Rocketmq源碼分析09:producer 消息發(fā)送流程
注:本系列源碼分析基于RocketMq 4.8.0,gitee倉庫鏈接:https://gitee.com/funcy/rocketmq.git.
接上文,我們繼續(xù)分析producer消息發(fā)送流程。
3. DefaultMQProducer#send(...):發(fā)送消息
接下來我們來看看producer發(fā)送消息的流程,進(jìn)入方法DefaultMQProducer#send(...):
public SendResult send(
Message msg) throws MQClientException, RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException {
Validators.checkMessage(msg, this);
msg.setTopic(withNamespace(msg.getTopic()));
// 調(diào)用 defaultMQProducerImpl 方法
return this.defaultMQProducerImpl.send(msg);
}
調(diào)用的是DefaultMQProducerImpl#send(...)方法,繼續(xù):
public SendResult send(Message msg) throws MQClientException, RemotingException,
MQBrokerException, InterruptedException {
return send(msg, this.defaultMQProducer.getSendMsgTimeout());
}
public SendResult send(Message msg, long timeout) throws MQClientException,
RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException {
// 默認(rèn)使用異步方法發(fā)送
return this.sendDefaultImpl(msg, CommunicationMode.SYNC, null, timeout);
}
最終來到了DefaultMQProducerImpl#sendDefaultImpl方法:
private SendResult sendDefaultImpl(
Message msg,
final CommunicationMode communicationMode,
final SendCallback sendCallback,
final long timeout
) throws MQClientException, RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException {
...
// 1. 找到了一個(gè)topic
TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo = this.tryToFindTopicPublishInfo(msg.getTopic());
if (topicPublishInfo != null && topicPublishInfo.ok()) {
...
// 2. 重試次數(shù),同步發(fā)送時(shí)才會重試
int timesTotal = communicationMode == CommunicationMode.SYNC
? 1 + this.defaultMQProducer.getRetryTimesWhenSendFailed() : 1;
int times = 0;
String[] brokersSent = new String[timesTotal];
for (; times < timesTotal; times++) {
String lastBrokerName = null == mq ? null : mq.getBrokerName();
// 3. 找到一個(gè)消息隊(duì)列
MessageQueue mqSelected
= this.selectOneMessageQueue(topicPublishInfo, lastBrokerName);
if (mqSelected != null) {
...
try {
// 4. 發(fā)送
sendResult = this.sendKernelImpl(msg, mq, communicationMode,
sendCallback, topicPublishInfo, timeout - costTime);
...
} catch (...) {
// 省略異常處理
...
}
} else {
break;
}
}
...
throw mqClientException;
}
validateNameServerSetting();
throw new MQClientException(...);
}
以上方法就是發(fā)送消息的方法,該方法還是非常長,不過關(guān)鍵點(diǎn)就3個(gè):
根據(jù) topic找到對應(yīng)的發(fā)布信息獲取重試次數(shù),同步發(fā)送時(shí)才會重試 選擇一個(gè)要發(fā)送的消息隊(duì)列 發(fā)送消息
接下來我們就來分析這幾個(gè)步驟。
3.1 根據(jù)topic找到對應(yīng)的發(fā)布信息
獲取topic發(fā)布信息的方法為DefaultMQProducerImpl#tryToFindTopicPublishInfo:
/**
* 根據(jù)topic獲取發(fā)布信息
* 如果topic信息不存在,就先從`nameServer`獲取topic信息
* @param topic
* @return
*/
private TopicPublishInfo tryToFindTopicPublishInfo(final String topic) {
TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo = this.topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic);
if (null == topicPublishInfo || !topicPublishInfo.ok()) {
this.topicPublishInfoTable.putIfAbsent(topic, new TopicPublishInfo());
// 更新 topicRouteInfo
this.mQClientFactory.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(topic);
topicPublishInfo = this.topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic);
}
if (topicPublishInfo.isHaveTopicRouterInfo() || topicPublishInfo.ok()) {
return topicPublishInfo;
} else {
this.mQClientFactory.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(
topic, true, this.defaultMQProducer);
topicPublishInfo = this.topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic);
return topicPublishInfo;
}
}
這里主要是調(diào)用了MQClientInstance#updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer方法來更新topic的訂閱信息,更新時(shí)會向broker發(fā)送一條code為GET_ROUTEINFO_BY_TOPIC的請求(方法為MQClientAPIImpl#getTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer),具體內(nèi)容就不展開了.
