面試官為什么喜歡問 HashMap 和 ConcurrentHashMap ?
點(diǎn)擊“開發(fā)者技術(shù)前線”,選擇“星標(biāo)”
讓一部分開發(fā)者看到未來
數(shù)組
線性鏈表
對(duì)于鏈表的新增,刪除等操作(在找到指定操作位置后),僅需處理結(jié)點(diǎn)間的引用即可,時(shí)間復(fù)雜度為O(1),而查找操作需要遍歷鏈表逐一進(jìn)行比對(duì),復(fù)雜度為O(n)
二叉樹
數(shù)組
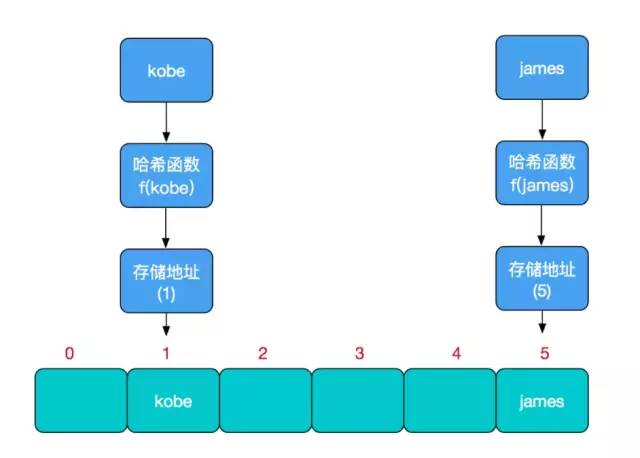
哈希函數(shù)的設(shè)計(jì)至關(guān)重要,好的哈希函數(shù)會(huì)盡可能地保證 計(jì)算簡單和散列地址分布均勻,但是不可能設(shè)計(jì)出一個(gè)絕對(duì)完美的哈希函數(shù),我們需要清楚的是,數(shù)組是一塊連續(xù)的固定長度的內(nèi)存空間,再好的哈希函數(shù)也不能保證得到的存儲(chǔ)地址絕對(duì)不發(fā)生沖突。
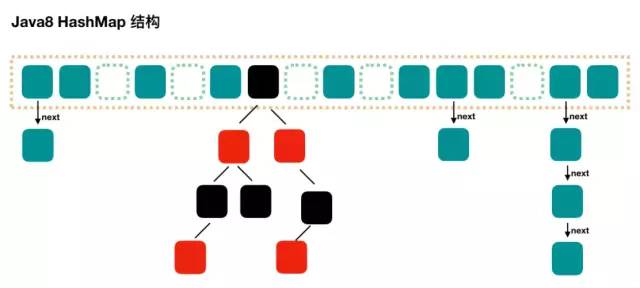
JDK7 使用了數(shù)組+鏈表的方式
JDK8 使用了數(shù)組+鏈表+紅黑樹的方式
HashMap的主干是一個(gè)Entry數(shù)組。Entry是HashMap的基本組成單元,每一個(gè)Entry包含一個(gè)key-value鍵值對(duì)。
transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {final K key;V value;Entry<K,V> next;//存儲(chǔ)指向下一個(gè)Entry的引用,單鏈表結(jié)構(gòu)int hash;//對(duì)key的hashcode值進(jìn)行hash運(yùn)算后得到的值,存儲(chǔ)在Entry,避免重復(fù)計(jì)算/*** Creates new entry.*/Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {value = v;next = n;key = k;hash = h;}
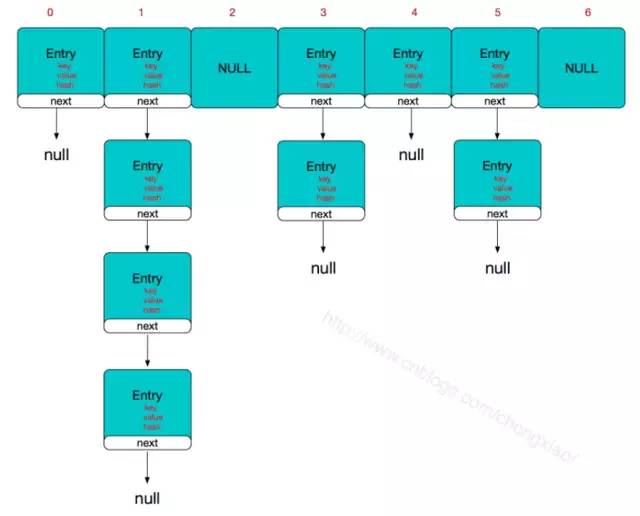
解決沖突的鏈表的長度影響到HashMap查詢的效率
簡單來說,HashMap由數(shù)組+鏈表組成的,數(shù)組是HashMap的主體,鏈表則是主要為了解決哈希沖突而存在的,如果定位到的數(shù)組位置不含鏈表(當(dāng)前entry的next指向null),那么對(duì)于查找,添加等操作很快,僅需一次尋址即可;如果定位到的數(shù)組包含鏈表,對(duì)于添加操作,其時(shí)間復(fù)雜度為O(n),首先遍歷鏈表,存在即覆蓋,否則新增;對(duì)于查找操作來講,仍需遍歷鏈表,然后通過key對(duì)象的equals方法逐一比對(duì)查找。所以,性能考慮,HashMap中的鏈表出現(xiàn)越少,性能才會(huì)越好。
發(fā)生沖突關(guān)于entry節(jié)點(diǎn)插入鏈表還是鏈頭呢?
JDK7:插入鏈表的頭部,頭插法
JDK8:插入鏈表的尾部,尾插法
JDK7
