從 Babel 到 AST 進(jìn)階,學(xué)起來(lái)!
大廠技術(shù) 高級(jí)前端 Node進(jìn)階
點(diǎn)擊上方 程序員成長(zhǎng)指北,關(guān)注公眾號(hào)
回復(fù)1,加入高級(jí)Node交流群
Babel
在我很小的時(shí)候,有人告訴我代碼要寫(xiě)的有藝術(shù)感。我當(dāng)時(shí)內(nèi)心:......真高級(jí)啊,裝起來(lái)了。但是伴隨著時(shí)代的變遷,各種提案的通過(guò),js的寫(xiě)法也逐漸升級(jí),語(yǔ)法糖也多了起來(lái),原來(lái)的三四行代碼,啪嘰,一個(gè)不留神,一行就能搞定,整篇代碼一眼望去,會(huì)讓人覺(jué)得,嗯,有點(diǎn)東西。如下是一個(gè)小小的demo:
const demo = () => [1,2,3].map(e => e + 1)
Babel轉(zhuǎn)換后,這行代碼其實(shí)是這樣子的:
var demo = function demo() {
return [1, 2, 3].map(function (e) {
return e + 1;
});
};
如此,才能做到向下兼容,以便可以運(yùn)行在各種有可能存在的環(huán)境中,所以Babel的主要作用如下:
-
代碼轉(zhuǎn)換 -
通過(guò)Polyfill方式在目標(biāo)環(huán)境中添加缺失的特性(@babel/polyfill)
@babel/polyfill 模塊包括 core-js 和一個(gè)自定義的 regenerator runtime 模塊,可以模擬完整的 ES2015+ 環(huán)境,這意味著可以使用諸如 Promise 和 WeakMap 之類(lèi)的新的內(nèi)置組件、 Array.from 或 Object.assign 之類(lèi)的靜態(tài)方法、Array.prototype.includes 之類(lèi)的實(shí)例方法以及生成器函數(shù)(前提是使用了 @babel/plugin-transform-regenerator 插件)。為了添加這些功能,polyfill 將添加到全局范圍和類(lèi)似 String 這樣的內(nèi)置原型中(會(huì)對(duì)全局環(huán)境造成污染)。其實(shí)在Babel7.4.0以后,@babel/polyfill就已經(jīng)被棄用,在源碼中直接引入了corejs 和 regenerator,而在實(shí)際運(yùn)用中可用@babel/preset-env進(jìn)行替代。
在實(shí)際項(xiàng)目中,Babel可通過(guò)多種方式進(jìn)行配置(詳情可以在下文源碼分析中有所了解),在這里,我們以babel.config.js為實(shí)例:
module.exports = {
presets: [...],
plugins: [...],
}
plugins插件是Babel得以進(jìn)行轉(zhuǎn)換的基礎(chǔ)和規(guī)則,而presets預(yù)設(shè)則是一組插件的集合,具體可以在源碼分析中進(jìn)行了解。 當(dāng)兩個(gè)轉(zhuǎn)換插件都將處理“程序(Program)”的某個(gè)代碼片段,則將根據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)換plugins或 presets的排列順序依次執(zhí)行:
-
插件在 Presets 前運(yùn)行。 -
插件順序從前往后排列。 -
Preset 順序是顛倒的(從后往前(具體原因源碼分析也會(huì)有所解釋))。
而B(niǎo)abel的編譯過(guò)程可以分為三個(gè)階段:
-
解析(Parsing):將代碼字符串解析成抽象語(yǔ)法樹(shù)。 -
轉(zhuǎn)換(Transformation):對(duì)抽象語(yǔ)法樹(shù)進(jìn)行轉(zhuǎn)換操作。 -
生成(Code Generation): 根據(jù)變換后的抽象語(yǔ)法樹(shù)再生成代碼字符串。
而在這個(gè)過(guò)程中,最重要的便是AST,如下。
AST
What is AST
經(jīng)典面試問(wèn)題:Babel的原理是什么? 答:解析-轉(zhuǎn)換-生成。其實(shí)說(shuō)白了就是把代碼通過(guò)某種規(guī)則變成一種特定的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu),然后在這種數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)上做一些增刪改查,然后再把這個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)變回代碼,然后因?yàn)槭恰肚岸恕罚鞣N層級(jí)分明的樹(shù),所以AST就是這么一棵樹(shù)。往深了走就是那門(mén)絕學(xué)--《編譯原理》。
作為一名前端,很難不和AST有接觸,Webpack、Eslint...又或者是底層、優(yōu)化...都和AST有著密不可分的關(guān)系。
AST (abstract syntax tree (抽象語(yǔ)法樹(shù)))作為源代碼語(yǔ)法結(jié)構(gòu)的一種抽象表示。它以樹(shù)狀的形式表現(xiàn)編程語(yǔ)言的語(yǔ)法結(jié)構(gòu),樹(shù)上的每個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)都表示源代碼中的一種結(jié)構(gòu)。
生成AST主要分為兩個(gè)步驟:
詞法分析(lexical analyzer)
對(duì)代碼進(jìn)行拆分,通過(guò)預(yù)先設(shè)定好的規(guī)則遍歷代碼將每個(gè)字符轉(zhuǎn)換為詞法單元(token),從而生成token列表。 將demo代碼轉(zhuǎn)換為token如下:
[
{
"type": "Keyword",
"value": "const"
},
{
"type": "Identifier",
"value": "demo"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": "="
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": "("
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": ")"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": "=>"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": "["
},
{
"type": "Numeric",
"value": "1"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": ","
},
{
"type": "Numeric",
"value": "2"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": ","
},
{
"type": "Numeric",
"value": "3"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": "]"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": "."