3.2 獲取重試次數(shù)
在使用同步模式發(fā)送消息時(shí),當(dāng)消息發(fā)送失敗時(shí),rocketmq會有重試機(jī)制,發(fā)送前會獲取重試次數(shù):
int timesTotal = communicationMode == CommunicationMode.SYNC
? 1 + this.defaultMQProducer.getRetryTimesWhenSendFailed() : 1;
這是一個(gè)三目運(yùn)算符,一開始便會判斷是否為同步模式,如果是同步模式,發(fā)送次數(shù)就為this.defaultMQProducer.getRetryTimesWhenSendFailed()+1,其中1為真正要發(fā)送的次數(shù),retryTimesWhenSendFailed為失敗時(shí)重試的次數(shù),在值在DefaultMQProducer#retryTimesWhenSendFailed中維護(hù),默認(rèn)為2,也就是說,一條消息最多發(fā)送3次。
3.3 找到一個(gè)消息隊(duì)列:
在發(fā)送消息前,需要找到一個(gè)消息送達(dá)的隊(duì)列,方法為DefaultMQProducerImpl#selectOneMessageQueue:
public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue(final TopicPublishInfo tpInfo,
final String lastBrokerName) {
return this.mqFaultStrategy.selectOneMessageQueue(tpInfo, lastBrokerName);
}
繼續(xù)跟進(jìn),來到 MQFaultStrategy#selectOneMessageQueue:
public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue(final TopicPublishInfo tpInfo,
final String lastBrokerName) {
if (this.sendLatencyFaultEnable) {
try {
// 當(dāng)前topic發(fā)送的消息次數(shù)
int index = tpInfo.getSendWhichQueue().getAndIncrement();
// 獲取一個(gè)可用的broker
for (int i = 0; i < tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().size(); i++) {
// 取模運(yùn)算
int pos = Math.abs(index++) % tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().size();
if (pos < 0)
pos = 0;
MessageQueue mq = tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().get(pos);
// 如果mq所在broker可用,直接返回
if (latencyFaultTolerance.isAvailable(mq.getBrokerName()))
return mq;
}
// 經(jīng)過上面的步驟還沒找到 broker,從不可用的broker中獲取一條記錄,獲取時(shí)同樣使用取模處理
final String notBestBroker = latencyFaultTolerance.pickOneAtLeast();
int writeQueueNums = tpInfo.getQueueIdByBroker(notBestBroker);
if (writeQueueNums > 0) {
final MessageQueue mq = tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue();
if (notBestBroker != null) {
mq.setBrokerName(notBestBroker);
mq.setQueueId(tpInfo.getSendWhichQueue().getAndIncrement() % writeQueueNums);
}
return mq;
} else {
latencyFaultTolerance.remove(notBestBroker);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Error occurred when selecting message queue", e);
}
return tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue();
}
// 獲取一條消息隊(duì)列
return tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue(lastBrokerName);
}
以上方法就是獲取消息隊(duì)列的所有內(nèi)容了,主要分為兩大塊:
如果啟用了發(fā)送到最近故障 MessageQueue的功能,獲取到MessageQueue后,會判斷該MessageQueue所在的broker是否可用,不可用時(shí)會再次獲取如果以上操作獲取失敗,或未啟用發(fā)送到最近故障 MessageQueue的功能,獲取到MessageQueue后就直接返回
獲取MessageQueue時(shí),最核心的操作為%(取模):
// 當(dāng)前topic發(fā)送的消息次數(shù)
int index = tpInfo.getSendWhichQueue().getAndIncrement();
...
