虛擬DOM到底是什么?
是什么?
虛擬 DOM (Virtual DOM )這個(gè)概念相信大家都不陌生,從 React 到 Vue ,虛擬 DOM 為這兩個(gè)框架都帶來了跨平臺(tái)的能力(React-Native 和 Weex)。因?yàn)楹芏嗳耸窃趯W(xué)習(xí) React 的過程中接觸到的虛擬 DOM ,所以為先入為主,認(rèn)為虛擬 DOM 和 JSX 密不可分。其實(shí)不然,虛擬 DOM 和 JSX 固然契合,但 JSX 只是虛擬 DOM 的充分不必要條件,Vue 即使使用模版,也能把虛擬 DOM 玩得風(fēng)生水起,同時(shí)也有很多人通過 babel 在 Vue 中使用 JSX。
很多人認(rèn)為虛擬 DOM 最大的優(yōu)勢(shì)是 diff 算法,減少 JavaScript 操作真實(shí) DOM 的帶來的性能消耗。雖然這一個(gè)虛擬 DOM 帶來的一個(gè)優(yōu)勢(shì),但并不是全部。虛擬 DOM 最大的優(yōu)勢(shì)在于抽象了原本的渲染過程,實(shí)現(xiàn)了跨平臺(tái)的能力,而不僅僅局限于瀏覽器的 DOM,可以是安卓和 IOS 的原生組件,可以是近期很火熱的小程序,也可以是各種GUI。
回到最開始的問題,虛擬 DOM 到底是什么,說簡(jiǎn)單點(diǎn),就是一個(gè)普通的 JavaScript 對(duì)象,包含了 tag、props、children 三個(gè)屬性。
<div id="app">
<p class="text">hello world!!!</p>
</div>
上面的 HTML 轉(zhuǎn)換為虛擬 DOM 如下:
{
tag: 'div',
props: {
id: 'app'
},
chidren: [
{
tag: 'p',
props: {
className: 'text'
},
chidren: [
'hello world!!!'
]
}
]
}
該對(duì)象就是我們常說的虛擬 DOM 了,因?yàn)?DOM 是樹形結(jié)構(gòu),所以使用 JavaScript 對(duì)象就能很簡(jiǎn)單的表示。而原生 DOM 因?yàn)闉g覽器廠商需要實(shí)現(xiàn)眾多的規(guī)范(各種 HTML5 屬性、DOM事件),即使創(chuàng)建一個(gè)空的 div 也要付出昂貴的代價(jià)。虛擬 DOM 提升性能的點(diǎn)在于 DOM 發(fā)生變化的時(shí)候,通過 diff 算法比對(duì) JavaScript 原生對(duì)象,計(jì)算出需要變更的 DOM,然后只對(duì)變化的 DOM 進(jìn)行操作,而不是更新整個(gè)視圖。
那么我們到底該如何將一段 HTML 轉(zhuǎn)換為虛擬 DOM 呢?
