【爬蟲(chóng)、算法】基于Dijkstra算法的武漢地鐵路徑規(guī)劃!
前言
最近爬取了武漢地鐵線路的信息,通過(guò)調(diào)用高德地圖的api 獲得各個(gè)站點(diǎn)的進(jìn)度和緯度信息,使用Dijkstra算法對(duì)路徑進(jìn)行規(guī)劃。
1.數(shù)據(jù)爬取
首先是需要獲得武漢各個(gè)地鐵的地鐵站信息,通過(guò)爬蟲(chóng)爬取武漢各個(gè)地鐵站點(diǎn)的信息,并存儲(chǔ)到xlsx文件中
武漢地鐵線路圖,2021最新武漢地鐵線路圖,武漢地鐵地圖-武漢本地寶wh.bendibao.com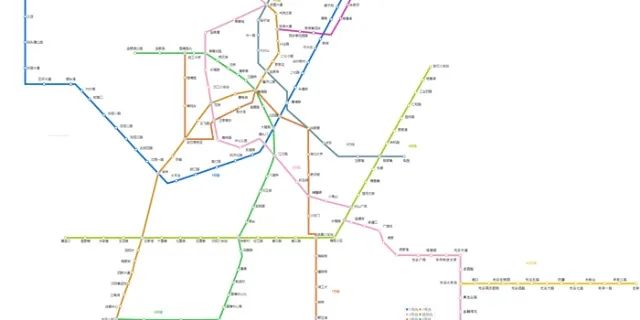
方法:requests、BeautifulSoup、pandas
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import pandas as pd
def spyder():
#獲得武漢的地鐵信息
url='http://wh.bendibao.com/ditie/linemap.shtml'
user_agent='Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_8; en-us) AppleWebKit/534.50 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.1 Safari/534.50'
headers = {'User-Agent': user_agent}
r = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
soup = BeautifulSoup(r.text, 'lxml')
all_info = soup.find_all('div', class_='line-list')
df=pd.DataFrame(columns=['name','site'])
for info in all_info:
title=info.find_all('div',class_='wrap')[0].get_text().split()[0].replace('線路圖','')
station_all=info.find_all('a',class_='link')
for station in station_all:
station_name=station.get_text()
temp={'name':station_name,'site':title}
df =df.append(temp,ignore_index=True)
df.to_excel('./subway.xlsx',index=False)
我們將爬取的地鐵信息保存到excel文件中
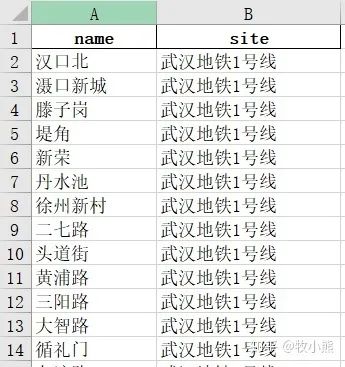
如果要做路徑規(guī)劃的話,我們還需要知道地鐵站的位置信息
因此我們選擇了高德地圖的api接口
2.高德地圖api接口配置
高德開(kāi)放平臺(tái) | 高德地圖 APIlbs.amap.com? 鏈接:https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//lbs.amap.com/%3Fref%3Dhttps%3A//console.amap.com)
首先我們注冊(cè)賬號(hào)
選擇為個(gè)人開(kāi)發(fā)者
填寫(xiě)個(gè)人信息...