// 取模運(yùn)算,得到MessageQueue的下標(biāo)
int pos = Math.abs(index++) % tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().size();
if (pos < 0)
pos = 0;
// 根據(jù)下標(biāo)索引得到 MessageQueue
MessageQueue mq = tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().get(pos);
根據(jù)取模運(yùn)算的規(guī)律,如果所有的MessageQueue所在的broker都無故障,則消息會均勻分布在各個(gè)隊(duì)列上。
3.4 發(fā)送消息
消息的發(fā)送方法為 DefaultMQProducerImpl#sendKernelImpl,代碼如下:
private SendResult sendKernelImpl(final Message msg,
final MessageQueue mq,
final CommunicationMode communicationMode,
final SendCallback sendCallback,
final TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo,
final long timeout) throws MQClientException, RemotingException,
MQBrokerException, InterruptedException {
long beginStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 根據(jù) broker 名稱獲取 broker 地址
String brokerAddr = this.mQClientFactory.findBrokerAddressInPublish(mq.getBrokerName());
if (null == brokerAddr) {
// 如果找不到 broker 的地址,就再一次從 nameServer 獲取主題發(fā)布信息
tryToFindTopicPublishInfo(mq.getTopic());
brokerAddr = this.mQClientFactory.findBrokerAddressInPublish(mq.getBrokerName());
}
SendMessageContext context = null;
if (brokerAddr != null) {
brokerAddr = MixAll.brokerVIPChannel(
this.defaultMQProducer.isSendMessageWithVIPChannel(), brokerAddr);
// 消息內(nèi)容
byte[] prevBody = msg.getBody();
try {
...
int sysFlag = 0;
boolean msgBodyCompressed = false;
// 數(shù)據(jù)壓縮
if (this.tryToCompressMessage(msg)) {
sysFlag |= MessageSysFlag.COMPRESSED_FLAG;
msgBodyCompressed = true;
}
...
// 構(gòu)建 RequestHeader
SendMessageRequestHeader requestHeader = new SendMessageRequestHeader();
// 省略好多的set操作
...
SendResult sendResult = null;
switch (communicationMode) {
case ASYNC:
...
// 發(fā)送消息
sendResult = this.mQClientFactory.getMQClientAPIImpl().sendMessage(
// 省略一大堆的參數(shù)
...
);
break;
case ONEWAY:
case SYNC:
long costTimeSync = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime;
if (timeout < costTimeSync) {
throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException("...");
}
sendResult = this.mQClientFactory.getMQClientAPIImpl().sendMessage(
// 省略一大堆的參數(shù)
...
);
break;
default:
assert false;
break;
}
...
} catch (...) {
...
} finally {
msg.setBody(prevBody);
msg.setTopic(NamespaceUtil.withoutNamespace(
msg.getTopic(), this.defaultMQProducer.getNamespace()));
}
}
throw new MQClientException(...);
}
這個(gè)方法中主要是組裝參數(shù),然后調(diào)用this.mQClientFactory.getMQClientAPIImpl().sendMessage(...)方法處理消息發(fā)送,發(fā)送消息時(shí),還區(qū)分了消息模式:ASYNC、ONEWAY、SYNC,不過不管哪種模式,最終調(diào)用的方法都是MQClientAPIImpl#sendMessage(...)方法:
public SendResult sendMessage(
final String addr,
final String brokerName,
final Message msg,
final SendMessageRequestHeader requestHeader,
final long timeoutMillis,
final CommunicationMode communicationMode,
final SendCallback sendCallback,
final TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo,
final MQClientInstance instance,
final int retryTimesWhenSendFailed,
final SendMessageContext context,
final DefaultMQProducerImpl producer
) throws RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException {
long beginStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
RemotingCommand request = null;
String msgType = msg.getProperty(MessageConst.PROPERTY_MESSAGE_TYPE);
boolean isReply = msgType != null && msgType.equals(MixAll.REPLY_MESSAGE_FLAG);
// 構(gòu)造request命令
if (isReply) {
if (sendSmartMsg) {
SendMessageRequestHeaderV2 requestHeaderV2 =
SendMessageRequestHeaderV2.createSendMessageRequestHeaderV2(requestHeader);
request = RemotingCommand.createRequestCommand(
RequestCode.SEND_REPLY_MESSAGE_V2, requestHeaderV2);
} else {
request = RemotingCommand.createRequestCommand(
RequestCode.SEND_REPLY_MESSAGE, requestHeader);
}
} else {
if (sendSmartMsg || msg instanceof MessageBatch) {
SendMessageRequestHeaderV2 requestHeaderV2
= SendMessageRequestHeaderV2.createSendMessageRequestHeaderV2(requestHeader);
request = RemotingCommand.createRequestCommand(msg instanceof MessageBatch
? RequestCode.SEND_BATCH_MESSAGE : RequestCode.SEND_MESSAGE_V2, requestHeaderV2);
} else {
request = RemotingCommand
.createRequestCommand(RequestCode.SEND_MESSAGE, requestHeader);
}
}
request.setBody(msg.getBody());
// 調(diào)用發(fā)送方法
switch (communicationMode) {
case ONEWAY:
this.remotingClient.invokeOneway(addr, request, timeoutMillis);
return null;
case ASYNC:
...