},
{
"type": "Identifier",
"value": "map"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": "("
},
{
"type": "Identifier",
"value": "e"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": "=>"
},
{
"type": "Identifier",
"value": "e"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": "+"
},
{
"type": "Numeric",
"value": "1"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": ")"
}
]
語(yǔ)法分析(Syntax analyzer)
在得到token列表之后,通過(guò)語(yǔ)法規(guī)則可以將其關(guān)聯(lián)起來(lái),形成AST,demo代碼所生成的AST樹(shù)如下所示(實(shí)在太長(zhǎng)了,不全放出了):
在線AST轉(zhuǎn)換網(wǎng)站:https://astexplorer.net/[1]
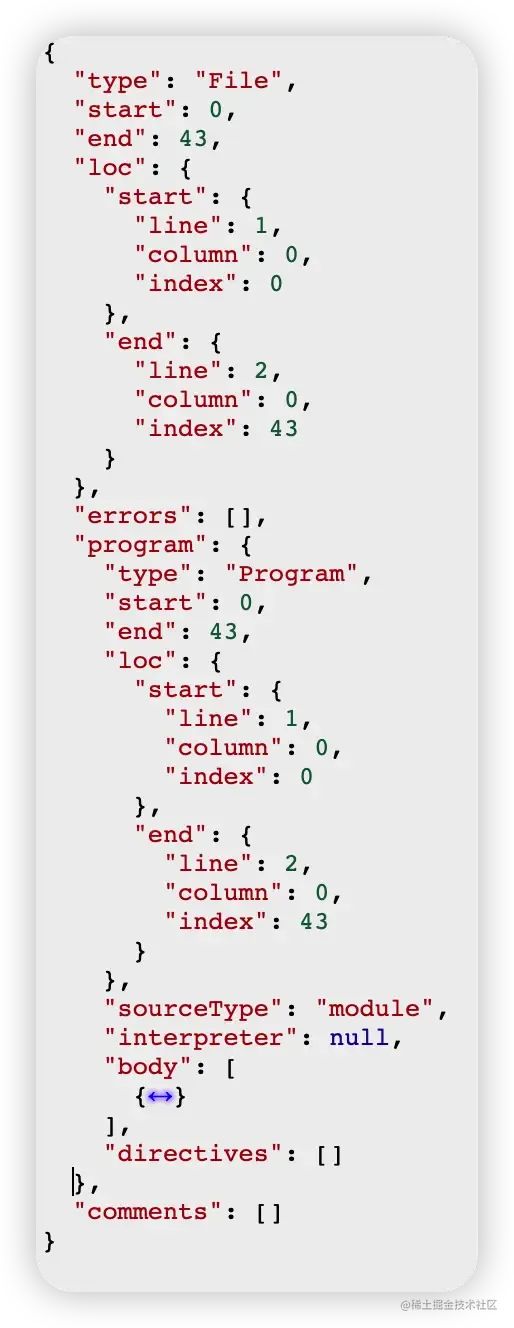

AST with Babel
ok, 我們想通過(guò)Babel做如此一系列操作,去生成AST,去轉(zhuǎn)換AST,然后再變回js,我們以demo為例,通過(guò)調(diào)用Babel所提供的API實(shí)現(xiàn)這一操作:
const transformLetToVar = babel.transformSync(`${beforeFile}`, {
plugins: [
{
visitor: {
// [const, let] 轉(zhuǎn)化為 var
VariableDeclaration(path) {
if (path.node.kind === 'let' || path.node.kind === 'const') {
path.node.kind = 'var';
}
},
// () => {} 轉(zhuǎn)化為 function,注意沒(méi)有{}的情況
ArrowFunctionExpression(path) {
let body = path.node.body;
if (!t.isBlockStatement(body)) {
body = t.blockStatement([t.returnStatement(body)]);
}
path.replaceWith(t.functionExpression(null, path.node.params, body, false, false));
},
// 處理數(shù)組
CallExpression(path) {
if (path.get('callee.property').node.name === 'map') {
const callback = path.node.arguments[0];
if (t.isArrowFunctionExpression(callback)) {
let body = callback.body;
if (!t.isBlockStatement(body)) {
body = t.blockStatement([t.returnStatement(body)]);
}
path.node.arguments[0] = t.functionExpression(
null,
callback.params,
body,
false,
false,
);
}
}
},
},
},
],
});
代碼中采用了@Babel/core中的transformSync方法,它是@Babel/parser / @babel/traverse / @babel/generator的集合,如采用這三種方法,代碼如下:
// Step 1: Parse the code to AST
const ast = parser.parse(code);
// Step 2: Traverse and modify the AST
traverse(ast, {
VariableDeclaration(path) {
if (path.node.kind === 'let' || path.node.kind === 'const') {
path.node.kind = 'var';
}
},
ArrowFunctionExpression(path) {
let body = path.node.body;
if (!t.isBlockStatement(body)) {
body = t.blockStatement([t.returnStatement(body)]);
}
path.replaceWith(t.functionExpression(null, path.node.params, body, false, false));
},
CallExpression(path) {
if (path.get('callee.property').node.name === 'map') {
const callback = path.node.arguments[0];
if (t.isArrowFunctionExpression(callback)) {
let body = callback.body;
if (!t.isBlockStatement(body)) {
body = t.blockStatement([t.returnStatement(body)]);
}
path.node.arguments[0] = t.functionExpression(null, callback.params, body, false, false);
}
}
},
});
// Step 3: Generate new code from the modified AST
const output = generator(ast, {}, code);
@Babel/core 源碼解析
在上文通過(guò)Babel轉(zhuǎn)換時(shí),用到了babel.transformSync,其便是來(lái)自@Babel/core,我們以它為開(kāi)始,進(jìn)行一波較為簡(jiǎn)易的源碼分析。 首先來(lái)到Babel/core/index.js,主要包含一些基本的導(dǎo)入導(dǎo)出,其中有關(guān)babel.transformSync的如下:
export {
transform,
transformSync,
transformAsync,
type FileResult,
} from "./transform";
直接來(lái)到Babel/core/transform:
type Transform = {
(code: string, callback: FileResultCallback): void,
(code: string, opts: InputOptions | undefined | null, callback: FileResultCallback): void,
(code: string, opts?: InputOptions | null): FileResult | null,
};
const transformRunner = gensync(function* transform(
code: string,
opts?: InputOptions,
): Handler<FileResult | null> {
const config: ResolvedConfig | null = yield* loadConfig(opts);
if (config === null) return null;
return yield* run(config, code);
});
export const transform: Transform = function transform(
code,
optsOrCallback?: InputOptions | null | undefined | FileResultCallback,
maybeCallback?: FileResultCallback,
) {
let opts: InputOptions | undefined | null;
let callback: FileResultCallback | undefined;
if (typeof optsOrCallback === 'function') {
callback = optsOrCallback;
opts = undefined;
} else {
opts = optsOrCallback;
callback = maybeCallback;
}
if (callback === undefined) {
if (process.env.BABEL_8_BREAKING) {
throw new Error(
"Starting from Babel 8.0.0, the 'transform' function expects a callback. If you need to call it synchronously, please use 'transformSync'.",
);
} else {
// console.warn(
// "Starting from Babel 8.0.0, the 'transform' function will expect a callback. If you need to call it synchronously, please use 'transformSync'.",
// );
return beginHiddenCallStack(transformRunner.sync)(code, opts);
}
}
beginHiddenCallStack(transformRunner.errback)(code, opts, callback);
};
export function transformSync(...args: Parameters<typeof transformRunner.sync>) {
return beginHiddenCallStack(transformRunner.sync)(...args);
}
export function transformAsync(...args: Parameters<typeof transformRunner.async>) {
return beginHiddenCallStack(transformRunner.async)(...args);
}
我們會(huì)發(fā)現(xiàn)其實(shí)他們都在調(diào)用transformRunner,該方法傳入兩個(gè)參數(shù)code和opts:
const transformRunner = gensync(function* transform(
code: string,
opts?: InputOptions,
): Handler<FileResult | null> {
const config: ResolvedConfig | null = yield* loadConfig(opts);
if (config === null) return null;
return yield* run(config, code);
});
其中InputOptions為:
export type InputOptions = ValidatedOptions;
export type ValidatedOptions = {
cwd?: string,
filename?: string,
filenameRelative?: string,
babelrc?: boolean,
babelrcRoots?: BabelrcSearch,
configFile?: ConfigFileSearch,
root?: string,
rootMode?: RootMode,
code?: boolean,
ast?: boolean,
cloneInputAst?: boolean,
inputSourceMap?: RootInputSourceMapOption,
envName?: string,
caller?: CallerMetadata,
extends?: string,
env?: EnvSet<ValidatedOptions>,
ignore?: IgnoreList,
only?: IgnoreList,
overrides?: OverridesList,
// Generally verify if a given config object should be applied to the given file.
