基于Dijkstra算法的武漢地鐵路徑規(guī)劃!

導讀:最近爬取了武漢地鐵線路的信息,通過調(diào)用高德地圖的api 獲得各個站點的進度和緯度信息,使用Dijkstra算法對路徑進行規(guī)劃。
01 數(shù)據(jù)爬取
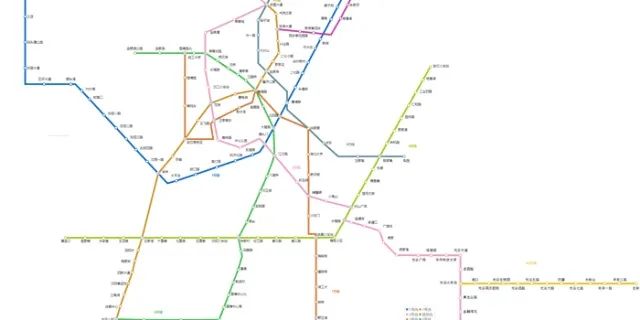
方法:requests、BeautifulSoup、pandas
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import pandas as pd
def spyder():
#獲得武漢的地鐵信息
url='http://wh.bendibao.com/ditie/linemap.shtml'
user_agent='Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_8; en-us) AppleWebKit/534.50 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.1 Safari/534.50'
headers = {'User-Agent': user_agent}
r = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
soup = BeautifulSoup(r.text, 'lxml')
all_info = soup.find_all('div', class_='line-list')
df=pd.DataFrame(columns=['name','site'])
for info in all_info:
title=info.find_all('div',class_='wrap')[0].get_text().split()[0].replace('線路圖','')
station_all=info.find_all('a',class_='link')
for station in station_all:
station_name=station.get_text()
temp={'name':station_name,'site':title}
df =df.append(temp,ignore_index=True)
df.to_excel('./subway.xlsx',index=False)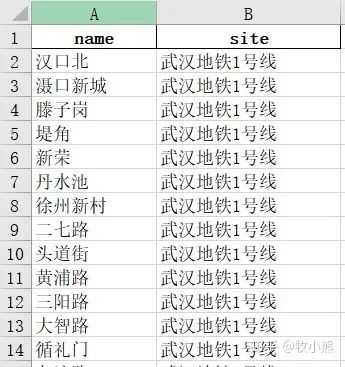
02 高德地圖api接口配置