this.sendMessageAsync(addr, brokerName, msg, timeoutMillis - costTimeAsync,
request, sendCallback, topicPublishInfo, instance,
retryTimesWhenSendFailed, times, context, producer);
return null;
case SYNC:
...
return this.sendMessageSync(addr, brokerName, msg,
timeoutMillis - costTimeSync, request);
default:
assert false;
break;
}
return null;
}
可以看到,在這個(gè)方法里,先是指定了請求的code,然后分別處理了ASYNC、ONEWAY、SYNC三種類型的消息發(fā)送。
4. 消息的發(fā)送模式
在消息的發(fā)送過程中,我們發(fā)現(xiàn)消息發(fā)送有如下三種模式:
SYNC:同步模式,消息發(fā)送完成后會返回發(fā)送的結(jié)果ASYNC:異步模式,不會返回發(fā)送結(jié)果,不過可以注意監(jiān)聽器監(jiān)聽消息發(fā)送結(jié)果ONEWAY:只發(fā)送一次,不管結(jié)果還是失敗
下面我們分別來看看這三種消息是如何發(fā)送的。
4.1 同步模式
同步模式的發(fā)送示例如下:
public static void main(String[] args) throws MQClientException, InterruptedException {
String nameServer = "localhost:9876";
DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer("ProducerGroupName");
producer.setNamesrvAddr(nameServer);
producer.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1; i++)
try {
Message msg = new Message("TopicTest",
"TagA",
"OrderID188",
"Hello world".getBytes(RemotingHelper.DEFAULT_CHARSET));
// 同步發(fā)送,等待發(fā)送完成并返回結(jié)果
SendResult sendResult = producer.send(msg);
System.out.printf("%s%n", sendResult);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
producer.shutdown();
}
這種模式下,發(fā)送完成后,會返回發(fā)送結(jié)果,當(dāng)結(jié)果為失敗時(shí),我們可以對其進(jìn)行額外的處理。
另外,在同步模式下,如果消息發(fā)送失敗了,rocketMq會自動重試(默認(rèn)重試2次)。
處理同步發(fā)送的方法為NettyRemotingAbstract#invokeSyncImpl:
public RemotingCommand invokeSyncImpl(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request,
final long timeoutMillis) throws InterruptedException, RemotingSendRequestException,
RemotingTimeoutException {
final int opaque = request.getOpaque();
try {
final ResponseFuture responseFuture = new ResponseFuture(
channel, opaque, timeoutMillis, null, null);
this.responseTable.put(opaque, responseFuture);
final SocketAddress addr = channel.remoteAddress();
// 發(fā)送請求
channel.writeAndFlush(request)
// 監(jiān)聽結(jié)果
.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
if (f.isSuccess()) {
responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(true);
return;
} else {
responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(false);
}
responseTable.remove(opaque);
responseFuture.setCause(f.cause());
responseFuture.putResponse(null);
log.warn("send a request command to channel <" + addr + "> failed.");
}
});
// 等待返回結(jié)果
RemotingCommand responseCommand = responseFuture.waitResponse(timeoutMillis);
if (null == responseCommand) {
if (responseFuture.isSendRequestOK()) {
throw new RemotingTimeoutException(RemotingHelper.parseSocketAddressAddr(addr),
timeoutMillis, responseFuture.getCause());
} else {
throw new RemotingSendRequestException(
RemotingHelper.parseSocketAddressAddr(addr), responseFuture.getCause());
}
}
return responseCommand;
} finally {
this.responseTable.remove(opaque);
}
}
可以看到,在底層處理消息的發(fā)送時(shí),netty使用的是異步監(jiān)聽的模式獲得返回結(jié)果,而所謂的同步模式,就是人為地等待netty完成請求與響應(yīng)操作,得到結(jié)果。
4.2 異步模式
異步模式的發(fā)送示例如下:
public static void main(String[] args) throws MQClientException,
InterruptedException, UnsupportedEncodingException {
String nameServer = "localhost:9876";
DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer("Jodie_Daily_test");