test?: ConfigApplicableTest,
include?: ConfigApplicableTest,
exclude?: ConfigApplicableTest,
presets?: PluginList,
plugins?: PluginList,
passPerPreset?: boolean,
assumptions?: {
[name: string]: boolean,
},
// browserslists-related options
targets?: TargetsListOrObject,
browserslistConfigFile?: ConfigFileSearch,
browserslistEnv?: string,
// Options for @babel/generator
retainLines?: boolean,
comments?: boolean,
shouldPrintComment?: Function,
compact?: CompactOption,
minified?: boolean,
auxiliaryCommentBefore?: string,
auxiliaryCommentAfter?: string,
// Parser
sourceType?: SourceTypeOption,
wrapPluginVisitorMethod?: Function,
highlightCode?: boolean,
// Sourcemap generation options.
sourceMaps?: SourceMapsOption,
sourceMap?: SourceMapsOption,
sourceFileName?: string,
sourceRoot?: string,
// Deprecate top level parserOpts
parserOpts?: ParserOptions,
// Deprecate top level generatorOpts
generatorOpts?: GeneratorOptions,
};
這里面便包含例如plugins和presets這些屬性,其中plugins便是上文我們調(diào)用babel.transformSync時(shí)的第二個(gè)參數(shù),既插件,Babel的插件是實(shí)現(xiàn)代碼轉(zhuǎn)換的基礎(chǔ)單位。每個(gè)插件都是一個(gè)小的 JavaScript 程序,它告訴 Babel 如何進(jìn)行特定的代碼轉(zhuǎn)換。而presets則是一組預(yù)先定義好的插件的集合。因?yàn)?JavaScript 的新特性太多,如果每次都要手動(dòng)指定所有需要的插件,那么配置起來(lái)會(huì)非常繁瑣,因此Babel 提供了預(yù)設(shè),讓我們可以用一行代碼引入一整組插件。
回到transformRunner,該方法主體分為兩步,調(diào)用loadConfig方法和調(diào)用run方法。首先來(lái)看loadConfig,該方法實(shí)為babel-core/src/config/full.ts中的loadFullConfig方法,這個(gè)方法主體就干了三件事,分別是處理配置、處理presets以及處理plugins,源碼如下逐步分解進(jìn)行分析:
export default gensync(function* loadFullConfig(
inputOpts: unknown,
): Handler<ResolvedConfig | null> {
const result = yield* loadPrivatePartialConfig(inputOpts);
if (!result) {
return null;
}
const { options, context, fileHandling } = result;
if (fileHandling === 'ignored') {
return null;
}
const optionDefaults = {};
const { plugins, presets } = options;
if (!plugins || !presets) {
throw new Error('Assertion failure - plugins and presets exist');
}
// 創(chuàng)建presetContext對(duì)象,在原有context基礎(chǔ)上增加options.targets
const presetContext: Context.FullPreset = {
...context,
targets: options.targets,
};
// ...
});
首先調(diào)用loadPrivatePartialConfig,構(gòu)建配置鏈。該方法接收opts,通過(guò)各種驗(yàn)證和轉(zhuǎn)換,最終返回一個(gè)處理后的配置對(duì)象。在這個(gè)過(guò)程中,它還將輸入選項(xiàng)中的一些值轉(zhuǎn)換成絕對(duì)路徑,并創(chuàng)建了一些新的對(duì)象和屬性:
export default function* loadPrivatePartialConfig(
inputOpts: unknown,
): Handler<PrivPartialConfig | null> {
if (inputOpts != null && (typeof inputOpts !== 'object' || Array.isArray(inputOpts))) {
throw new Error('Babel options must be an object, null, or undefined');
}
const args = inputOpts ? validate('arguments', inputOpts) : {};
const {
envName = getEnv(),
cwd = '.',
root: rootDir = '.',
rootMode = 'root',
caller,
cloneInputAst = true,
} = args;
// 將cwd和rootDir轉(zhuǎn)化為絕對(duì)路徑
const absoluteCwd = path.resolve(cwd);
const absoluteRootDir = resolveRootMode(path.resolve(absoluteCwd, rootDir), rootMode);
// 若filename為string,則轉(zhuǎn)換為絕對(duì)路徑
const filename = typeof args.filename === 'string' ? path.resolve(cwd, args.filename) : undefined;
// resolveShowConfigPath方法用于解析文件路徑,若路徑存在并指向一個(gè)文件,則返回該路徑
const showConfigPath = yield* resolveShowConfigPath(absoluteCwd);
// 將轉(zhuǎn)換好的數(shù)據(jù)重新組裝成一個(gè)名為context的對(duì)象
const context: ConfigContext = {
filename,
cwd: absoluteCwd,
root: absoluteRootDir,
envName,
caller,
showConfig: showConfigPath === filename,
};
// 調(diào)用buildRootChain,buildRootChain源碼分解在下方
const configChain = yield* buildRootChain(args, context);
if (!configChain) return null;
const merged: ValidatedOptions = {
assumptions: {},
};
// 遍歷configChain.options,合并到merged
configChain.options.forEach(opts => {
mergeOptions(merged as any, opts);
});
// 定義一個(gè)新的options對(duì)象
const options: NormalizedOptions = {
...merged,
targets: resolveTargets(merged, absoluteRootDir),
// Tack the passes onto the object itself so that, if this object is
// passed back to Babel a second time, it will be in the right structure
// to not change behavior.
cloneInputAst,
babelrc: false,
configFile: false,
browserslistConfigFile: false,
passPerPreset: false,
envName: context.envName,
cwd: context.cwd,
root: context.root,
rootMode: 'root',
filename: typeof context.filename === 'string' ? context.filename : undefined,
plugins: configChain.plugins.map(descriptor => createItemFromDescriptor(descriptor)),
presets: configChain.presets.map(descriptor => createItemFromDescriptor(descriptor)),
};
return {
options,
context,
fileHandling: configChain.fileHandling,
ignore: configChain.ignore,
babelrc: configChain.babelrc,
config: configChain.config,
files: configChain.files,
};
}
buildRootChain方法源碼分解如下,該方法加載了當(dāng)前目錄配置文件和相對(duì)配置文件,并合并成配置鏈:
export function* buildRootChain(
opts: ValidatedOptions,
context: ConfigContext,
): Handler<RootConfigChain | null> {
let configReport, babelRcReport;
const programmaticLogger = new ConfigPrinter();
// 生成programmatic options(編程選項(xiàng)),通過(guò)`@babel/cli`或者`babel.transfrom`的方式使用時(shí)會(huì)用到
const programmaticChain = yield* loadProgrammaticChain(
{
options: opts,
dirname: context.cwd,
},
context,
undefined,
programmaticLogger,
);
if (!programmaticChain) return null;
const programmaticReport = yield* programmaticLogger.output();
let configFile;
// 如果制定了配置文件,則調(diào)用loadConfig方法去加載,若沒(méi)有,則調(diào)用findRootConfig加載根目錄配置
if (typeof opts.configFile === 'string') {
configFile = yield* loadConfig(opts.configFile, context.cwd, context.envName, context.caller);
} else if (opts.configFile !== false) {
configFile = yield* findRootConfig(context.root, context.envName, context.caller);
}
// ...
