Vue 3.0 diff 算法及原理
(給前端大全加星標,提升前端技能)
轉自:GitHub - liuhanqu
Vue 3.0 采取的 diff 算法和 2.0 的雙端比較有點不同。大概的原理如下
//?c1:?a?b?[?c?d?e?]?f?g??
//?c2:?a?b?[?d?e?c?h?]?f?g
假如有如上的 c1 和 c2 新舊 children,在 diff 的時候,會有一個預處理的過程。
先從前往后比較,當節(jié)點不同時,不再往后進行比較。接著又從后往前進行比較,當節(jié)點不同時,不再往前進行比較。
經過預處理之后,c1 和 c2 真正需要進行 diff 的部分如下所示:
//?c1:?c?d?e
//?c2:?d?e?c?h
最后利用 “最長遞增子序列”,完成上述差異部分的比較,提高 diff 效率。
處理相同的前后節(jié)點
預處理過程代碼如下所示:
const?patchKeyedChildren?=?(
????c1,
????c2,
????container,
????parentAnchor,
????parentComponent,
????parentSuspense,
????isSVG,
????optimized
)?=>?{
????let?i?=?0;??
????const?l2?=?c2.length
????let?e1?=?c1.length?-?1
????let?e2?=?c2.length?-?1
????//?1.?sync?from?start
????while?(i?<=?e1?&&?i?<=?e2)?{
??????const?n1?=?c1[i]
??????const?n2?=?c2[i]
??????if?(isSameVNodeType(n1,?n2))?{
????????patch(
??????????n1,
??????????n2,
??????????container,
??????????parentAnchor,
??????????parentComponent,
??????????parentSuspense,
??????????isSVG,
??????????optimized
????????)
??????}?else?{
????????break
??????}
??????i++
????}
????//?2.?sync?from?end
????while?(i?<=?e1?&&?i?<=?e2)?{
??????const?n1?=?c1[e1]
??????const?n2?=?c2[e2]
??????if?(isSameVNodeType(n1,?n2))?{
????????patch(
??????????n1,
??????????n2,
??????????container,
??????????parentAnchor,
??????????parentComponent,
??????????parentSuspense,
??????????isSVG,
??????????optimized
????????)
??????}?else?{
????????break
??????}
??????e1--
??????e2--
????}
}
僅有節(jié)點新增或移除
進行預處理還有一個好處,就是在某些情況下,我們可以明確的知道有節(jié)點的新增或者刪除。
- 節(jié)點新增
i、e1、e2 滿足下述關系時,可以認為是有節(jié)點新增
//?3.?common?sequence?+?mount
//?(a?b)
//?(a?b)?c
//?i?=?2,?e1?=?1,?e2?=?2
//?(a?b)
//?c?(a?b)
//?i?=?0,?e1?=?-1,?e2?=?0
if?(i?>?e1)?{
????if?(i?<=?e2)?{
????????const?nextPos?=?e2?+?1;
????????const?anchor?=?nextPos?
????????while?(i?<=?e2)?{
????????????patch(
????????????????null,
????????????????c2[i],
????????????????container,
????????????????anchor,
????????????????parentComponent,
????????????????parentSuspense,
????????????????isSVG
????????????)
????????????i++
????????}
????}
}?else?if?{
????//
}?else?{
????//
}
- 節(jié)點移除
i、e1、e2 滿足下述關系時,可以認為是有節(jié)點被移除
//?4.?common?sequence?+?unmount
//?(a?b)?c
//?(a?b)
//?i?=?2,?e1?=?2,?e2?=?1
//?a?(b?c)
//?(b?c)
//?i?=?0,?e1?=?0,?e2?=?-1
if?(i?>?e1)?{
??//
}?else?if?(i?>?e2)?{
????while?(i?<=?e1)?{
????????unmount(c1[i],?parentComponent,?parentSuspense,?true)
????????i++
????}
}?else?{
????//
}
有節(jié)點移動、新增或刪除
有時候情況可能沒有上述那么地簡單,即 i、e1、e2 并不滿足上述兩種情形時,我們就要尋找其中需要被移除、新增的節(jié)點,又或是判斷哪些節(jié)點需要進行移動。
為此,我們需要去遍歷 c1 中還沒有進行處理的節(jié)點,然后查看在 c2 中是否有對應的節(jié)點(key 相同)。沒有,則說明該節(jié)點已經被移除,那就執(zhí)行 unmount 操作。
首先,為了快速確認 c1 的節(jié)點在 c2 中是否有對應的節(jié)點及所在的位置,對 c2 中的節(jié)點建立一個映射 (key: index)
//?5.?unknown?sequence
//?[i?...?e1?+?1]:?a?b?[c?d?e]?f?g
//?[i?...?e2?+?1]:?a?b?[d?e?c?h]?f?g
//?i?=?2,?e1?=?4,?e2?=?5
if?(i?>?e1)?{
??//
}?else?if?(i?>?e2)?{
??//
}?else?{
????const?s1?=?i
????const?s2?=?i
????const?keyToNewIndexMap?=?new?Map()
????//?5.1?build?key:index?map?for?newChildren
????for?(i?=?s2;?i?<=?e2;?i++)?{
????????const?nextChild?=?c2[i]
????????if?(nextChild.key?!==?null)?{
????????????keyToNewIndexMap.set(nextChild.key,?i)
????????}
????}
}
接著,定義以下幾個變量
let?j?
let?patched?=?0
const?toBePatched?=?e2?-?s2?+?1??//?c2?中待處理的節(jié)點數目
let?moved?=?false
//?used?to?track?whether?any?node?has?moved
let?maxNewIndexSoFar?=?0??//?已遍歷的待處理的?c1?節(jié)點在?c2?中對應的索引最大值
//?works?as?Map
//?Note?that?oldIndex?is?offset?by?+1
//?and?oldIndex?=?0?is?a?special?value?indicating?the?new?node?has
//?no?corresponding?old?node.
//?used?for?determining?longest?stable?subsequence
const?newIndexToOldIndexMap?=?new?Array(toBePatched)?//?用于后面求最長遞增子序列
for?(i?=?0;?i?????newIndexToOldIndexMap[i]?=?0
}
然后,遍歷 c1 中待處理的節(jié)點,判斷否 c2 中是有相同 key 的節(jié)點存在。
- 沒有,說明該節(jié)點已經被移除,unmount。
- 有,調用 patch 函數。并記錄節(jié)點在 c1 中的索引。同時,記錄節(jié)點在 c2 中的最大索引,假如節(jié)點在 c2 中的索引位置小于這個最大索引,那么說明是有元素需要進行移動。
//?5.2?loop?through?old?children?left?to?be?patched?and?try?to?patch
//?matching?nodes?&?remove?nodes?that?are?no?longer?present
for?(i?=?s1;?i?<=?e1;?i++)?{
????const?prevChild?=?c1[i]
????//?(A)
????let?newIndex?
????if?(prevChild.key?!==?null)?{
????????newIndex?=?keyToNewIndexMap.get(prevChild.key)
????}?else?{
????????for?(j?=?s2;?i?<=?e2;?j++)?{
????????????if?(
??????????????newIndexToOldIndexMap[j?-?s2]?===?0?&&
??????????????isSameVNodeType(prevChild,?c2[j])
????????????)?{
??????????????newIndex?=?j
??????????????break
????????????}
????????}
????}
????if?(newIndex?===?void?0)?{
????????unmount(prevChild,?parentComponent,?parentSuspense,?true)
????}?else?{
????????newIndexToOldIndexMap[newIndex??-?s2]?=?i?+?1??//?(B)
????????if?(newIndex?>=?maxNewIndexSoFar)?{
????????????maxNewIndexSoFar?=?newIndex
????????}?else?{
????????????moved?=?true
????????}
????????patch(
????????????prevChild,
????????????c2[i],
????????????container,
????????????null,
????????????parentComponent,
????????????parentSuspense,
????????????isSVG,
????????????optimized
????????)
????????patched++??//?(C)
????}
}
是不是 c1 中的所有節(jié)點都需要在 c2 中尋找對應節(jié)點,然后調用 patch 呢。
注意到上面的代碼 (C),我們會更新已經 patched 的節(jié)點的數目,那么當 patched > toBePatched,可以認為接下來遍歷的 c1 中的節(jié)點都是多余的了,直接移除就好。
所以在上面的 (A) 處需要補充一下代碼
if?(patched?>=?toBePatched)?{
????//?all?new?children?have?been?patched?so?this?can?only?be?a?removal
????unmount(prevChild,?parentComponent,?parentSuspense,?true)
????continue
}
到這里,就是較難理解的部分了。
開篇我們說過,預處理過后,剩下的節(jié)點會借助最長遞增子序列來提高 diff 效率。
求解最長遞增子序列,主要的目的就是為了減少 dom 元素的移動,也可以理解為最少的 dom 操作。
首先,我們需要求解得到最長遞增子序列
//?generate?longest?stable?subsequence?only?when?nodes?have?moved
const?increasingNewIndexSequence?=?moved
??????getSequence(newIndexToOldIndexMap)
????:?EMPTY_ARR?
先看看這里的 newIndexToOldIndexMap 的值是什么。
結合一下具體的例子,假設 c1 、c2 如下圖所示
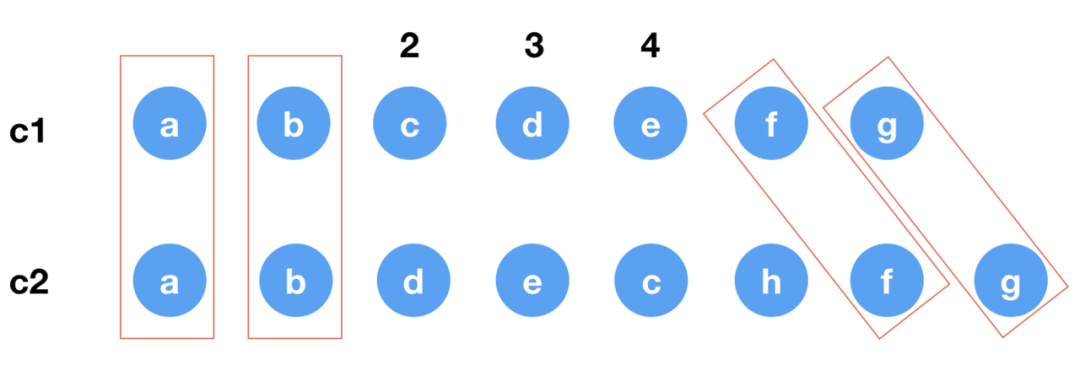 image
image定義并初始化 newIndexToOldIndexMap
const?newIndexToOldIndexMap?=?new?Array(toBePatched)
for?(i?=?0;?i?????newIndexToOldIndexMap[i]?=?0
}
toBePatched 即預處理后,c2 中待處理的節(jié)點數目。對應這里的例子,會有
toBePatched?=?4
newIndexToOldIndexMap?=?[0,?0,?0,?0]
注意到上面 5.2 遍歷 c1 中節(jié)點的代碼的 (B) 處,有
//?這里是?i?+?1,不是?i?
//?因為?0?是一個特殊值,表示這個是新增的節(jié)點
newIndexToOldIndexMap[newIndex??-?s2]?=?i?+?1??//?(B)
所以處理完 c1 中的節(jié)點后,將有
moved?=?true
newIndexToOldIndexMap?=?[4,?5,?3,?0]
那么,increasingNewIndexSequence 的值就是 getSequence(newIndexToOldIndexMap) 的返回值
//?[4,?5,?3,?0]??-->?最長遞增子序列是?[4,?5]?
//?對應的索引是?[0,?1]
increasingNewIndexSequence?=?[0,?1]
在求解得到最長遞增子序列之后,剩下的就是遍歷 c2 中的待處理節(jié)點,判斷是否節(jié)點是否屬于新增,是否需要進行移動。
j?=?increasingNewIndexSequence.length?-?1
//?looping?backwards?so?that?we?can?use?last?patched?node?as?anchor
//?注意:這里是從后往前遍歷
for?(i?=?toBePatched?-?1;?i?>=?0;?i--)?{
????const?nextIndex?=?s2?+?i
????const?nextChild?=?c2[nextIndex]
????const?anchor?=
????????nextIndex?+?1?
????//?newIndexToOldIndexMap?里的值默認初始化為?0?
????//?這里?===?0?表示?c2?中的節(jié)點在?c1?中沒有對應的節(jié)點,屬于新增
????if?(newIndexToOldIndexMap[i]?===?0)?{
????????//?mount?new
????????patch(
????????????null,
????????????nextChild,
????????????container,
????????????anchor,
????????????parentComponent,
????????????parentSuspense,
????????????isSVG
????????)
????}?else?if?(moved)?{
????????//?move?if:
????????//?There?is?no?stable?subsequence?(e.g.?a?reverse)
????????//?OR?current?node?is?not?among?the?stable?sequence
????????
????????//?j??最長遞增子序列為?[]?
????????if?(j?????????????move(nextChild,?container,?anchor,?MoveType.REORDER)
????????}?else?{
????????????j--
????????}
????}
}
最長遞增子序列
在計算機科學中,最長遞增子序列(longest increasing subsequence)問題是指,在一個給定的數值序列中,找到一個子序列,使得這個子序列元素的數值依次遞增,并且這個子序列的長度盡可能地大。最長遞增子序列中的元素在原序列中不一定是連續(xù)的。-- 維基百科
對于以下的原始序列
0,?8,?4,?12,?2,?10,?6,?14,?1,?9,?5,?13,?3,?11,?7,?15
最長遞增子序列為
0,?2,?6,?9,?11,?15.
值得注意的是原始序列的最長遞增子序列并不一定唯一,對于該原始序列,實際上還有以下兩個最長遞增子序列
0,?4,?6,?9,?11,?15
0,?4,?6,?9,?13,?15
最后
至此,Vue 3.0 的 diff 代碼就分析完了,歡迎一起討論。
具體的代碼:https://github.com/vuejs/vue-next/blob/master/packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts
- EOF -
3、Vitural Dom & diff算法 (一) 偽代碼實現
覺得本文對你有幫助?請分享給更多人
推薦關注「前端大全」,提升前端技能
點贊和在看就是最大的支持??