producer.setNamesrvAddr(nameServer);
producer.start();
producer.setRetryTimesWhenSendAsyncFailed(0);
int messageCount = 100;
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(messageCount);
for (int i = 0; i < messageCount; i++) {
try {
final int index = i;
Message msg = new Message("Jodie_topic_1023",
"TagA",
"OrderID188",
"Hello world".getBytes(RemotingHelper.DEFAULT_CHARSET));
// 發(fā)送,異步發(fā)送的精髓在于 SendCallback
producer.send(msg, new SendCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(SendResult sendResult) {
countDownLatch.countDown();
System.out.printf("%-10d OK %s %n", index, sendResult.getMsgId());
}
@Override
public void onException(Throwable e) {
countDownLatch.countDown();
System.out.printf("%-10d Exception %s %n", index, e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
countDownLatch.await(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
producer.shutdown();
}
與同步模式相比,該模式下,發(fā)送方法不會返回發(fā)送結(jié)果,不過發(fā)送方法的參數(shù)多了一個(gè)SendCallback,當(dāng)我們想要監(jiān)聽消息的發(fā)送結(jié)果時(shí),可以重寫該類的onSuccess(...)與onException(...)方法,從而達(dá)到監(jiān)聽發(fā)送結(jié)果的目的。
在該模式下,如果消息發(fā)送失敗了,我們可以重寫SendCallback#onException方法,在其中定制失敗處理的邏輯。
處理異步發(fā)送的方法為NettyRemotingAbstract#invokeAsyncImpl:
public void invokeAsyncImpl(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request,
final long timeoutMillis, final InvokeCallback invokeCallback)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingTooMuchRequestException,
RemotingTimeoutException, RemotingSendRequestException {
long beginStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
final int opaque = request.getOpaque();
// 獲取鎖
boolean acquired = this.semaphoreAsync.tryAcquire(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (acquired) {
final SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce once = new SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce(this.semaphoreAsync);
long costTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime;
if (timeoutMillis < costTime) {
once.release();
throw new RemotingTimeoutException("invokeAsyncImpl call timeout");
}
final ResponseFuture responseFuture = new ResponseFuture(channel, opaque,
timeoutMillis - costTime, invokeCallback, once);
// 添加responseTable中
this.responseTable.put(opaque, responseFuture);
try {
// netty的異步操作
channel.writeAndFlush(request)
// 監(jiān)聽結(jié)果
.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
// 處理完成的操作
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
if (f.isSuccess()) {
responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(true);
return;
}
// 處理失敗
requestFail(opaque);
log.warn(...);
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
} else {
...
}
}
從以上方法可以看到,在監(jiān)聽執(zhí)行結(jié)果的邏輯中,如果成功,就調(diào)用responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(true),然后返回;如果失敗了,就調(diào)用requestFail,這些操作是怎么與SendCallback關(guān)聯(lián)起來的呢?我們接下來就好好分析一番。
在調(diào)用writeAndFlush(...)方法前,會先this.responseTable.put(opaque, responseFuture)方法,將responseFuture添加到responseTable中,這是個(gè)Map結(jié)構(gòu),rocketMq正是定時(shí)從responseTable中獲取responseFuture并判斷其狀態(tài)來決定調(diào)用SendCallback的哪個(gè)方法的。
讓我們回到NettyRemotingClient的啟動流程,方法為NettyRemotingClient#start:
public void start() {
...
