Java線程池的使用及工作原理
點(diǎn)擊上方藍(lán)色字體,選擇“標(biāo)星公眾號”
優(yōu)質(zhì)文章,第一時間送達(dá)
前言
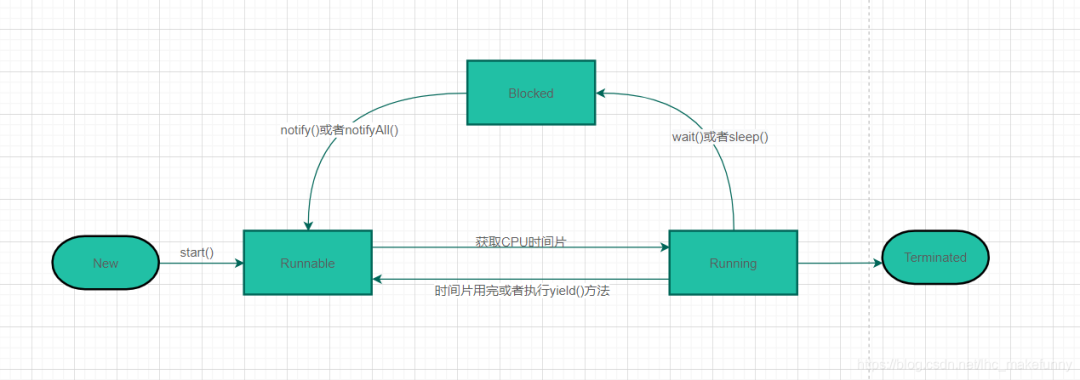
什么是線程池?
線程池要解決什么問題?
線程池的使用
線程池的創(chuàng)建
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
常用阻塞隊(duì)列
ArrayBlockingQueue
LinkedBlockingQueue
線程工廠
ThreadFactory threadFactory = ThreadFactoryBuilder.create().setNamePrefix("myThread-").build();
拒絕策略
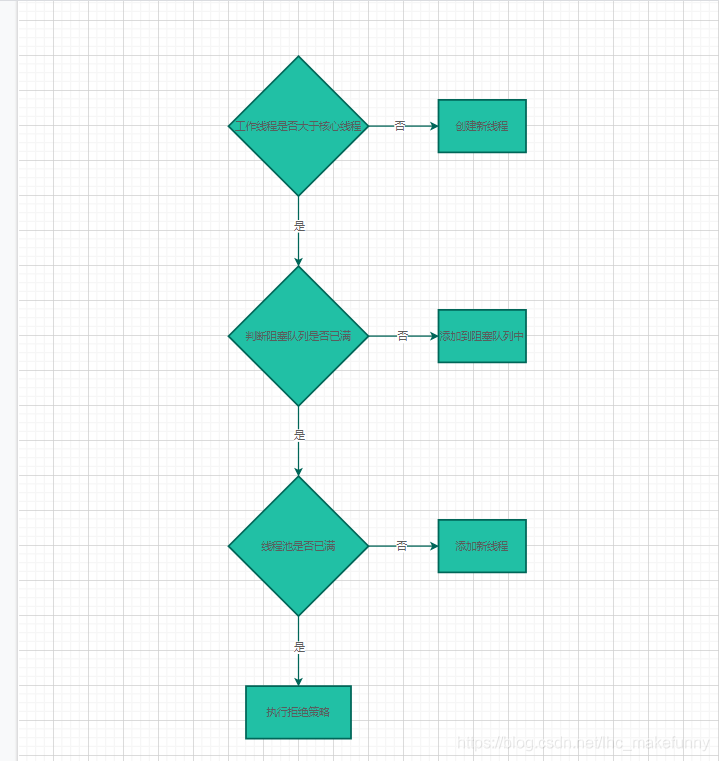
線程池的執(zhí)行邏輯
// 創(chuàng)建線程工廠
ThreadFactory threadFactory = ThreadFactoryBuilder.create().setNamePrefix("myThread-").build();
// 創(chuàng)建線程池
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(100), threadFactory, new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
execute()方法
// 組合值;保存了線程池的工作狀態(tài)和工作線程數(shù)
private final AtomicInteger ctl = new AtomicInteger(ctlOf(RUNNING, 0));
public void execute(Runnable command) {
// 任務(wù)為空 拋出NPE
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
// 獲取線程池狀態(tài)
int c = ctl.get();
// 如果工作線程數(shù)小于核心線程數(shù)就創(chuàng)建新線程
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) {
if (addWorker(command, true))
return;
c = ctl.get();
}
// 如果線程池處于Running狀態(tài),就把任務(wù)放在隊(duì)列尾部
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
// 重新檢查線程池狀態(tài)
int recheck = ctl.get();
// 如果線程池不是Running狀態(tài),就移除剛才添加的任務(wù),并執(zhí)行拒絕策略
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
reject(command);
// 是Running狀態(tài),就添加線程
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
// 添加任務(wù)失敗,執(zhí)行拒絕策略
else if (!addWorker(command, false))
reject(command);
}
// addWorker()完成線程的創(chuàng)建
執(zhí)行流程
版權(quán)聲明:本文為博主原創(chuàng)文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版權(quán)協(xié)議,轉(zhuǎn)載請附上原文出處鏈接和本聲明。
本文鏈接:
https://blog.csdn.net/lhc_makefunny/article/details/117308066


評論
圖片
表情