待,所以此時如果啟用Network Throttle機制,減小寫入數(shù)據(jù)量,反而會提升網(wǎng)絡(luò)請求的成功率。
iOS實現(xiàn)
理解了Throttle和Debounce的概念后,在單個業(yè)務(wù)場景中實現(xiàn)起來是很容易的事情,但是考慮到其應(yīng)用如此廣泛,就應(yīng)該封裝成為業(yè)務(wù)無關(guān)的組件,減小重復(fù)勞動,提升開發(fā)效率。
前文提過,Throttle和Debounce在Web前端已經(jīng)有相當(dāng)成熟的實現(xiàn),Ben Alman之前做過一個JQuery插件(不再維護),一年后Jeremy Ashkenas把它加入了underscore.js,而后又加入了Lodash[1]。但是在iOS開發(fā)領(lǐng)域,尤其是對于Objective-C語言,尚且沒有一個可靠、穩(wěn)定且全面的第三方庫。
楊蕭玉曾經(jīng)開源過一個 MessageThrottle[2] 庫,該庫使用Objective-C的runtime與消息轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)機制,使用非常便捷。但是這個庫的缺點也比較明顯,使用了大量的底層HOOK方法,系統(tǒng)兼容性方面還需要進一步的驗證和測試,如果集成的項目中同時使用了其他使用底層runtime的方法,可能會產(chǎn)生沖突,導(dǎo)致非預(yù)期后果。另外該庫是完全面向切面的,作用于全局且隱藏較深,增加了一定的調(diào)試成本。為此筆者封裝了一個新的實現(xiàn)HWThrottle,并借鑒了Lodash的接口及實現(xiàn)方式,該庫有以下特點:
1、未使用任何runtime API,全部由頂層API實現(xiàn);
2、每個業(yè)務(wù)場景需要使用者自己定義一個實例對象,自行管理生命周期,旨在把對項目的影響控制在最小范圍;
3、區(qū)分Throttle和Debounce,提供Leading和Trailing選項。
Demo
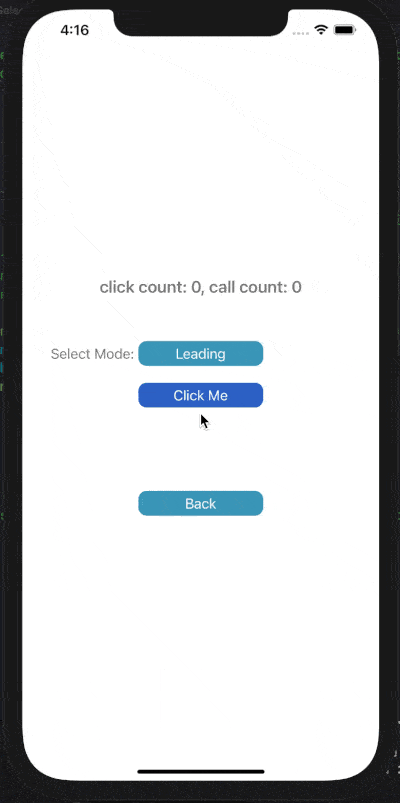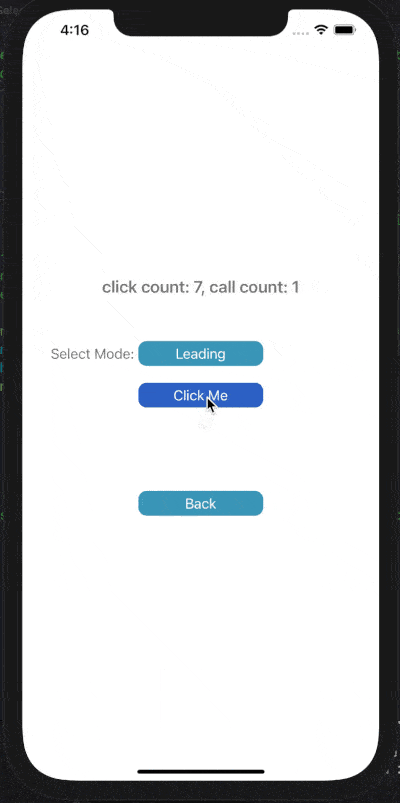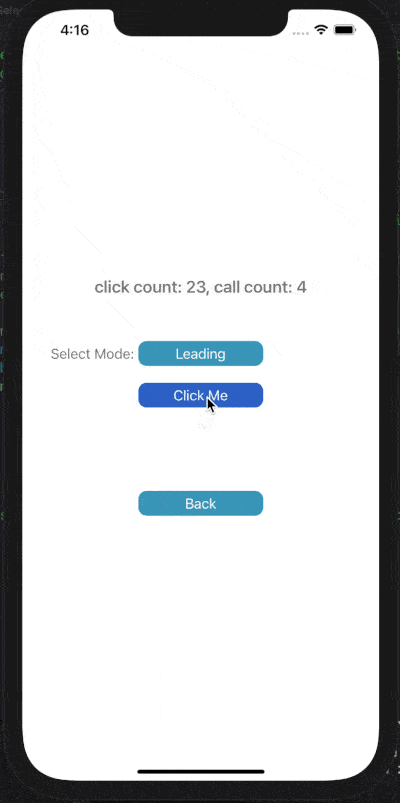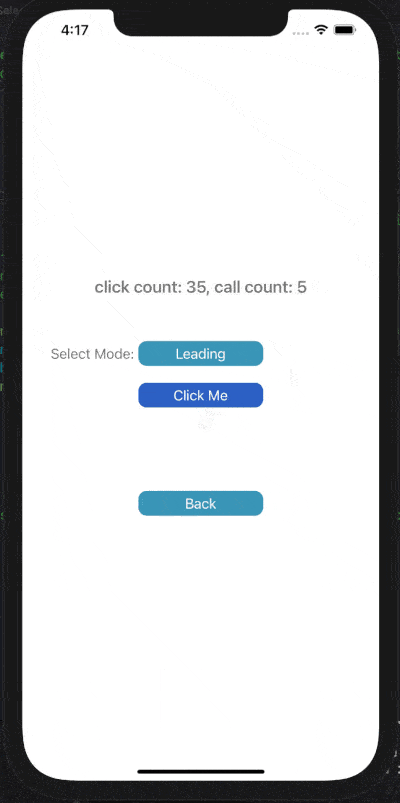
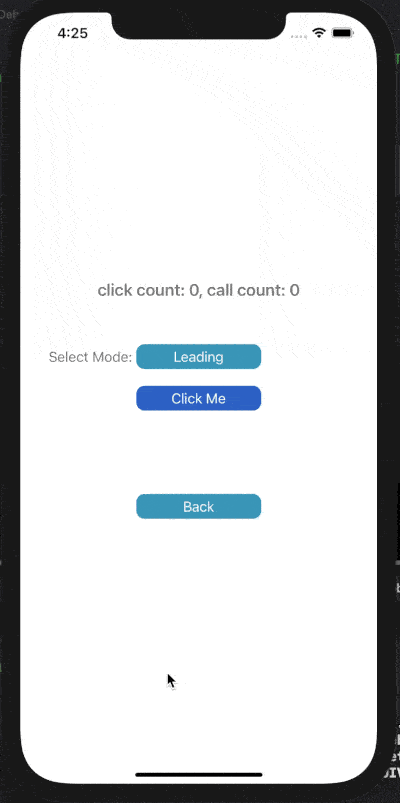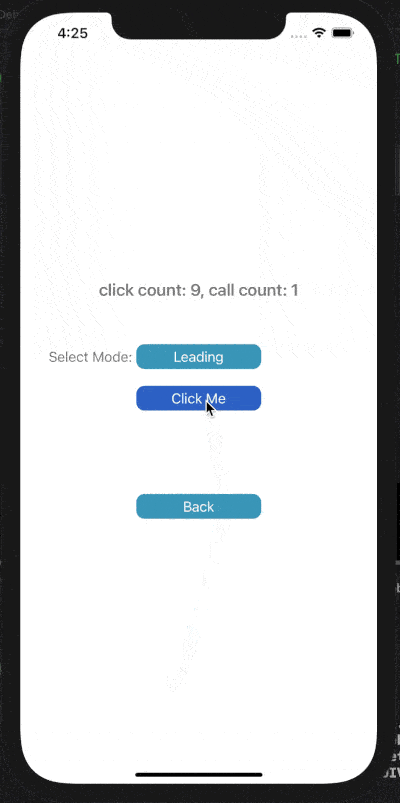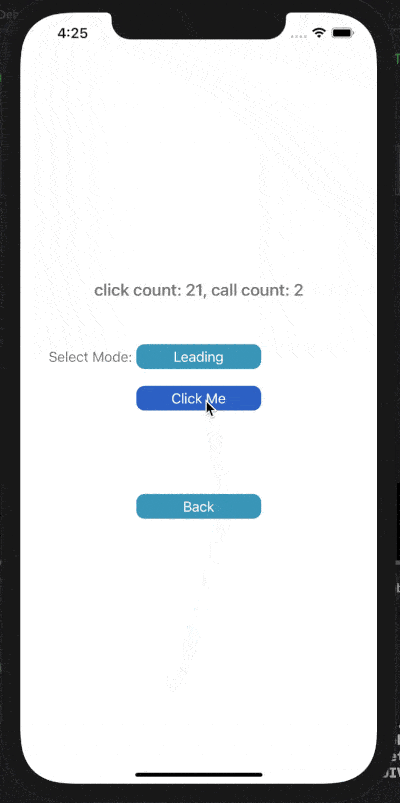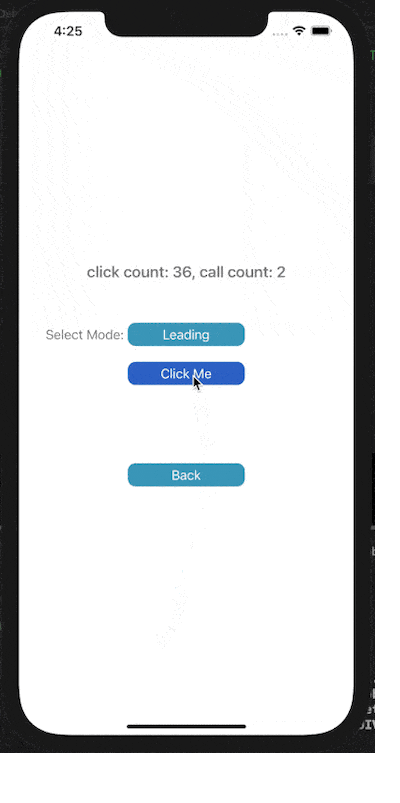