}
loadConfig和findRootConfi方法如下,其中findRootConfig遍歷ROOT_CONFIG_FILENAMES,逐個(gè)尋找根目錄(當(dāng)前執(zhí)行目錄)配置文件并加載,兩種方法都是調(diào)用readConfig:
export const ROOT_CONFIG_FILENAMES = [
'babel.config.js',
'babel.config.cjs',
'babel.config.mjs',
'babel.config.json',
'babel.config.cts',
];
export function findRootConfig(
dirname: string,
envName: string,
caller: CallerMetadata | undefined,
): Handler<ConfigFile | null> {
// 調(diào)用loadOneConfig, 傳入ROOT_CONFIG_FILENAMES
return loadOneConfig(ROOT_CONFIG_FILENAMES, dirname, envName, caller);
}
function* loadOneConfig(
names: string[],
dirname: string,
envName: string,
caller: CallerMetadata | undefined,
previousConfig: ConfigFile | null = null,
): Handler<ConfigFile | null> {
const configs = yield* gensync.all(
// 遍歷調(diào)用readConfig,所以配置文件加載順序?yàn)?js、.cjs、.mjs、.json以及.cts
names.map(filename => readConfig(path.join(dirname, filename), envName, caller)),
);
// 若存在重復(fù)配置文件則報(bào)錯(cuò)
const config = configs.reduce((previousConfig: ConfigFile | null, config) => {
if (config && previousConfig) {
throw new ConfigError(
`Multiple configuration files found. Please remove one:\n` +
` - ${path.basename(previousConfig.filepath)}\n` +
` - ${config.filepath}\n` +
`from ${dirname}`,
);
}
return config || previousConfig;
}, previousConfig);
if (config) {
debug('Found configuration %o from %o.', config.filepath, dirname);
}
return config;
}
export function* loadConfig(
name: string,
dirname: string,
envName: string,
caller: CallerMetadata | undefined,
): Handler<ConfigFile> {
const filepath = require.resolve(name, { paths: [dirname] });
const conf = yield* readConfig(filepath, envName, caller);
if (!conf) {
throw new ConfigError(`Config file contains no configuration data`, filepath);
}
debug('Loaded config %o from %o.', name, dirname);
return conf;
}
/**
* Read the given config file, returning the result. Returns null if no config was found, but will
* throw if there are parsing errors while loading a config.
*/
function readConfig(
filepath: string,
envName: string,
caller: CallerMetadata | undefined,
): Handler<ConfigFile | null> {
const ext = path.extname(filepath);
// 讀取config內(nèi)容
switch (ext) {
case '.js':
case '.cjs':
case '.mjs':
case '.cts':
return readConfigCode(filepath, { envName, caller });
default:
return readConfigJSON5(filepath);
}
}
然后繼續(xù)分析buildRootChain:
{
// ...
let { babelrc, babelrcRoots } = opts;
let babelrcRootsDirectory = context.cwd;
// 生成一個(gè)空配置鏈,結(jié)構(gòu)如下{options: [],presets: [],plugins: [],files: new Set(),}
const configFileChain = emptyChain();
const configFileLogger = new ConfigPrinter();
// 對(duì)加載的配置文件進(jìn)行處理,并且與configFileChain合并
if (configFile) {
const validatedFile = validateConfigFile(configFile);
const result = yield * loadFileChain(validatedFile, context, undefined, configFileLogger);
if (!result) return null;
configReport = yield * configFileLogger.output();
// Allow config files to toggle `.babelrc` resolution on and off and
// specify where the roots are.
if (babelrc === undefined) {
babelrc = validatedFile.options.babelrc;
}
if (babelrcRoots === undefined) {
babelrcRootsDirectory = validatedFile.dirname;
babelrcRoots = validatedFile.options.babelrcRoots;
}
mergeChain(configFileChain, result);
}
let ignoreFile, babelrcFile;
let isIgnored = false;
const fileChain = emptyChain();
// resolve all .babelrc files
if ((babelrc === true || babelrc === undefined) && typeof context.filename === 'string') {
const pkgData = yield * findPackageData(context.filename);
if (pkgData && babelrcLoadEnabled(context, pkgData, babelrcRoots, babelrcRootsDirectory)) {
// 調(diào)用findRelativeConfig加載相對(duì)配置,相對(duì)位置為從當(dāng)前目錄向上尋找第一個(gè)包含package.json的目錄
// findRelativeConfig源碼分析在下方
({ ignore: ignoreFile, config: babelrcFile } =
yield * findRelativeConfig(pkgData, context.envName, context.caller));
if (ignoreFile) {
fileChain.files.add(ignoreFile.filepath);
}
if (ignoreFile && shouldIgnore(context, ignoreFile.ignore, null, ignoreFile.dirname)) {
isIgnored = true;
}
// 將讀取的相對(duì)配置內(nèi)容轉(zhuǎn)換成配置鏈
if (babelrcFile && !isIgnored) {
const validatedFile = validateBabelrcFile(babelrcFile);
const babelrcLogger = new ConfigPrinter();
const result = yield * loadFileChain(validatedFile, context, undefined, babelrcLogger);
if (!result) {
isIgnored = true;
} else {
babelRcReport = yield * babelrcLogger.output();
mergeChain(fileChain, result);
}
}
if (babelrcFile && isIgnored) {
fileChain.files.add(babelrcFile.filepath);
}
}
}
if (context.showConfig) {
console.log(
`Babel configs on "${context.filename}" (ascending priority):\n` +
// print config by the order of ascending priority
[configReport, babelRcReport, programmaticReport].filter(x => !!x).join('\n\n') +
'\n-----End Babel configs-----',
);
}
// Insert file chain in front so programmatic options have priority
// over configuration file chain items.
// 將得到的配置鏈合并
const chain = mergeChain(
mergeChain(mergeChain(emptyChain(), configFileChain), fileChain),
programmaticChain,
);
return {
plugins: isIgnored ? [] : dedupDescriptors(chain.plugins),
presets: isIgnored ? [] : dedupDescriptors(chain.presets),
options: isIgnored ? [] : chain.options.map(o => normalizeOptions(o)),
fileHandling: isIgnored ? 'ignored' : 'transpile',
ignore: ignoreFile || undefined,
babelrc: babelrcFile || undefined,
config: configFile || undefined,
files: chain.files,
};
}
findRelativeConfig方法依次尋找.babelrc、.babelrc.js、.babelrc.cjs等等,找到一個(gè)加載并停止尋找
js
復(fù)制代碼
const RELATIVE_CONFIG_FILENAMES = [
'.babelrc',
'.babelrc.js',
'.babelrc.cjs',
'.babelrc.mjs',
'.babelrc.json',
'.babelrc.cts',
];
export function* findRelativeConfig(
packageData: FilePackageData,
envName: string,
caller: CallerMetadata | undefined,
): Handler<RelativeConfig> {
let config = null;
let ignore = null;
const dirname = path.dirname(packageData.filepath);
// 調(diào)用loadOneConfig讀取相對(duì)配置
// 第五個(gè)參數(shù)為packageData.pkg?.dirname === loc? packageToBabelConfig(packageData.pkg): null,
// 存在多個(gè)配置文件會(huì)覆蓋,不會(huì)報(bào)錯(cuò)
for (const loc of packageData.directories) {
if (!config) {
config = yield* loadOneConfig(
RELATIVE_CONFIG_FILENAMES,
loc,
envName,
caller,
packageData.pkg?.dirname === loc ? packageToBabelConfig(packageData.pkg) : null,
);
}
// 讀取忽略文件列表
if (!ignore) {
const ignoreLoc = path.join(loc, BABELIGNORE_FILENAME);
ignore = yield* readIgnoreConfig(ignoreLoc);
if (ignore) {
debug('Found ignore %o from %o.', ignore.filepath, dirname);
}
}
}
return { config, ignore };
}
ok,這一串子終于走完了,其實(shí)的配置文件讀取的經(jīng)驗(yàn)非常值得借鑒,回到loadFullConfig:
{
// ...
