用Python輕松開發(fā)數(shù)據(jù)庫取數(shù)下載工具
?本文示例代碼已上傳至我的
?Github倉庫https://github.com/CNFeffery/DataScienceStudyNotes
1 簡介
這是我的系列教程「Python+Dash快速web應(yīng)用開發(fā)」的第十四期,在前兩期中,我們針對dash_table的自定義樣式、前后端分頁、單元格內(nèi)容編輯等特點展開了介紹。
而在dash_table中還有很多高級特性,可以極大程度上豐富DataTable()所渲染網(wǎng)頁表格的交互能力,今天的文章作為「交互表格篇」的下篇,我們就來一起學(xué)習(xí)其中比較實用的一些特性。

2 dash_table的更多實用功能
2.1 更多表格交互特性
上一期文章最后我們學(xué)習(xí)了通過設(shè)置參數(shù)editable=True,使得渲染出的表格可以通過鼠標(biāo)雙擊進(jìn)行編輯,而dash_table除此之外,還有更多實用的交互能力:
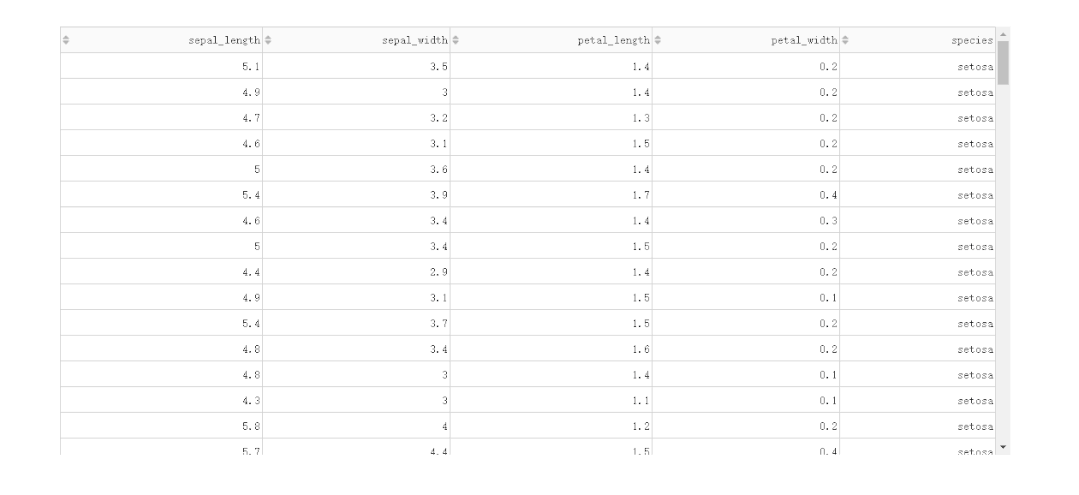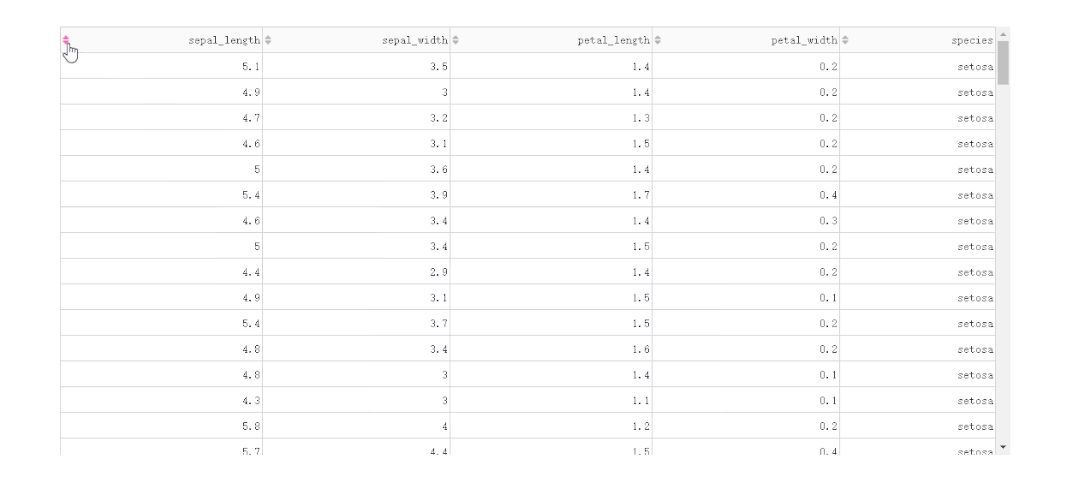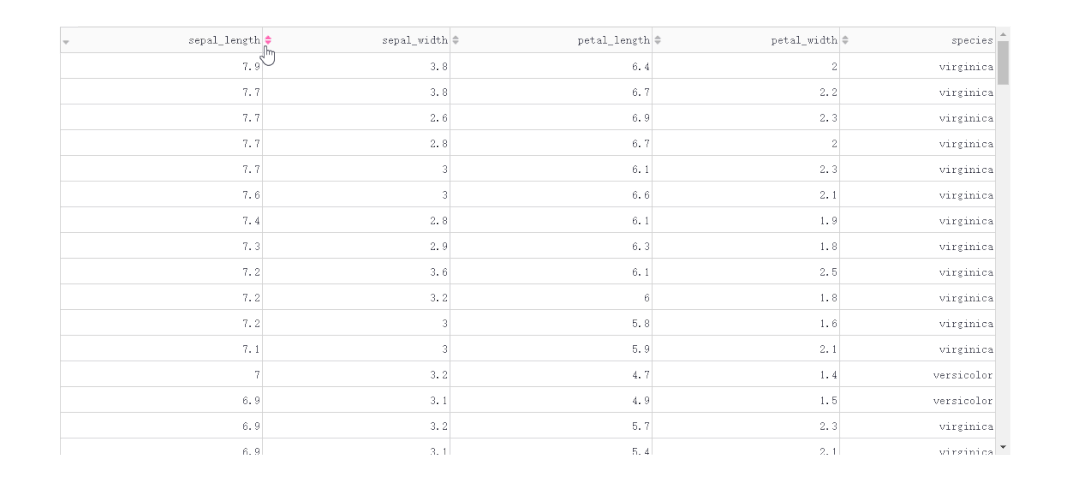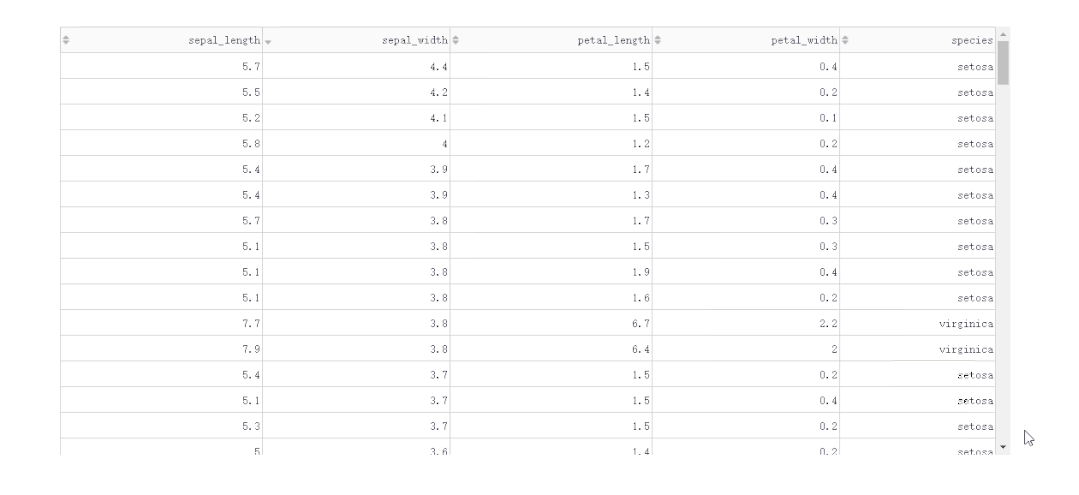