從 h 函數(shù)說起
觀察主流的虛擬 DOM 庫(snabbdom、virtual-dom),通常都有一個(gè) h 函數(shù),也就是 React 中的 React.createElement,以及 Vue 中的 render 方法中的 createElement,另外 React 是通過 babel 將 jsx 轉(zhuǎn)換為 h 函數(shù)渲染的形式,而 Vue 是使用 vue-loader 將模版轉(zhuǎn)為 h 函數(shù)渲染的形式(也可以通過 babel-plugin-transform-vue-jsx 插件在 vue 中使用 jsx,本質(zhì)還是轉(zhuǎn)換為 h 函數(shù)渲染形式)。
我們先使用 babel,將一段 jsx 代碼,轉(zhuǎn)換為一段 js 代碼:
安裝 babel 依賴
npm i -D @babel/cli @babel/core @babel/plugin-transform-react-jsx
配置 .babelrc
{
"plugins": [
[
"@babel/plugin-transform-react-jsx",
{
"pragma": "h", // default pragma is React.createElement
}
]
]
}
轉(zhuǎn)譯 jsx
在目錄下新建一個(gè) main.jsx
function getVDOM() {
return (
<div id="app">
<p className="text">hello world!!!</p>
</div>
)
}
使用如下命令進(jìn)行轉(zhuǎn)譯:
npx babel main.jsx --out-file main-compiled.js
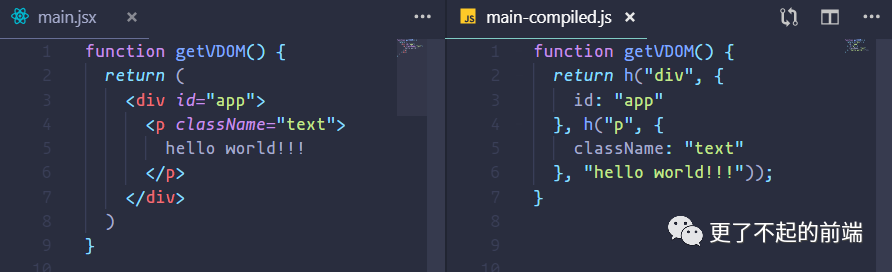
可以看到,最終 HTML 代碼會(huì)被轉(zhuǎn)譯成 h 函數(shù)的渲染形式。h 函數(shù)接受是三個(gè)參數(shù),分別代表是 DOM 元素的標(biāo)簽名、屬性、子節(jié)點(diǎn),最終返回一個(gè)虛擬 DOM 的對(duì)象。
function h(tag, props, ...children) {
return {
tag,
props: props || {},
children: children.flat()
}
}
渲染虛擬 DOM
雖然虛擬 DOM 可以渲染到多個(gè)平臺(tái),但是這里講一下在瀏覽器環(huán)境下如何渲染虛擬 DOM。
function render(vdom) {
// 如果是字符串或者數(shù)字,創(chuàng)建一個(gè)文本節(jié)點(diǎn)
if (typeof vdom === 'string' || typeof vdom === 'number') {
return document.createTextNode(vdom)
}
const { tag, props, children } = vdom
// 創(chuàng)建真實(shí)DOM
const element = document.createElement(tag)
// 設(shè)置屬性
setProps(element, props)
// 遍歷子節(jié)點(diǎn),并獲取創(chuàng)建真實(shí)DOM,插入到當(dāng)前節(jié)點(diǎn)
children
.map(render)
.forEach(element.appendChild.bind(element))
// 虛擬 DOM 中緩存真實(shí) DOM 節(jié)點(diǎn)
vdom.dom = element
// 返回 DOM 節(jié)點(diǎn)
return element
}
function setProps (element, props) {
Object.entries(props).forEach(([key, value]) => {
setProp(element, key, value)
})
}
function setProp (element, key, vlaue) {
element.setAttribute(
// className使用class代替
key === 'className' ? 'class' : key,
vlaue
)
}
將虛擬 DOM 渲染成真實(shí) DOM 后,只需要插入到對(duì)應(yīng)的根節(jié)點(diǎn)即可。
const vdom = <div>hello world!!!</div> // h('div', {}, 'hello world!!!')