下面展示了對按鈕點擊事件進行Throttle或Debounce的效果,click count表示點擊按鈕次數(shù),call count表示實際調(diào)用目標(biāo)事件的次數(shù)。
在leading模式下,會在指定時間間隔的開始處觸發(fā)調(diào)用;Trailing模式下,會在指定時間間隔的末尾處觸發(fā)調(diào)用。
1) Throttle Leading
2) Throttle Trailing
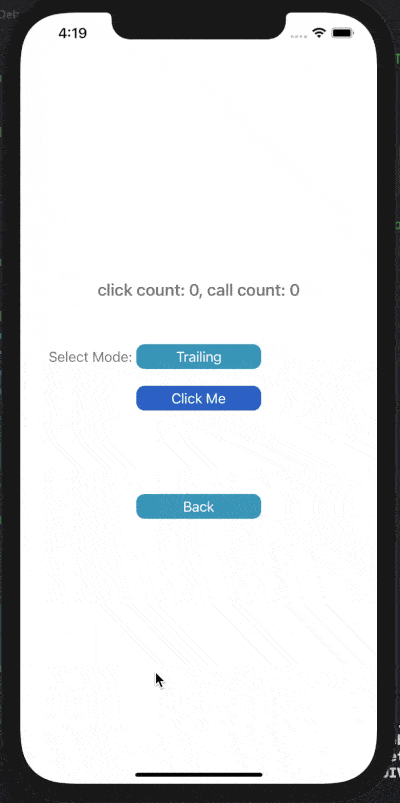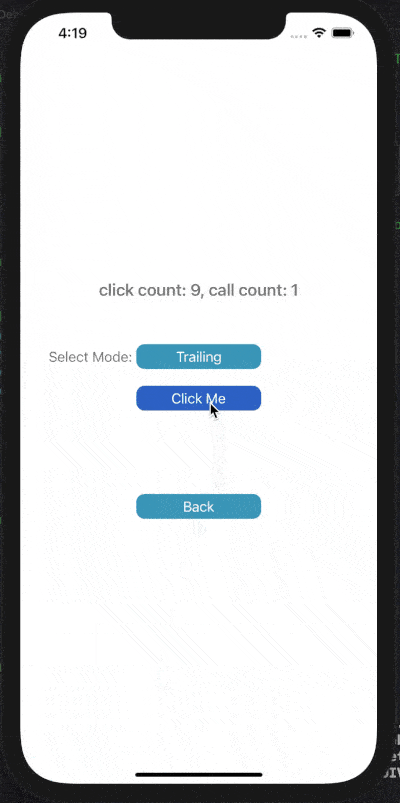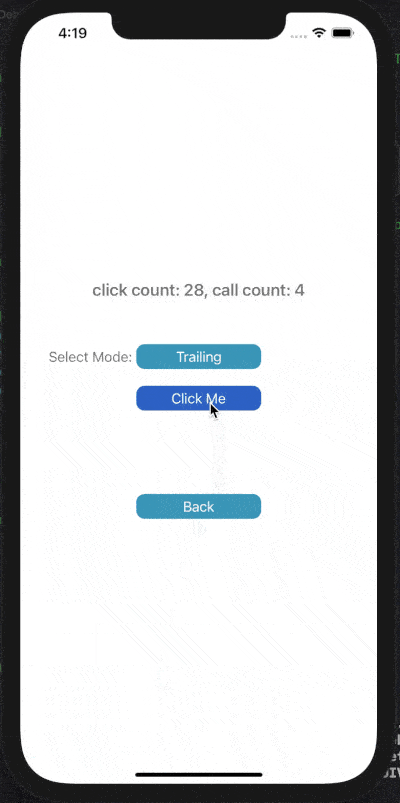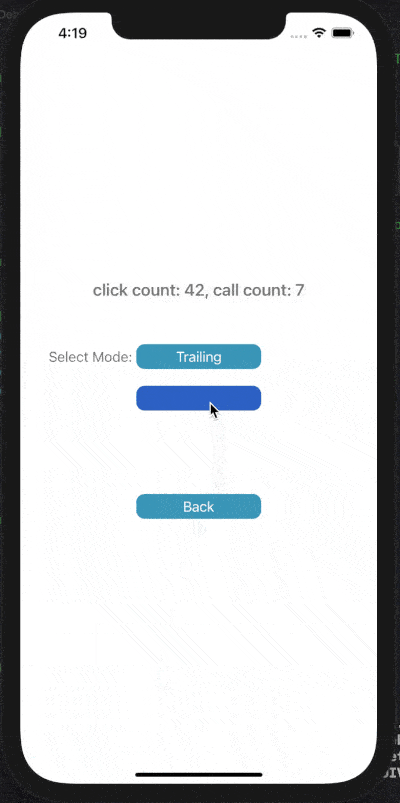
3) Debounce Trailing
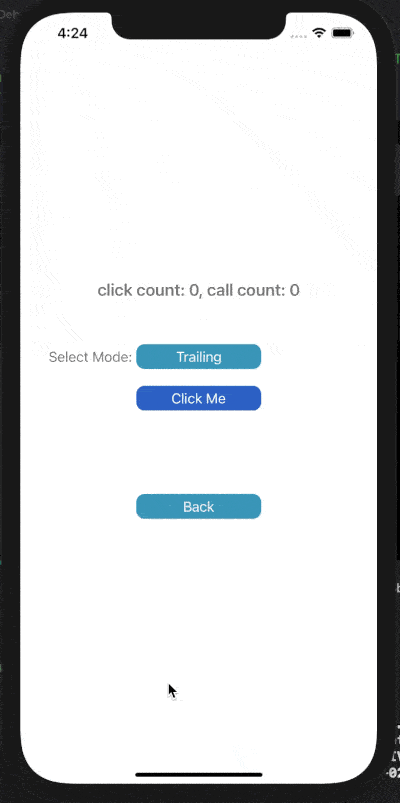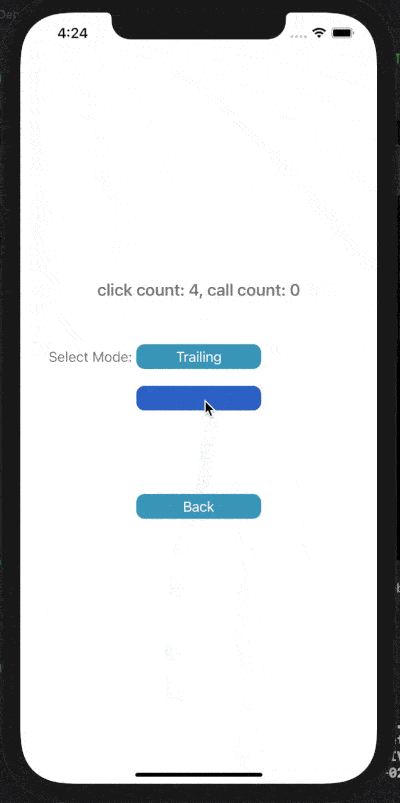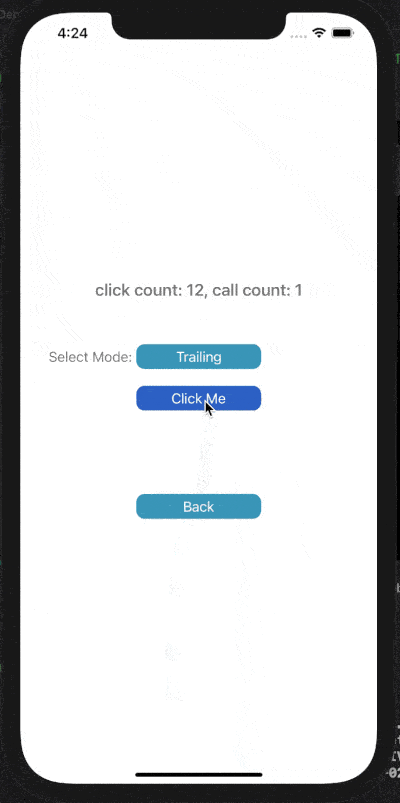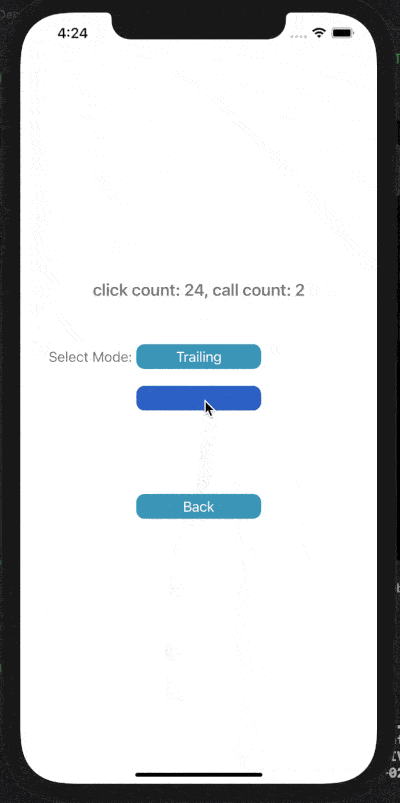
4) Debounce Leading
使用示例:
if (!self.testThrottler) {
self.testThrottler = [[HWThrottle alloc] initWithThrottleMode:HWThrottleModeLeading
interval:1
onQueue:dispatch_get_main_queue()
taskBlock:^{
//do some heavy tasks
}];
}
[self.testThrottler call];
由于使用到了block,注意在Throttle或Debounce對象所有者即將釋放時,即不再使用block時調(diào)用invalidate,該方法會將持有的task block置空,防止循環(huán)引用。如果是在頁面中使用Throttle或Debounce對象,可在disappear回調(diào)中調(diào)用invalidate方法。
- (void)viewWillDisappear:(BOOL)animated {
[super viewWillDisappear:animated];
[self.testThrottler invalidate];
}
接口API:
HWThrottle.h:
#pragma mark - public class
typedef NS_ENUM(NSUInteger, HWThrottleMode) {
HWThrottleModeLeading, //invoking on the leading edge of the timeout
HWThrottleModeTrailing, //invoking on the trailing edge of the timeout
};