注冊(cè)成功后,我們來(lái)登陸高德地圖api
選擇我的應(yīng)用
創(chuàng)建新應(yīng)用
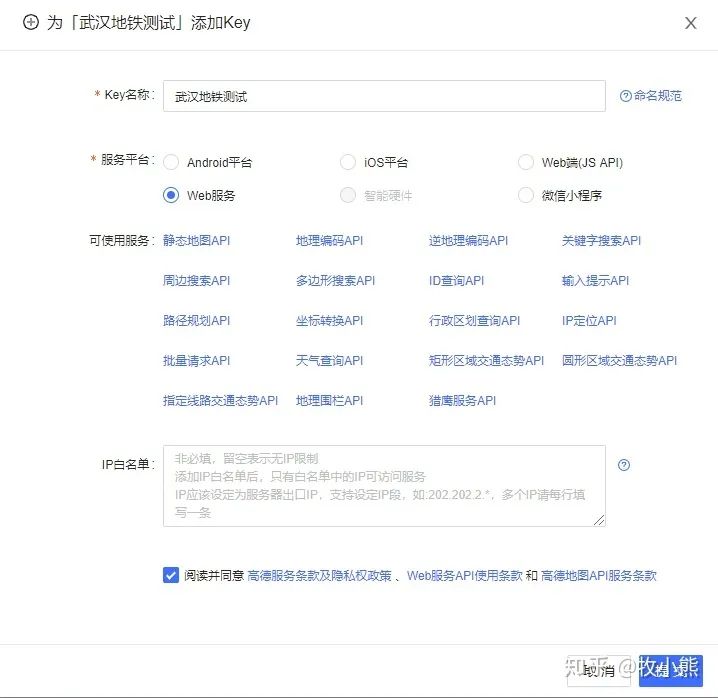
選擇web服務(wù)

這個(gè)時(shí)候高德地圖就給你了一個(gè)key
3.得到地鐵站的經(jīng)度和緯度
配置一個(gè)get_location函數(shù)區(qū)訪問(wèn)高德地圖的api 然后返回經(jīng)度和緯度
def get_location(keyword,city):
#獲得經(jīng)緯度
user_agent='Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_8; en-us) AppleWebKit/534.50 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.1 Safari/534.50'
headers = {'User-Agent': user_agent}
url='http://restapi.amap.com/v3/place/text?key='+keynum+'&keywords='+keyword+'&types=&city='+city+'&children=1&offset=1&page=1&extensions=all'
data = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
data.encoding='utf-8'
data=json.loads(data.text)
result=data['pois'][0]['location'].split(',')
return result[0],result[1]
keyword是你要查詢(xún)的地址,city代表城市
我們這里city就設(shè)置為武漢
我們邊爬取地鐵站信息 邊獲得經(jīng)度和緯度
于是得到了改進(jìn)版的爬蟲(chóng)
def spyder():
#獲得武漢的地鐵信息
print('正在爬取武漢地鐵信息...')
url='http://wh.bendibao.com/ditie/linemap.shtml'
user_agent='Opera/9.80 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.6.8; U; en) Presto/2.8.131 Version/11.11'
headers = {'User-Agent': user_agent}
r = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
soup = BeautifulSoup(r.text, 'lxml')
all_info = soup.find_all('div', class_='line-list')
df=pd.DataFrame(columns=['name','site'])
for info in tqdm(all_info):
title=info.find_all('div',class_='wrap')[0].get_text().split()[0].replace('線路圖','')
station_all=info.find_all('a',class_='link')
for station in station_all:
station_name=station.get_text()
longitude,latitude=get_location(station_name,'武漢')
temp={'name':station_name,'site':title,'longitude':longitude,'latitude':latitude}
df =df.append(temp,ignore_index=True)
df.to_excel('./subway.xlsx',index=False)
4.得到地鐵站之間的距離并構(gòu)建圖
計(jì)算各個(gè)地鐵站的信息,并生成地鐵站網(wǎng)絡(luò)
現(xiàn)在我們得到了地鐵站的經(jīng)度和緯度 可以通過(guò)geopy.distance這個(gè)包來(lái)計(jì)算2點(diǎn)之間的距離
from geopy.distance import geodesic
print(geodesic((緯度,經(jīng)度), (緯度,經(jīng)度)).m) #計(jì)算兩個(gè)坐標(biāo)直線距離
當(dāng)然高德地圖api也同樣提供了計(jì)算距離的接口
我們來(lái)配置計(jì)算距離的函數(shù)
輸入經(jīng)度和緯度就可以計(jì)算距離
def compute_distance(longitude1,latitude1,longitude2,latitude2):
#計(jì)算2點(diǎn)之間的距離
user_agent='Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_8; en-us) AppleWebKit/534.50 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.1 Safari/534.50'
headers = {'User-Agent': user_agent}
url='http://restapi.amap.com/v3/distance?key='+keynum+'&origins='+str(longitude1)+','+str(latitude1)+'&destination='+str(longitude2)+','+str(latitude2)+'&type=1'
data=requests.get(url,headers=headers)
data.encoding='utf-8'
data=json.loads(data.text)
result=data['results'][0]['distance']
return result
那么接下來(lái)就構(gòu)建地鐵站之間的圖網(wǎng)絡(luò)
因?yàn)榕廊〉罔F站信息比較耗時(shí),我們將制作好的圖網(wǎng)絡(luò)保存為pickle文件方便以后使用
def get_graph():
print('正在創(chuàng)建pickle文件...')