// 創(chuàng)建一個(gè)toDescriptor方法用于獲取presets和plugin的描述符
const toDescriptor = (item: PluginItem) => {
const desc = getItemDescriptor(item);
if (!desc) {
throw new Error('Assertion failure - must be config item');
}
return desc;
};
// 映射所有presets和plugin以獲取其描述符,并存儲(chǔ)在presetsDescriptors和 initialPluginsDescriptors`中
const presetsDescriptors = presets.map(toDescriptor);
const initialPluginsDescriptors = plugins.map(toDescriptor);
// 初始化一個(gè)空數(shù)組用于存儲(chǔ)描述符
const pluginDescriptorsByPass: Array<Array<UnloadedDescriptor>> = [[]];
// 初始化一個(gè)空數(shù)組用于存儲(chǔ)pass
const passes: Array<Array<Plugin>> = [];
// 初始化一個(gè)空數(shù)組用于存儲(chǔ)外部依賴(lài)
const externalDependencies: DeepArray<string> = [];
// 調(diào)用recursePresetDescriptors處理presets描述符,將presets描述符加載并處理,處理過(guò)程中如果遇到錯(cuò)誤會(huì)拋出
const ignored =
yield *
enhanceError(
context,
function* recursePresetDescriptors(
rawPresets: Array<UnloadedDescriptor>,
pluginDescriptorsPass: Array<UnloadedDescriptor>,
): Handler<true | void> {
// 初始化一個(gè)presets
const presets: Array<{
preset: ConfigChain | null;
pass: Array<UnloadedDescriptor>;
}> = [];
// 遍歷rawPresets
for (let i = 0; i < rawPresets.length; i++) {
const descriptor = rawPresets[i];
if (descriptor.options !== false) {
try {
// eslint-disable-next-line no-var
// 調(diào)用loadPrivatePartialConfig,構(gòu)建preset配置鏈
var preset = yield* loadPresetDescriptor(descriptor, presetContext);
} catch (e) {
if (e.code === 'BABEL_UNKNOWN_OPTION') {
checkNoUnwrappedItemOptionPairs(rawPresets, i, 'preset', e);
}
throw e;
}
externalDependencies.push(preset.externalDependencies);
// Presets normally run in reverse order, but if they
// have their own pass they run after the presets
// in the previous pass.
// descriptor.ownPass為false時(shí),則unshift處理過(guò)后的preset到presets,所以presets在執(zhí)行時(shí)時(shí)倒序的
if (descriptor.ownPass) {
presets.push({ preset: preset.chain, pass: [] });
} else {
presets.unshift({
preset: preset.chain,
pass: pluginDescriptorsPass,
});
}
}
}
// resolve presets
if (presets.length > 0) {
// The passes are created in the same order as the preset list, but are inserted before any
// existing additional passes.
pluginDescriptorsByPass.splice(
1,
0,
...presets.map(o => o.pass).filter(p => p !== pluginDescriptorsPass),
);
for (const { preset, pass } of presets) {
if (!preset) return true;
// 如果preset有自己的pass,則添加到新的pass中
pass.push(...preset.plugins);
// 如果preset有自己的presets,則遞歸調(diào)用
const ignored = yield* recursePresetDescriptors(preset.presets, pass);
if (ignored) return true;
// 將preset的options進(jìn)行合并
preset.options.forEach(opts => {
mergeOptions(optionDefaults, opts);
});
}
}
},
)(presetsDescriptors, pluginDescriptorsByPass[0]);
if (ignored) return null;
const opts: any = optionDefaults;
mergeOptions(opts, options);
const pluginContext: Context.FullPlugin = {
...presetContext,
assumptions: opts.assumptions ?? {},
};
// 加載插件描述符,如果加載過(guò)程中遇到錯(cuò)誤會(huì)拋出
yield *
enhanceError(context, function* loadPluginDescriptors() {
pluginDescriptorsByPass[0].unshift(...initialPluginsDescriptors);
for (const descs of pluginDescriptorsByPass) {
const pass: Plugin[] = [];
// 將處理過(guò)的plugin放入passes,并返回
passes.push(pass);
for (let i = 0; i < descs.length; i++) {
const descriptor: UnloadedDescriptor = descs[i];
if (descriptor.options !== false) {
try {
// eslint-disable-next-line no-var
// 加載插件
var plugin = yield* loadPluginDescriptor(descriptor, pluginContext);
} catch (e) {
if (e.code === 'BABEL_UNKNOWN_PLUGIN_PROPERTY') {
// print special message for `plugins: ["@babel/foo", { foo: "option" }]`
checkNoUnwrappedItemOptionPairs(descs, i, 'plugin', e);
}
throw e;
}
pass.push(plugin);
externalDependencies.push(plugin.externalDependencies);
}
}
}
})();
opts.plugins = passes[0];
opts.presets = passes
.slice(1)
.filter(plugins => plugins.length > 0)
.map(plugins => ({ plugins }));
opts.passPerPreset = opts.presets.length > 0;
return {
options: opts,
passes: passes,
externalDependencies: freezeDeepArray(externalDependencies),
};
}
終于講完了transformRunner方法中的loadConfig調(diào)用,接下來(lái)來(lái)到了至關(guān)重要的run,位于babel-core/src/transformation/index.ts,該方法接收三個(gè)參數(shù),config為上文源碼所處理的配置返回值,code為代碼字符串,ast是一顆可選的AST:
export function* run(
config: ResolvedConfig,
code: string,
ast?: t.File | t.Program | null,
): Handler<FileResult> {
// 調(diào)用normalizeFile函數(shù)標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化文件
const file = yield* normalizeFile(
config.passes,
normalizeOptions(config),
code,
ast,
);
// ...
}
normalizeFile代碼如下,該函數(shù)使用 config.passes(一組插件數(shù)組)、標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化后的配置、源代碼和可選的 ast 作為參數(shù):
export default function* normalizeFile(
pluginPasses: PluginPasses,
options: { [key: string]: any },
code: string,
ast?: t.File | t.Program | null,
): Handler<File> {
code = `${code || ''}`;
// 如果存在ast
if (ast) {
// 對(duì)ast進(jìn)行校驗(yàn),root是否type為Program
if (ast.type === 'Program') {
// 進(jìn)一步校驗(yàn)
ast = file(ast, [], []);
} else if (ast.type !== 'File') {
throw new Error('AST root must be a Program or File node');
}
if (options.cloneInputAst) {
ast = cloneDeep(ast);
}
} else {
// 如果不存在ast,則調(diào)用parser生成
// @ts-expect-error todo: use babel-types ast typings in Babel parser
ast = yield* parser(pluginPasses, options, code);
}
let inputMap = null;
// 判斷如果需要`sourceMap`的話,會(huì)嘗試調(diào)用`convertSourceMap.fromObject`、 `convertSourceMap.fromComment`等生成`inputMap`
if (options.inputSourceMap !== false) {
// If an explicit object is passed in, it overrides the processing of
// source maps that may be in the file itself.