typedef void(^HWThrottleTaskBlock)(void);
@interface HWThrottle : NSObject
/// Initialize a throttle object, the throttle mode is the default HWThrottleModeLeading, the execution queue defaults to the main queue. Note that throttle is for the same HWThrottle object, and different HWThrottle objects do not interfere with each other
/// @param interval Throttle time interval, unit second
/// @param taskBlock The task to be throttled
- (instancetype)initWithInterval:(NSTimeInterval)interval
taskBlock:(HWThrottleTaskBlock)taskBlock;
/// Initialize a throttle object, the throttle mode is the default HWThrottleModeLeading. Note that throttle is for the same HWThrottle object, and different HWThrottle objects do not interfere with each other
/// @param interval Throttle time interval, unit second
/// @param queue Execution queue, defaults the main queue
/// @param taskBlock The task to be throttled
- (instancetype)initWithInterval:(NSTimeInterval)interval
onQueue:(dispatch_queue_t)queue
taskBlock:(HWThrottleTaskBlock)taskBlock;
/// Initialize a debounce object. Note that debounce is for the same HWThrottle object, and different HWThrottle objects do not interfere with each other
/// @param throttleMode The throttle mode, defaults HWThrottleModeLeading
/// @param interval Throttle time interval, unit second
/// @param queue Execution queue, defaults the main queue
/// @param taskBlock The task to be throttled
- (instancetype)initWithThrottleMode:(HWThrottleMode)throttleMode
interval:(NSTimeInterval)interval
onQueue:(dispatch_queue_t)queue
taskBlock:(HWThrottleTaskBlock)taskBlock;
/// throttling call the task
- (void)call;
/// When the owner of the HWThrottle object is about to release, call this method on the HWThrottle object first to prevent circular references
- (void)invalidate;
@end
Throttle默認模式為Leading,因為實際使用中,多數(shù)的Throttle場景是在指定時間間隔的開始處調(diào)用,比如防止按鈕重復(fù)點擊時,一般會響應(yīng)第一次點擊,而忽略之后的點擊。
HWDebounce.h:
#pragma mark - public class
typedef NS_ENUM(NSUInteger, HWDebounceMode) {
HWDebounceModeTrailing, //invoking on the trailing edge of the timeout
HWDebounceModeLeading, //invoking on the leading edge of the timeout
};
typedef void(^HWDebounceTaskBlock)(void);
@interface HWDebounce : NSObject
/// Initialize a debounce object, the debounce mode is the default HWDebounceModeTrailing, the execution queue defaults to the main queue. Note that debounce is for the same HWDebounce object, and different HWDebounce objects do not interfere with each other
/// @param interval Debounce time interval, unit second
/// @param taskBlock The task to be debounced