public V put(K key, V value) {if (key == null)return putForNullKey(value);int hash = hash(key.hashCode());int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {Object k;if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {V oldValue = e.value;e.value = value;e.recordAccess(this);return oldValue;}}modCount++;addEntry(hash, key, value, i);return null;}
voidaddEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);if (size++ >= threshold)resize(2 * table.length);}
int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {value = v;next = n;key = k;hash = h;}
JDK8
//e是p的下一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)if ((e = p.next) == null) {//插入鏈表的尾部p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);//如果插入后鏈表長度大于8則轉(zhuǎn)化為紅黑樹if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1sttreeifyBin(tab, hash);break;}
為了減少hash值的碰撞,需要實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)盡量均勻分布的hash函數(shù),在HashMap中通過利用key的hashcode值,來進(jìn)行位運(yùn)算。

/*** Returns index for hash code h.*/static int indexFor(int h, int length) {return h & (length-1);}
1.計(jì)算"book"的hashcode
十進(jìn)制 : 3029737
二進(jìn)制 : 101110001110101110 1001
十進(jìn)制 : 15
二進(jìn)制 : 1111
101110001110101110 1001 & 1111 = 1001
1001的十進(jìn)制 : 9,所以 index=9
現(xiàn)在,我們假設(shè)HashMap的長度是10,重復(fù)剛才的運(yùn)算步驟:
hashcode : 101110001110101110 1001
length - 1 : 1001
index : 1001
hashcode : 101110001110101110 1111
length - 1 : 1001
index : 1001
2.HashMap擴(kuò)容限制的負(fù)載因子為什么是0.75呢?為什么不能是0.1或者1呢?