const app = document.getElementById('app')
const ele = render(vdom)
app.appendChild(ele)
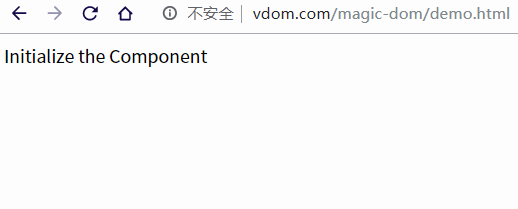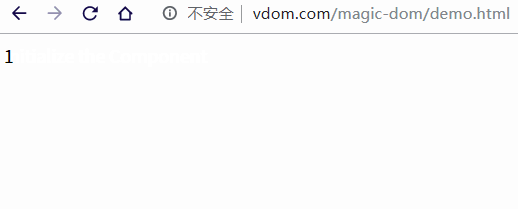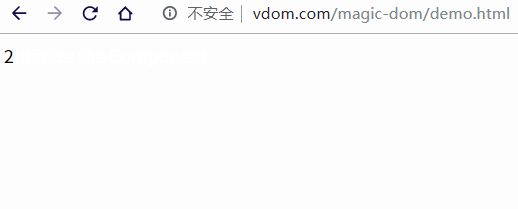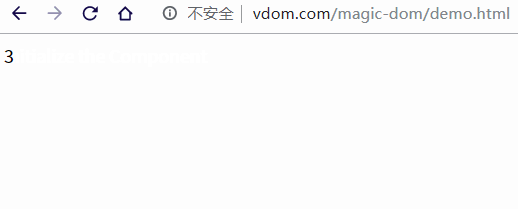
當(dāng)然在現(xiàn)代化的框架中,一般會(huì)有一個(gè)組件文件專門用來構(gòu)造虛擬 DOM,我們模仿 React 使用 class 的方式編寫組件,然后渲染到頁面中。
class Component {
vdom = null // 組件的虛擬DOM表示
$el = null // 虛擬DOM生成的真實(shí)節(jié)點(diǎn)
state = {
text: 'Initialize the Component'
}
render() {
const { text } = this.state
return (
<div>{ text }</div>
)
}
}
function createElement (app, component) {
const vdom = component.render()
component.vdom = vdom
component.$el = render(vdom) // 將虛擬 DOM 轉(zhuǎn)換為真實(shí) DOM
app.appendChild(component.$el)
}
const app = document.getElementById('app')
const component = new Component
createElement(app, component)
diff 算法
diff 算法,顧名思義,就是比對(duì)新老 VDOM 的變化,然后將變化的部分更新到視圖上。對(duì)應(yīng)到代碼上,就是一個(gè) diff 函數(shù),返回一個(gè) patches (補(bǔ)丁)。
const before = h('div', {}, 'before text')
const after = h('div', {}, 'after text')
const patches = diff(before, after)
修改我們之前的組件,增加 setState 方法,用于修改組件的內(nèi)部狀態(tài)。
class Component {
vdom = null // 組件的虛擬DOM表示
$el = null // 虛擬DOM生成的真實(shí)節(jié)點(diǎn)
state = {
text: 'Initialize the Component'
}
// 手動(dòng)修改組件state
setState(newState) {
this.state = {
...this.state,
...newState
}
const newVdom = this.render()
const patches = diff(this.vdom, newVdom)
patch(this.$el, patches)
}
changeText(text) {
this.setState({
text
})
}
render() {
const { text } = this.state
return (
<div>{ text }</div>
)
}
}
