Spark讀寫Hbase(用戶畫像)
背景
依舊是公司用戶畫像項目,目前方案是將hive聚合之后的標簽表全部倒入mysql,然后在ES建立索引,雖然限定了最大查詢范圍為90天的數(shù)據(jù),但是面對千萬級的用戶量,90天的數(shù)據(jù)依舊是非常龐大,每天查詢的效率依舊是在30分鐘以上,所以準備對這塊進行優(yōu)化。
在公司層面進行調(diào)研之后發(fā)現(xiàn),公司遺留了一個小的Hbase集群,集群配置:
1 active master, 1 backup masters, 2 servers。
但是問題是集群的版本為:1.1.2,非常低,在上篇文章中:
為了做用戶畫像的流程打通,本地建立的Hbase版本為1.3.6,spark版本為2.4,所以整套體系都不支持公司原來的hbase集群體系,為了保障之后的用戶畫像能落地,有兩套解決方案:
1、公司層面的Hbase集群升級,由于歷史包袱太重,之前的版本雖然老,但是依舊有部分的數(shù)據(jù)在上面跑,如果版本升級,后續(xù)對應的下游系統(tǒng)中間件可能會出現(xiàn)不兼容的問題,而且在Hbase層做適配需要調(diào)研太多的下游業(yè)務的使用場景,成本太高,所以未選用。
2、將本地的偽分布式Hbase進行降級,同時spark版本也進行降級處理。目前測試環(huán)境選定的Hbase版本為1.1.2,spark版本為2.1.1。
下面的文章主要是基于這兩個版本的中間件,進行spark對Hbase的讀寫操作。
介紹
1、Hbase版本降級,1.1.2版本為2015年的版本
wget archive.apache.org/dist2、按照上篇文章對Hbase進行配置和按照測試
訪問頁面:localhost:60010/master-

啟動hbase shell,并插入數(shù)據(jù):
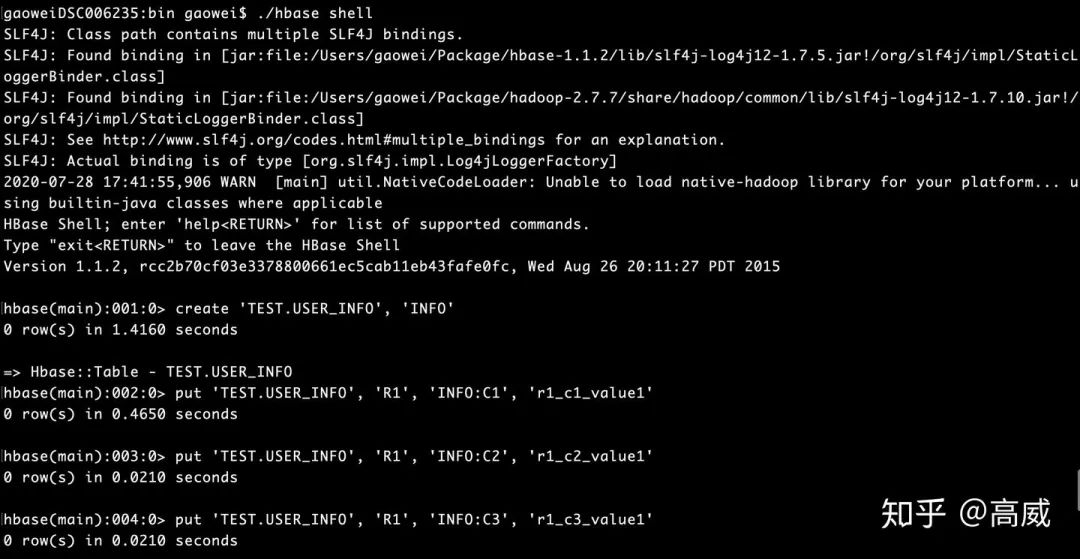
Scan的結果:Row_key、列族、列名、時間戳、value值
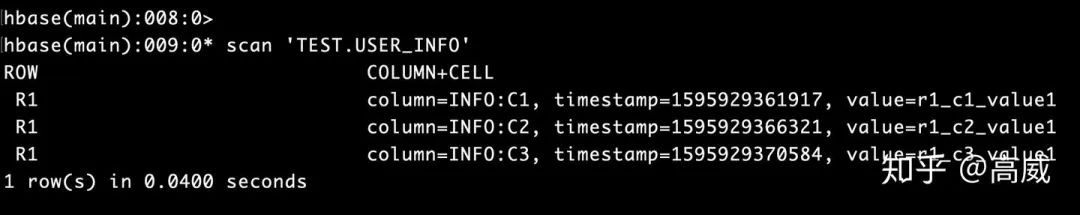
實際結果用圖標展現(xiàn)為:
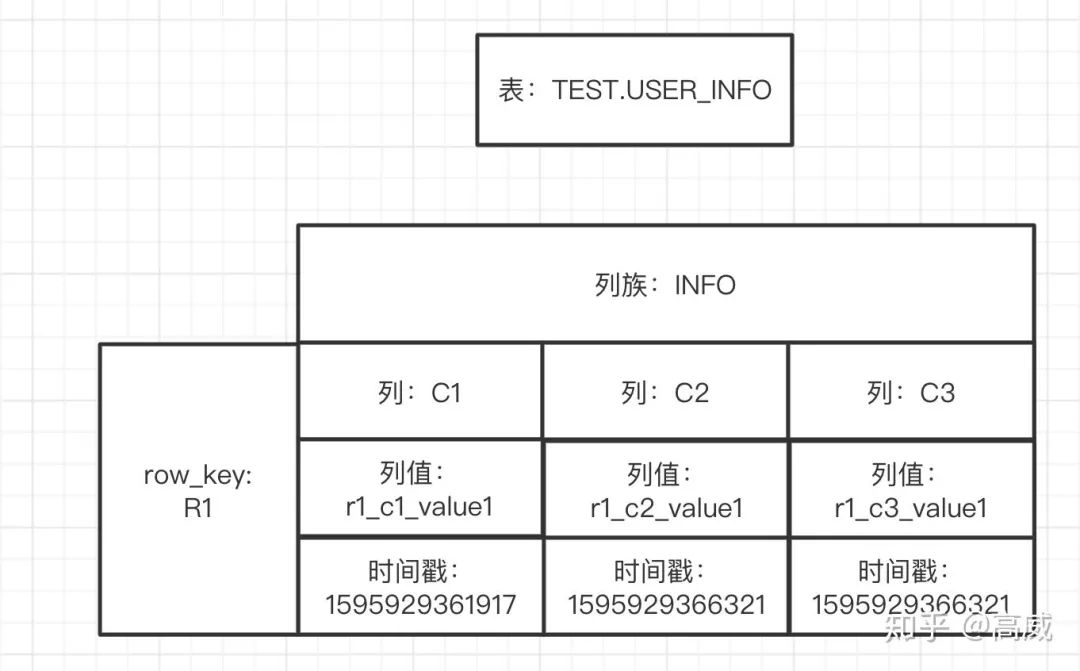
轉換為常見的關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫的視角來看的話:

從表述中能看出來在關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫中的存儲同一份數(shù)據(jù)需要3行,而在Hbase是一行的,而且同一個列族是在同一個Store里面的,更加方便查詢。
3、修改pom.xml文件
<properties>
<scala.version>2.11</scala.version>
<spark.version>2.1.1</spark.version>
<hadoop.version>2.7.7</hadoop.version>
</properties>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>scala-tools.org</id>
<name>Scala-Tools Maven2 Repository</name>
<url>http://scala-tools.org/repo-releases</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<id>scala-tools.org</id>
<name>Scala-Tools Maven2 Repository</name>
<url>http://scala-tools.org/repo-releases</url>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.scala-lang</groupId>
<artifactId>scala-library</artifactId>
<version>2.11.8</version>
<!-- <scope>provided</scope>-->
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-core_${scala.version}</artifactId>
<version>${spark.version}</version>
<!-- <scope>provided</scope>-->
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-sql_${scala.version}</artifactId>
<version>${spark.version}</version>
<!-- <scope>provided</scope>-->