threshold = (int)(capacity * loadFactor);void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {resize(2 * table.length);//當(dāng)size超過臨界閾值threshold,并且即將發(fā)生哈希沖突時(shí)進(jìn)行擴(kuò)容hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);}createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);}
如果負(fù)載因子為0.5甚至更低的可能的話,最后得到的臨時(shí)閾值明顯會(huì)很小,這樣的情況就會(huì)造成分配的內(nèi)存的浪費(fèi),存在多余的沒用的內(nèi)存空間,也不滿足了哈希表均勻分布的情況。
如果負(fù)載因子達(dá)到了1的情況,也就是Entry數(shù)組存滿了才發(fā)生擴(kuò)容,這樣會(huì)出現(xiàn)大量的哈希沖突的情況,出現(xiàn)鏈表過長,因此造成get查詢數(shù)據(jù)的效率。
因此選擇了0.5~1的折中數(shù)也就是0.75,均衡解決了上面出現(xiàn)的情況。
區(qū)別
使用一個(gè)Node數(shù)組取代了JDK7的Entry數(shù)組來存儲(chǔ)數(shù)據(jù),這個(gè)Node可能是鏈表結(jié)構(gòu),也可能是紅黑樹結(jié)構(gòu);
如果插入的元素key的hashcode值相同,那么這些key也會(huì)被定位到Node數(shù)組的同一個(gè)格子里,如果不超過8個(gè)使用鏈表存儲(chǔ);
超過8個(gè),會(huì)調(diào)用treeifyBin函數(shù),將鏈表轉(zhuǎn)換為紅黑樹。那么即使所有key的hashcode完全相同,由于紅黑樹的特點(diǎn),查找某個(gè)特定元素,也只需要O(logn)的開銷。
put
和 Java7 稍微有點(diǎn)不一樣的地方就是,Java7 是先擴(kuò)容后插入新值的,Java8 先插值再擴(kuò)容,不過這個(gè)不重要。
get
計(jì)算 key 的 hash 值,根據(jù) hash 值找到對(duì)應(yīng)數(shù)組下標(biāo): hash & (length-1)
判斷數(shù)組該位置處的元素是否剛好就是我們要找的,如果不是,走第三步
判斷該元素類型是否是 TreeNode,如果是,用紅黑樹的方法取數(shù)據(jù),如果不是,走第四步 遍歷鏈表,直到找到相等(==或equals)的 key
JDK7下的CurrentHashMap
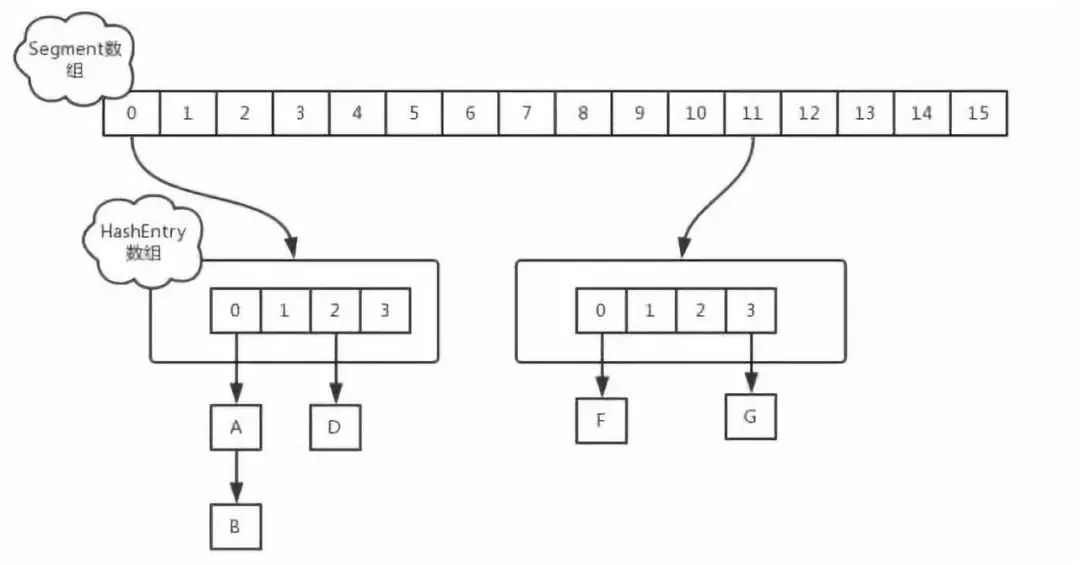
ConcurrentHashMap 與HashMap和Hashtable 最大的不同在于:put和 get 兩次Hash到達(dá)指定的HashEntry,第一次hash到達(dá)Segment,第二次到達(dá)Segment里面的Entry,然后在遍歷entry鏈表.