// 掃描消息獲取結(jié)果,每秒執(zhí)行1次
this.timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
NettyRemotingClient.this.scanResponseTable();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("scanResponseTable exception", e);
}
}
}, 1000 * 3, 1000);
...
}
在這個(gè)方法中,啟動了一個(gè)定時(shí)任務(wù),每秒執(zhí)行1次,所做的工作就是掃描在responseTable中的responseFuture,我們再進(jìn)入NettyRemotingAbstract#scanResponseTable方法:
public void scanResponseTable() {
//本次要處理的返回
final List<ResponseFuture> rfList = new LinkedList<ResponseFuture>();
Iterator<Entry<Integer, ResponseFuture>> it = this.responseTable.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry<Integer, ResponseFuture> next = it.next();
ResponseFuture rep = next.getValue();
// 判斷時(shí)間,時(shí)間到了才轉(zhuǎn)移到 rfList 中
if ((rep.getBeginTimestamp() + rep.getTimeoutMillis() + 1000)
<= System.currentTimeMillis()) {
rep.release();
it.remove();
rfList.add(rep);
log.warn("remove timeout request, " + rep);
}
}
// 處理返回
for (ResponseFuture rf : rfList) {
try {
executeInvokeCallback(rf);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.warn("scanResponseTable, operationComplete Exception", e);
}
}
}
在這個(gè)方法里,先遍歷所有的ResponseFuture,然后判斷每個(gè)ResponseFuture的時(shí)間,時(shí)間到了才會進(jìn)行處理,從這里可以看出,并不是一有結(jié)果就立即處理,而是在消息發(fā)送后過了4秒(rep.getTimeoutMillis()的值為3)才去處理結(jié)果,處理方法為NettyRemotingAbstract#executeInvokeCallback,我們繼續(xù)跟進(jìn)去:
private void executeInvokeCallback(final ResponseFuture responseFuture) {
boolean runInThisThread = false;
// 如果有線程池,就提交到線程池中執(zhí)行
ExecutorService executor = this.getCallbackExecutor();
if (executor != null) {
try {
executor.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 這是是具體操作
responseFuture.executeInvokeCallback();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.warn(...);
} finally {
responseFuture.release();
}
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
runInThisThread = true;
log.warn(...);
}
} else {
runInThisThread = true;
}
if (runInThisThread) {
try {
// 直接執(zhí)行
responseFuture.executeInvokeCallback();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.warn("executeInvokeCallback Exception", e);
} finally {
responseFuture.release();
}
}
}
這個(gè)方法沒做啥事,只是判斷要不要在線程池中執(zhí)行操作,之后就調(diào)用了 ResponseFuture#executeInvokeCallback方法:
public void executeInvokeCallback() {
if (invokeCallback != null) {
if (this.executeCallbackOnlyOnce.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
// 繼續(xù)處理
invokeCallback.operationComplete(this);
}
}
}
到這個(gè)就是關(guān)鍵了,我們跟進(jìn)invokeCallback.operationComplete(this)方法,發(fā)現(xiàn)來到了MQClientAPIImpl#sendMessageAsync(...)方法:
private void sendMessageAsync(
...
// sendCallback 由參數(shù)傳入
final SendCallback sendCallback,
// 省略其他參數(shù)
...
) throws InterruptedException, RemotingException {
final long beginStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// remotingClient.invokeAsync 最終會調(diào)用到 NettyRemotingAbstract#invokeAsyncImpl
this.remotingClient.invokeAsync(addr, request, timeoutMillis,
// InvokeCallback 參數(shù)
new InvokeCallback() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ResponseFuture responseFuture) {
long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime;
RemotingCommand response = responseFuture.getResponseCommand();
...
if (response != null) {
try {
SendResult sendResult = MQClientAPIImpl.this
.processSendResponse(brokerName, msg, response, addr);
...
try {
// 這里執(zhí)行 sendCallback 的 onSuccess(...) 方法
sendCallback.onSuccess(sendResult);
} catch (Throwable e) {
}
} catch (Exception e) {
onExceptionImpl(brokerName, msg, timeoutMillis - cost, request,
sendCallback, topicPublishInfo, instance,
retryTimesWhenSendFailed, times, e, context, false, producer);
}
} else {
// 處理各異常
...
// 調(diào)用異常處理方法
onExceptionImpl(brokerName, msg, timeoutMillis - cost, request,
sendCallback, topicPublishInfo, instance,
retryTimesWhenSendFailed, times, ex, context, true, producer);
...
}
}
});
}
這個(gè)方法主要調(diào)用了remotingClient.invokeAsync()方法,而remotingClient.invokeAsync()最終會調(diào)用到 NettyRemotingAbstract#invokeAsyncImpl,也就是uemd提到的最終使用異常發(fā)送的netty方法。
remotingClient.invokeAsync()方法共有3個(gè)參數(shù),這里我們只關(guān)注最后一個(gè)參數(shù):InvokeCallback,該參數(shù)的operationComplete(...)方法中,就是處理操作完成的邏輯了,這里我們重點(diǎn)關(guān)注兩個(gè)操作就可以了:
sendCallback.onSuccess(sendResult):響應(yīng)成功時(shí)調(diào)用,執(zhí)行的就是sendCallback的onSuccess(...)方法,sendCallback由參數(shù)傳入onExceptionImpl(...):方法,出現(xiàn)異常時(shí)調(diào)用
我們繼續(xù)進(jìn)入MQClientAPIImpl#onExceptionImpl方法:
private void onExceptionImpl(final String brokerName,
...
// sendCallback 由方法參數(shù)傳入
final SendCallback sendCallback,
...
) {
int tmp = curTimes.incrementAndGet();
// 處理重試操作
if (needRetry && tmp <= timesTotal) {
...
} else {
...
try {
// 執(zhí)行 sendCallback的onException(..,) 方法
sendCallback.onException(e);
} catch (Exception ignored) {
}
}
}
可以看到,sendCallback的onException(..,) 方法就是在這里調(diào)用的。
在這個(gè)方法里,也會對消息進(jìn)行重試操作,這個(gè)重試次數(shù)是在DefaultMQProducerImpl#sendKernelImpl中傳入的:
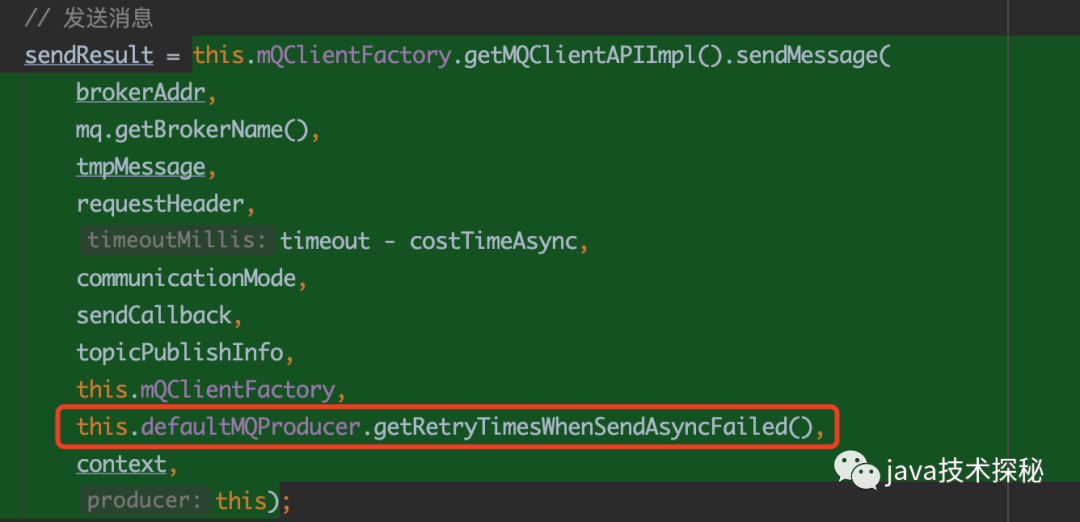
4.3 oneway 模式
該模式的使用示例如下:
public static void main(String[] args) throws MQClientException, InterruptedException {
String nameServer = "localhost:9876";
DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer("ProducerGroupName");
producer.setNamesrvAddr(nameServer);
producer.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1; i++)
try {
Message msg = new Message("TopicTest",
"TagA",
"OrderID188",
"Hello world".getBytes(RemotingHelper.DEFAULT_CHARSET));
// oneway模式,發(fā)送方法沒有返回值
producer.sendOneway(msg);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
producer.shutdown();
}
不同于前面兩種模式,該模式下,消息只會發(fā)送一次,且不會返回任何結(jié)果,也無監(jiān)聽參數(shù)可以監(jiān)聽消息結(jié)果,總之,該模式下,消息只發(fā)送一次且不管結(jié)果。