當(dāng)我們調(diào)用 setState 時(shí),state 內(nèi)部狀態(tài)發(fā)生變動(dòng),再次調(diào)用 render 方法就會(huì)生成一個(gè)新的虛擬 DOM 樹,這樣我們就能使用 diff 方法計(jì)算出新老虛擬 DOM 發(fā)送變化的部分,最后使用 patch 方法,將變動(dòng)渲染到視圖中。
const app = document.getElementById('app')
const component = new Component
createElement(app, component)
// 將文本更改為數(shù)字,每秒 +1
let count = 0
setInterval(() => {
component.changeText(++count)
}, 1000);
diff 算法的進(jìn)化
關(guān)于 diff 算法的最經(jīng)典的就是 Matt Esch 的 virtual-dom,以及 snabbdom(被整合進(jìn) vue 2.0中)。
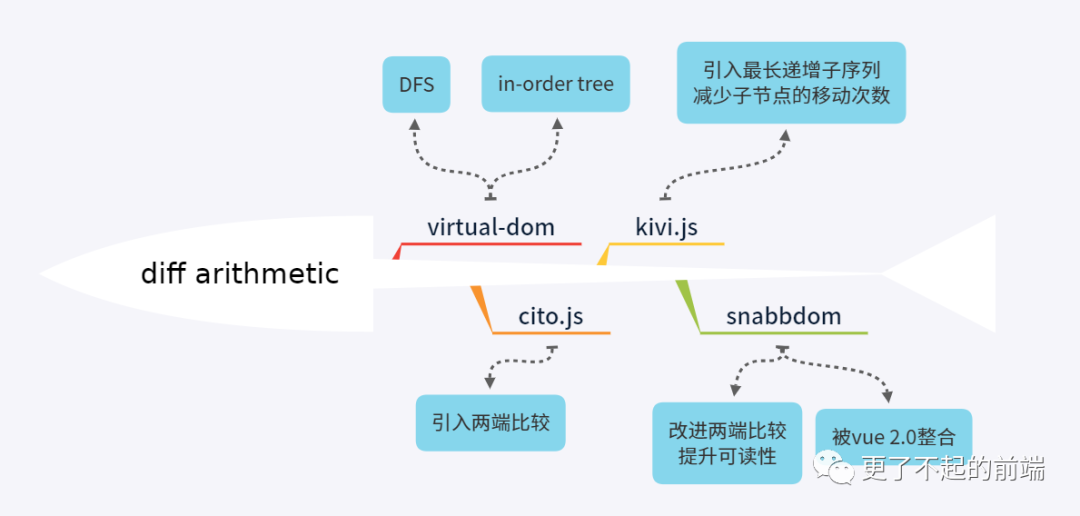
“最開始出現(xiàn)的是 virtual-dom 這個(gè)庫,是大家好奇 React 為什么這么快而搞鼓出來的。它的實(shí)現(xiàn)是非常學(xué)院風(fēng)格,通過深度優(yōu)先搜索與 in-order tree 來實(shí)現(xiàn)高效的 diff 。它與 React 后來公開出來的算法是很不一樣。然后是 cito.js 的橫空出世,它對(duì)今后所有虛擬 DOM 的算法都有重大影響。它采用兩端同時(shí)進(jìn)行比較的算法,將 diff 速度拉高到幾個(gè)層次。緊隨其后的是 kivi.js,在 cito.js 的基出提出兩項(xiàng)優(yōu)化方案,使用 key 實(shí)現(xiàn)移動(dòng)追蹤以及及基于 key 的最長(zhǎng)自增子序列算法應(yīng)用(算法復(fù)雜度 為O(n^2))。但這樣的 diff 算法太過復(fù)雜了,于是后來者 snabbdom 將 kivi.js 進(jìn)行簡(jiǎn)化,去掉編輯長(zhǎng)度矩離算法,調(diào)整兩端比較算法。速度略有損失,但可讀性大大提高。再之后,就是著名的vue2.0 把sanbbdom整個(gè)庫整合掉了。
“引用自司徒正美的文章 去哪兒網(wǎng)迷你React的研發(fā)心得
下面我們就來講講這幾個(gè)虛擬 DOM 庫 diff 算法的具體實(shí)現(xiàn):
1?? virtual-dom
virtual-dom 作為虛擬 DOM 開天辟地的作品,采用了對(duì) DOM 樹進(jìn)行了深度優(yōu)先的遍歷的方法。
DOM 樹的遍歷
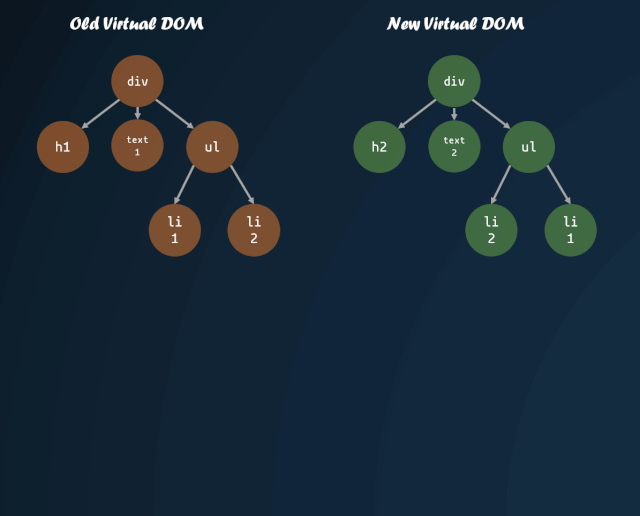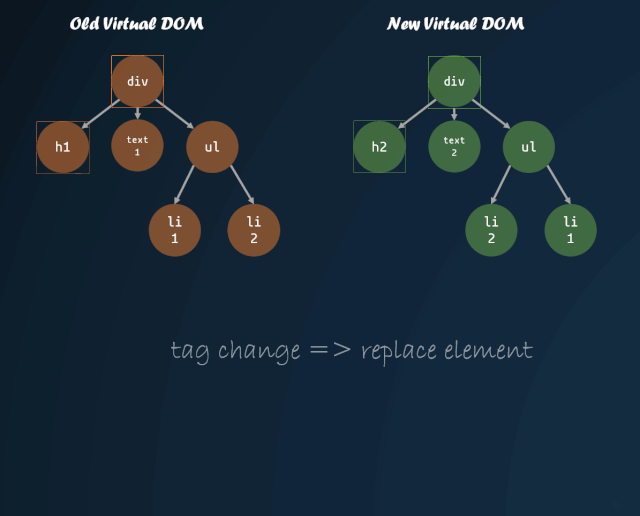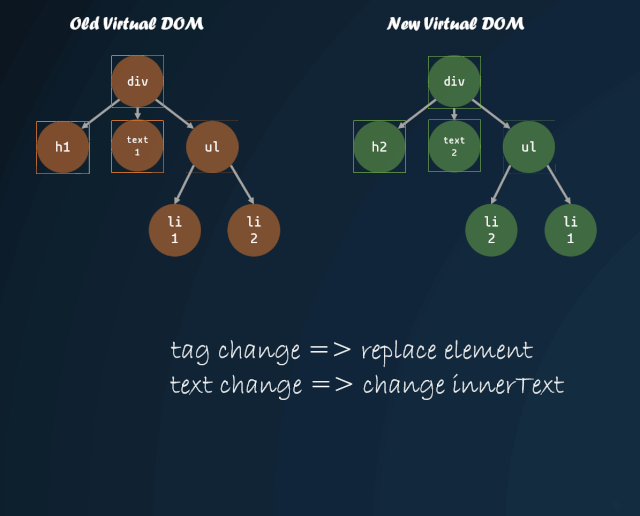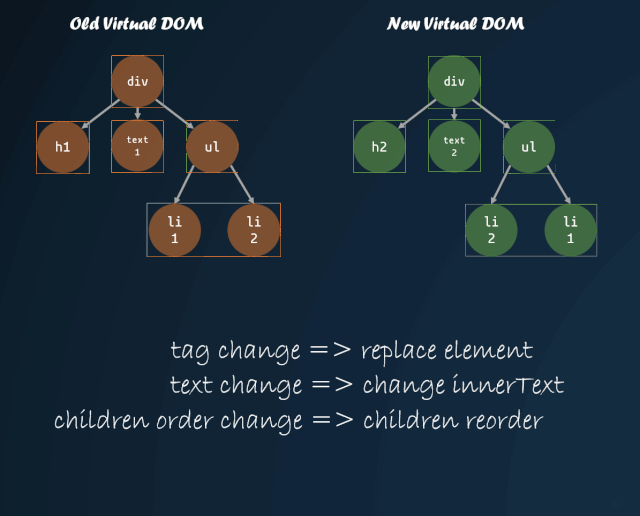
體現(xiàn)到代碼上:
function diff (oldNode, newNode) {
const patches = []
walk(oldNode, newNode, patches, 0) // 進(jìn)行深度優(yōu)先遍歷
return patches
}
function walk(oldNode, newNode, patches, index) {
if (newNode === oldNode) {
return
}