初始化
private static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)throws java.io.IOException {// For serialization compatibility// Emulate segment calculation from previous version of this classint sshift = 0;int ssize = 1;while (ssize < DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL) {++sshift;ssize <<= 1;}int segmentShift = 32 - sshift;int segmentMask = ssize - 1;
int cap = 1;while (cap < c)cap <<= 1
put操作
staticclass Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 2249069246763182397L;final float loadFactor;Segment(float lf) { this.loadFactor = lf; }}
get操作
size 返回ConcurrentHashMap元素大小
try {for (;;) {if (retries++ == RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) {for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j) ensureSegment(j).lock(); // force creation}sum = 0L;size = 0;overflow = false;for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j) {Segment<K,V> seg = segmentAt(segments, j);if (seg != null) { sum += seg.modCount; int c = seg.count; if (c < 0 || (size += c) < 0)overflow = true;} }if (sum == last) break;last = sum; } }finally {if (retries > RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) {for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j)segmentAt(segments, j).unlock();}}
1、第一種方案他會(huì)使用不加鎖的模式去嘗試多次計(jì)算ConcurrentHashMap的size,最多三次,比較前后兩次計(jì)算的結(jié)果,結(jié)果一致就認(rèn)為當(dāng)前沒有元素加入,計(jì)算的結(jié)果是準(zhǔn)確的.
2、第二種方案是如果第一種方案不符合,他就會(huì)給每個(gè)Segment加上鎖,然后計(jì)算ConcurrentHashMap的size返回.
JDK8的ConcurrentHashMap

// node數(shù)組最大容量:2^30=1073741824private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;// 默認(rèn)初始值,必須是2的幕數(shù)private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 16//數(shù)組可能最大值,需要與toArray()相關(guān)方法關(guān)聯(lián)static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;//并發(fā)級(jí)別,遺留下來的,為兼容以前的版本private static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;// 負(fù)載因子private static final float LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;// 鏈表轉(zhuǎn)紅黑樹閥值,> 8 鏈表轉(zhuǎn)換為紅黑樹static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;//樹轉(zhuǎn)鏈表閥值,小于等于6(tranfer時(shí),lc、hc=0兩個(gè)計(jì)數(shù)器分別++記錄原bin、新binTreeNode數(shù)量,<=UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD 則untreeify(lo))static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;private static final int MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE = 16;private static int RESIZE_STAMP_BITS = 16;// 2^15-1,help resize的最大線程數(shù)private static final int MAX_RESIZERS = (1 << (32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS)) - 1;// 32-16=16,sizeCtl中記錄size大小的偏移量private static final int RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT = 32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS;// forwarding nodes的hash值static final int MOVED = -1;// 樹根節(jié)點(diǎn)的hash值static final int TREEBIN = -2;// ReservationNode的hash值static final int RESERVED = -3;// 可用處理器數(shù)量static final int NCPU = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();//存放node的數(shù)組transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table;/*控制標(biāo)識(shí)符,用來控制table的初始化和擴(kuò)容的操作,不同的值有不同的含義*當(dāng)為負(fù)數(shù)時(shí):-1代表正在初始化,-N代表有N-1個(gè)線程正在 進(jìn)行擴(kuò)容*當(dāng)為0時(shí):代表當(dāng)時(shí)的table還沒有被初始化*當(dāng)為正數(shù)時(shí):表示初始化或者下一次進(jìn)行擴(kuò)容的大小private transient volatile int sizeCtl;