data=pd.read_excel('./subway.xlsx')
#創(chuàng)建點(diǎn)之間的距離
graph=defaultdict(dict)
for i in range(data.shape[0]):
site1=data.iloc[i]['site']
if i0]-1:
site2=data.iloc[i+1]['site']
#如果是共一條線
if site1==site2:
longitude1,latitude1=data.iloc[i]['longitude'],data.iloc[i]['latitude']
longitude2,latitude2=data.iloc[i+1]['longitude'],data.iloc[i+1]['latitude']
name1=data.iloc[i]['name']
name2=data.iloc[i+1]['name']
distance=compute_distance(longitude1,latitude1,longitude2,latitude2)
graph[name1][name2]=distance
graph[name2][name1]=distance
output=open('graph.pkl','wb')
pickle.dump(graph,output)
5.得到當(dāng)前位置距離最近的地鐵站
我們要去找距離最近的地鐵站 首先是獲得位置的坐標(biāo)
然后將當(dāng)前的坐標(biāo)遍歷所有地鐵站 找到最近的地鐵站
longitude1,latitude1=get_location(site1,'武漢')
longitude2,latitude2=get_location(site2,'武漢')
data=pd.read_excel('./subway.xlsx')
定義get_nearest_subway函數(shù)來(lái)尋找最近的地鐵站
def get_nearest_subway(data,longitude1,latitude1):
#找最近的地鐵站
longitude1=float(longitude1)
latitude1=float(latitude1)
distance=float('inf')
nearest_subway=None
for i in range(data.shape[0]):
site1=data.iloc[i]['name']
longitude=float(data.iloc[i]['longitude'])
latitude=float(data.iloc[i]['latitude'])
temp=geodesic((latitude1,longitude1), (latitude,longitude)).m
if temp distance=temp
nearest_subway=site1
return nearest_subway
通過(guò)遍歷地鐵站的距離找到了最近的上車(chē)點(diǎn)和下車(chē)點(diǎn)
6.使用Dijkstra算法對(duì)地鐵線路進(jìn)行規(guī)劃
Dijkstra算法是求最短路徑的經(jīng)典算法
Dijkstra算法主要特點(diǎn)是從起始點(diǎn)開(kāi)始,采用貪心算法的策略,每次遍歷到始點(diǎn)距離最近且未訪問(wèn)過(guò)的頂點(diǎn)的鄰接節(jié)點(diǎn),直到擴(kuò)展到終點(diǎn)為止。
首先是讀取構(gòu)建的圖信息
def subway_line(start,end):
file=open('graph.pkl','rb')
graph=pickle.load(file)
#創(chuàng)建點(diǎn)之間的距離
#現(xiàn)在我們有了各個(gè)地鐵站之間的距離存儲(chǔ)在graph
#創(chuàng)建節(jié)點(diǎn)的開(kāi)銷(xiāo)表,cost是指從start到該節(jié)點(diǎn)的距離
costs={}
parents={}
parents[end]=None
for node in graph[start].keys():
costs[node]=float(graph[start][node])
parents[node]=start
#終點(diǎn)到起始點(diǎn)距離為無(wú)窮大
costs[end]=float('inf')
#記錄處理過(guò)的節(jié)點(diǎn)list
processed=[]
shortest_path=dijkstra(start,end,graph,costs,processed,parents)
return shortest_path
構(gòu)建dijkstra算法
#計(jì)算圖中從start到end的最短路徑
def dijkstra(start,end,graph,costs,processed,parents):
#查詢(xún)到目前開(kāi)銷(xiāo)最小的節(jié)點(diǎn)
node=find_lowest_cost_node(costs,processed)
#使用找到的開(kāi)銷(xiāo)最小節(jié)點(diǎn),計(jì)算它的鄰居是否可以通過(guò)它進(jìn)行更新
#如果所有的節(jié)點(diǎn)都在processed里面 就結(jié)束
while node is not None:
#獲取節(jié)點(diǎn)的cost
cost=costs[node] #cost 是從node 到start的距離
#獲取節(jié)點(diǎn)的鄰居
neighbors=graph[node]
#遍歷所有的鄰居,看是否可以通過(guò)它進(jìn)行更新
for neighbor in neighbors.keys():