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.14</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.4</version>
<!--<scope>test</scope>-->
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.specs</groupId>
<artifactId>specs</artifactId>
<version>1.2.5</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.scala-lang</groupId>
<artifactId>scala-reflect</artifactId>
<version>2.11.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.scala-lang</groupId>
<artifactId>scala-compiler</artifactId>
<version>2.11.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.scala-lang</groupId>
<artifactId>scala-library</artifactId>
<version>2.11.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-client</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-common</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-server</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2</version>
</dependency>主要是添加hbase-client、hbase-server、hbase-common,并將spark版本修改為2.1.1。
3、spark讀寫Hbase測試
往Hbase里面寫數(shù)據(jù):
通過HTable中put方法:
package Flink
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.{HBaseConfiguration, HTableDescriptor, TableName}
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.{HBaseAdmin, HTable, Put, Result}
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapred.TableOutputFormat
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes
import org.apache.log4j.{Level, Logger}
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.io.ImmutableBytesWritable
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.JobConf
/** *
*
* @autor gaowei
* @Date 2020-07-28 17:55
*/
object HbaseT1 {
def getHBaseConfiguration(quorum:String, port:String, tableName:String) = {
val conf = HBaseConfiguration.create()
conf.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum",quorum)
conf.set("hbase.zookeeper.property.clientPort",port)
conf
}
def getHBaseAdmin(conf:Configuration,tableName:String) = {
val admin = new HBaseAdmin(conf)
if (!admin.isTableAvailable(tableName)) {
val tableDesc = new HTableDescriptor(TableName.valueOf(tableName))
admin.createTable(tableDesc)
}
admin
}
def getTable(conf:Configuration,tableName:String) = {