if (typeof options.inputSourceMap === 'object') {
inputMap = convertSourceMap.fromObject(options.inputSourceMap);
}
if (!inputMap) {
const lastComment = extractComments(INLINE_SOURCEMAP_REGEX, ast);
if (lastComment) {
try {
inputMap = convertSourceMap.fromComment(lastComment);
} catch (err) {
debug('discarding unknown inline input sourcemap', err);
}
}
}
if (!inputMap) {
const lastComment = extractComments(EXTERNAL_SOURCEMAP_REGEX, ast);
if (typeof options.filename === 'string' && lastComment) {
try {
// when `lastComment` is non-null, EXTERNAL_SOURCEMAP_REGEX must have matches
const match: [string, string] = EXTERNAL_SOURCEMAP_REGEX.exec(lastComment) as any;
const inputMapContent = fs.readFileSync(
path.resolve(path.dirname(options.filename), match[1]),
'utf8',
);
inputMap = convertSourceMap.fromJSON(inputMapContent);
} catch (err) {
debug('discarding unknown file input sourcemap', err);
}
} else if (lastComment) {
debug('discarding un-loadable file input sourcemap');
}
}
}
// 返回一個(gè)新的File對(duì)象
return new File(options, {
code,
ast: ast as t.File,
inputMap,
});
}
其中parser源碼最終指向babel-core/src/parser/index.ts,如下:
export default function* parser(
pluginPasses: PluginPasses,
{ parserOpts, highlightCode = true, filename = 'unknown' }: any,
code: string,
): Handler<ParseResult> {
try {
const results = [];
// 從pluginPasses雙重遍歷取出plugin,并解構(gòu)出其中的parser轉(zhuǎn)換方法,如果存在該方法,則調(diào)用,并且push到results中
for (const plugins of pluginPasses) {
for (const plugin of plugins) {
const { parserOverride } = plugin;
if (parserOverride) {
const ast = parserOverride(code, parserOpts, parse);
if (ast !== undefined) results.push(ast);
}
}
}
// 如果results為空,則調(diào)用@babel/parser中的parser方法
if (results.length === 0) {
return parse(code, parserOpts);
} else if (results.length === 1) {
// @ts-expect-error - If we want to allow async parsers
yield* [];
if (typeof results[0].then === 'function') {
throw new Error(
`You appear to be using an async parser plugin, ` +
`which your current version of Babel does not support. ` +
`If you're using a published plugin, you may need to upgrade ` +
`your @babel/core version.`,
);
}
return results[0];
}
// TODO: Add an error code
throw new Error('More than one plugin attempted to override parsing.');
} catch (err) {
if (err.code === 'BABEL_PARSER_SOURCETYPE_MODULE_REQUIRED') {
err.message +=
"\nConsider renaming the file to '.mjs', or setting sourceType:module " +
'or sourceType:unambiguous in your Babel config for this file.';
// err.code will be changed to BABEL_PARSE_ERROR later.
}
const { loc, missingPlugin } = err;
if (loc) {
const codeFrame = codeFrameColumns(
code,
{
start: {
line: loc.line,
column: loc.column + 1,
},
},
{
highlightCode,
},
);
if (missingPlugin) {
err.message =
`${filename}: ` + generateMissingPluginMessage(missingPlugin[0], loc, codeFrame);
} else {
err.message = `${filename}: ${err.message}\n\n` + codeFrame;
}
err.code = 'BABEL_PARSE_ERROR';
}
throw err;
}
}
回到run方法,得到AST后調(diào)用transformFile方法進(jìn)行轉(zhuǎn)化:
{
// ...
const opts = file.opts;
try {
yield* transformFile(file, config.passes);
} catch (e) {
e.message = `${opts.filename ?? "unknown file"}: ${e.message}`;
if (!e.code) {
e.code = "BABEL_TRANSFORM_ERROR";
}
throw e;
}
// ...
}
transformFile方法源碼如下:
function* transformFile(file: File, pluginPasses: PluginPasses): Handler<void> {
for (const pluginPairs of pluginPasses) {
// 初始化
const passPairs: [Plugin, PluginPass][] = [];
const passes = [];
const visitors = [];
for (const plugin of pluginPairs.concat([loadBlockHoistPlugin()])) {
// 為每個(gè)plugin創(chuàng)建一個(gè)新的pass
const pass = new PluginPass(file, plugin.key, plugin.options);
passPairs.push([plugin, pass]);
passes.push(pass);
// 將visitor(轉(zhuǎn)換方法)push到visitors
visitors.push(plugin.visitor);
}
for (const [plugin, pass] of passPairs) {
// 判斷插件是否有pre方法,如果有,則在當(dāng)前的插件通道和文件上下文中調(diào)用該方法
const fn = plugin.pre;
if (fn) {
// eslint-disable-next-line @typescript-eslint/no-confusing-void-expression
const result = fn.call(pass, file);
// @ts-expect-error - If we want to support async .pre
yield* [];
// 若返回的是一個(gè) Promise,報(bào)錯(cuò)
if (isThenable(result)) {
throw new Error(
`You appear to be using an plugin with an async .pre, ` +
`which your current version of Babel does not support. ` +
`If you're using a published plugin, you may need to upgrade ` +
`your @babel/core version.`,
);
}
}
}
// 合并所有插件中的visitors
const visitor = traverse.visitors.merge(visitors, passes, file.opts.wrapPluginVisitorMethod);
// 調(diào)用@babel/traverse進(jìn)行轉(zhuǎn)換
traverse(file.ast, visitor, file.scope);
for (const [plugin, pass] of passPairs) {
// 判斷插件是否有post方法,如果有,則在當(dāng)前的插件通道和文件上下文中調(diào)用該方法
const fn = plugin.post;
if (fn) {
// eslint-disable-next-line @typescript-eslint/no-confusing-void-expression
const result = fn.call(pass, file);
// @ts-expect-error - If we want to support async .post
yield* [];
if (isThenable(result)) {
throw new Error(
`You appear to be using an plugin with an async .post, ` +
`which your current version of Babel does not support. ` +
`If you're using a published plugin, you may need to upgrade ` +
`your @babel/core version.`,
);
}
}
}
}
}
在transformFile方法中依照順序,前中后分別為pre,visitor和post,它們分別為:
-
pre(state: PluginPass): 這個(gè)方法在遍歷開(kāi)始前被調(diào)用。通常用于在插件狀態(tài)對(duì)象上設(shè)置需要在整個(gè)遍歷過(guò)程中保持的一些初始狀態(tài)信息。state參數(shù)是一個(gè)PluginPass實(shí)例,它包含了與插件執(zhí)行上下文相關(guān)的信息。 -
visitor: 這個(gè)對(duì)象定義了在遍歷過(guò)程中需要調(diào)用的方法。每個(gè)方法的鍵是要訪問(wèn)的節(jié)點(diǎn)類(lèi)型,值是對(duì)應(yīng)的訪問(wèn)者方法或者一個(gè)包含enter和exit方法的對(duì)象。 -
post(state: PluginPass): 這個(gè)方法在遍歷完成后被調(diào)用,通常用于執(zhí)行一些清理工作,或者收集和使用在遍歷過(guò)程中計(jì)算出的結(jié)果。state參數(shù)同pre方法。
接下來(lái)繼續(xù)回到run方法:
{
// ...
