如何高效管理深度學(xué)習(xí)實(shí)驗(yàn)?
【GiantPandaCV導(dǎo)語(yǔ)】這學(xué)期參加了一個(gè)比賽,有比較大的代碼量,在這個(gè)過(guò)程中暴露出來(lái)很多問(wèn)題。由于實(shí)驗(yàn)記錄很糟糕,導(dǎo)致結(jié)果非常混亂、無(wú)法進(jìn)行有效分析,也沒(méi)能進(jìn)行有效的回溯。趁比賽完結(jié),打算重構(gòu)一下代碼,順便參考一些大型項(xiàng)目的管理方法。本文將總結(jié)如何高效、標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化管理深度學(xué)習(xí)實(shí)驗(yàn)。以下總結(jié)偏個(gè)人,可能不適宜所有項(xiàng)目,僅供參考。
1. 目前的管理方法
因?yàn)橛泻芏嘈枰獓L試的想法,但是又按照下圖這種時(shí)間格式來(lái)命名文件夾,保存權(quán)重。每次運(yùn)行嘗試的方法只是記錄在本子上和有道云筆記上。
筆記截圖:
總體來(lái)說(shuō),這種管理方法不是很理想。一個(gè)實(shí)驗(yàn)運(yùn)行的時(shí)間比較久,跨度很久,而之前調(diào)的參數(shù)、修改的核心代碼、想要驗(yàn)證的想法都已經(jīng)很模糊了,甚至有些時(shí)候可能看到一組實(shí)驗(yàn)跑完了,忘記了這個(gè)實(shí)驗(yàn)想要驗(yàn)證什么。
這樣的實(shí)驗(yàn)管理是低效的,筆者之前就了解到很多實(shí)驗(yàn)管理的方法、庫(kù)的模塊化設(shè)計(jì),但這些方法都沉寂在收藏夾中,無(wú)用武之地。趁著這次比賽結(jié)束,好好對(duì)代碼進(jìn)行重構(gòu)、完善實(shí)驗(yàn)管理方法、總結(jié)經(jīng)驗(yàn)教訓(xùn)。同時(shí)也參考了交流群里蔣神、雪神等大佬的建議,總結(jié)了以下方法。
2. 大型項(xiàng)目實(shí)例
先推薦一個(gè)模板,是L1aoXingyu@Github分享的模板項(xiàng)目,鏈接如下:
https://github.com/L1aoXingyu/Deep-Learning-Project-Template
如果長(zhǎng)期維護(hù)一個(gè)深度學(xué)習(xí)項(xiàng)目,代碼的組織就比較重要了。如何設(shè)計(jì)一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單而可擴(kuò)展的結(jié)構(gòu)是非常重要的。這就需要用到軟件工程中的OOP設(shè)計(jì)
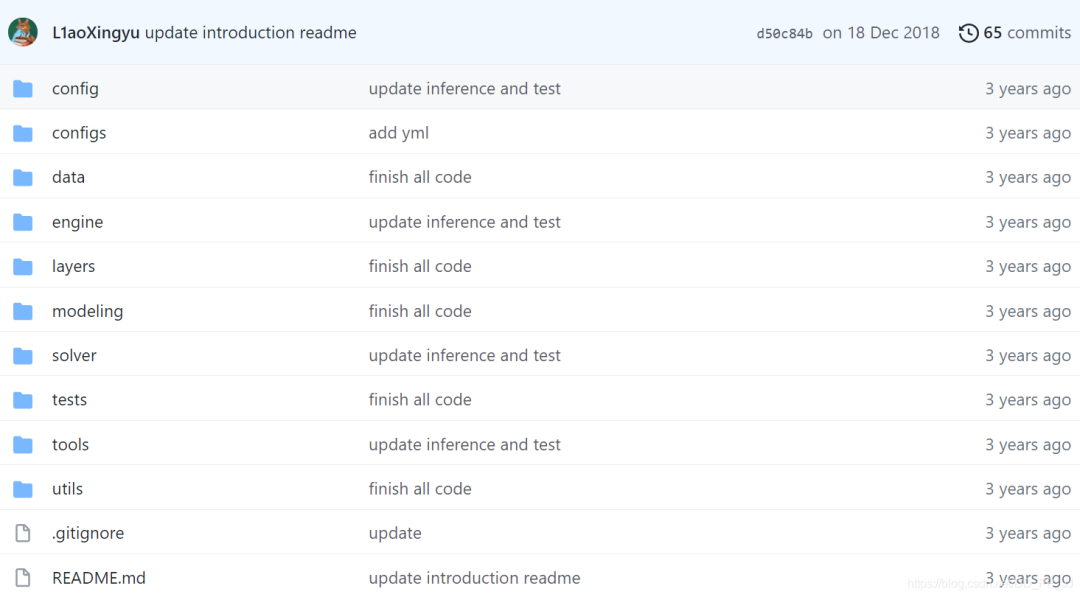
簡(jiǎn)單介紹一下:
實(shí)驗(yàn)配置的管理(實(shí)驗(yàn)配置就是深度學(xué)習(xí)實(shí)驗(yàn)中的各種參數(shù)) 使用yacs管理配置。 配置文件一般分默認(rèn)配置(default)和新增配置(argparse) 模型的管理 使用工廠模式,根據(jù)傳入?yún)?shù)得到對(duì)應(yīng)模型。
├── config
│ └── defaults.py - here's the default config file.
│
│
├── configs
│ └── train_mnist_softmax.yml - here's the specific config file for specific model or dataset.
│
│
├── data
│ └── datasets - here's the datasets folder that is responsible for all data handling.
│ └── transforms - here's the data preprocess folder that is responsible for all data augmentation.
│ └── build.py - here's the file to make dataloader.
│ └── collate_batch.py - here's the file that is responsible for merges a list of samples to form a mini-batch.
│
│
├── engine
│ ├── trainer.py - this file contains the train loops.
│ └── inference.py - this file contains the inference process.
│
│
├── layers - this folder contains any customed layers of your project.
│ └── conv_layer.py
│
│
├── modeling - this folder contains any model of your project.
│ └── example_model.py
│
│
├── solver - this folder contains optimizer of your project.
│ └── build.py
│ └── lr_scheduler.py
│
│
├── tools - here's the train/test model of your project.
│ └── train_net.py - here's an example of train model that is responsible for the whole pipeline.
│
│
└── utils
│ ├── logger.py
│ └── any_other_utils_you_need
│
│
└── tests - this foler contains unit test of your project.
├── test_data_sampler.py
另外推薦一個(gè)封裝的非常完善的庫(kù),deep-person-reid, 鏈接:https://github.com/KaiyangZhou/deep-person-reid,這次總結(jié)中有一部分代碼參考自以上模型庫(kù)。
3. 熟悉工具
與上邊推薦的模板庫(kù)不同,個(gè)人覺(jué)得可以進(jìn)行簡(jiǎn)化處理,主要用到的python工具有:
argparse yaml logging
前兩個(gè)用于管理配置,最后一個(gè)用于管理日志。
3.1 argparse
argparse是命令行解析工具,分為四個(gè)步驟:
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument()
parser.parse_args()
第2步創(chuàng)建了一個(gè)對(duì)象,第3步為這個(gè)對(duì)象添加參數(shù)。
parser.add_argument('--batch_size', type=int, default=2048,
help='batch size') # 8192
parser.add_argument('--save_dir', type=str,
help="save exp floder name", default="exp1_sandwich")
--batch_size將作為參數(shù)的key,它對(duì)應(yīng)的value是通過(guò)解析命令行(或者默認(rèn))得到的。type可以選擇int,str。
parser.add_argument('--finetune', action='store_true',
help='finetune model with distill')
action可以指定參數(shù)處理方式,默認(rèn)是“store”代表存儲(chǔ)的意思。如果使用"store_true", 表示他出現(xiàn),那么對(duì)應(yīng)參數(shù)為true,否則為false。
第4步,解析parser對(duì)象,得到的是可以通過(guò)參數(shù)訪問(wèn)的對(duì)象。比如可以通過(guò)args.finetune 得到finetune的參數(shù)值。
3.2 yaml
yaml是可讀的數(shù)據(jù)序列化語(yǔ)言,常用于配置文件。
支持類(lèi)型有:
標(biāo)量(字符串、證書(shū)、浮點(diǎn)) 列表 關(guān)聯(lián)數(shù)組 字典
語(yǔ)法特點(diǎn):
大小寫(xiě)敏感 縮進(jìn)表示層級(jí)關(guān)系 列表通過(guò) "-" 表示,字典通過(guò) ":"表示 注釋使用 "#"
安裝用命令:
pip install pyyaml
舉個(gè)例子:
name: tosan
age: 22
skill:
name1: coding
time: 2years
job:
- name2: JD
pay: 2k
- name3: HW
pay: 4k
注意:關(guān)鍵字不能重復(fù);不能使用tab,必須使用空格。
處理的腳本:
import yaml
f = open("configs/test.yml", "r")
y = yaml.load(f)
print(y)
輸出結(jié)果:
YAMLLoadWarning: calling yaml.load() without Loader=... is deprecated, as the default Loader is unsafe. Please read https://msg.pyyaml.org/load for full details.