處理該模式的方法為 NettyRemotingAbstract#invokeOnewayImpl:
public void invokeOnewayImpl(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request,
final long timeoutMillis) throws InterruptedException, RemotingTooMuchRequestException,
RemotingTimeoutException, RemotingSendRequestException {
request.markOnewayRPC();
boolean acquired = this.semaphoreOneway.tryAcquire(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (acquired) {
final SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce once = new SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce(this.semaphoreOneway);
try {
channel.writeAndFlush(request)
// 監(jiān)聽結(jié)果,操作完成,僅打印了一條日志
.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
once.release();
if (!f.isSuccess()) {
log.warn(...);
}
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
} else {
...
}
}
在這個(gè)方法中可以看到,消息發(fā)送結(jié)果的監(jiān)聽邏輯中,當(dāng)消息發(fā)送失敗了,僅僅只是打了一條warn級別的日志。
5. 總結(jié)
本文主要是梳理了producer啟動及發(fā)送消息的流程,這里我們來做一個(gè)總結(jié)。
rocketMq在啟動時(shí),啟動所做的工作如下:
裝配了netty客戶端相關(guān)配置 啟動定時(shí)任務(wù),如獲取 nameserver地址,定時(shí)更新topic的路由信息,定時(shí)發(fā)送心跳信息
發(fā)送消息時(shí),rocketmq主要支持三種發(fā)放方式:同步(sync),異步(async)及單向(oneway)
同步:消息發(fā)放后,線程會阻塞,直到返回結(jié)果 異步:在發(fā)送消息時(shí),可以設(shè)置消息發(fā)送結(jié)果的監(jiān)聽,消息發(fā)送后,線程不會阻塞,消息發(fā)送完成后,發(fā)送結(jié)果會被監(jiān)聽到 單向:消息發(fā)送完成后,線程不會阻塞,不會有結(jié)果返回,也無法設(shè)置發(fā)送結(jié)果的監(jiān)聽,即發(fā)送就可以,不關(guān)心發(fā)送結(jié)果,不關(guān)心是否發(fā)送成功
在消息可靠性方面,
同步發(fā)送:消息發(fā)送失敗時(shí),內(nèi)部會重試(默認(rèn)1次發(fā)送+2次失敗重試,共3次),另外,由于發(fā)送完成后可以得到發(fā)送結(jié)果,因此也可對失敗的結(jié)果進(jìn)行自主處理 異步發(fā)送:消息發(fā)送失敗時(shí),同時(shí)有內(nèi)部重試(默認(rèn)1次發(fā)送+2次失敗重試,共3次),另外,發(fā)送消息時(shí)可以設(shè)置消息的監(jiān)聽規(guī)則,當(dāng)發(fā)送失敗時(shí),可以在監(jiān)聽代碼中自主對失敗的消息進(jìn)行處理 單向發(fā)送:該模式下,消息發(fā)送失敗時(shí)無重試(只是打出一條 warn級別的日志),且無發(fā)送結(jié)果返回、無結(jié)果監(jiān)聽
好了,關(guān)于producer就介紹到這里了。
限于作者個(gè)人水平,文中難免有錯(cuò)誤之處,歡迎指正!原創(chuàng)不易,商業(yè)轉(zhuǎn)載請聯(lián)系作者獲得授權(quán),非商業(yè)轉(zhuǎn)載請注明出處。
本文首發(fā)于微信公眾號 「Java技術(shù)探秘」,如果您喜歡本文,歡迎關(guān)注該公眾號,讓我們一起在技術(shù)的世界里探秘吧!