03 得到地鐵站的經(jīng)度和緯度
def get_location(keyword,city):
#獲得經(jīng)緯度
user_agent='Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_8; en-us) AppleWebKit/534.50 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.1 Safari/534.50'
headers = {'User-Agent': user_agent}
url='http://restapi.amap.com/v3/place/text?key='+keynum+'&keywords='+keyword+'&types=&city='+city+'&children=1&offset=1&page=1&extensions=all'
data = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
data.encoding='utf-8'
data=json.loads(data.text)
result=data['pois'][0]['location'].split(',')
return result[0],result[1]def spyder():
#獲得武漢的地鐵信息
print('正在爬取武漢地鐵信息...')
url='http://wh.bendibao.com/ditie/linemap.shtml'
user_agent='Opera/9.80 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.6.8; U; en) Presto/2.8.131 Version/11.11'
headers = {'User-Agent': user_agent}
r = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
soup = BeautifulSoup(r.text, 'lxml')
all_info = soup.find_all('div', class_='line-list')
df=pd.DataFrame(columns=['name','site'])
for info in tqdm(all_info):
title=info.find_all('div',class_='wrap')[0].get_text().split()[0].replace('線路圖','')
station_all=info.find_all('a',class_='link')
for station in station_all:
station_name=station.get_text()
longitude,latitude=get_location(station_name,'武漢')
temp={'name':station_name,'site':title,'longitude':longitude,'latitude':latitude}
df =df.append(temp,ignore_index=True)
df.to_excel('./subway.xlsx',index=False)04 得到地鐵站之間的距離并構(gòu)建圖
from geopy.distance import geodesic
print(geodesic((緯度,經(jīng)度), (緯度,經(jīng)度)).m) #計算兩個坐標直線距離def compute_distance(longitude1,latitude1,longitude2,latitude2):
#計算2點之間的距離
user_agent='Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_8; en-us) AppleWebKit/534.50 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.1 Safari/534.50'
headers = {'User-Agent': user_agent}
url='http://restapi.amap.com/v3/distance?key='+keynum+'&origins='+str(longitude1)+','+str(latitude1)+'&destination='+str(longitude2)+','+str(latitude2)+'&type=1'
data=requests.get(url,headers=headers)
data.encoding='utf-8'
data=json.loads(data.text)
result=data['results'][0]['distance']
return resultdef get_graph():
print('正在創(chuàng)建pickle文件...')
data=pd.read_excel('./subway.xlsx')
#創(chuàng)建點之間的距離
graph=defaultdict(dict)
for i in range(data.shape[0]):
site1=data.iloc[i]['site']
if i<data.shape[0]-1:
site2=data.iloc[i+1]['site']
#如果是共一條線
if site1==site2:
longitude1,latitude1=data.iloc[i]['longitude'],data.iloc[i]['latitude']
longitude2,latitude2=data.iloc[i+1]['longitude'],data.iloc[i+1]['latitude']
name1=data.iloc[i]['name']
name2=data.iloc[i+1]['name']
distance=compute_distance(longitude1,latitude1,longitude2,latitude2)
graph[name1][name2]=distance
graph[name2][name1]=distance
output=open('graph.pkl','wb')
pickle.dump(graph,output)
05 得到當前位置距離最近的地鐵站
longitude1,latitude1=get_location(site1,'武漢')
longitude2,latitude2=get_location(site2,'武漢')
data=pd.read_excel('./subway.xlsx')
def get_nearest_subway(data,longitude1,latitude1):
#找最近的地鐵站
longitude1=float(longitude1)
latitude1=float(latitude1)
distance=float('inf')
nearest_subway=None
for i in range(data.shape[0]):
site1=data.iloc[i]['name']
longitude=float(data.iloc[i]['longitude'])
latitude=float(data.iloc[i]['latitude'])
temp=geodesic((latitude1,longitude1), (latitude,longitude)).m
if temp<distance:
distance=temp
nearest_subway=site1
return nearest_subway06 使用Dijkstra算法對地鐵線路進行規(guī)劃
def subway_line(start,end):
file=open('graph.pkl','rb')
graph=pickle.load(file)
#創(chuàng)建點之間的距離
#現(xiàn)在我們有了各個地鐵站之間的距離存儲在graph
#創(chuàng)建節(jié)點的開銷表,cost是指從start到該節(jié)點的距離
costs={}
parents={}
parents[end]=None
for node in graph[start].keys():
costs[node]=float(graph[start][node])
parents[node]=start
#終點到起始點距離為無窮大
costs[end]=float('inf')
#記錄處理過的節(jié)點list
processed=[]
shortest_path=dijkstra(start,end,graph,costs,processed,parents)
return shortest_path#計算圖中從start到end的最短路徑
def dijkstra(start,end,graph,costs,processed,parents):
#查詢到目前開銷最小的節(jié)點
node=find_lowest_cost_node(costs,processed)
#使用找到的開銷最小節(jié)點,計算它的鄰居是否可以通過它進行更新
#如果所有的節(jié)點都在processed里面 就結(jié)束
while node isnotNone:
#獲取節(jié)點的cost
cost=costs[node] #cost 是從node 到start的距離
#獲取節(jié)點的鄰居
neighbors=graph[node]
#遍歷所有的鄰居,看是否可以通過它進行更新
for neighbor in neighbors.keys():
#計算鄰居到當前節(jié)點+當前節(jié)點的開銷
new_cost=cost+float(neighbors[neighbor])
if neighbor notin costs or new_cost<costs[neighbor]:
costs[neighbor]=new_cost
#經(jīng)過node到鄰居的節(jié)點,cost最少
parents[neighbor]=node
#將當前節(jié)點標記為已處理
processed.append(node)
#下一步繼續(xù)找U中最短距離的節(jié)點 costs=U,processed=S
node=find_lowest_cost_node(costs,processed)
#循環(huán)完成 說明所有節(jié)點已經(jīng)處理完
shortest_path=find_shortest_path(start,end,parents)
shortest_path.reverse()
return shortest_path
#找到開銷最小的節(jié)點
def find_lowest_cost_node(costs,processed):
#初始化數(shù)據(jù)
lowest_cost=float('inf') #初始化最小值為無窮大
lowest_cost_node=None
#遍歷所有節(jié)點
for node in costs:
#如果該節(jié)點沒有被處理
ifnot node in processed:
#如果當前的節(jié)點的開銷比已經(jīng)存在的開銷小,那么久更新該節(jié)點為最小開銷的節(jié)點
if costs[node]<lowest_cost:
lowest_cost=costs[node]
lowest_cost_node=node
return lowest_cost_node
#找到最短路徑
def find_shortest_path(start,end,parents):
node=end
shortest_path=[end]
#最終的根節(jié)點為start
while parents[node] !=start:
shortest_path.append(parents[node])
node=parents[node]
shortest_path.append(start)
return shortest_path07 將所有的函數(shù)封裝
def main(site1,site2):
ifnot os.path.exists('./subway.xlsx'):
spyder()
ifnot os.path.exists('./graph.pkl'):
get_graph()
longitude1,latitude1=get_location(site1,'武漢')
longitude2,latitude2=get_location(site2,'武漢')
data=pd.read_excel('./subway.xlsx')
#求最近的地鐵站
start=get_nearest_subway(data,longitude1,latitude1)
end=get_nearest_subway(data,longitude2,latitude2)
shortest_path=subway_line(start,end)
if site1 !=start:
shortest_path.insert(0,site1)
if site2 !=end:
shortest_path.append(site2)
print('路線規(guī)劃為:','-->'.join(shortest_path))
if __name__ == '__main__':
global keynum
keynum=''#輸入自己的key
main('華中農(nóng)業(yè)大學','東亭')路線規(guī)劃為:華中農(nóng)業(yè)大學-->野芷湖-->板橋-->湖工大-->建安街-->瑞安街-->武昌火車站-->梅苑小區(qū)-->中南路-->洪山廣場-->楚河漢街-->青魚嘴-->東亭

08 可以繼續(xù)完善的點
09 項目源碼


評論
圖片
表情