- (instancetype)initWithInterval:(NSTimeInterval)interval
taskBlock:(HWDebounceTaskBlock)taskBlock;
/// Initialize a debounce object, the debounce mode is the default HWDebounceModeTrailing. Note that debounce is for the same HWDebounce object, and different HWDebounce objects do not interfere with each other
/// @param interval Debounce time interval, unit second
/// @param queue Execution queue, defaults the main queue
/// @param taskBlock The task to be debounced
- (instancetype)initWithInterval:(NSTimeInterval)interval
onQueue:(dispatch_queue_t)queue
taskBlock:(HWDebounceTaskBlock)taskBlock;
/// Initialize a debounce object. Note that debounce is for the same HWDebounce object, and different HWDebounce objects do not interfere with each other
/// @param debounceMode The debounce mode, defaults HWDebounceModeTrailing
/// @param interval Debounce time interval, unit second
/// @param queue Execution queue, defaults the main queue
/// @param taskBlock The task to be debounced
- (instancetype)initWithDebounceMode:(HWDebounceMode)debounceMode
interval:(NSTimeInterval)interval
onQueue:(dispatch_queue_t)queue
taskBlock:(HWDebounceTaskBlock)taskBlock;
/// debouncing call the task
- (void)call;
/// When the owner of the HWDebounce object is about to release, call this method on the HWDebounce object first to prevent circular references
