【深度學(xué)習(xí)】Pytorch 如何高效使用GPU
然而,在單核CPU上執(zhí)行時,矩陣運算會被展開成循環(huán)的形式,本質(zhì)上還是串行執(zhí)行。GPU(Graphic Process Units,圖形處理器)的眾核體系結(jié)構(gòu)包含幾千個流處理器,可將矩陣運算并行化執(zhí)行,大幅縮短計算時間。
隨著NVIDIA、AMD等公司不斷推進(jìn)其GPU的大規(guī)模并行架構(gòu),面向通用計算的GPU已成為加速可并行應(yīng)用程序的重要手段。得益于GPU眾核(many-core)體系結(jié)構(gòu),程序在GPU系統(tǒng)上的運行速度相較于單核CPU往往提升幾十倍乃至上千倍。
目前,GPU已經(jīng)發(fā)展到了較為成熟的階段。利用GPU來訓(xùn)練深度神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò),可以充分發(fā)揮其數(shù)以千計計算核心的能力,在使用海量訓(xùn)練數(shù)據(jù)的場景下,所耗費的時間大幅縮短,占用的服務(wù)器也更少。如果對適當(dāng)?shù)纳疃壬窠?jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)進(jìn)行合理優(yōu)化,一塊GPU卡相當(dāng)于數(shù)十甚至上百臺CPU服務(wù)器的計算能力,因此GPU已經(jīng)成為業(yè)界在深度學(xué)習(xí)模型訓(xùn)練方面的首選解決方案。
如何使用GPU?現(xiàn)在很多深度學(xué)習(xí)工具都支持GPU運算,使用時只要簡單配置即可。Pytorch支持GPU,可以通過to(device)函數(shù)來將數(shù)據(jù)從內(nèi)存中轉(zhuǎn)移到GPU顯存,如果有多個GPU還可以定位到哪個或哪些GPU。Pytorch一般把GPU作用于張量(Tensor)或模型(包括torch.nn下面的一些網(wǎng)絡(luò)模型以及自己創(chuàng)建的模型)等數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)上。
單GPU加速
使用GPU之前,需要確保GPU是可以使用,可通過torch.cuda.is_available()的返回值來進(jìn)行判斷。返回True則具有能夠使用的GPU。
通過torch.cuda.device_count()可以獲得能夠使用的GPU數(shù)量。
如何查看平臺GPU的配置信息?在命令行輸入命令nvidia-smi即可 (適合于Linux或Windows環(huán)境)。圖5-13是GPU配置信息樣例,從中可以看出共有2個GPU。
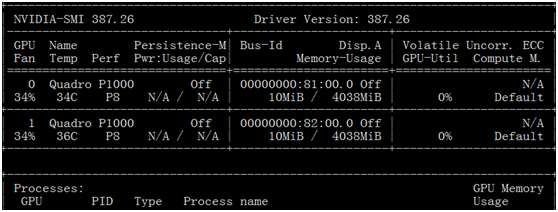
GPU配置信息
把數(shù)據(jù)從內(nèi)存轉(zhuǎn)移到GPU,一般針對張量(我們需要的數(shù)據(jù))和模型。
對張量(類型為FloatTensor或者是LongTensor等),一律直接使用方法.to(device)或.cuda()即可。
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")#或device = torch.device("cuda:0")device1 = torch.device("cuda:1")for batch_idx, (img, label) in enumerate(train_loader):img=img.to(device)label=label.to(device)
對于模型來說,也是同樣的方式,使用.to(device)或.cuda來將網(wǎng)絡(luò)放到GPU顯存。
#實例化網(wǎng)絡(luò)model = Net()model.to(device) #使用序號為0的GPU#或model.to(device1) #使用序號為1的GPU
多GPU加速
這里我們介紹單主機(jī)多GPUs的情況,單機(jī)多GPUs主要采用的DataParallel函數(shù),而不是DistributedParallel,后者一般用于多主機(jī)多GPUs,當(dāng)然也可用于單機(jī)多GPU。
使用多卡訓(xùn)練的方式有很多,當(dāng)然前提是我們的設(shè)備中存在兩個及以上的GPU。
使用時直接用model傳入torch.nn.DataParallel函數(shù)即可,如下代碼:
#對模型net = torch.nn.DataParallel(model)
這時,默認(rèn)所有存在的顯卡都會被使用。
如果你的電腦有很多顯卡,但只想利用其中一部分,如只使用編號為0、1、3、4的四個GPU,那么可以采用以下方式:
#假設(shè)有4個GPU,其id設(shè)置如下device_ids =[0,1,2,3]#對數(shù)據(jù)input_data=input_data.to(device=device_ids[0])#對于模型net = torch.nn.DataParallel(model)net.to(device)
或者
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = ','.join(map(str, [0,1,2,3]))net = torch.nn.DataParallel(model)
其中CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES 表示當(dāng)前可以被Pytorch程序檢測到的GPU。
下面為單機(jī)多GPU的實現(xiàn)代碼。
(1)背景說明
這里使用波士頓房價數(shù)據(jù)為例,共506個樣本,13個特征。數(shù)據(jù)劃分成訓(xùn)練集和測試集,然后用data.DataLoader轉(zhuǎn)換為可批加載的方式。采用nn.DataParallel并發(fā)機(jī)制,環(huán)境有2個GPU。當(dāng)然,數(shù)據(jù)量很小,按理不宜用nn.DataParallel,這里只是為了說明使用方法。
(2)加載數(shù)據(jù)
boston = load_boston()X,y = (boston.data, boston.target)X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=0)#組合訓(xùn)練數(shù)據(jù)及標(biāo)簽myset = list(zip(X_train,y_train))
(2)把數(shù)據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)換為批處理加載方式
批次大小為128,打亂數(shù)據(jù)。
from torch.utils import datadevice = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")dtype = torch.FloatTensortrain_loader = data.DataLoader(myset,batch_size=128,shuffle=True)
(3)定義網(wǎng)絡(luò)