#計(jì)算鄰居到當(dāng)前節(jié)點(diǎn)+當(dāng)前節(jié)點(diǎn)的開(kāi)銷(xiāo)
new_cost=cost+float(neighbors[neighbor])
if neighbor not in costs or new_cost costs[neighbor]=new_cost
#經(jīng)過(guò)node到鄰居的節(jié)點(diǎn),cost最少
parents[neighbor]=node
#將當(dāng)前節(jié)點(diǎn)標(biāo)記為已處理
processed.append(node)
#下一步繼續(xù)找U中最短距離的節(jié)點(diǎn) costs=U,processed=S
node=find_lowest_cost_node(costs,processed)
#循環(huán)完成 說(shuō)明所有節(jié)點(diǎn)已經(jīng)處理完
shortest_path=find_shortest_path(start,end,parents)
shortest_path.reverse()
return shortest_path
#找到開(kāi)銷(xiāo)最小的節(jié)點(diǎn)
def find_lowest_cost_node(costs,processed):
#初始化數(shù)據(jù)
lowest_cost=float('inf') #初始化最小值為無(wú)窮大
lowest_cost_node=None
#遍歷所有節(jié)點(diǎn)
for node in costs:
#如果該節(jié)點(diǎn)沒(méi)有被處理
if not node in processed:
#如果當(dāng)前的節(jié)點(diǎn)的開(kāi)銷(xiāo)比已經(jīng)存在的開(kāi)銷(xiāo)小,那么久更新該節(jié)點(diǎn)為最小開(kāi)銷(xiāo)的節(jié)點(diǎn)
if costs[node] lowest_cost=costs[node]
lowest_cost_node=node
return lowest_cost_node
#找到最短路徑
def find_shortest_path(start,end,parents):
node=end
shortest_path=[end]
#最終的根節(jié)點(diǎn)為start
while parents[node] !=start:
shortest_path.append(parents[node])
node=parents[node]
shortest_path.append(start)
return shortest_path
7.將所有的函數(shù)封裝
構(gòu)建main文件將整個(gè)流程封裝起來(lái)
def main(site1,site2):
if not os.path.exists('./subway.xlsx'):
spyder()
if not os.path.exists('./graph.pkl'):
get_graph()
longitude1,latitude1=get_location(site1,'武漢')
longitude2,latitude2=get_location(site2,'武漢')
data=pd.read_excel('./subway.xlsx')
#求最近的地鐵站
start=get_nearest_subway(data,longitude1,latitude1)
end=get_nearest_subway(data,longitude2,latitude2)
shortest_path=subway_line(start,end)
if site1 !=start:
shortest_path.insert(0,site1)
if site2 !=end:
shortest_path.append(site2)
print('路線規(guī)劃為:','-->'.join(shortest_path))
if __name__ == '__main__':
global keynum
keynum='' #輸入自己的key
main('華中農(nóng)業(yè)大學(xué)','東亭')
比方我想去東亭,想坐地鐵過(guò)去
我們看看通過(guò)規(guī)劃的地鐵線路
路線規(guī)劃為:華中農(nóng)業(yè)大學(xué)-->野芷湖-->板橋-->湖工大-->建安街-->瑞安街-->武昌火車(chē)站-->梅苑小區(qū)-->中南路-->洪山廣場(chǎng)-->楚河漢街-->青魚(yú)嘴-->東亭
我們來(lái)看看高德地圖給我們的規(guī)劃

不得了,一模一樣~
8.可以繼續(xù)完善的點(diǎn)
這個(gè)項(xiàng)目我們只做了地鐵的相關(guān)信息,沒(méi)有引入公交的信息加入道路線規(guī)劃中,因此后續(xù)可以爬取武漢的公交線路進(jìn)行地鐵、公交混合線路規(guī)劃
同時(shí)給出的規(guī)劃信息只有文字描述,沒(méi)有顯示在地圖上不夠直觀,我們可以進(jìn)行flask的部署將規(guī)劃的線路顯示在地圖上,更加不容易出錯(cuò)~
9.項(xiàng)目源碼
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1dmstu7PlF12Bdgk9QTjsPA??提取碼:r8es
往期精彩回顧
獲取本站知識(shí)星球優(yōu)惠券,復(fù)制鏈接直接打開(kāi):
https://t.zsxq.com/qFiUFMV
本站qq群704220115。
加入微信群請(qǐng)掃碼:
