Rocketmq源碼分析07:broker 消息投遞流程
注:本系列源碼分析基于RocketMq 4.8.0,gitee倉庫鏈接:https://gitee.com/funcy/rocketmq.git.
RocketMq消息處理整個流程如下:
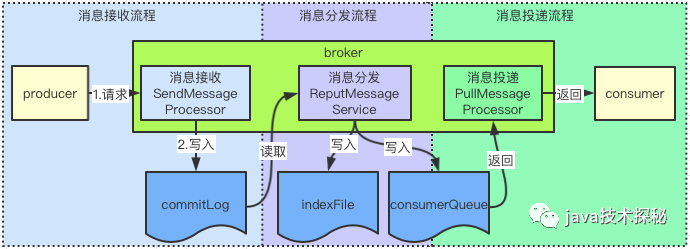
消息接收:消息接收是指接收 producer的消息,處理類是SendMessageProcessor,將消息寫入到commigLog文件后,接收流程處理完畢;消息分發(fā): broker處理消息分發(fā)的類是ReputMessageService,它會啟動一個線程,不斷地將commitLong分到到對應的consumerQueue,這一步操作會寫兩個文件:consumerQueue與indexFile,寫入后,消息分發(fā)流程處理 完畢;消息投遞:消息投遞是指將消息發(fā)往 consumer的流程,consumer會發(fā)起獲取消息的請求,broker收到請求后,調用PullMessageProcessor類處理,從consumerQueue文件獲取消息,返回給consumer后,投遞流程處理完畢。
以上就是rocketMq處理消息的流程了,接下來我們就從源碼來分析消息投遞的實現(xiàn)。
1. 處理PULL_MESSAGE請求
與producer不同,consumer從broker拉取消息時,發(fā)送的請求code為PULL_MESSAGE,processor為PullMessageProcessor,我們直接進入它的processRequest方法:
@Override
public RemotingCommand processRequest(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand request)
throws RemotingCommandException {
// 調用方法
return this.processRequest(ctx.channel(), request, true);
}
這個方法就只是調用了一個重載方法,多出來的參數true表示允許broker掛起請求,我們繼續(xù),
/**
* 繼續(xù)處理
*/
private RemotingCommand processRequest(final Channel channel, RemotingCommand request,
boolean brokerAllowSuspend)throws RemotingCommandException {
RemotingCommand response = RemotingCommand
.createResponseCommand(PullMessageResponseHeader.class);
final PullMessageResponseHeader responseHeader
= (PullMessageResponseHeader) response.readCustomHeader();
final PullMessageRequestHeader requestHeader = (PullMessageRequestHeader)
request.decodeCommandCustomHeader(PullMessageRequestHeader.class);
response.setOpaque(request.getOpaque());
// 省略權限校驗流程
// 1. rocketMq 可以設置校驗信息,以阻擋非法客戶端的連接
// 2. 同時,對topic可以設置DENY(拒絕)、ANY(PUB 或者 SUB 權限)、PUB(發(fā)送權限)、SUB(訂閱權限)等權限,
// 可以細粒度控制客戶端對topic的操作內容
...
// 獲取訂閱組
SubscriptionGroupConfig subscriptionGroupConfig =
this.brokerController.getSubscriptionGroupManager()
.findSubscriptionGroupConfig(requestHeader.getConsumerGroup());
...
// 獲取訂閱主題
TopicConfig topicConfig = this.brokerController.getTopicConfigManager()
.selectTopicConfig(requestHeader.getTopic());
...
// 處理filter
// consumer在訂閱消息時,可以對訂閱的消息進行過濾,過濾方法有兩種:tag與sql92
// 這里我們重點關注拉取消息的流程,具體的過濾細節(jié)后面再分析
...
// 獲取消息
// 1. 根據 topic 與 queueId 獲取 ConsumerQueue 文件
// 2. 根據 ConsumerQueue 文件的信息,從 CommitLog 中獲取消息內容
final GetMessageResult getMessageResult = this.brokerController.getMessageStore().getMessage(
requestHeader.getConsumerGroup(), requestHeader.getTopic(), requestHeader.getQueueId(),
requestHeader.getQueueOffset(), requestHeader.getMaxMsgNums(), messageFilter);
if (getMessageResult != null) {
// 省略一大堆的校驗過程
...
switch (response.getCode()) {
// 表示消息可以處理,這里會把消息內容寫入到 response 中
case ResponseCode.SUCCESS:
...
// 處理消息消息內容,就是把消息從 getMessageResult 讀出來,放到 response 中
if (this.brokerController.getBrokerConfig().isTransferMsgByHeap()) {
final long beginTimeMills = this.brokerController.getMessageStore().now();
// 將消息內容轉為byte數組
final byte[] r = this.readGetMessageResult(getMessageResult,
requestHeader.getConsumerGroup(), requestHeader.getTopic(),
requestHeader.getQueueId());
...
response.setBody(r);
} else {
try {
// 消息轉換
FileRegion fileRegion = new ManyMessageTransfer(response.encodeHeader(
getMessageResult.getBufferTotalSize()), getMessageResult);
channel.writeAndFlush(fileRegion).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
...
});
} catch (Throwable e) {
...
}
response = null;
}
break;
// 未找到滿足條件的消息
case ResponseCode.PULL_NOT_FOUND:
// 如果支持掛起,就掛起當前請求
if (brokerAllowSuspend && hasSuspendFlag) {
...
PullRequest pullRequest = new PullRequest(request, channel, pollingTimeMills,
this.brokerController.getMessageStore().now(), offset, subscriptionData,
messageFilter);
// 沒有找到相關的消息,掛起操作
this.brokerController.getPullRequestHoldService()
.suspendPullRequest(topic, queueId, pullRequest);
response = null;
break;
}
// 省略其他類型的處理
...
break;
default:
assert false;
}
} else {
response.setCode(ResponseCode.SYSTEM_ERROR);
response.setRemark("store getMessage return null");
}
...
return response;
}
在源碼中,這個方法也是非常長,這里我抹去了各種細枝末節(jié),僅留下了一些重要的流程,整個處理流程如下:
權限校驗: rocketMq可以設置校驗信息,以阻擋非法客戶端的連接,同時也可以設置客戶端的發(fā)布、訂閱權限,細節(jié)度控制訪問權限;獲取訂閱組、訂閱主題等,這塊主要是通過請求消息里的內容獲取 broker中對應的記錄創(chuàng)建過濾組件: consumer在訂閱消息時,可以對訂閱的消息進行過濾,過濾方法有兩種:tag與sql92獲取消息:先是根據 topic與queueId獲取ConsumerQueue文件,根據ConsumerQueue文件的信息,從CommitLog中獲取消息內容,消息的過濾操作也是發(fā)生在這一步轉換消息:如果獲得了消息,就是把具體的消息內容,復制到 reponse中掛起請求:如果沒獲得消息,而當前請求又支持掛起,就掛起當前請求
以上代碼還是比較清晰的,相關流程代碼中都作了注釋。
以上流程就是整個消息的獲取流程了,在本文中,我們僅關注與獲取消息相關的步驟,重點關注以下兩個操作:
獲取消息 掛起請求
2. 獲取消息
獲取消息的方法為DefaultMessageStore#getMessage,代碼如下:
public GetMessageResult getMessage(final String group, final String topic, final int queueId,
final long offset, final int maxMsgNums, final MessageFilter messageFilter) {
// 省略一些判斷
...
// 根據topic與queueId一個ConsumeQueue,consumeQueue記錄的是消息在commitLog的位置
ConsumeQueue consumeQueue = findConsumeQueue(topic, queueId);
if (consumeQueue != null) {
minOffset = consumeQueue.getMinOffsetInQueue();
maxOffset = consumeQueue.getMaxOffsetInQueue();
if (...) {
// 判斷 offset 是否符合要求
...