const patch = { type: 'update', vNode: newNode }
const oldChildren = oldNode.children
const newChildren = newNode.children
const oldLen = oldChildren.length
const newLen = newChildren.length
const len = oldLen > newLen ? oldLen : newLen
// 找到對(duì)應(yīng)位置的子節(jié)點(diǎn)進(jìn)行比對(duì)
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const oldChild = oldChildren[i]
const newChild = newChildren[i]
index++
// 相同節(jié)點(diǎn)進(jìn)行比對(duì)
walk(oldChild, newChild, patches, index)
if (isArray(oldChild.children)) {
index += oldChild.children.length
}
}
if (patch) {
patches[index] = patch
}
}
VDOM 節(jié)點(diǎn)的對(duì)比
上面代碼只是對(duì) VDOM 進(jìn)行了簡(jiǎn)單的深度優(yōu)先遍歷,在遍歷中,還需要對(duì)每個(gè) VDOM 進(jìn)行一些對(duì)比,具體分為以下幾種情況:
舊節(jié)點(diǎn)不存在,插入新節(jié)點(diǎn);新節(jié)點(diǎn)不存在,刪除舊節(jié)點(diǎn) 新舊節(jié)點(diǎn)如果都是 VNode,且新舊節(jié)點(diǎn) tag 相同 對(duì)比新舊節(jié)點(diǎn)的屬性 對(duì)比新舊節(jié)點(diǎn)的子節(jié)點(diǎn)差異,通過 key 值進(jìn)行重排序,key 值相同節(jié)點(diǎn)繼續(xù)向下遍歷 新舊節(jié)點(diǎn)如果都是 VText,判斷兩者文本是否發(fā)生變化 其他情況直接用新節(jié)點(diǎn)替代舊節(jié)點(diǎn)
import { isVNode, isVText, isArray } from '../utils/type'
function walk(oldNode, newNode, patches, index) {
if (newNode === oldNode) {
return
}
let patch = patches[index]
if (!oldNode) {
// 舊節(jié)點(diǎn)不存在,直接插入
patch = appendPatch(patch, {
type: PATCH.INSERT,
vNode: newNode,
})
} else if (!newNode) {
// 新節(jié)點(diǎn)不存在,刪除舊節(jié)點(diǎn)
patch = appendPatch(patch, {
type: PATCH.REMOVE,
vNode: null,
})
} else if (isVNode(newNode)) {
if (isVNode(oldNode)) {
// 相同類型節(jié)點(diǎn)的 diff
if (newNode.tag === oldNode.tag && newNode.key === oldNode.key) {
// 新老節(jié)點(diǎn)屬性的對(duì)比
