【手撕算法】PatchMatch圖像修復算法
點擊上方“新機器視覺”,選擇加"星標"或“置頂”
重磅干貨,第一時間送達
PatchMatch: A Randomized Correspondence Algorithm for Structural Image Editing

首先是建立圖像的下采樣金字塔模型,代碼中設定為五層,建立模型后
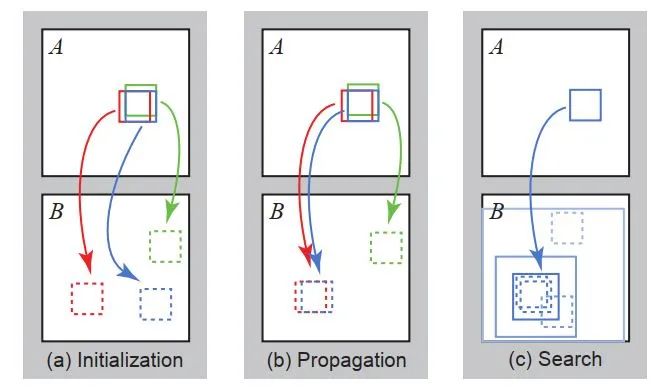
對A的待修復區(qū)域每個patch塊隨機在B已知區(qū)域中匹配一個patch塊,即初始化偏置地圖(上圖a步驟)。
/*********************************函數聲明:初始化偏置圖像參數:NONE注釋:NONE測試:NONE**********************************/void PatchMatch::InitOff(Mat Mask, Mat &Off){//為方便起見,將所有的都附上,要求不能賦值到非搜索區(qū)域//初始化格式Off = Mat(Mask.size(), CV_32FC2, Scalar::all(0));//2維無符號32位精度浮點數for (int i = 0; i < Mask.rows; i++){for (int j = 0; j < Mask.cols; j++){//不考慮search區(qū)域,沒有破損,他們的最佳偏移向量當然是0,自己if (Mask.at<uchar>(i, j) == search){Off.at<Vec2f>(i, j)[0] = 0; //<Vec2f> 向量,2維,浮點數Off.at<Vec2f>(i, j)[1] = 0;}else//處理hole,采用隨機偏置{//先初始化2個偏置數r_col,r_rowint r_col = rand() % Mask.cols; //rand()產生隨機數,主要是產生一個偏置的初始值int r_row = rand() % Mask.rows;r_col = r_col + j < Mask.cols ? r_col : r_col - Mask.cols;//邊界檢測r_row = r_row + i < Mask.rows ? r_row : r_row - Mask.rows;//為什么要有這個循環(huán)?因為一次的隨機賦值,很可能會出現偏置后的塊跑到破損區(qū)域,或者是超出限定搜索框的邊界while (!(Mask.at<uchar>(r_row + i, r_col + j) == search //這里加上I,j,是因為他是A投影到B中的搜索偏置&& abs(r_row) < searchrowratio*Mask.rows)) //searchrowratio=0.5,搜索的時候,確保r_row偏置不會太遠,一定是在原圖像的大小里{r_col = rand() % Mask.cols;r_row = rand() % Mask.rows;//邊界檢測r_col = r_col + j < Mask.cols ? r_col : r_col - Mask.cols;r_row = r_row + i < Mask.rows ? r_row : r_row - Mask.rows;}//賦偏置值Off.at<Vec2f>(i, j)[0] = r_row;Off.at<Vec2f>(i, j)[1] = r_col;}}}}
之后從低分辨率開始,對于每一層金字塔模型進行迭代:
每一次迭代都會遍歷原圖A待修復區(qū)域所有像素。當遍歷到當前像素時,執(zhí)行下面的步驟來進行修復:
步驟一:傳播(圖中b步驟)
傳播會計算原圖A當前像素塊patch_A(藍色)對應的B中的patch_B_1,patch_A上方(綠色)(奇數次迭代為下方)對應的B中的patch_B_2,patch_A左側(紅色)(奇數次迭代為右側)對應的B中的patch_B_3這三個patch塊中與patch_A相似度最高的patch塊。
計算相似度函數為
//以塊為單位,用所有像素點的相同顏色通道的差平方來簡單判斷相似度float PatchMatch::Distance(Mat Dst, Mat Src){float distance = 0;for (int i = 0; i < Dst.rows; i++){for (int j = 0; j < Dst.cols; j++){for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++)//K=3個顏色通道{int tem = Src.at < Vec3b >(i, j)[k] - Dst.at < Vec3b >(i, j)[k];distance += tem * tem;//差平方}}}return distance;}
傳播函數:
//迭代第一步:傳播//(now_row, now_col):patch里的像素//odd:當前迭代次void PatchMatch::Propagation(Mat Dst, Mat Src, Mat Mask, Mat &Off, int row, int col,int odd){Mat DstPatch = GetPatch(Dst, row, col);//獲取長度為 patchsize = 3 的邊界框, (row, col)代表的是中心像素點坐標if (odd % 2 == 0)//偶次迭代{//提取(row, col)的match塊Mat SrcPatch = GetPatch(Src, row + Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[0],col + Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[1]);//提取(row, col-1)的match塊Mat LSrcPatch = GetPatch(Src, row + Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col - 1)[0],col - 1 + Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col - 1)[1]);//提取(row-1, col)的match塊Mat USrcPatch = GetPatch(Src,row - 1 + Off.at < Vec2f >(row - 1, col)[0],col + Off.at < Vec2f >(row - 1, col)[1]);//返回上面4個塊最相似的塊的代表數字,用于switch判斷int location = GetMinPatch1(DstPatch, SrcPatch, LSrcPatch, USrcPatch);//利用上面的信息更新像素點的偏置地圖switch (location){//若是1則不更新case 2:Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[0] = Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col - 1)[0];Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[1] = Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col - 1)[1] - 1;break;case 3:Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[0] = Off.at < Vec2f >(row - 1, col)[0] - 1;Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[1] = Off.at < Vec2f >(row - 1, col)[1];break;}}else//奇數次迭代{Mat SrcPatch = GetPatch(Src, row + Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[0],col + Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[1]);Mat RSrcPatch = GetPatch(Src, row + Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col + 1)[0],col + 1 + Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col + 1)[1]);Mat DSrcPatch = GetPatch(Src,row + 1 + Off.at < Vec2f >(row + 1, col)[0],col + Off.at < Vec2f >(row + 1, col)[1]);int location = GetMinPatch1(DstPatch, SrcPatch, RSrcPatch, DSrcPatch);switch (location){case 2:Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[0] = Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col + 1)[0];Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[1] = Off.at < Vec2f>(row, col + 1)[1] + 1;break;case 3:Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[0] = Off.at < Vec2f>(row + 1, col)[0] + 1;Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[1] = Off.at < Vec2f >(row + 1, col)[1];break;}}}
步驟二:隨機擾動搜索(圖中c步驟)
為了避免陷入局部極值,再額外再隨機生成幾個patch位置作為候選patch塊,若小于當前patch,則更新。
隨機擾動會在原圖A中,以當前像素為中心點,初始半徑區(qū)域為全圖,在此區(qū)域內隨機找尋patch塊并與patch_A原本對應的B中的patch塊對比,若更相似則更新對應關系offset,然后以新的patch_B為中心,半徑縮小一倍,繼續(xù)搜索,直到半徑縮小為1,更新完畢。
//迭代第二步:隨機搜索//(row,col)=(now_row, now_col):修復patch里的像素void PatchMatch::RandomSearch(Mat Dst, Mat Src, Mat Mask, Mat &Off, int row, int col){Mat DstPatch = GetPatch(Dst, row, col);//獲取修復基準框,在框內操作//迭代指數int attenuate = 0;while (true){//獲取隨機參數,在 [-1;1] 間float divcol = rand() % 2000 / 1000.0f - 1.0f;float divrow = rand() % 2000 / 1000.0f - 1.0f;//減小框大小的公式,??_??=??_0+??*??^??*??_??//行列分別處理,MaxWindow:原始框寬度;divcol:隨機系數;pow(A,B):A的B次方。隨迭代次數而變小的縮小系數;RandomAttenuation=0.5;float veccol = MaxWindow * pow(RandomAttenuation, attenuate)* divcol;float vecrow = MaxWindow * pow(RandomAttenuation, attenuate)* divrow;float length = sqrt(veccol * veccol + vecrow * vecrow);//如果低于1個像素,沒有意義,直接結束整個循環(huán),對下一個像素處理if (length < 1)break;//x方向,前2項指向(row, col)的match塊,后面是公式的后一項int nowrow = row + Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[0] + vecrow;//y方向int nowcol = col + Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[1] + veccol;//判斷隨機搜索的patch不越界,在search內if (nowcol >= 0 && nowcol <= Off.cols - 1 && nowrow >= 0&& nowrow <= Off.rows - 1&& Mask.at < uchar >(nowrow, nowcol) == search&& abs(nowrow - row) < searchrowratio * Mask.rows)//abs:絕對值{//取出原來的match塊Mat SrcPatch1 = GetPatch(Src, Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[0] + row,Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[1] + col);//取出現在的隨機match塊Mat SrcPatch2 = GetPatch(Src, nowrow, nowcol);//對比相似性,找出最好的塊int location = GetMinPatch2(DstPatch, SrcPatch1, SrcPatch2);//結合最好的相似塊給像素新的偏置值switch (location){case 2:Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[1] = nowcol - col;Off.at < Vec2f >(row, col)[0] = nowrow - row;break;}}//迭代指數增加attenuate++;}}
經過該兩個步驟,本次迭代完畢。
當最終迭代完成后,就完成了整個修復過程。
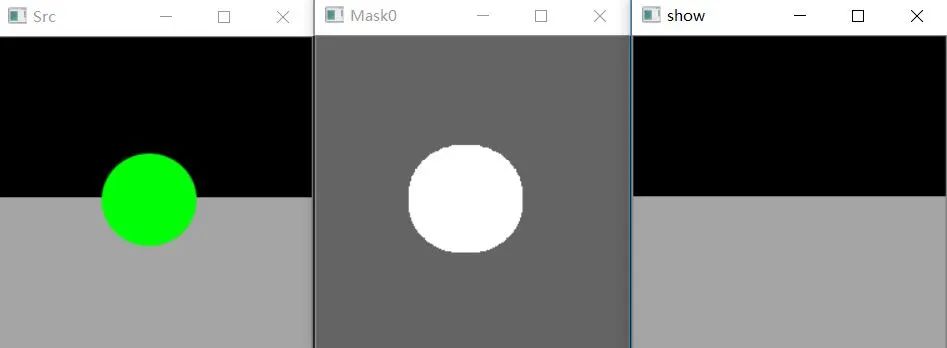

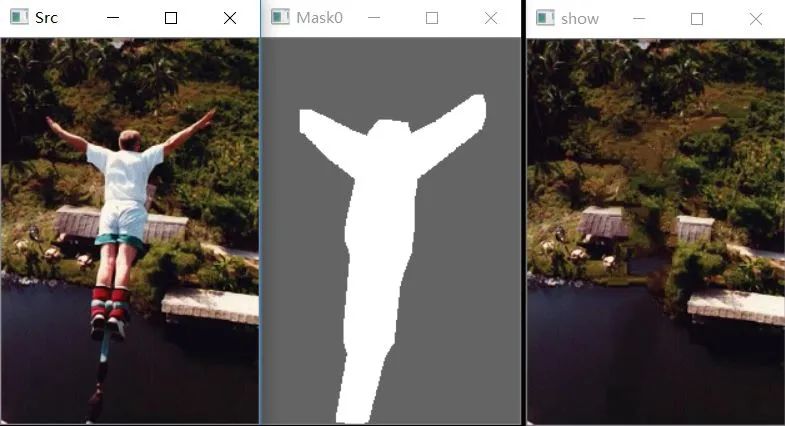
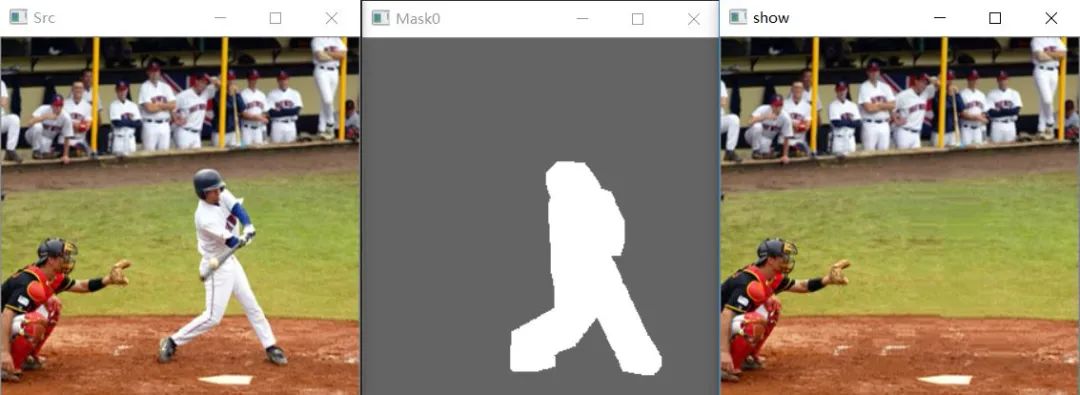
可以看到效果還是可以的,速度也比較快。
 End
End 
聲明:部分內容來源于網絡,僅供讀者學術交流之目的。文章版權歸原作者所有。如有不妥,請聯系刪除。
評論
圖片
表情