2.1.1 按列排序
「普通單列排序」
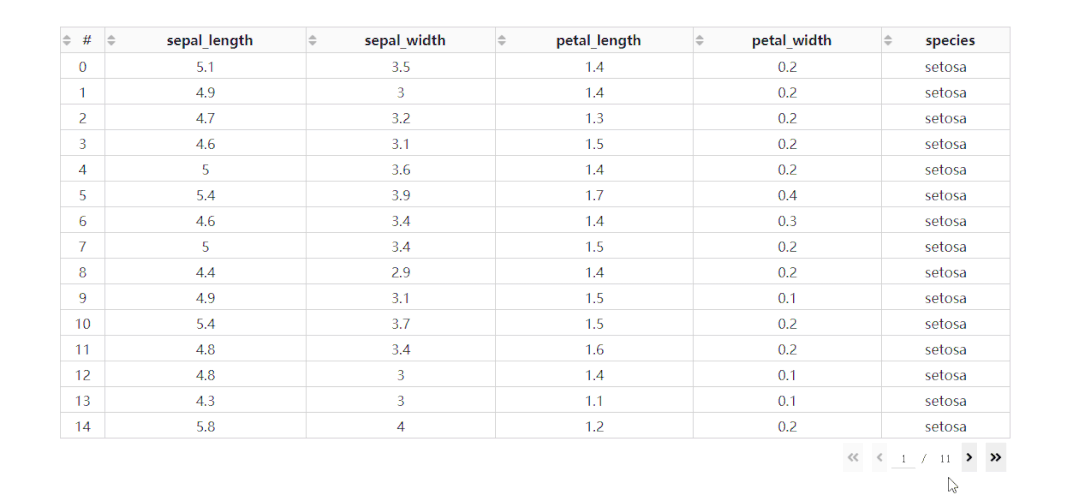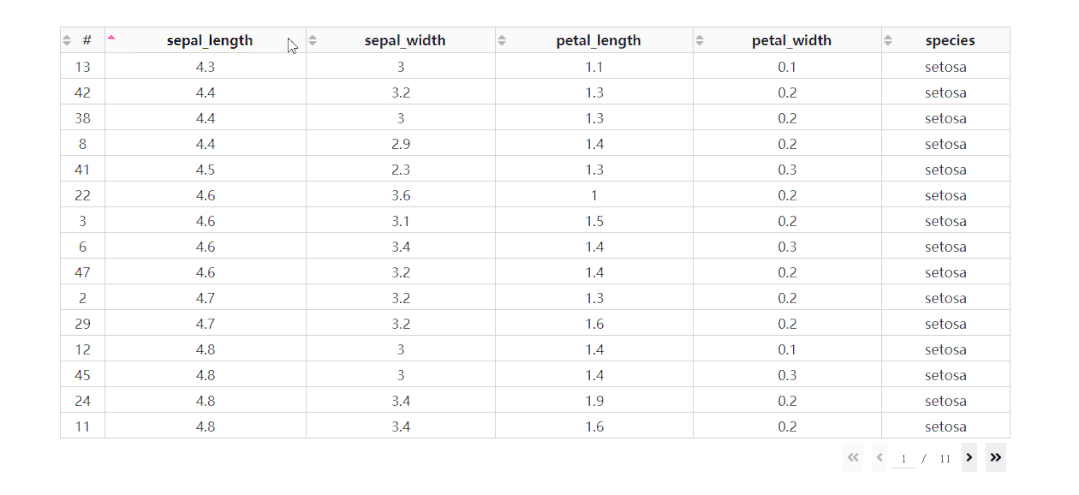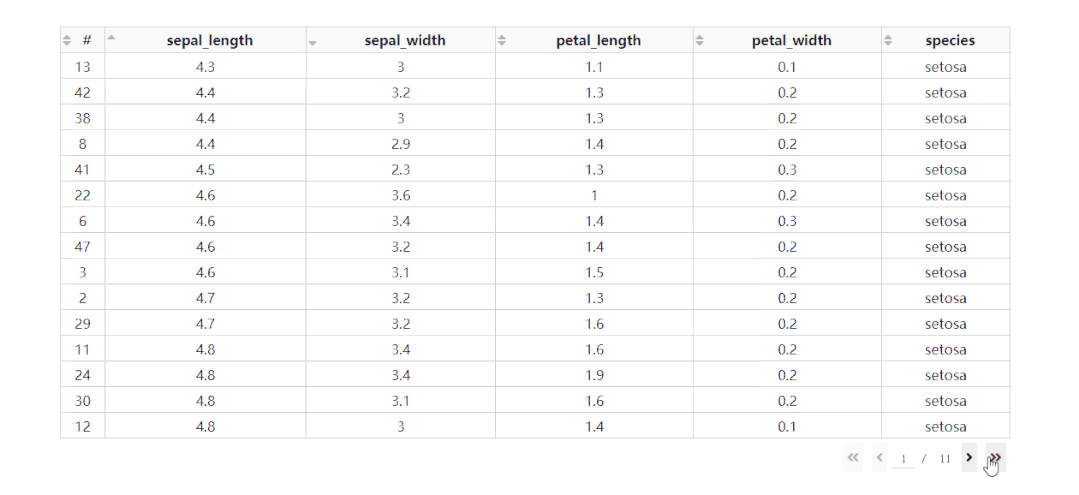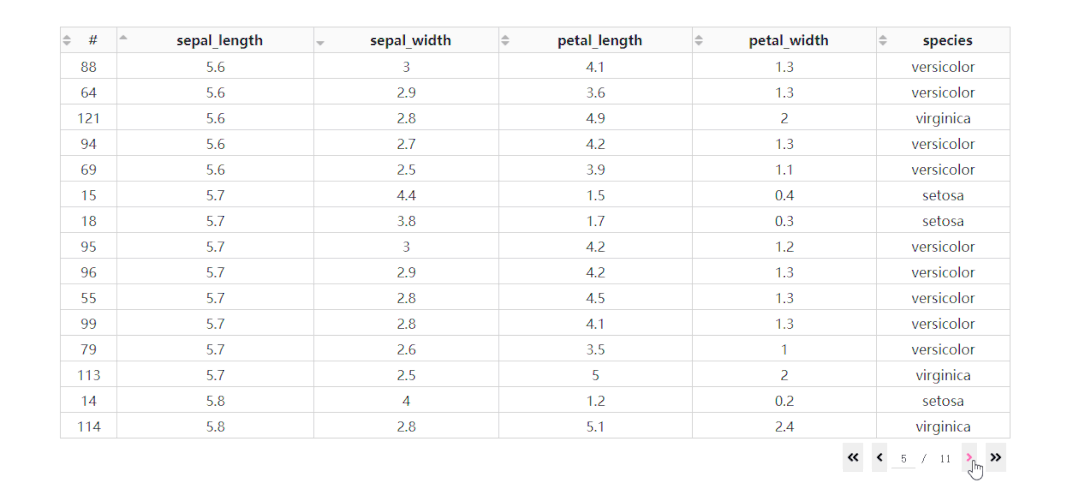
在DataTable()中,我們只需要設(shè)置參數(shù)sort_action='native',即可開啟列排序功能,此時每一列列名單元格內(nèi)都會出現(xiàn)部件供我們點擊切換排序方式:
?app1.py
?
import dash
import dash_table
import dash_bootstrap_components as dbc
import seaborn as sns
df = sns.load_dataset('iris')
app = dash.Dash(__name__)
app.layout = dbc.Container(
[
dash_table.DataTable(
data=df.to_dict('records'),
columns=[
{'name': column, 'id': column}
for column in df.columns
],
style_table={
'height': '500px',
'overflow-y': 'auto'
},
sort_action='native'
)
],
style={
'margin-top': '50px'
}
)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run_server(debug=True)
「基于后端排序的多列排序」
在DataTable()中設(shè)置sort_action='native'時,對應(yīng)的是「按列排序」的前端模式,也即是數(shù)據(jù)一次性灌注到瀏覽器的前提下進(jìn)行排序,這種方式不僅不適合大型數(shù)據(jù)集,而且只支持「單列排序」。
而當(dāng)數(shù)據(jù)渲染方式為后端模式時,我們通過設(shè)置參數(shù)sort_action='custom'以及sort_mode='multi',配合在回調(diào)中獲取屬性sort_by中記錄的參與排序的列名及升序降序方式,就可以實現(xiàn)多列排序。
我們在上一期的app2.py的基礎(chǔ)上修改得到下面的例子:
?app2.py
?