class Net1(nn.Module):"""使用sequential構(gòu)建網(wǎng)絡(luò),Sequential()函數(shù)的功能是將網(wǎng)絡(luò)的層組合到一起"""def __init__(self, in_dim, n_hidden_1, n_hidden_2, out_dim):super(Net1, self).__init__()self.layer1 = torch.nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(in_dim, n_hidden_1))self.layer2 = torch.nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(n_hidden_1, n_hidden_2))self.layer3 = torch.nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(n_hidden_2, out_dim))def forward(self, x):x1 = F.relu(self.layer1(x))x1 = F.relu(self.layer2(x1))x2 = self.layer3(x1)#顯示每個GPU分配的數(shù)據(jù)大小print("\tIn Model: input size", x.size(),"output size", x2.size())return x2
(4)把模型轉(zhuǎn)換為多GPU并發(fā)處理格式
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")#實例化網(wǎng)絡(luò)model = Net1(13, 16, 32, 1)if torch.cuda.device_count() > 1:print("Let's use", torch.cuda.device_count(), "GPUs")# dim = 0 [64, xxx] -> [32, ...], [32, ...] on 2GPUsmodel = nn.DataParallel(model)model.to(device)
運行結(jié)果
Let's use 2 GPUs
DataParallel(
(module): Net1(
(layer1): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=13, out_features=16, bias=True)
)
(layer2): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=16, out_features=32, bias=True)
)
(layer3): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=32, out_features=1, bias=True)
)
)
)
(5)選擇優(yōu)化器及損失函數(shù)
optimizer_orig = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss()
(6)模型訓(xùn)練,并可視化損失值。
from tensorboardX import SummaryWriterwriter = SummaryWriter(log_dir='logs')for epoch in range(100):model.train()for data,label in train_loader:input = data.type(dtype).to(device)label = label.type(dtype).to(device)output = model(input)loss = loss_func(output, label)# 反向傳播optimizer_orig.zero_grad()loss.backward()optimizer_orig.step()print("Outside: input size", input.size() ,"output_size", output.size())writer.add_scalar('train_loss_paral',loss, epoch)
運行的部分結(jié)果
In Model: input size torch.Size([64, 13]) output size torch.Size([64, 1])
In Model: input size torch.Size([64, 13]) output size torch.Size([64, 1])
Outside: input size torch.Size([128, 13]) output_size torch.Size([128, 1])
In Model: input size torch.Size([64, 13]) output size torch.Size([64, 1])
In Model: input size torch.Size([64, 13]) output size torch.Size([64, 1])
Outside: input size torch.Size([128, 13]) output_size torch.Size([128, 1])
從運行結(jié)果可以看出,一個批次數(shù)據(jù)(batch-size=128)拆分成兩份,每份大小為64,分別放在不同的GPU上。此時用GPU監(jiān)控也可發(fā)現(xiàn),兩個GPU都同時在使用。

(7)通過web查看損失值的變化情況
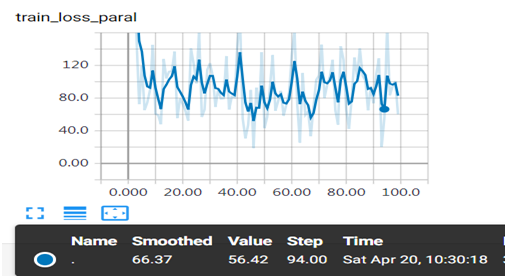
并發(fā)運行訓(xùn)練損失值變化情況
圖形中出現(xiàn)較大振幅,是由于采用批次處理,而且數(shù)據(jù)沒有做任何預(yù)處理,對數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行規(guī)范化應(yīng)該更平滑一些,大家可以嘗試一下。
單機(jī)多GPU也可使用DistributedParallel,它多用于分布式訓(xùn)練,但也可以用在單機(jī)多GPU的訓(xùn)練,配置比使用nn.DataParallel稍微麻煩一點,但是訓(xùn)練速度和效果更好一點。具體配置為:
#初始化使用nccl后端torch.distributed.init_process_group(backend="nccl")#模型并行化model=torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel(model)
單機(jī)運行時使用下面方法啟動
python -m torch.distributed.launch main.py使用GPU注意事項
使用GPU可以提升我們訓(xùn)練的速度,如果使用不當(dāng),可能影響使用效率,具體使用時要注意以下幾點:
(1)GPU的數(shù)量盡量為偶數(shù),奇數(shù)的GPU有可能會出現(xiàn)異常中斷的情況;
(2)GPU很快,但數(shù)據(jù)量較小時,效果可能沒有單GPU好,甚至還不如CPU;
(3)如果內(nèi)存不夠大,使用多GPU訓(xùn)練的時候可通過設(shè)置pin_memory為False,當(dāng)然使用精度稍微低一點的數(shù)據(jù)類型有時也效果。

作者:吳茂貴,資深大數(shù)據(jù)和人工智能技術(shù)專家,就職于中國外匯交易中心,在BI、數(shù)據(jù)挖掘與分析、數(shù)據(jù)倉庫、機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)等領(lǐng)域工作超過20年!在基于Spark、TensorFlow、Pytorch、Keras等機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)和深度學(xué)習(xí)方面有大量的工程實踐經(jīng)驗。代表作有《Python深度學(xué)習(xí)基于Pytorch》和《Python深度學(xué)習(xí)基于TensorFlow》。
往期精彩回顧 本站qq群851320808,加入微信群請掃碼:
