詳述Java線程池實(shí)現(xiàn)原理
點(diǎn)擊上方藍(lán)色字體,選擇“標(biāo)星公眾號(hào)”
優(yōu)質(zhì)文章,第一時(shí)間送達(dá)
一、寫(xiě)在前面
1.1 線程池是什么
線程池(Thread Pool) 是一種池化思想管理線程的工具,經(jīng)常出現(xiàn)在多線程服務(wù)器中,如MySQL。
線程過(guò)多會(huì)帶來(lái)額外的開(kāi)銷,其中包括創(chuàng)建銷毀線程的開(kāi)銷,操作系統(tǒng)調(diào)度線程的開(kāi)銷等等,同時(shí)也降低了計(jì)算機(jī)的整體性能。線程池維護(hù)多個(gè)線程,等待監(jiān)督管理者分配可并發(fā)執(zhí)行的任務(wù)。這種做法,一方面避免了處理任務(wù)是創(chuàng)建銷毀線程開(kāi)銷代價(jià),另一方面避免了線程數(shù)量膨脹導(dǎo)致的過(guò)分調(diào)度問(wèn)題,保證了對(duì)操作系統(tǒng)內(nèi)核的充分利用。
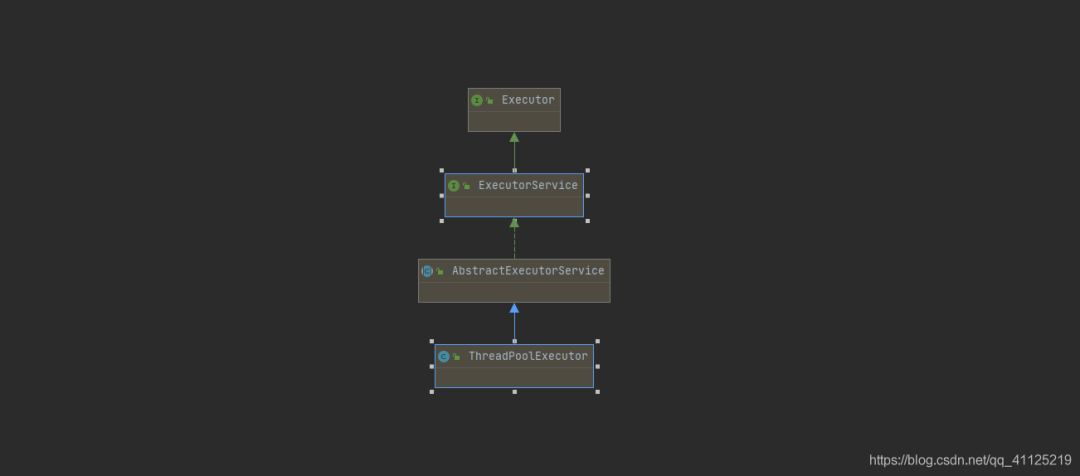
本文描述的線程池是JDK提供的ThreadPoolExecutor類
1.2 線程池解決的問(wèn)題是什么
線程池解決的問(wèn)題就是資源管理的問(wèn)題。在并發(fā)環(huán)境下,系統(tǒng)不能夠確定在任意時(shí)刻有多少任務(wù)需要執(zhí)行,有多少資源需要投入。
二、線程池和核心設(shè)計(jì)與實(shí)現(xiàn)
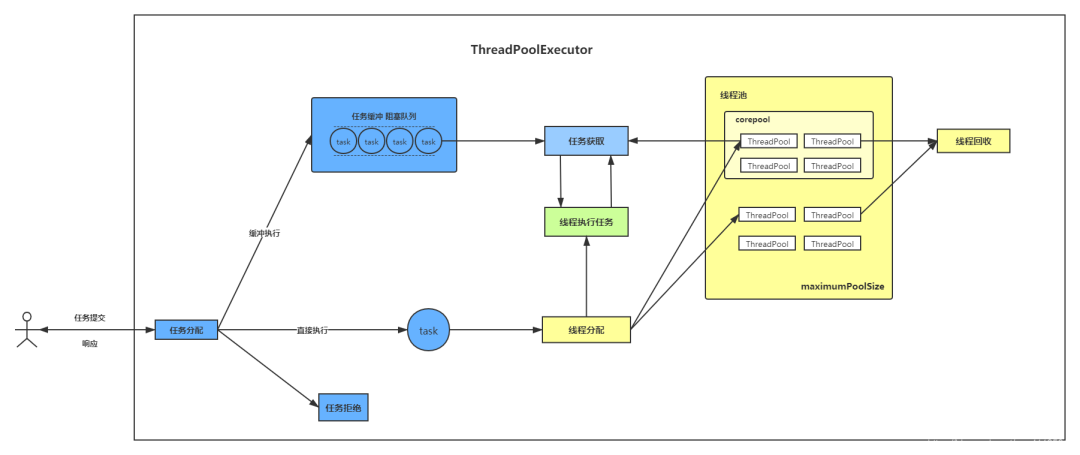
2.1 總體設(shè)計(jì)
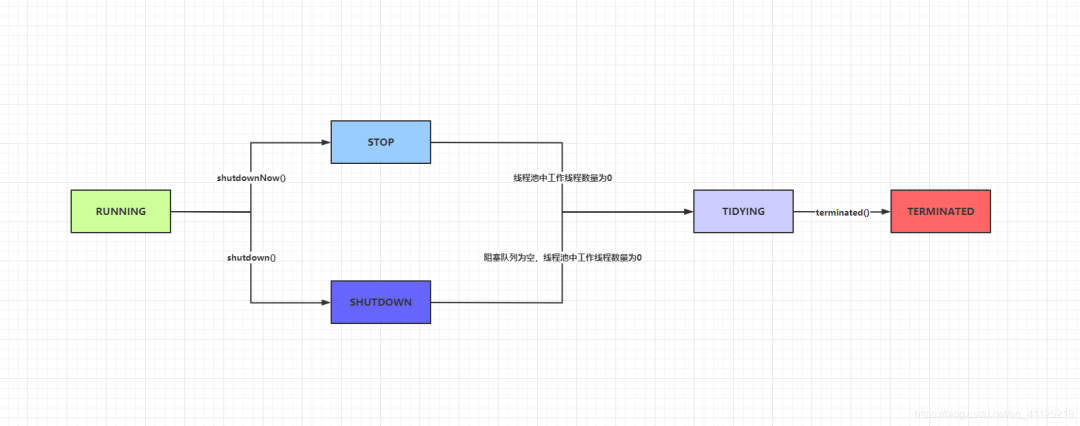
2.2 生命周期管理
private final AtomicInteger ctl = new AtomicInteger(ctlOf(RUNNING, 0));
// Packing and unpacking ctl
// 計(jì)算當(dāng)前運(yùn)行狀態(tài)
private static int runStateOf(int c) { return c & ~CAPACITY; }
// 計(jì)算當(dāng)前線程數(shù)據(jù)
private static int workerCountOf(int c) { return c & CAPACITY; }
// 通過(guò)狀態(tài)和線程數(shù)生成ctl
private static int ctlOf(int rs, int wc) { return rs | wc; }
// runState is stored in the high-order bits
private static final int RUNNING = -1 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int SHUTDOWN = 0 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int STOP = 1 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int TIDYING = 2 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int TERMINATED = 3 << COUNT_BITS;
| 運(yùn)行狀態(tài) | 狀態(tài)描述 |
|---|---|
| RUNNING | 能接受新提交的任務(wù),并且也能處理阻塞隊(duì)列中的任務(wù) |
| SHUTDOWN | 狀態(tài)關(guān)閉,不在接受新提交的任務(wù),但是能繼續(xù)處理阻塞隊(duì)列已保存的讓任務(wù) |
| STOP | 不接受新任務(wù),也不處理隊(duì)列中的任務(wù),會(huì)中斷正在處理任務(wù)的線程 |
| TIDYING | 所有讓任務(wù)都已終止,workerCount(有效處理讓任務(wù)線程)狀態(tài)為0 |
| TERMINATED | 在terminated()方法執(zhí)行結(jié)束后進(jìn)入該狀態(tài) |
2.3 任務(wù)調(diào)度機(jī)制
2.3.1 任務(wù)調(diào)度
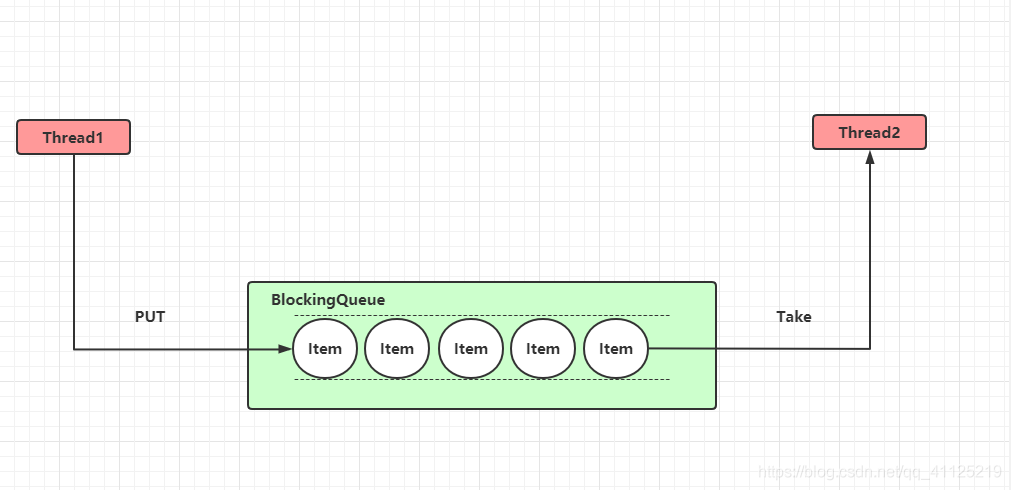
2.3.2 任務(wù)緩沖
| 名稱 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ArrayBlockingQueue | 一個(gè)用數(shù)組實(shí)現(xiàn)的有界阻塞隊(duì)列,此隊(duì)列按照先進(jìn)先出(FIFO)的原則對(duì)元素進(jìn)行排序。支持公平鎖和非公平鎖 |
| LinkedBlockingDeque | 一個(gè)由鏈表結(jié)構(gòu)組成的有界隊(duì)列,此隊(duì)列按照先進(jìn)先出(FIFO)的原則對(duì)元素進(jìn)行排序。此隊(duì)列的默認(rèn)長(zhǎng)度為Integer.MAX_VALUE,所以默認(rèn)創(chuàng)建此隊(duì)列有容量危險(xiǎn) |
| PriorityBlockingQueue | 一個(gè)支持線程優(yōu)先級(jí)排序的無(wú)界隊(duì)列,默認(rèn)自然進(jìn)行排序,也可以自定義實(shí)現(xiàn)compareTo()方法指定排序故障,不能保證同優(yōu)先級(jí)元素的順序。 |
| DelayQueue | 一個(gè)實(shí)現(xiàn)PriorityBlockingQueue實(shí)現(xiàn)延遲獲取的無(wú)界隊(duì)列,在創(chuàng)建元素時(shí),可以指定多久才能從隊(duì)列中獲取當(dāng)前元素。只有延遲期滿后才能從隊(duì)列中獲取元素。 |
| SynchronousQueue | 一個(gè)不存儲(chǔ)元素的阻塞隊(duì)列,每個(gè)put操作必須等待take操作,否則不能添加元素。支持公平鎖和非公平鎖。SynchronousQueue的一個(gè)使用場(chǎng)景是在線程池里。Executors.newCachedThreadPool()就使用了SynchronousQueue,這個(gè)線程池根據(jù)需要(新任務(wù)來(lái))創(chuàng)建新的線程,如果有空閑的線程就使用空閑線程,線程空閑60秒會(huì)被回收。 return new ThreadPoolExecutor( 0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue()); |
| LinkedTransferQueue | 一個(gè)由鏈表結(jié)構(gòu)組成的無(wú)界阻塞隊(duì)列,相當(dāng)于其他隊(duì)列,LinkedTransferQueue多了transfer和tryTransfer方法 |
| LinkedBlockingQueue | 一個(gè)由鏈表結(jié)構(gòu)組成的雙向阻塞隊(duì)列,隊(duì)列的頭部和尾部都可以插入和刪除元素,多線程并發(fā)時(shí),可以將鎖的競(jìng)爭(zhēng)最多降到一半 |
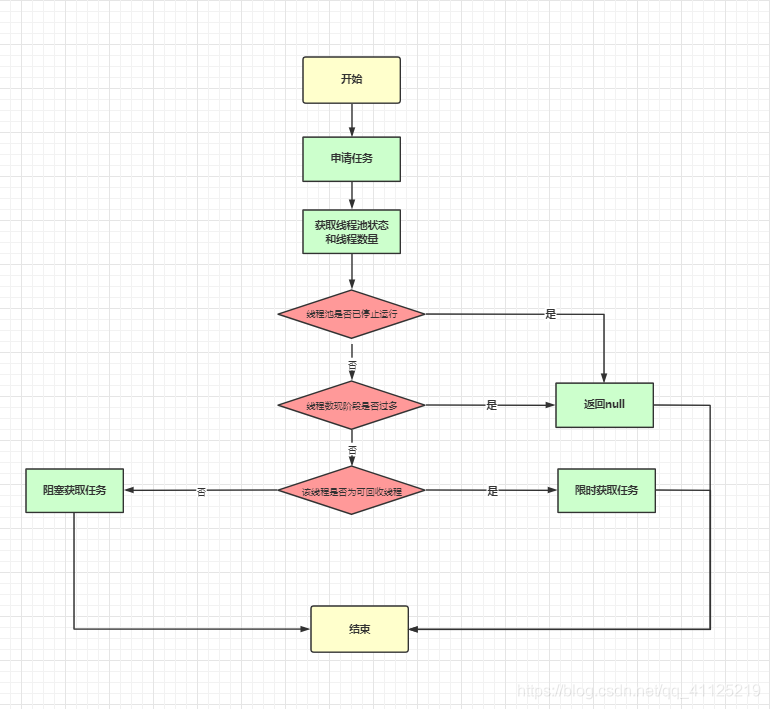
2.3.3 任務(wù)申請(qǐng)
private Runnable getTask() {
boolean timedOut = false; // Did the last poll() time out?
for (;;) {
int c = ctl.get();
int rs = runStateOf(c);
// Check if queue empty only if necessary.
// 判斷線程池是否已停止運(yùn)行
if (rs >= SHUTDOWN && (rs >= STOP || workQueue.isEmpty())) {
decrementWorkerCount();
return null;
}
int wc = workerCountOf(c);
// Are workers subject to culling?
boolean timed = allowCoreThreadTimeOut || wc > corePoolSize;
// 判斷線程現(xiàn)階段是否夠多
if ((wc > maximumPoolSize || (timed && timedOut))
&& (wc > 1 || workQueue.isEmpty())) {
if (compareAndDecrementWorkerCount(c))
return null;
continue;
}
// 限時(shí)任務(wù)獲取和阻塞獲取
try {
Runnable r = timed ?
workQueue.poll(keepAliveTime, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS) :
workQueue.take();
if (r != null)
return r;
timedOut = true;
} catch (InterruptedException retry) {
timedOut = false;
}
}
}
2.3.4 任務(wù)拒絕
public interface RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Method that may be invoked by a {@link ThreadPoolExecutor} when
* {@link ThreadPoolExecutor#execute execute} cannot accept a
* task. This may occur when no more threads or queue slots are
* available because their bounds would be exceeded, or upon
* shutdown of the Executor.
*
* <p>In the absence of other alternatives, the method may throw
* an unchecked {@link RejectedExecutionException}, which will be
* propagated to the caller of {@code execute}.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param executor the executor attempting to execute this task
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if there is no remedy
*/
void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor);
}
| 名稱 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy | 丟棄任務(wù)并拋出RejectedExecutionException異常。這是線程池默認(rèn)的拒絕策略,在任務(wù)不能在提交的時(shí)候,拋出異常,及時(shí)反饋程序運(yùn)行狀態(tài)。如果是比較關(guān)鍵的業(yè)務(wù),推薦使用該策略,這樣子在系統(tǒng)不能承載更大并發(fā)的時(shí)候,能過(guò)及時(shí)的通過(guò)異常發(fā)現(xiàn)。 |
| ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy | 丟棄任務(wù),但是不拋出異常。使用該策略,可能會(huì)使我們無(wú)法發(fā)現(xiàn)系統(tǒng)的異常狀態(tài)。建議一些無(wú)關(guān)緊要的業(yè)務(wù)采用此策略。 |
| ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy | 丟棄隊(duì)列最前面的任務(wù),然后重新提交比拒接的任務(wù)。是否要采用此種策略,需要根據(jù)實(shí)際業(yè)務(wù)是否允許丟棄老任務(wù)來(lái)認(rèn)真衡量 |
| ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy | 由調(diào)用線程(提交任務(wù)的線程)來(lái)處理任務(wù)。這種情況是需要讓所有的任務(wù)都執(zhí)行完畢,那么就適合大量計(jì)算的任務(wù)類型去執(zhí)行,多線程僅僅是增加大吞吐量的手段,最終必須要讓每個(gè)任務(wù)都執(zhí)行 |
/**
* A handler for rejected tasks that runs the rejected task
* directly in the calling thread of the {@code execute} method,
* unless the executor has been shut down, in which case the task
* is discarded.
*/
public static class CallerRunsPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates a {@code CallerRunsPolicy}.
*/
public CallerRunsPolicy() { }
/**
* Executes task r in the caller's thread, unless the executor
* has been shut down, in which case the task is discarded.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
if (!e.isShutdown()) {
r.run();
}
}
}
/**
* A handler for rejected tasks that throws a
* {@code RejectedExecutionException}.
*/
public static class AbortPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates an {@code AbortPolicy}.
*/
public AbortPolicy() { }
/**
* Always throws RejectedExecutionException.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
* @throws RejectedExecutionException always
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Task " + r.toString() +
" rejected from " +
e.toString());
}
}
/**
* A handler for rejected tasks that silently discards the
* rejected task.
*/
public static class DiscardPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates a {@code DiscardPolicy}.
*/
public DiscardPolicy() { }
/**
* Does nothing, which has the effect of discarding task r.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
}
}
/**
* A handler for rejected tasks that discards the oldest unhandled
* request and then retries {@code execute}, unless the executor
* is shut down, in which case the task is discarded.
*/
public static class DiscardOldestPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates a {@code DiscardOldestPolicy} for the given executor.
*/
public DiscardOldestPolicy() { }
/**
* Obtains and ignores the next task that the executor
* would otherwise execute, if one is immediately available,
* and then retries execution of task r, unless the executor
* is shut down, in which case task r is instead discarded.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
if (!e.isShutdown()) {
e.getQueue().poll();
e.execute(r);
}
}
}
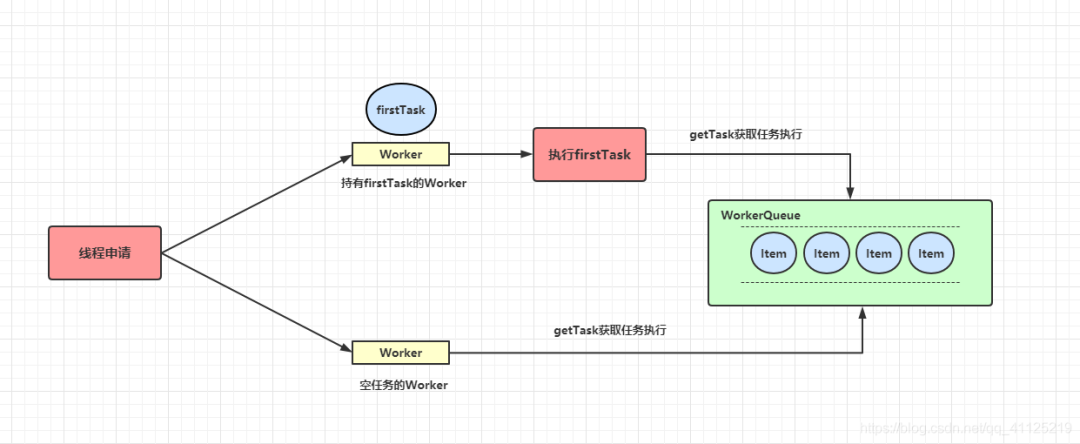
2.4 Worker線程管理
2.4.1 Worker線程
private final class Worker
extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
implements Runnable
{
/** Thread this worker is running in. Null if factory fails. */
// worker持有的線程
final Thread thread;
/** Initial task to run. Possibly null. */
// 初始化的任務(wù),可以為null
Runnable firstTask;
...
}
/**
* The queue used for holding tasks and handing off to worker
* threads. We do not require that workQueue.poll() returning
* null necessarily means that workQueue.isEmpty(), so rely
* solely on isEmpty to see if the queue is empty (which we must
* do for example when deciding whether to transition from
* SHUTDOWN to TIDYING). This accommodates special-purpose
* queues such as DelayQueues for which poll() is allowed to
* return null even if it may later return non-null when delays
* expire.
*/
# workerQueue 源碼定義
private final BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue;
/**
* Set containing all worker threads in pool. Accessed only when
* holding mainLock.
*/
private final HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<Worker>();
private final class Worker
extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
implements Runnable
public void shutdown() {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
checkShutdownAccess();
advanceRunState(SHUTDOWN);
// 執(zhí)行interruptIdleWorkers方法
interruptIdleWorkers();
onShutdown(); // hook for ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
tryTerminate();
}
final void tryTerminate() {
for (;;) {
int c = ctl.get();
if (isRunning(c) ||
runStateAtLeast(c, TIDYING) ||
(runStateOf(c) == SHUTDOWN && ! workQueue.isEmpty()))
return;
if (workerCountOf(c) != 0) { // Eligible to terminate
// 執(zhí)行interruptIdleWorkers
interruptIdleWorkers(ONLY_ONE);
return;
}
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
if (ctl.compareAndSet(c, ctlOf(TIDYING, 0))) {
try {
terminated();
} finally {
ctl.set(ctlOf(TERMINATED, 0));
termination.signalAll();
}
return;
}
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
// else retry on failed CAS
}
}
private void interruptIdleWorkers(boolean onlyOne) {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
for (Worker w : workers) {
Thread t = w.thread;
if (!t.isInterrupted() && w.tryLock()) {
try {
t.interrupt();
} catch (SecurityException ignore) {
} finally {
w.unlock();
}
}
if (onlyOne)
break;
}
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
}
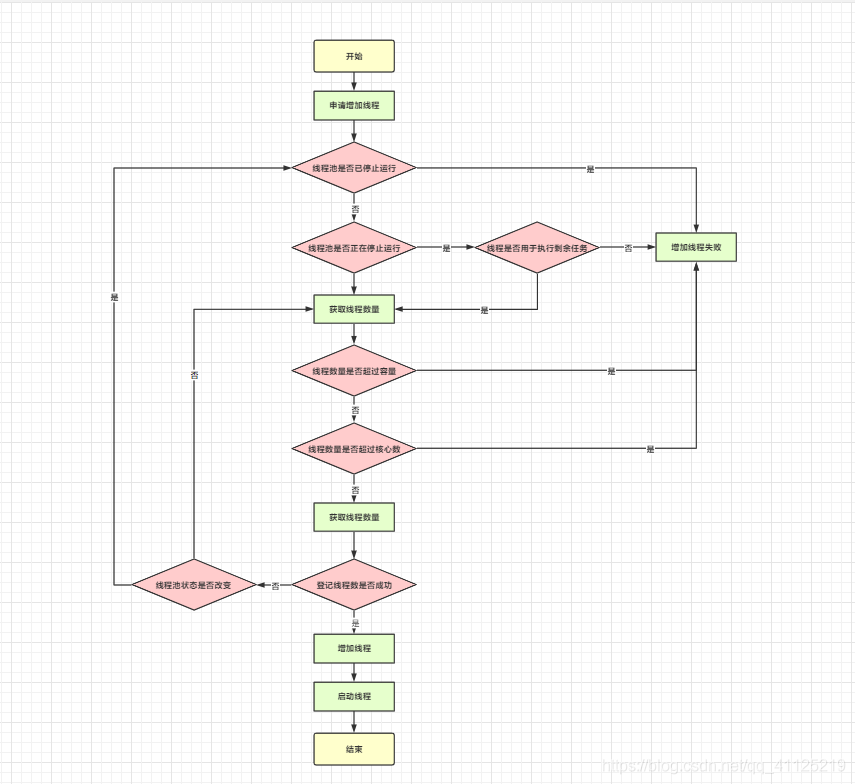
2.4.2 worker線程增加
private boolean addWorker(Runnable firstTask, boolean core) {
retry:
for (;;) {
int c = ctl.get();
int rs = runStateOf(c);
// 判斷線程是否已經(jīng)停止
// 判斷線程是否正在停止 如果是則判斷線程是否用于執(zhí)行剩余任務(wù)firstTask
// workQueue是否為空
if (rs >= SHUTDOWN &&
! (rs == SHUTDOWN &&
firstTask == null &&
! workQueue.isEmpty()))
return false;
for (;;) {
// 獲取線程數(shù)量
int wc = workerCountOf(c);
// 判斷線程是否超過(guò)容量
// 判斷線程是否超過(guò)對(duì)應(yīng)核心數(shù) 上面講了core 傳true/false區(qū)別
if (wc >= CAPACITY ||
wc >= (core ? corePoolSize : maximumPoolSize))
return false;
if (compareAndIncrementWorkerCount(c))
break retry;
c = ctl.get(); // Re-read ctl
if (runStateOf(c) != rs)
continue retry;
// else CAS failed due to workerCount change; retry inner loop
}
}
// 嘗試登記線程
boolean workerStarted = false;
boolean workerAdded = false;
Worker w = null;
try {
w = new Worker(firstTask);
final Thread t = w.thread;
if (t != null) {
// 加鎖
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
// Recheck while holding lock.
// Back out on ThreadFactory failure or if
// shut down before lock acquired.
int rs = runStateOf(ctl.get());
// 判斷線程池狀態(tài)是否改變
if (rs < SHUTDOWN ||
(rs == SHUTDOWN && firstTask == null)) {
if (t.isAlive()) // precheck that t is startable
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
// 增加線程
workers.add(w);
int s = workers.size();
if (s > largestPoolSize)
largestPoolSize = s;
workerAdded = true;
}
} finally {
// 釋放鎖
mainLock.unlock();
}
// 增加成功啟動(dòng)線程
if (workerAdded) {
t.start();
workerStarted = true;
}
}
} finally {
if (! workerStarted)
addWorkerFailed(w);
}
return workerStarted;
}
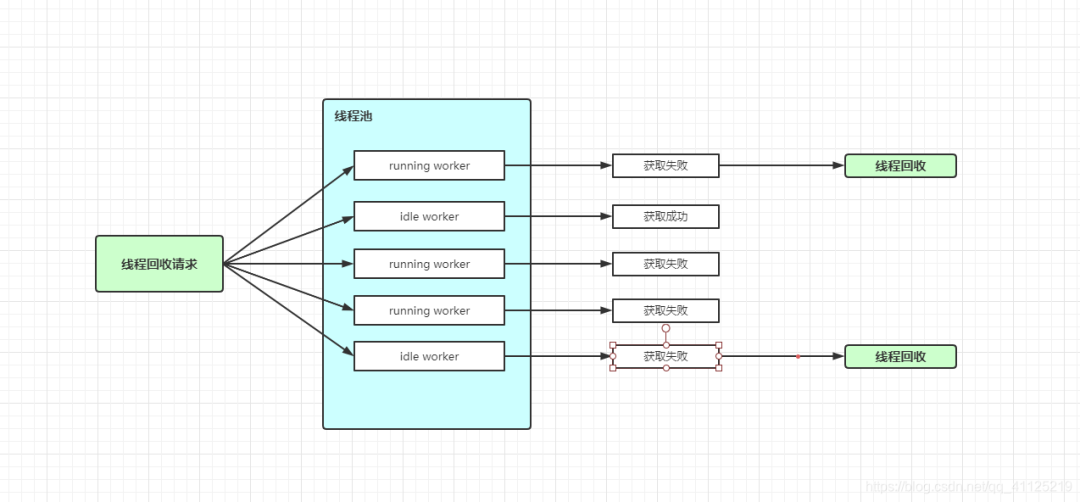
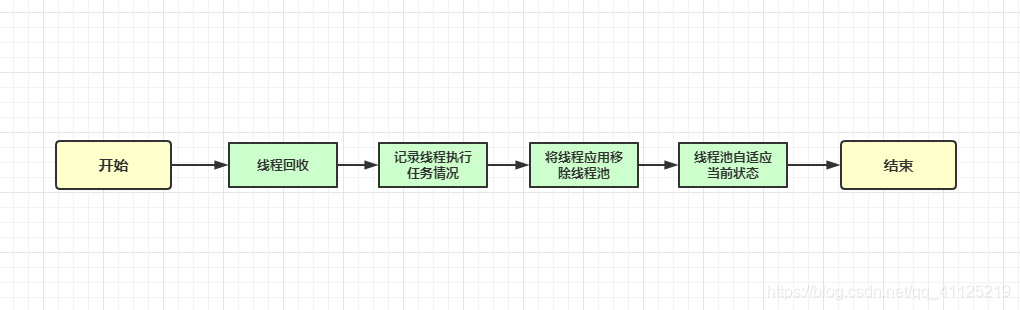
2.4.3 worker線程回收
final void runWorker(Worker w) {
Thread wt = Thread.currentThread();
Runnable task = w.firstTask;
w.firstTask = null;
w.unlock(); // allow interrupts
boolean completedAbruptly = true;
try {
while (task != null || (task = getTask()) != null) {
// 執(zhí)行任務(wù)
} finally {
// 獲取不到任務(wù),主動(dòng)回收自己
processWorkerExit(w, completedAbruptly);
}
}
private void processWorkerExit(Worker w, boolean completedAbruptly) {
if (completedAbruptly) // If abrupt, then workerCount wasn't adjusted
decrementWorkerCount();
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
completedTaskCount += w.completedTasks;
// 回收
workers.remove(w);
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
...
}
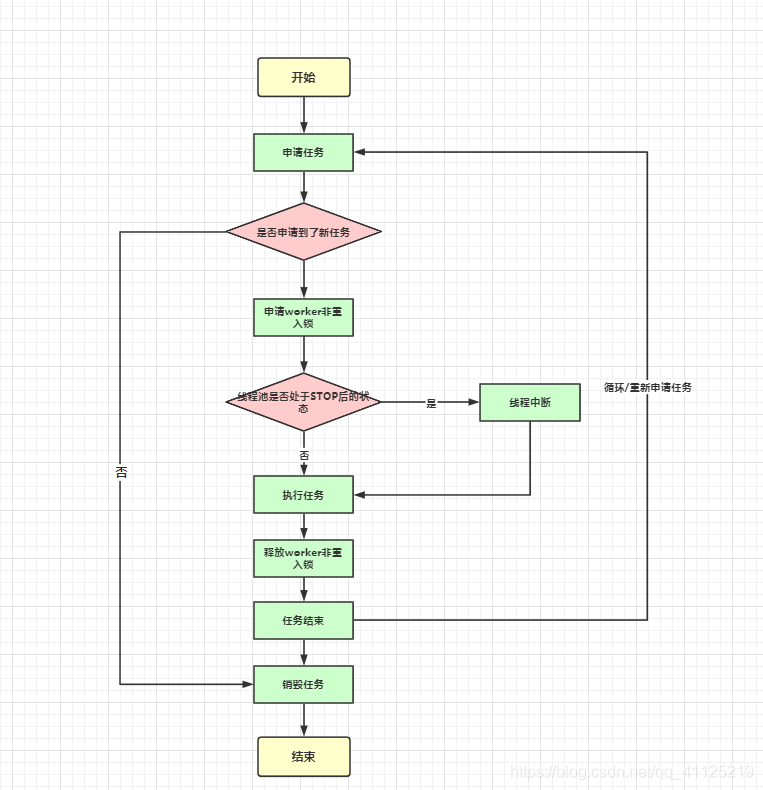
2.4.4 worker線程執(zhí)行任務(wù)
2.4.5 worker如何保證核心線程不被回收
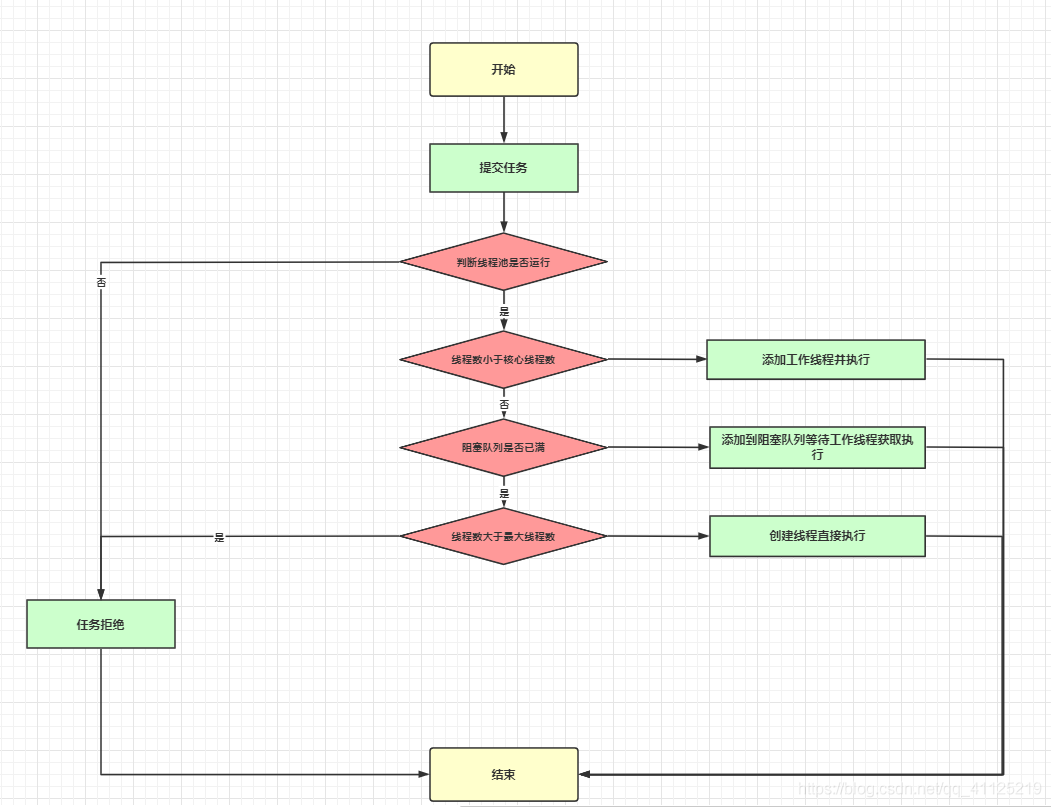
public void execute(Runnable command) {
// 提交任務(wù)為null 拋出異常
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
// 獲取線程池狀態(tài)\線程池線程數(shù)據(jù)
int c = ctl.get();
// 小于核心線程數(shù) addWorker()
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) {
if (addWorker(command, true))
return;
c = ctl.get();
}
// 大于核心線程數(shù),當(dāng)前線程池是運(yùn)行狀態(tài),向阻塞隊(duì)列中添加任務(wù)
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
int recheck = ctl.get();
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
reject(command);
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
// 隊(duì)列添加失敗 拒絕策略處理
else if (!addWorker(command, false))
reject(command);
}
private boolean addWorker(Runnable firstTask, boolean core) {
retry:
// 死循環(huán)
for (;;) {
int c = ctl.get();
int rs = runStateOf(c);
// 如果當(dāng)前線程狀態(tài)是SHUTDOWN STOP TIDYING TERMINATED 并且SHUTDOWN狀態(tài)時(shí)任務(wù)隊(duì)列為空 返回false
// Check if queue empty only if necessary.
if (rs >= SHUTDOWN &&
! (rs == SHUTDOWN &&
firstTask == null &&
! workQueue.isEmpty()))
return false;
// 死循環(huán)
for (;;) {
int wc = workerCountOf(c);
// core參數(shù) true corePoolSize核心線程數(shù) false maximumPoolSize最大線程數(shù)
// CAPACITY integer最大值 (1 << COUNT_BITS) - 1;
if (wc >= CAPACITY ||
wc >= (core ? corePoolSize : maximumPoolSize))
return false;
// 如果增加任務(wù)成功,退出該循環(huán)執(zhí)行下面代碼,否則繼續(xù)
if (compareAndIncrementWorkerCount(c))
break retry;
c = ctl.get(); // Re-read ctl
if (runStateOf(c) != rs)
continue retry;
// else CAS failed due to workerCount change; retry inner loop
}
}
boolean workerStarted = false;
boolean workerAdded = false;
Worker w = null;
try {
// 重點(diǎn)代碼 后續(xù)分析
w = new Worker(firstTask);
final Thread t = w.thread;
if (t != null) {
// 內(nèi)置鎖 加鎖
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
// Recheck while holding lock.
// Back out on ThreadFactory failure or if
// shut down before lock acquired.
int rs = runStateOf(ctl.get());
// 判斷線程池狀態(tài),防止使用過(guò)程中線程池被關(guān)閉
if (rs < SHUTDOWN ||
(rs == SHUTDOWN && firstTask == null)) {
if (t.isAlive()) // precheck that t is startable
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
// 向正在被執(zhí)行的任務(wù)隊(duì)列workers中添加worker
// 注意區(qū)分
// HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<Worker>() 線程池中線程
// private final BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue 等待被執(zhí)行的任務(wù)
workers.add(w);
int s = workers.size();
// 記錄任務(wù)最大數(shù)
if (s > largestPoolSize)
largestPoolSize = s;
// 添加任務(wù)成功
workerAdded = true;
}
} finally {
// 釋放鎖
mainLock.unlock();
}
// 添加任務(wù)成功,那么開(kāi)始執(zhí)行任務(wù)
if (workerAdded) {
// 重點(diǎn)代碼 -- 我們需要查看worker中的run()
t.start();
workerStarted = true;
}
}
} finally {
if (! workerStarted)
addWorkerFailed(w);
}
return workerStarted;
}
/** Delegates main run loop to outer runWorker */
public void run() {
runWorker(this);
}
final void runWorker(Worker w) {
Thread wt = Thread.currentThread();
// 獲取worker對(duì)象中的任務(wù) 可以為null
Runnable task = w.firstTask;
w.firstTask = null;
w.unlock(); // allow interrupts
boolean completedAbruptly = true;
try {
// 死循環(huán)
// 判斷任務(wù)是否為空,如果為空則getTask()獲取任務(wù)
while (task != null || (task = getTask()) != null) {
w.lock();
// If pool is stopping, ensure thread is interrupted;
// if not, ensure thread is not interrupted. This
// requires a recheck in second case to deal with
// shutdownNow race while clearing interrupt
if ((runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP) ||
(Thread.interrupted() &&
runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP))) &&
!wt.isInterrupted())
wt.interrupt();
try {
// 任務(wù)執(zhí)行前調(diào)用
beforeExecute(wt, task);
Throwable thrown = null;
try {
task.run();
} catch (RuntimeException x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Error x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Throwable x) {
thrown = x; throw new Error(x);
} finally {
// 任務(wù)執(zhí)行后調(diào)用
afterExecute(task, thrown);
}
} finally {
// 重點(diǎn)代碼,執(zhí)行完任務(wù)將task設(shè)置為null 則會(huì)從getTask()重新獲取
task = null;
w.completedTasks++;
w.unlock();
}
}
completedAbruptly = false;
} finally {
// 回收worker
processWorkerExit(w, completedAbruptly);
}
}
private Runnable getTask() {
boolean timedOut = false; // Did the last poll() time out?
// 死循環(huán)
for (;;) {
int c = ctl.get();
int rs = runStateOf(c);
// 判斷線程池狀態(tài)
// Check if queue empty only if necessary.
if (rs >= SHUTDOWN && (rs >= STOP || workQueue.isEmpty())) {
decrementWorkerCount();
return null;
}
// 統(tǒng)計(jì)worker
int wc = workerCountOf(c);
// 如果設(shè)置了allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true) 或者當(dāng)前運(yùn)行的統(tǒng)計(jì)worker數(shù)大于設(shè)置的核心線程數(shù),那么timed =true
// Are workers subject to culling?
boolean timed = allowCoreThreadTimeOut || wc > corePoolSize;
if ((wc > maximumPoolSize || (timed && timedOut))
&& (wc > 1 || workQueue.isEmpty())) {
if (compareAndDecrementWorkerCount(c))
return null;
continue;
}
// 核心代碼
try {
// 看完這里就明白了
// 阻塞隊(duì)列獲取
// workQueue.poll() 規(guī)定時(shí)間獲取任務(wù)
// workQueue.take() 會(huì)一直等待,知道阻塞隊(duì)列中任務(wù)不為空
Runnable r = timed ?
workQueue.poll(keepAliveTime, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS) :
workQueue.take();
// 獲取任務(wù)返回
if (r != null)
return r;
timedOut = true;
} catch (InterruptedException retry) {
timedOut = false;
}
}
}
版權(quán)聲明:本文為博主原創(chuàng)文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版權(quán)協(xié)議,轉(zhuǎn)載請(qǐng)附上原文出處鏈接和本聲明。
本文鏈接:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41125219/article/details/117535516


評(píng)論
圖片
表情