import dash
import dash_bootstrap_components as dbc
import dash_table
from dash.dependencies import Input, Output
import seaborn as sns
df = sns.load_dataset('iris')
df.insert(0, '#', df.index)
app = dash.Dash(__name__)
app.layout = dbc.Container(
[
dbc.Spinner(
dash_table.DataTable(
id='dash-table',
columns=[
{'name': column, 'id': column}
for column in df.columns
],
page_size=15, # 設(shè)置單頁顯示15行記錄行數(shù)
page_action='custom',
page_current=0,
style_header={
'font-family': 'Times New Romer',
'font-weight': 'bold',
'text-align': 'center'
},
style_data={
'font-family': 'Times New Romer',
'text-align': 'center'
},
sort_action='custom',
sort_mode='multi'
)
)
],
style={
'margin-top': '50px'
}
)
@app.callback(
[Output('dash-table', 'data'),
Output('dash-table', 'page_count')],
[Input('dash-table', 'page_current'),
Input('dash-table', 'page_size'),
Input('dash-table', 'sort_by')]
)
def refresh_page_data(page_current, page_size, sort_by):
if sort_by:
return (
df
.sort_values(
[col['column_id'] for col in sort_by],
ascending=[
col['direction'] == 'asc'
for col in sort_by
]
)
.iloc[page_current * page_size:(page_current + 1) * page_size]
.to_dict('records'),
1 + df.shape[0] // page_size
)