new HTable(conf,tableName)
}
def main(args: Array[String]) {
// 屏蔽不必要的日志顯示在終端上
Logger.getLogger("org.apache.spark").setLevel(Level.WARN)
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("HBaseWriteTest").setMaster("local[2]")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
val tableName = "TEST.USER_INFO"
val quorum = "localhost"
val port = "2181"
// 配置相關信息
val conf = getHBaseConfiguration(quorum,port,tableName)
conf.set(TableOutputFormat.OUTPUT_TABLE,tableName)
val indataRDD = sc.makeRDD(Array("R6,jack,16,t1", "R7,Lucy,15,t2", "R8,mike,17,t3", "R9,Lily,14,t4"))
indataRDD.foreachPartition(x=> {
val conf = getHBaseConfiguration(quorum,port,tableName)
conf.set(TableOutputFormat.OUTPUT_TABLE,tableName)
val htable = getTable(conf,tableName)
x.foreach(y => {
val arr = y.split(",")
val key = arr(0)
val value = arr(1)
val value1 = arr(2)
val value2 = arr(3)
val put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(key))
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("INFO"),Bytes.toBytes("C1"),Bytes.toBytes(value))
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("INFO"),Bytes.toBytes("C2"),Bytes.toBytes(value1))
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("INFO"),Bytes.toBytes("C3"),Bytes.toBytes(value2))
htable.put(put)
})
})
sc.stop()
}
}
TableOutputFormat向HBase寫數(shù)據(jù)
package Flink
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.{HBaseConfiguration, HTableDescriptor, TableName}
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.{HBaseAdmin, HTable, Put, Result}
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapred.TableOutputFormat
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes
import org.apache.log4j.{Level, Logger}
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.io.ImmutableBytesWritable
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.JobConf
/** *
*
* @autor gaowei
* @Date 2020-07-28 17:55
*/
object HbaseT1 {
def getHBaseConfiguration(quorum:String, port:String, tableName:String) = {
val conf = HBaseConfiguration.create()
conf.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum",quorum)
conf.set("hbase.zookeeper.property.clientPort",port)
conf
}