y = yaml.load(f)
{'name': 'tosan', 'age': 22, 'skill': {'name1': 'coding', 'time': '2years'}, 'job': [{'name2': 'JD', 'pay': '2k'}, {'name3': 'HW', 'pay': '4k'}]}
這個(gè)警告取消方法是:添加默認(rèn)loader
import yaml
f = open("configs/test.yml", "r")
y = yaml.load(f, Loader=yaml.FullLoader)
print(y)
保存:
content_dict = {
'name':"ch",
}
f = open("./config.yml","w")
print(yaml.dump(content_dict, f))
支持的類(lèi)型:
# 支持?jǐn)?shù)字,整形、float
pi: 3.14
# 支持布爾變量
islist: true
isdict: false
# 支持None
cash: ~
# 時(shí)間日期采用ISO8601
time1: 2021-6-9 21:59:43.10-05:00
#強(qiáng)制轉(zhuǎn)化類(lèi)型
int_to_str: !!str 123
bool_to_str: !!str true
# 支持list
- 1
- 2
- 3
# 復(fù)合list和dict
test2:
- name: xxx
attr1: sunny
attr2: rainy
attr3: cloudy
3.3 logging
日志對(duì)程序執(zhí)行情況的排查非常重要,通過(guò)日志文件,可以快速定位出現(xiàn)的問(wèn)題。本文將簡(jiǎn)單介紹使用logging生成日志的方法。
logging模塊介紹
logging是python自帶的包,一共有五個(gè)level:
debug: 查看程序運(yùn)行的信息,調(diào)試過(guò)程中需要使用。 info: 程序是否如預(yù)期執(zhí)行的信息。 warn: 警告信息,但不影響程序執(zhí)行。 error: 出現(xiàn)錯(cuò)誤,影響程序執(zhí)行。 critical: 嚴(yán)重錯(cuò)誤
logging用法
import logging
logging.basicConfig(format='%(asctime)s - %(message)s', datefmt='%d-%b-%y %H:%M:%S')
logging.info("program start")
format參數(shù)設(shè)置了時(shí)間,規(guī)定了輸出的格式。
import logging
#先聲明一個(gè) Logger 對(duì)象
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
logger.setLevel(level=logging.INFO)
#然后指定其對(duì)應(yīng)的 Handler 為 FileHandler 對(duì)象
handler = logging.FileHandler('Alibaba.log')
#然后 Handler 對(duì)象單獨(dú)指定了 Formatter 對(duì)象單獨(dú)配置輸出格式
formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
handler.setFormatter(formatter)
logger.addHandler(handler)
Filehandler用于將日志寫(xiě)入到文件,如這里將所有日志輸出到Alibaba.log文件夾中。
3.4 補(bǔ)充argparse和yaml的配合
# process argparse & yaml
if not args.config:
opt = vars(args)
args = yaml.load(open(args.config), Loader=yaml.FullLoader)
opt.update(args)
args = opt
else: # yaml priority is higher than args
opt = yaml.load(open(args.config), Loader=yaml.FullLoader)
opt.update(vars(args))
args = argparse.Namespace(**opt)
4. 實(shí)驗(yàn)管理
實(shí)驗(yàn)的完整記錄需要以下幾方面內(nèi)容:
日志文件:記錄運(yùn)行全過(guò)程的日志。 權(quán)重文件:運(yùn)行過(guò)程中保存的checkpoint。 可視化文件:tensorboard中運(yùn)行得到的文件。 配置文件:詳細(xì)記錄當(dāng)前運(yùn)行的配置(調(diào)參必備)。 文件備份:用于保存當(dāng)前版本的代碼,可以用于回滾。
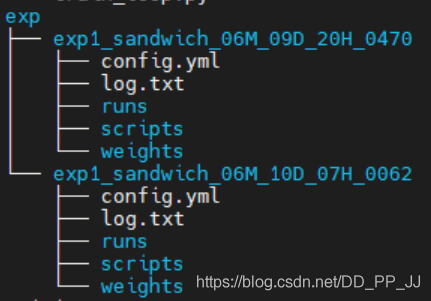
那么按照以下方式進(jìn)行組織:
exp
- 實(shí)驗(yàn)名+日期
- runs: tensorboard保存的文件
- weights: 權(quán)重文件
- config.yml: 配置文件
- scripts: 核心文件備份
- train.py
- xxxxxxxx
代碼實(shí)現(xiàn):
import logging
import argparse
import yaml
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser("ResNet20-cifar100")
parser.add_argument('--batch_size', type=int, default=2048,
help='batch size') # 8192
parser.add_argument('--learning_rate', type=float,
default=0.1, help='init learning rate') parser.add_argument('--config', help="configuration file",
type=str, default="configs/meta.yml")
parser.add_argument('--save_dir', type=str,
help="save exp floder name", default="exp1")
args = parser.parse_args()
# process argparse & yaml
if not args.config:
opt = vars(args)
args = yaml.load(open(args.config), Loader=yaml.FullLoader)
opt.update(args)
args = opt
else: # yaml priority is higher than args
opt = yaml.load(open(args.config), Loader=yaml.FullLoader)
opt.update(vars(args))
args = argparse.Namespace(**opt)
args.exp_name = args.save_dir + "_" + datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%mM_%dD_%HH") + "_" + \
"{:04d}".format(random.randint(0, 1000))
# 文件處理
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join("exp", args.exp_name)):
os.makedirs(os.path.join("exp", args.exp_name))
# 日志文件
log_format = "%(asctime)s %(message)s"
logging.basicConfig(stream=sys.stdout, level=logging.INFO,
format=log_format, datefmt="%m/%d %I:%M:%S %p")
fh = logging.FileHandler(os.path.join("exp", args.exp_name, 'log.txt'))
fh.setFormatter(logging.Formatter(log_format))
logging.getLogger().addHandler(fh)
logging.info(args)
# 配置文件
with open(os.path.join("exp", args.exp_name, "config.yml"), "w") as f:
yaml.dump(args, f)
# Tensorboard文件
writer = SummaryWriter("exp/%s/runs/%s-%05d" %
(args.exp_name, time.strftime("%m-%d", time.localtime()), random.randint(0, 100)))
# 文件備份
create_exp_dir(os.path.join("exp", args.exp_name),
scripts_to_save=glob.glob('*.py'))
def create_exp_dir(path, scripts_to_save=None):
if not os.path.exists(path):
os.mkdir(path)
print('Experiment dir : {}'.format(path))
if scripts_to_save is not None:
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(path, 'scripts')):
os.mkdir(os.path.join(path, 'scripts'))
for script in scripts_to_save:
dst_file = os.path.join(path, 'scripts', os.path.basename(script))
shutil.copyfile(script, dst_file)
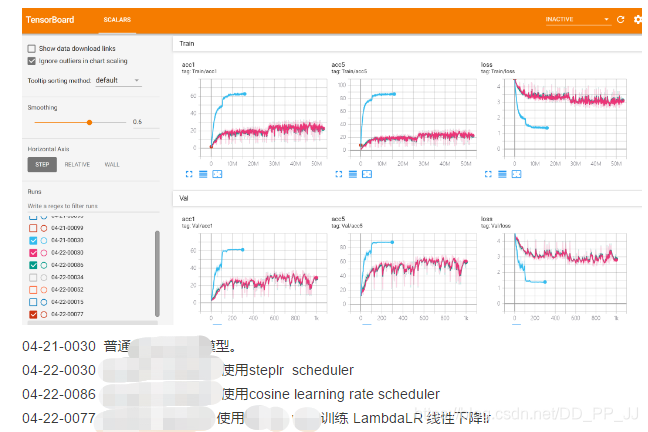
5. 結(jié)果
6. 參考文獻(xiàn)
https://github.com/L1aoXingyu/Deep-Learning-Project-Template
https://sungwookyoo.github.io/tips/ArgParser/
https://github.com/KaiyangZhou/deep-person-reid
https://www.cnblogs.com/pprp/p/10624655.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/pprp/p/14865416.html
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/56968001
-END-
歡迎添加筆者微信加入交流群,或者對(duì)文章內(nèi)容有疑問(wèn),也可以添加筆者微信。