- (void)invalidate;
@end
Debounce默認模式為Trailing,因為實際使用中,多數(shù)的Debounce場景是在指定時間間隔的末尾處調(diào)用,比如監(jiān)聽用戶輸入時,一般是在用戶停止輸入后再觸發(fā)調(diào)用。
核心代碼:
Throttle leading:
- (void)call {
if (self.lastRunTaskDate) {
if ([[NSDate date] timeIntervalSinceDate:self.lastRunTaskDate] > self.interval) {
[self runTaskDirectly];
}
} else {
[self runTaskDirectly];
}
}
- (void)runTaskDirectly {
dispatch_async(self.queue, ^{
if (self.taskBlock) {
self.taskBlock();
}
self.lastRunTaskDate = [NSDate date];
});
}
- (void)invalidate {
self.taskBlock = nil;
}
Throttle trailing:
- (void)call {
NSDate *now = [NSDate date];
if (!self.nextRunTaskDate) {
if (self.lastRunTaskDate) {
if ([now timeIntervalSinceDate:self.lastRunTaskDate] > self.interval) {
self.nextRunTaskDate = [NSDate dateWithTimeInterval:self.interval sinceDate:now];
} else {
self.nextRunTaskDate = [NSDate dateWithTimeInterval:self.interval sinceDate:self.lastRunTaskDate];
}
} else {
self.nextRunTaskDate = [NSDate dateWithTimeInterval:self.interval sinceDate:now];
}
NSTimeInterval nextInterval = [self.nextRunTaskDate timeIntervalSinceDate:now];
dispatch_after(dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, (int64_t)(nextInterval * NSEC_PER_SEC)), self.queue, ^{
if (self.taskBlock) {
self.taskBlock();
}
self.lastRunTaskDate = [NSDate date];
self.nextRunTaskDate = nil;
});
}
}
- (void)invalidate {
self.taskBlock = nil;
}
Debounce trailing:
- (void)call {
if (self.block) {
dispatch_block_cancel(self.block);
}
__weak typeof(self)weakSelf = self;
self.block = dispatch_block_create(DISPATCH_BLOCK_INHERIT_QOS_CLASS, ^{
if (weakSelf.taskBlock) {
weakSelf.taskBlock();
}
});
dispatch_after(dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, (int64_t)(self.interval * NSEC_PER_SEC)), self.queue, self.block);
}
- (void)invalidate {
self.taskBlock = nil;
self.block = nil;
}
Debounce leading:
- (void)call {
if (self.lastCallTaskDate) {
if ([[NSDate date] timeIntervalSinceDate:self.lastCallTaskDate] > self.interval) {
[self runTaskDirectly];
}
} else {
[self runTaskDirectly];
}
self.lastCallTaskDate = [NSDate date];
}
- (void)runTaskDirectly {
dispatch_async(self.queue, ^{
if (self.taskBlock) {
self.taskBlock();
}
});
}
- (void)invalidate {
self.taskBlock = nil;
self.block = nil;
}
總結(jié)
希望此篇文章能幫助你全面理解Throttle和Debounce的概念,趕快看看項目中有哪些可以用到Throttle或Debounce來提升性能的地方吧。
再次附上OC實現(xiàn)HWThrottle[3],歡迎issue和討論。
參考資料
Lodash documentation: https://lodash.com/docs/
[2]MessageThrottle: https://github.com/yulingtianxia/MessageThrottle
[3]HWThrottle: https://github.com/HighwayLaw/HWThrottle