return (
df.iloc[page_current * page_size:(page_current + 1) * page_size].to_dict('records'),
1 + df.shape[0] // page_size
)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run_server(debug=True)
2.1.2 按列條件篩選
除了基于指定字段進(jìn)行排序之外,dash_table還支持列的條件篩選,設(shè)置filter_action="native",就可以開啟基礎(chǔ)的按列條件篩選功能,此時每一列表頭下都會多出供用戶輸入篩選條件的單元格:
?app3.py
?
import dash
import dash_table
import dash_bootstrap_components as dbc
import seaborn as sns
df = sns.load_dataset('iris')
app = dash.Dash(__name__)
app.layout = dbc.Container(
[
dash_table.DataTable(
data=df.to_dict('records'),
columns=[
{'name': column, 'id': column}
for column in df.columns
],
# 自定義條件篩選單元格樣式
style_filter={
'font-family': 'Times New Romer',
'background-color': '#e3f2fd'
},
style_table={
'height': '500px',
'overflow-y': 'auto'
},
style_header={
'font-family': 'Times New Romer',
'font-weight': 'bold',
'text-align': 'center'
},
style_data={
'font-family': 'Times New Romer',
'text-align': 'center'
},
filter_action="native"
)
],
style={
'margin-top': '50px'
}
)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run_server(debug=True)
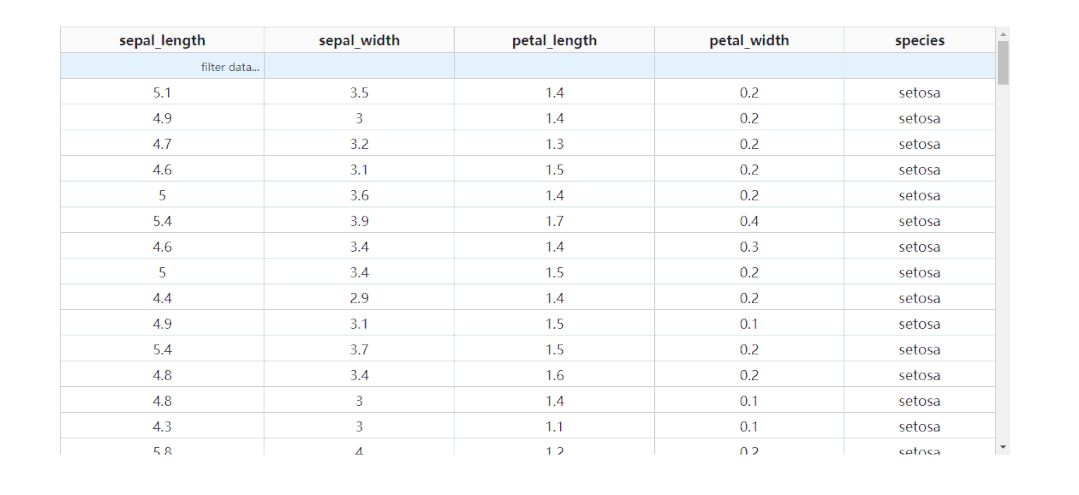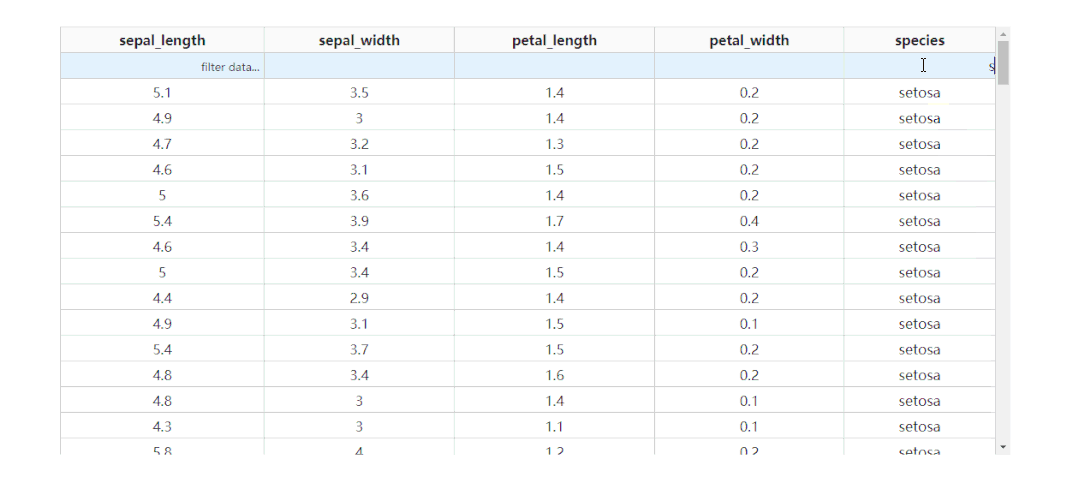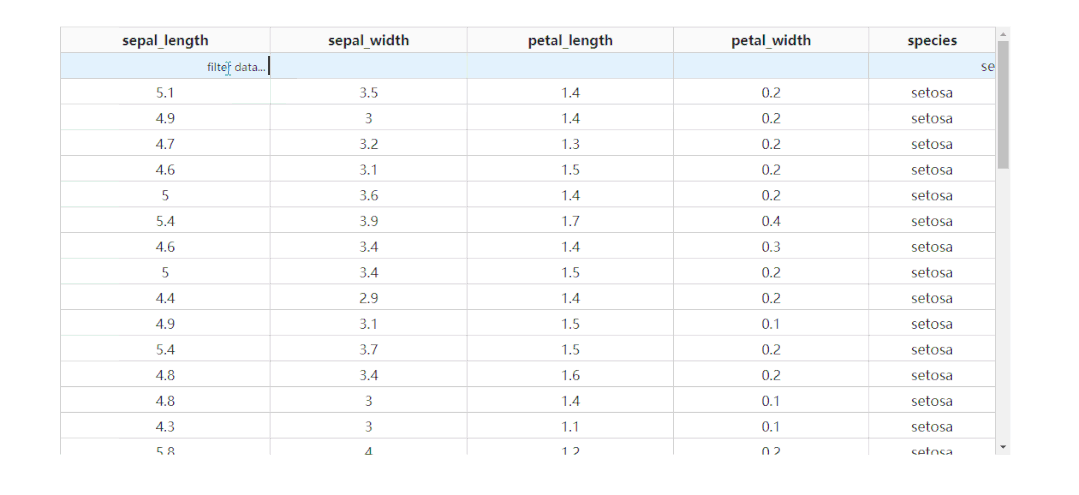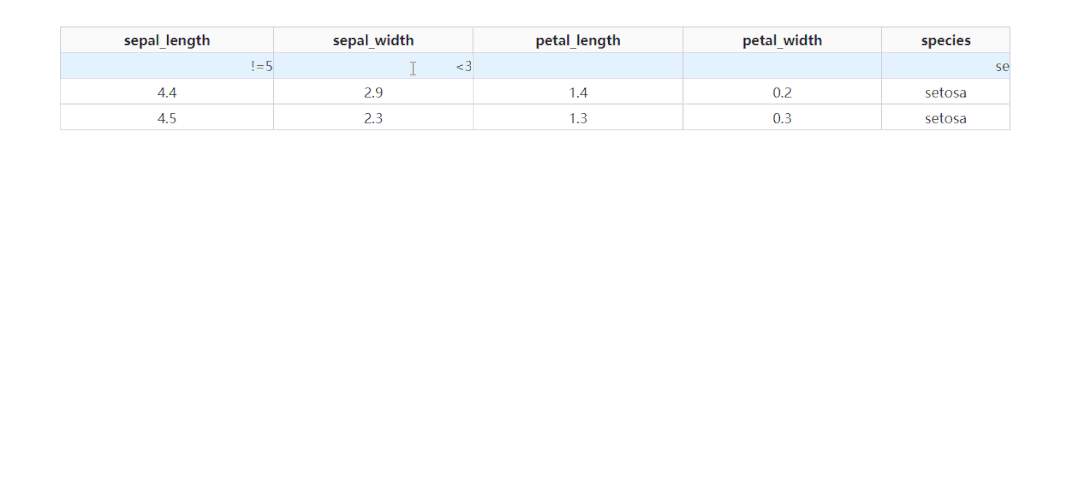