} else {
// 從 consumerQueue 文件中獲取消息
SelectMappedBufferResult bufferConsumeQueue = consumeQueue.getIndexBuffer(offset);
if (bufferConsumeQueue != null) {
...
for (; i < bufferConsumeQueue.getSize() && i < maxFilterMessageCount;
i += ConsumeQueue.CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE) {
// 省略一大堆的消息過濾操作
...
// 從 commitLong 獲取消息
SelectMappedBufferResult selectResult
= this.commitLog.getMessage(offsetPy, sizePy);
if (null == selectResult) {
if (getResult.getBufferTotalSize() == 0) {
status = GetMessageStatus.MESSAGE_WAS_REMOVING;
}
nextPhyFileStartOffset = this.commitLog.rollNextFile(offsetPy);
continue;
}
// 省略一大堆的消息過濾操作
...
}
}
} else {
status = GetMessageStatus.NO_MATCHED_LOGIC_QUEUE;
nextBeginOffset = nextOffsetCorrection(offset, 0);
}
if (GetMessageStatus.FOUND == status) {
this.storeStatsService.getGetMessageTimesTotalFound().incrementAndGet();
} else {
this.storeStatsService.getGetMessageTimesTotalMiss().incrementAndGet();
}
long elapsedTime = this.getSystemClock().now() - beginTime;
this.storeStatsService.setGetMessageEntireTimeMax(elapsedTime);
getResult.setStatus(status);
// 又是處理 offset
getResult.setNextBeginOffset(nextBeginOffset);
getResult.setMaxOffset(maxOffset);
getResult.setMinOffset(minOffset);
return getResult;
}
這個方法不是比較長的,這里僅保留了關鍵流程,獲取消息的關鍵流程如下:
根據 topic與queueId找到ConsumerQueue從 ConsumerQueue對應的文件中獲取消息信息,如tag的hashCode、消息在commitLog中的位置信息根據位置信息,從 commitLog中獲取完整的消息
經過以上步驟,消息就能獲取到了,不過在獲取消息的前后,會進行消息過濾操作,即根據tag或sql語法來過濾消息,關于消息過濾的一些細節(jié),我們留到后面消息過濾相關章節(jié)作進一步分析。
3. 掛起請求:PullRequestHoldService#suspendPullRequest
當broker無新消息時,consumer拉取消息的請求就會掛起,方法為PullRequestHoldService#suspendPullRequest:
public class PullRequestHoldService extends ServiceThread {
private ConcurrentMap<String/* topic@queueId */, ManyPullRequest> pullRequestTable =
new ConcurrentHashMap<String, ManyPullRequest>(1024);
public void suspendPullRequest(final String topic, final int queueId,
final PullRequest pullRequest) {
String key = this.buildKey(topic, queueId);
ManyPullRequest mpr = this.pullRequestTable.get(key);
if (null == mpr) {
mpr = new ManyPullRequest();
ManyPullRequest prev = this.pullRequestTable.putIfAbsent(key, mpr);
if (prev != null) {
mpr = prev;
}
}
mpr.addPullRequest(pullRequest);
}
...
}
在suspendPullRequest方法中,所做的工作僅是把當前請求放入pullRequestTable中了。從代碼中可以看到,pullRequestTable是一個ConcurrentMap,key 是 topic@queueId,value 就是掛起的請求了。
請求掛起后,何時處理呢?這就是PullRequestHoldService線程的工作了。
3.1 處理掛起請求的線程:PullRequestHoldService
看完PullRequestHoldService#suspendPullRequest方法后,我們再來看看PullRequestHoldService。
PullRequestHoldService是ServiceThread的子類(上一次看到ServiceThread的子類還是ReputMessageService),它也會啟動一個新線程來處理掛起操作。
我們先來看看它是在哪里啟動PullRequestHoldService的線程的,在BrokerController的啟動方法start()中有這么一行:
BrokerController#start
public void start() throws Exception {
...
if (this.pullRequestHoldService != null) {
this.pullRequestHoldService.start();
}
...