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {final int hash;final K key;volatile V val;volatile Node<K,V> next;Node(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {this.hash = hash;this.key = key;this.val = val;this.next = next;}public final K getKey() { return key; }public final V getValue() { return val; }public final int hashCode() { return key.hashCode() ^ val.hashCode(); }public final String toString(){ return key + "=" + val; }public final V setValue(V value) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}public final boolean equals(Object o) {Object k, v, u; Map.Entry<?,?> e;return ((o instanceof Map.Entry) &&(k = (e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o).getKey()) != null &&(v = e.getValue()) != null &&(k == key || k.equals(key)) &&(v == (u = val) || v.equals(u)));}/*** Virtualized support for map.get(); overridden in subclasses.*/Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) {Node<K,V> e = this;if (k != null) {do {K ek;if (e.hash == h &&((ek = e.key) == k || (ek != null && k.equals(ek))))return e;} while ((e = e.next) != null);}return null;}}
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> {TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree linksTreeNode<K,V> left;TreeNode<K,V> right;TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletionboolean red;TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next,TreeNode<K,V> parent) {super(hash, key, val, next);this.parent = parent;}Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) {return findTreeNode(h, k, null);}/*** Returns the TreeNode (or null if not found) for the given key* starting at given root.*/final TreeNode<K,V> findTreeNode(int h, Object k, Class<?> kc) {if (k != null) {TreeNode<K,V> p = this;do {int ph, dir; K pk; TreeNode<K,V> q;TreeNode<K,V> pl = p.left, pr = p.right;if ((ph = p.hash) > h)p = pl;else if (ph < h)p = pr;else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (pk != null && k.equals(pk)))return p;else if (pl == null)p = pr;else if (pr == null)p = pl;else if ((kc != null ||(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) != null) &&(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) != 0)p = (dir < 0) ? pl : pr;else if ((q = pr.findTreeNode(h, k, kc)) != null)return q;elsep = pl;} while (p != null);}return null;}}
5、因?yàn)榱6冉档土耍谙鄬?duì)而言的低粒度加鎖方式,synchronized并不比ReentrantLock差,在粗粒度加鎖中ReentrantLock可能通過Condition來控制各個(gè)低粒度的邊界,更加的靈活,而在低粒度中,Condition的優(yōu)勢(shì)就沒有了
6、JVM的開發(fā)團(tuán)隊(duì)從來都沒有放棄synchronized,而且基于JVM的synchronized優(yōu)化空間更大,使用內(nèi)嵌的關(guān)鍵字比使用API更加自然
7、在大量的數(shù)據(jù)操作下,對(duì)于JVM的內(nèi)存壓力,基于API的ReentrantLock會(huì)開銷更多的內(nèi)存,雖然不是瓶頸,但是也是一個(gè)選擇依據(jù)。
最后給讀者整理了一份大廠面試真題,需要的可掃碼微信加備注:“大廠面試”獲取。

END
后臺(tái)回復(fù)“面試” “資料” 領(lǐng)取一份干貨,數(shù)百技術(shù)面試手冊(cè)等你 開發(fā)者技術(shù)前線 ,匯集技術(shù)前線快訊和關(guān)注行業(yè)趨勢(shì),大廠干貨,是開發(fā)者經(jīng)歷和成長的優(yōu)秀指南。
歷史推薦
為什么螞蟻金服的 ZSearch 比 ElasticSearh 還牛?
為什么 HashMap 默認(rèn)加載因子非得是0.75?
為什么ArrayList集合中不能使用foreach增刪改?
為什么不建議 for 循環(huán)里 String ++? 

好文點(diǎn)個(gè)在看吧! 
最后給讀者整理了一份大廠面試真題,需要的可掃碼微信加備注:“大廠面試”獲取。

后臺(tái)回復(fù)“面試” “資料” 領(lǐng)取一份干貨,數(shù)百技術(shù)面試手冊(cè)等你 開發(fā)者技術(shù)前線 ,匯集技術(shù)前線快訊和關(guān)注行業(yè)趨勢(shì),大廠干貨,是開發(fā)者經(jīng)歷和成長的優(yōu)秀指南。