而dash_table中自帶的條件篩選語法很豐富,有條件的朋友可以前往https://dash.plotly.com/datatable/filtering了解更多。
而dash_table同樣可以實現(xiàn)后端篩選,和前面的后端排序類似,主要利用filter_query屬性的回調(diào)變化在后臺基于pandas等框架進(jìn)行數(shù)據(jù)篩選,比較簡單,這里就不再贅述。
2.2 自帶的數(shù)據(jù)表格下載功能
dash_table還自帶了將當(dāng)前所渲染的表格內(nèi)容直接下載為csv或xlsx格式文件的簡易功能,通過參數(shù)export_format設(shè)置導(dǎo)出的文件格式,但自帶的下載按鈕樣式比較丑,如果你對此有比較高的要求,還是建議結(jié)合之前的「上傳下載篇」自己設(shè)計相關(guān)功能:
2.3 凍結(jié)首行
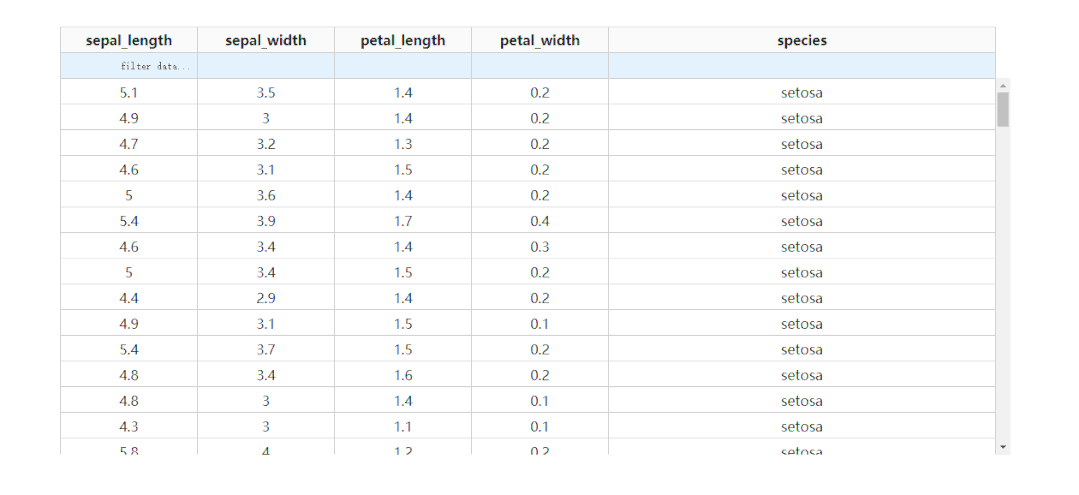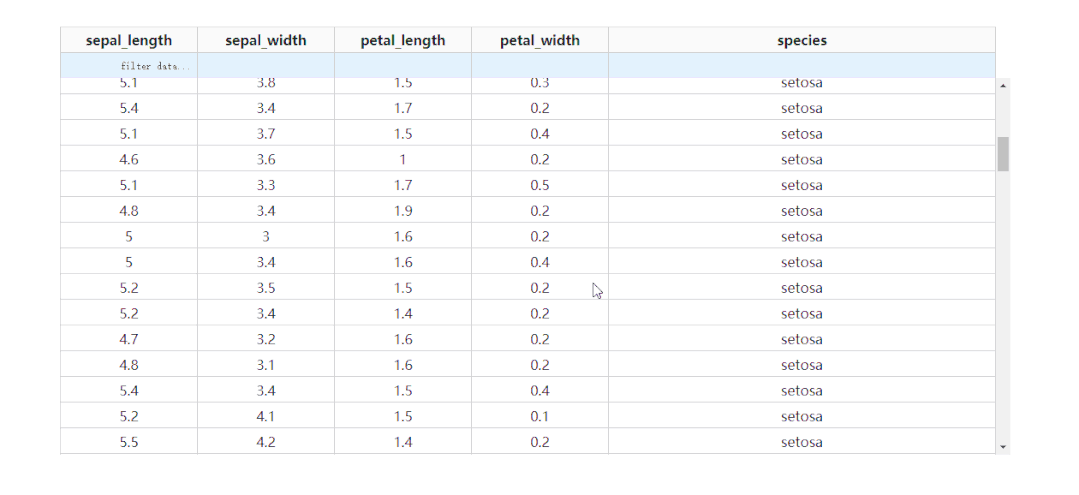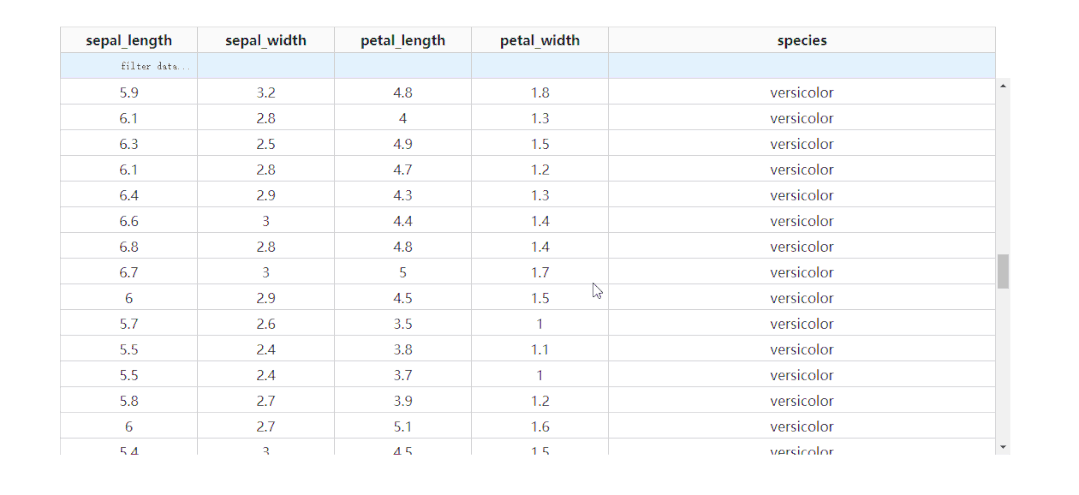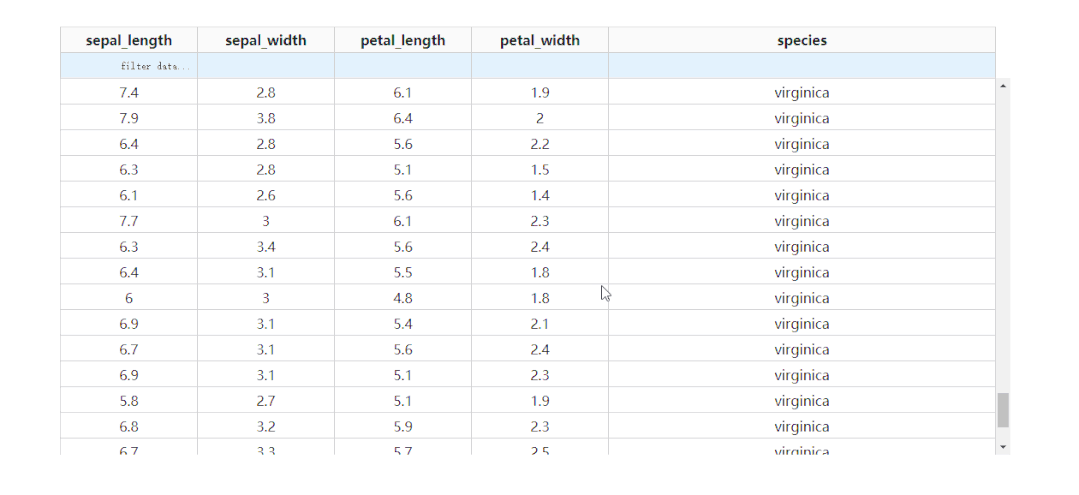
通過設(shè)置參數(shù)fixed_rows={'headers': True},我們可以實現(xiàn)下滑查看表格的過程中,始終保持表頭被凍結(jié):
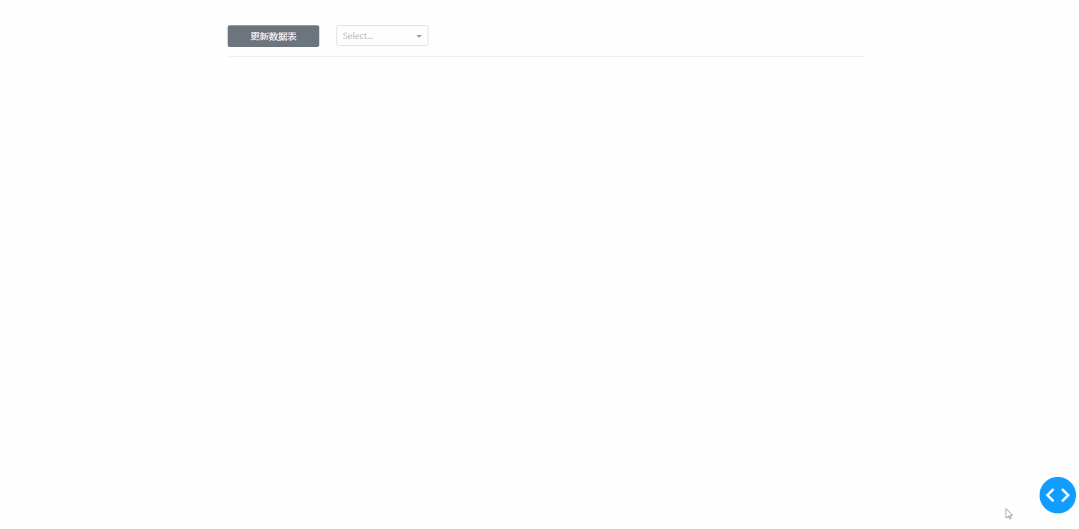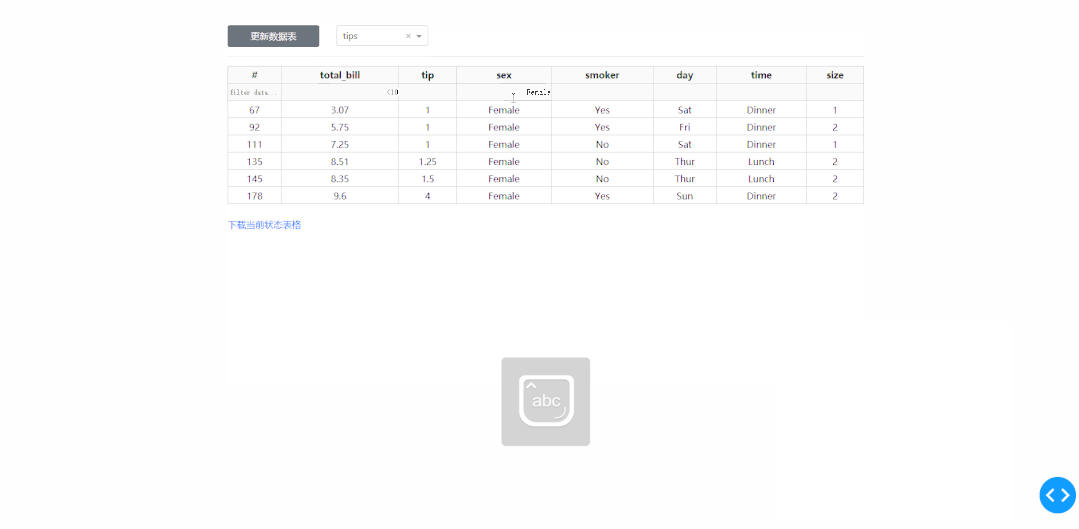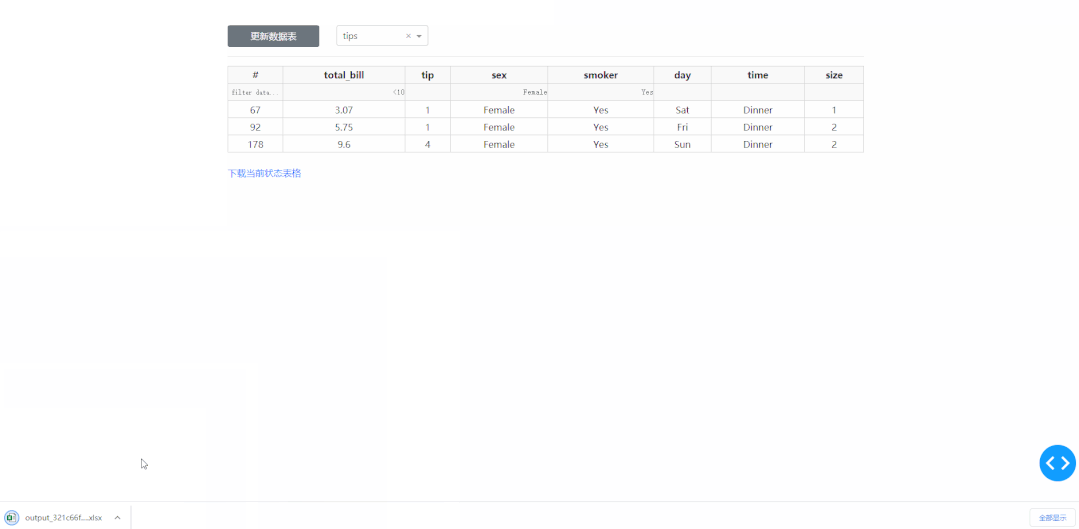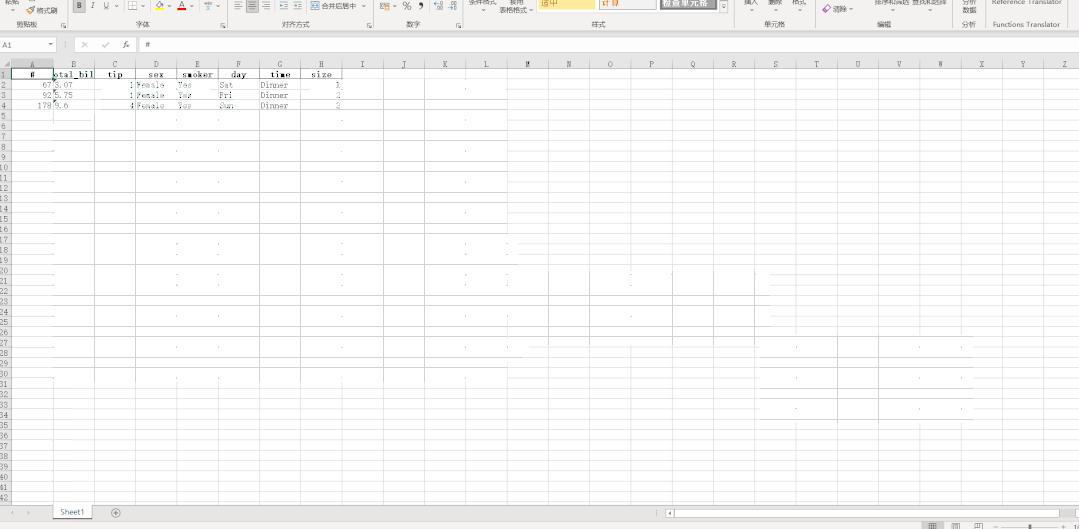
3 開發(fā)一個在線取數(shù)工具
在學(xué)習(xí)完今天的內(nèi)容之后,我們來結(jié)合之前「上傳下載篇」中提到的下載功能,來制作一個簡單的對指定數(shù)據(jù)庫中的數(shù)據(jù)表進(jìn)行快速條件篩選并下載的工具,其中DataTable的derived_virtual_data屬性記錄了經(jīng)過排序、條件篩選等操作后當(dāng)前顯示的表格數(shù)據(jù):
?app4.py
?
import dash
import dash_bootstrap_components as dbc
import dash_core_components as dcc
import dash_html_components as html
import dash_table
from dash.dependencies import Input, Output
from flask import send_from_directory
import os
import uuid
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
import pandas as pd
try:
os.mkdir("downloads")
except FileExistsError:
pass
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:mysql@localhost/DASH')
app = dash.Dash(__name__)
@app.server.route('/download/<file>')
def download(file):
return send_from_directory('downloads', file)
app.layout = dbc.Container(
[
dbc.Row(
[
dbc.Col(dbc.Button('更新數(shù)據(jù)表', id='refresh-tables', style={'width': '100%'}), width=2),
dbc.Col(dcc.Dropdown(id='table-select', style={'width': '100%'}), width=2)
]
),
html.Hr(),
dash_table.DataTable(
id='dash-table',
editable=True,
page_size=15,
style_header={
'font-family': 'Times New Romer',
'font-weight': 'bold',
'text-align': 'center'
},
style_data={
'font-family': 'Times New Romer',
'text-align': 'center'
},
style_data_conditional=[
{
# 對選中狀態(tài)下的單元格進(jìn)行自定義樣式
"if": {"state": "selected"},
"background-color": "#b3e5fc",
"border": "none"
},
],
filter_action="native"
),
html.Br(),
html.A(id='download-url', target="_blank")
],
style={
'margin-top': '50px'
}
)
@app.callback(
Output('table-select', 'options'),
Input('refresh-tables', 'n_clicks')
)
def refresh_tables(n_clicks):
if n_clicks:
return [
{
'label': table,
'value': table
}
for table in pd.read_sql_query('SHOW TABLES', con=engine)['Tables_in_dash']
]
return dash.no_update
@app.callback(
[Output('dash-table', 'data'),
Output('dash-table', 'columns')],
Input('table-select', 'value')
)
def render_dash_table(value):
if value:
df = pd.read_sql_table(value, con=engine)
return df.to_dict('records'), [
{'name': column, 'id': column}
for column in df.columns
]
else:
return [], []
@app.callback(
[Output("download-url", "href"),
Output("download-url", "children")],
[Input("dash-table", "derived_virtual_data"),
Input("dash-table", "filter_query")],
prevent_initial_call=True
)
def download_table(derived_virtual_data, filter_query):
if derived_virtual_data:
print(derived_virtual_data)
filename = f"output_{uuid.uuid1()}.xlsx"
pd.DataFrame(derived_virtual_data).to_excel("downloads/" + filename, index=False)
return "/download/" + filename, "下載當(dāng)前狀態(tài)表格"
return "", ""
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run_server(debug=True)
以上就是本文的全部內(nèi)容,歡迎在評論區(qū)發(fā)表你的意見與觀點。
推薦閱讀