}
這里就是啟動pullRequestHoldService的線程操作了。
為了探究這個線程做了什么,我們進入PullRequestHoldService#run方法:
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("{} service started", this.getServiceName());
while (!this.isStopped()) {
try {
// 等待中
if (this.brokerController.getBrokerConfig().isLongPollingEnable()) {
this.waitForRunning(5 * 1000);
} else {
this.waitForRunning(
this.brokerController.getBrokerConfig().getShortPollingTimeMills());
}
long beginLockTimestamp = this.systemClock.now();
// 檢查操作
this.checkHoldRequest();
long costTime = this.systemClock.now() - beginLockTimestamp;
if (costTime > 5 * 1000) {
log.info("[NOTIFYME] check hold request cost {} ms.", costTime);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);
}
}
log.info("{} service end", this.getServiceName());
}
從代碼來看,這個線程先是進行等待,然后調用PullRequestHoldService#checkHoldRequest方法,看來關注就是這個方法了,它的代碼如下:
private void checkHoldRequest() {
for (String key : this.pullRequestTable.keySet()) {
String[] kArray = key.split(TOPIC_QUEUEID_SEPARATOR);
if (2 == kArray.length) {
String topic = kArray[0];
int queueId = Integer.parseInt(kArray[1]);
final long offset = this.brokerController.getMessageStore()
.getMaxOffsetInQueue(topic, queueId);
try {
// 調用notifyMessageArriving方法操作
this.notifyMessageArriving(topic, queueId, offset);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error(...);
}
}
}
}
這個方法調用了PullRequestHoldService#notifyMessageArriving(...),我們繼續(xù)進入:
public void notifyMessageArriving(final String topic, final int queueId, final long maxOffset) {
// 繼續(xù)調用
notifyMessageArriving(topic, queueId, maxOffset, null, 0, null, null);
}
/**
* 這個方法就是最終調用的了
*/
public void notifyMessageArriving(final String topic, final int queueId, final long maxOffset,
final Long tagsCode, long msgStoreTime, byte[] filterBitMap, Map<String, String> properties) {
String key = this.buildKey(topic, queueId);
ManyPullRequest mpr = this.pullRequestTable.get(key);
if (mpr != null) {
List<PullRequest> requestList = mpr.cloneListAndClear();
if (requestList != null) {
List<PullRequest> replayList = new ArrayList<PullRequest>();
for (PullRequest request : requestList) {
// 判斷是否有新消息到達,要根據 comsumerQueue 的偏移量與request的偏移量判斷
long newestOffset = maxOffset;
if (newestOffset <= request.getPullFromThisOffset()) {
newestOffset = this.brokerController.getMessageStore()
.getMaxOffsetInQueue(topic, queueId);
}
if (newestOffset > request.getPullFromThisOffset()) {
boolean match = request.getMessageFilter().isMatchedByConsumeQueue(tagsCode,
new ConsumeQueueExt.CqExtUnit(tagsCode, msgStoreTime, filterBitMap));
if (match && properties != null) {
match = request.getMessageFilter().isMatchedByCommitLog(null, properties);
}
if (match) {
try {
// 喚醒操作
this.brokerController.getPullMessageProcessor()
.executeRequestWhenWakeup(request.getClientChannel(),
request.getRequestCommand());
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("execute request when wakeup failed.", e);
}
continue;
}
}
// 超時時間到了
if (System.currentTimeMillis() >=
(request.getSuspendTimestamp() + request.getTimeoutMillis())) {
try {
// 喚醒操作
this.brokerController.getPullMessageProcessor()
.executeRequestWhenWakeup(request.getClientChannel(),
request.getRequestCommand());
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("execute request when wakeup failed.", e);
}
continue;
}
replayList.add(request);
}
if (!replayList.isEmpty()) {
mpr.addPullRequest(replayList);
}
}
}
}
這個方法就是用來檢查是否有新消息送達的操作了,方法雖然有點長,但可以用一句話來總結:如果有新消息送達,或者pullRquest hold住的時間到了,就喚醒pullRquest(即調用PullMessageProcessor#executeRequestWhenWakeup方法)。
在判斷是否有新消息送達時,會獲取 comsumerQueue文件中的最大偏移量,與當前pullRquest中的偏移量進行比較,如果前者大,就表示有新消息送達了,需要喚醒pullRquest前面說過,當 consumer請求沒獲取到消息時,broker會hold這個請求一段時間(30s),當這個時間到了,也會喚醒pullRquest,之后就不會再hold住它了
3.2 喚醒請求:PullMessageProcessor#executeRequestWhenWakeup
我們再來看看 PullMessageProcessor#executeRequestWhenWakeup 方法:
public void executeRequestWhenWakeup(final Channel channel,
final RemotingCommand request) throws RemotingCommandException {
// 關注 Runnable#run() 方法即可
Runnable run = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 再一次調用 PullMessageProcessor#processRequest(...) 方法
final RemotingCommand response = PullMessageProcessor.this
.processRequest(channel, request, false);
...
} catch (RemotingCommandException e1) {
log.error("excuteRequestWhenWakeup run", e1);
}
}
};
// 提交任務
this.brokerController.getPullMessageExecutor()
.submit(new RequestTask(run, channel, request));
}
這個方法準備了一個任務,然后將其提交到線程池中執(zhí)行,任務內容很簡單,僅是調用了PullMessageProcessor#processRequest(...) 方法,這個方法就是本節(jié)一始提到的處理consumer拉取消息的方法了。
3.3 消息分發(fā)中喚醒consumer請求
在分析消息分發(fā)流程時,DefaultMessageStore.ReputMessageService#doReput方法中有這么一段:
private void doReput() {
...
// 分發(fā)消息
DefaultMessageStore.this.doDispatch(dispatchRequest);
// 長輪詢:如果有消息到了主節(jié)點,并且開啟了長輪詢
if (BrokerRole.SLAVE != DefaultMessageStore.this
.getMessageStoreConfig().getBrokerRole()
&&DefaultMessageStore.this.brokerConfig.isLongPollingEnable()){
// 調用NotifyMessageArrivingListener的arriving方法
DefaultMessageStore.this.messageArrivingListener.arriving(
dispatchRequest.getTopic(),
dispatchRequest.getQueueId(),
dispatchRequest.getConsumeQueueOffset() + 1,
dispatchRequest.getTagsCode(),
dispatchRequest.getStoreTimestamp(),
dispatchRequest.getBitMap(),
dispatchRequest.getPropertiesMap());
}
...
}
這段就是用來主動喚醒hold住的consumer請求的,我們進入NotifyMessageArrivingListener#arriving方法:
@Override
public void arriving(String topic, int queueId, long logicOffset, long tagsCode,
long msgStoreTime, byte[] filterBitMap, Map<String, String> properties) {
this.pullRequestHoldService.notifyMessageArriving(topic, queueId, logicOffset, tagsCode,
msgStoreTime, filterBitMap, properties);
}
最終它也是調用了 PullRequestHoldService#notifyMessageArriving(...) 方法。
4. 總結
本文主要分析了broker處理PULL_MESSAGE請求的流程,總結如下:
broker處理PULL_MESSAGE的processor為PullMessageProcessor,PullMessageProcessor的processRequest(...)就是整個消息獲取流程了broker在獲取消息時,先根據請求的topic與queueId找到consumerQueue,然后根據請求中的offset參數從consumerQueue文件中找到消息在commitLog的位置信息,最后根據位置信息從commitLog中獲取消息內容如果 broker中沒有當前consumerQueue的消息,broker會掛起當前線程,直到超時(默認30s)或收到新的消息時再喚醒
限于作者個人水平,文中難免有錯誤之處,歡迎指正!原創(chuàng)不易,商業(yè)轉載請聯(lián)系作者獲得授權,非商業(yè)轉載請注明出處。
本文首發(fā)于微信公眾號 Java技術探秘,如果您喜歡本文,歡迎關注該公眾號,讓我們一起在技術的世界里探秘吧!