def getHBaseAdmin(conf:Configuration,tableName:String) = {
val admin = new HBaseAdmin(conf)
if (!admin.isTableAvailable(tableName)) {
val tableDesc = new HTableDescriptor(TableName.valueOf(tableName))
admin.createTable(tableDesc)
}
admin
}
def getTable(conf:Configuration,tableName:String) = {
new HTable(conf,tableName)
}
def main(args: Array[String]) {
// 屏蔽不必要的日志顯示在終端上
Logger.getLogger("org.apache.spark").setLevel(Level.WARN)
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("HBaseWriteTest").setMaster("local[2]")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
val tableName = "TEST.USER_INFO"
val quorum = "localhost"
val port = "2181"
// 配置相關信息
val conf = getHBaseConfiguration(quorum,port,tableName)
conf.set(TableOutputFormat.OUTPUT_TABLE,tableName)
val indataRDD = sc.makeRDD(Array("R6,jack,16,t1", "R7,Lucy,15,t2", "R8,mike,17,t3", "R9,Lily,14,t4"))
val jobConf = new JobConf()
jobConf.setOutputFormat(classOf[TableOutputFormat])
jobConf.set(TableOutputFormat.OUTPUT_TABLE,tableName)
indataRDD.map(_.split(",")).map{arr => {
val put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(arr(0)))
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("INFO"),Bytes.toBytes("C1"),Bytes.toBytes(arr(1)))
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("INFO"),Bytes.toBytes("C2"),Bytes.toBytes(arr(2)))
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("INFO"),Bytes.toBytes("C3"),Bytes.toBytes(arr(3)))
(new ImmutableBytesWritable,put)
}}.saveAsHadoopDataset(jobConf)
sc.stop()
}
}4、讀Hbase的數(shù)據(jù)
package Flink
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableInputFormat
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.{HBaseConfiguration, HTableDescriptor, TableName}
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.{HBaseAdmin, HTable}
import org.apache.log4j.{Level, Logger}
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
/** *
*
* @autor gaowei
* @Date 2020-07-27 17:06
*/
object HbseTest {
def getHBaseConfiguration(quorum:String, port:String, tableName:String) = {
val conf = HBaseConfiguration.create()
conf.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum",quorum)
conf.set("hbase.zookeeper.property.clientPort",port)
conf
}
def getHBaseAdmin(conf:Configuration,tableName:String) = {
val admin = new HBaseAdmin(conf)
if (!admin.isTableAvailable(tableName)) {
val tableDesc = new HTableDescriptor(TableName.valueOf(tableName))
admin.createTable(tableDesc)
}
admin
}
def getTable(conf:Configuration,tableName:String) = {
new HTable(conf,tableName)
}
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
Logger.getLogger("org.apache.spark").setLevel(Level.WARN)
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("HBaseReadTest").setMaster("local[2]")
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
val tableName = "TEST.USER_INFO"
val quorum = "localhost"
val port = "2181"
// 配置相關信息
val conf = getHBaseConfiguration(quorum,port,tableName)
conf.set(TableInputFormat.INPUT_TABLE,tableName)
// HBase數(shù)據(jù)轉成RDD
val hBaseRDD = sc.newAPIHadoopRDD(conf,classOf[TableInputFormat],
classOf[org.apache.hadoop.hbase.io.ImmutableBytesWritable],
classOf[org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Result]).cache()
// RDD數(shù)據(jù)操作
val data = hBaseRDD.map(x => {
val result = x._2
val key = Bytes.toString(result.getRow)
val value = Bytes.toString(result.getValue("INFO".getBytes,"C1".getBytes))
val value1 = Bytes.toString(result.getValue("INFO".getBytes,"C2".getBytes))
val value2 = Bytes.toString(result.getValue("INFO".getBytes,"C3".getBytes))
(key,value,value1,value2)
})
data.foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
}
結果:

去Hbase查詢的結果:
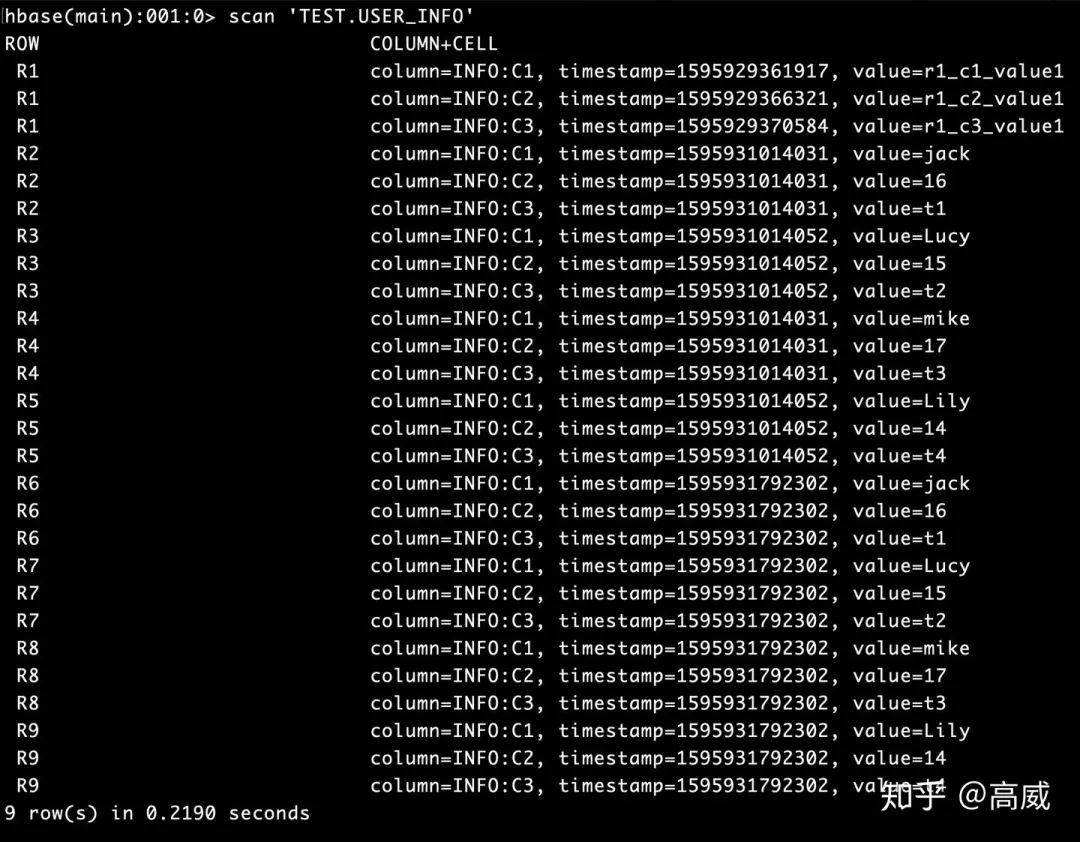
結論:
Hadoop本質(zhì)上是:分布式文件系統(tǒng)(HDFS) + 分布式計算框架(Mapreduce) + 調(diào)度系統(tǒng)Yarn搭建起來的分布式大數(shù)據(jù)處理框架。
Hive:是一個基于Hadoop的數(shù)據(jù)倉庫,適用于一些高延遲性的應用(離線開發(fā)),可以將結構化的數(shù)據(jù)文件映射為一張數(shù)據(jù)庫表,并提供簡單的sql查詢功能。
Hive可以認為是MapReduce的一個包裝,把好寫的HQL轉換為的MapReduce程序,本身不存儲和計算數(shù)據(jù),它完全依賴于HDFS和MapReduce,Hive中的表是純邏輯表。hive需要用到hdfs存儲文件,需要用到MapReduce計算框架。
HBase:是一個Hadoop的數(shù)據(jù)庫,一個分布式、可擴展、大數(shù)據(jù)的存儲。hbase是物理表,不是邏輯表,提供一個超大的內(nèi)存hash表,搜索引擎通過它來存儲索引,方便查詢操作。
HBase可以認為是HDFS的一個包裝。他的本質(zhì)是數(shù)據(jù)存儲,是個NoSql數(shù)據(jù)庫;HBase部署于HDFS之上,并且克服了hdfs在隨機讀寫方面的缺點,提高查詢效率。
推薦閱讀:
不是你需要中臺,而是一名合格的架構師(附各大廠中臺建設PPT)
企業(yè)10大管理流程圖,數(shù)字化轉型從業(yè)者必備!