let outputCode, outputMap;
try {
if (opts.code !== false) {
({ outputCode, outputMap } = generateCode(config.passes, file));
}
} catch (e) {
e.message = `${opts.filename ?? 'unknown file'}: ${e.message}`;
if (!e.code) {
e.code = 'BABEL_GENERATE_ERROR';
}
throw e;
}
return {
metadata: file.metadata,
options: opts,
ast: opts.ast === true ? file.ast : null,
code: outputCode === undefined ? null : outputCode,
map: outputMap === undefined ? null : outputMap,
sourceType: file.ast.program.sourceType,
externalDependencies: flattenToSet(config.externalDependencies),
};
}
最后調(diào)用generateCode方法將AST轉(zhuǎn)換回code,源碼如下,其和parser有異曲同工之妙:
export default function generateCode(
pluginPasses: PluginPasses,
file: File,
): {
outputCode: string;
outputMap: SourceMap | null;
} {
const { opts, ast, code, inputMap } = file;
const { generatorOpts } = opts;
generatorOpts.inputSourceMap = inputMap?.toObject();
const results = [];
// 取出plugin
for (const plugins of pluginPasses) {
for (const plugin of plugins) {
// 如果plugin中有生成方法,則調(diào)用,并push到results
const { generatorOverride } = plugin;
if (generatorOverride) {
const result = generatorOverride(ast, generatorOpts, code, generate);
if (result !== undefined) results.push(result);
}
}
}
let result;
// 如結(jié)果為空,調(diào)用@babel/generator
if (results.length === 0) {
result = generate(ast, generatorOpts, code);
} else if (results.length === 1) {
result = results[0];
if (typeof result.then === 'function') {
throw new Error(
`You appear to be using an async codegen plugin, ` +
`which your current version of Babel does not support. ` +
`If you're using a published plugin, ` +
`you may need to upgrade your @babel/core version.`,
);
}
} else {
throw new Error('More than one plugin attempted to override codegen.');
}
// Decoded maps are faster to merge, so we attempt to get use the decodedMap
// first. But to preserve backwards compat with older Generator, we'll fall
// back to the encoded map.
let { code: outputCode, decodedMap: outputMap = result.map } = result;
// For backwards compat.
if (result.__mergedMap) {
/**
* @see mergeSourceMap
*/
outputMap = { ...result.map };
} else {
if (outputMap) {
if (inputMap) {
// mergeSourceMap returns an encoded map
outputMap = mergeSourceMap(inputMap.toObject(), outputMap, generatorOpts.sourceFileName);
} else {
// We cannot output a decoded map, so retrieve the encoded form. Because
// the decoded form is free, it's fine to prioritize decoded first.
outputMap = result.map;
}
}
}
if (opts.sourceMaps === 'inline' || opts.sourceMaps === 'both') {
outputCode += '\n' + convertSourceMap.fromObject(outputMap).toComment();
}
if (opts.sourceMaps === 'inline') {
outputMap = null;
}
return { outputCode, outputMap };
}
至此run方法源碼解析完成,同時(shí)以babel.transformSync為開(kāi)始的@babel/core源碼解析也一并完成!
簡(jiǎn)易javascript編譯器(類(lèi)Babel)
接下來(lái),我們將以手撕一個(gè)以編譯demo為目的的簡(jiǎn)易編譯器,遵循的也是解析-轉(zhuǎn)換-生成這么一套流程,如下:
節(jié)點(diǎn)類(lèi)型(constants.js)
const TokenTypes = {
Keyword: "Keyword",
Identifier: "Identifier",
Punctuator: "Punctuator",
String: "String",
Numeric: "Numeric",
Paren: 'Paren',
Arrow: 'Arrow'
}
const AST_Types = {
Literal: "Literal",
Identifier: "Identifier",
AssignmentExpression: "AssignmentExpression",
VariableDeclarator: "VariableDeclarator",
VariableDeclaration: "VariableDeclaration",
Program: "Program",
NumericLiteral: "NumericLiteral",
ArrowFunctionExpression: 'ArrowFunctionExpression',
FunctionExpression: 'FunctionExpression'
}
module.exports = {
TokenTypes,
AST_Types
}
詞法分析(tokenizer.js)
const tokens = require('./constants');
// 匹配關(guān)鍵字
const KEYWORD = /let/;
// 匹配"="、";"
const PUNCTUATOR = /[\=;]/;
// 匹配空格
const WHITESPACE = /\s/;
// 匹配字符
const LETTERS = /[A-Za-z]/i;
// 匹配數(shù)字
const NUMERIC = /[0-9]/i;
const PAREN = /[()]/;
const { TokenTypes } = tokens;
function tokenizer(input) {
const tokens = [];
let current = 0;
// 遍歷字符串
while (current < input.length) {
let char = input[current];
// 處理關(guān)鍵字和變量名
if (LETTERS.test(char)) {
let value = '';
// 用一個(gè)循環(huán)遍歷所有的字母,把它們存入 value 中
while (LETTERS.test(char)) {
value += char;
char = input[++current];
}
// 判斷當(dāng)前字符串是否是關(guān)鍵字
KEYWORD.test(value)
? tokens.push({
type: TokenTypes.Keyword,
value: value,
})
: tokens.push({
type: TokenTypes.Identifier,
value: value,
});
continue;
}
// 檢查是否是括號(hào)
if (PAREN.test(char)) {
tokens.push({
type: TokenTypes.Paren,
value: char,
});
current++;
continue;
}
// 檢查是否是箭頭符號(hào)
if (char === '=' && input[current + 1] === '>') {
tokens.push({
type: TokenTypes.Arrow,
value: '=>',
});
current += 2; // Skip the two characters
continue;
}
// 判斷是否為數(shù)字
if (NUMERIC.test(char)) {
let value = '' + char;
char = input[++current];
while (NUMERIC.test(char) && current < input.length) {
value += char;
char = input[++current];
}
tokens.push({ type: TokenTypes.Numeric, value });
continue;
}
// 檢查是否是符號(hào),"="、";"
if (PUNCTUATOR.test(char)) {
const punctuators = char; // 創(chuàng)建變量用于保存匹配的符號(hào)
current++;
tokens.push({
type: TokenTypes.Punctuator,
value: punctuators,
});
continue;
}
// 處理空格,遇到空格直接跳過(guò)
if (WHITESPACE.test(char)) {
current++;
continue;
}
// 處理字符串
if (char === '"') {
let value = '';
// 忽略掉開(kāi)頭的引號(hào)
char = input[++current];
// 直到遇到下一個(gè)引號(hào)結(jié)束遍歷
while (char !== '"') {
value += char;
char = input[++current];
}
// 忽略掉結(jié)尾的引號(hào)
char = input[++current];
tokens.push({ type: TokenTypes.String, value: '"' + value + '"' });
continue;
}
// 如果不滿(mǎn)足當(dāng)前的匹配規(guī)則拋出錯(cuò)誤
throw new TypeError('Unknown' + char);
}
return tokens;
}
module.exports = tokenizer;
語(yǔ)法分析(parser.js)
const { TokenTypes, AST_Types } = require('./constants');
function parser(tokens) {
let current = 0;
function walk() {
let token = tokens[current];
if (token.type === TokenTypes.Numeric) {
current++;
return {
type: AST_Types.NumericLiteral,
value: token.value,
};
}
if (token.type === TokenTypes.String) {
current++;
return {
type: AST_Types.Literal,
value: token.value,
};
}
if (token.type === TokenTypes.Identifier) {
current++;
return {
type: AST_Types.Identifier,
name: token.value,
};
}
if (token.type === TokenTypes.Keyword && token.value === 'let') {
token = tokens[++current];
let node = {
type: AST_Types.VariableDeclaration,
kind: 'let',
declarations: [],
};
while (token.type === TokenTypes.Identifier) {
node.declarations.push({
type: AST_Types.VariableDeclarator,
id: {
type: AST_Types.Identifier,
name: token.value,
},
init: null,
});
token = tokens[++current];
if (token && token.type === TokenTypes.Punctuator && token.value === '=') {
token = tokens[++current];
if (token && token.type === TokenTypes.Paren) {
token = tokens[++current];
if (token && token.type === TokenTypes.Paren) {
token = tokens[++current];
if (token && token.type === TokenTypes.Arrow) {
token = tokens[++current];
let arrowFunction = {
type: AST_Types.ArrowFunctionExpression,
params: [],
body: walk(),
};
node.declarations[node.declarations.length - 1].init = arrowFunction;
}
}
} else {
node.declarations[node.declarations.length - 1].init = walk();
}
}
token = tokens[current];
if (token && token.type === TokenTypes.Punctuator && token.value === ';') {
current++;
break;
}
}
return node;
}
throw new TypeError(token.type);
}
let ast = {
type: AST_Types.Program,
body: [],
};
while (current < tokens.length) {
ast.body.push(walk());
}
return ast;
}
module.exports = parser;
遍歷器(traverser.js)
const constants = require('./constants');
const { AST_Types } = constants;
function traverser(ast, visitor) {
// 遍歷節(jié)點(diǎn),調(diào)用 traverseNode
function traverseArray(array, parent) {
array.forEach(function (child) {
traverseNode(child, parent);
});
}
function traverseNode(node, parent) {
// visitor 中有沒(méi)有對(duì)應(yīng) type 的處理函數(shù)。
const method = visitor[node.type];
if (method) {
method(node, parent);
}
// 下面對(duì)每一個(gè)不同類(lèi)型的結(jié)點(diǎn)分開(kāi)處理。
switch (node.type) {
case AST_Types.Program:
// 頂層的 Program 開(kāi)始,body是數(shù)組所以調(diào)用traverseArray
traverseArray(node.body, node);
break;
case AST_Types.VariableDeclaration:
traverseArray(node.declarations, node);
break;
case AST_Types.VariableDeclarator:
traverseNode(node.id, node);
traverseNode(node.init, node);
break;
case AST_Types.ArrowFunctionExpression:
traverseArray(node.params, node);
traverseNode(node.body, node);
case AST_Types.AssignmentExpression:
case AST_Types.Identifier:
case AST_Types.Literal:
case AST_Types.NumericLiteral:
break;
default:
throw new TypeError(node.type);
}
}
// 觸發(fā)遍歷AST,根節(jié)點(diǎn)沒(méi)有父節(jié)點(diǎn)所以這里傳入null
traverseNode(ast, null);
}
module.exports = traverser;
轉(zhuǎn)換器(transformer.js)
const traverser = require('./traverser');
const constants = require('./constants');
const { AST_Types } = constants;
function transformer(ast) {
const newAst = {
type: AST_Types.Program,
body: [],
sourceType: 'script',
};
ast._context = newAst.body;
// 將 AST 和 visitor 傳入traverser中
traverser(ast, {
// 將let轉(zhuǎn)換為var
VariableDeclaration: function (node, parent) {
const variableDeclaration = {
type: AST_Types.VariableDeclaration,
declarations: node.declarations,
kind: 'var',
};
parent._context.push(variableDeclaration);
},
ArrowFunctionExpression: function (node, parent) {
const functionExpression = {
type: AST_Types.FunctionExpression,
params: node.params, // 參數(shù)列表保持不變
body: node.body, // 函數(shù)體保持不變
};
if (parent.type === AST_Types.VariableDeclarator) {
parent.init = functionExpression;
}
},
});
return newAst;
}
module.exports = transformer;
代碼生成(codeGenerator.js)
const constants = require('./constants');
const { AST_Types } = constants;
function codeGenerator(node) {
// 處理不同類(lèi)型的結(jié)點(diǎn)
switch (node.type) {
// 如果是 Program 結(jié)點(diǎn),遍歷它的 body 屬性中的每一個(gè)結(jié)點(diǎn)并加入換行符號(hào)
case AST_Types.Program:
return node.body.map(codeGenerator).join('\n');
case AST_Types.VariableDeclaration:
return node.kind + ' ' + node.declarations.map(codeGenerator);
case AST_Types.VariableDeclarator:
return codeGenerator(node.id) + ' = ' + codeGenerator(node.init);
case AST_Types.Identifier:
return node.name;
case AST_Types.Literal:
return '"' + node.value + '"' + '; }';
case AST_Types.NumericLiteral:
return node.value + '; }';
case AST_Types.FunctionExpression:
return 'function(' + node.params + ') { return ' + codeGenerator(node.body);
default:
throw new TypeError(node.type);
}
}
module.exports = codeGenerator;
index.js
const tokenizer = require('./tokenizer')
const parser = require('./parser')
const transformer = require("./transformer")
const codeGenerator = require("./codeGenerator")
const demo = 'let a = () => 1;'
const tokens = tokenizer(demo)
const AST = parser(tokens)
const newAST = transformer(AST)
const newCode = codeGenerator(newAST)
console.log(newCode)
console.dir(newAST, {depth: null})
最終轉(zhuǎn)換結(jié)果如下:
var a = function() { return 1; }
生成的新的AST樹(shù)如下:
{
type: 'Program',
body: [
{
type: 'VariableDeclaration',
declarations: [
{
type: 'VariableDeclarator',
id: { type: 'Identifier', name: 'a' },
init: {
type: 'FunctionExpression',
params: [],
body: { type: 'NumericLiteral', value: '1' }
}
}
],
kind: 'var'
}
],
sourceType: 'script'
}
結(jié)束語(yǔ)
本來(lái)這篇文章是想從Babel開(kāi)始去分析Babel所有核心庫(kù)源碼以及相關(guān)知識(shí)體系,以AST為核心去開(kāi)闊javascript編譯這一話題,然后再去講一講SWC等等,但是由于最近工作有點(diǎn)忙碌,而且碩士畢業(yè)答辯在即,所以?xún)?nèi)容咩有寫(xiě)完,剩下的@Babel/parser / @babel/traverse / @babel/generator / @Babel/types / @Babel/cli源碼解析以及swc等等會(huì)在下一篇文章去展現(xiàn)!這篇文章斷斷續(xù)續(xù)寫(xiě)了大半個(gè)月,內(nèi)容可能有點(diǎn)斷斷續(xù)續(xù),還請(qǐng)見(jiàn)諒,有時(shí)間可能會(huì)做很多補(bǔ)全和修改。還是感謝我所參考的眾多文章,都是很棒的前輩們。加油,希望自己也可以多寫(xiě)寫(xiě),希望自己畢業(yè)順利,快發(fā)雙證,早點(diǎn)轉(zhuǎn)正!
參考資料
https://astexplorer.net/: https://link.juejin.cn?target=https%3A%2F%2Fastexplorer.net%2F
最后
Node 社群
我組建了一個(gè)氛圍特別好的 Node.js 社群,里面有很多 Node.js小伙伴,如果你對(duì)Node.js學(xué)習(xí)感興趣的話(后續(xù)有計(jì)劃也可以),我們可以一起進(jìn)行Node.js相關(guān)的交流、學(xué)習(xí)、共建。下方加 考拉 好友回復(fù)「Node」即可。
“分享、點(diǎn)贊、在看” 支持一