const propsPatch = diffProps(newNode.props, oldNode.props)
if (propsPatch && propsPatch.length > 0) {
patch = appendPatch(patch, {
type: PATCH.PROPS,
patches: propsPatch,
})
}
// 新老節(jié)點(diǎn)子節(jié)點(diǎn)的對(duì)比
patch = diffChildren(oldNode, newNode, patches, patch, index)
}
} else {
// 新節(jié)點(diǎn)替換舊節(jié)點(diǎn)
patch = appendPatch(patch, {
type: PATCH.REPLACE,
vNode: newNode,
})
}
} else if (isVText(newNode)) {
if (!isVText(oldNode)) {
// 將舊節(jié)點(diǎn)替換成文本節(jié)點(diǎn)
patch = appendPatch(patch, {
type: PATCH.VTEXT,
vNode: newNode,
})
} else if (newNode.text !== oldNode.text) {
// 替換文本
patch = appendPatch(patch, {
type: PATCH.VTEXT,
vNode: newNode,
})
}
}
if (patch) {
// 將補(bǔ)丁放入對(duì)應(yīng)位置
patches[index] = patch
}
}
// 一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)可能有多個(gè) patch
// 多個(gè)patch時(shí),使用數(shù)組進(jìn)行存儲(chǔ)
function appendPatch(patch, apply) {
if (patch) {
if (isArray(patch)) {
patch.push(apply)
} else {
patch = [patch, apply]
}
return patch
} else {
return apply
}
}
屬性的對(duì)比
function diffProps(newProps, oldProps) {
const patches = []
const props = Object.assign({}, newProps, oldProps)
Object.keys(props).forEach(key => {
const newVal = newProps[key]
const oldVal = oldProps[key]
if (!newVal) {
patches.push({
type: PATCH.REMOVE_PROP,
key,
value: oldVal,
})
}
if (oldVal === undefined || newVal !== oldVal) {
patches.push({
type: PATCH.SET_PROP,
key,
value: newVal,
})
}
})
return patches
}
子節(jié)點(diǎn)的對(duì)比
這一部分可以說是 diff 算法中,變動(dòng)最多的部分,因?yàn)榍懊娴牟糠郑鱾€(gè)庫對(duì)比的方向基本一致,而關(guān)于子節(jié)點(diǎn)的對(duì)比,各個(gè)倉庫都在前者基礎(chǔ)上不斷得進(jìn)行改進(jìn)。
首先需要明白,為什么需要改進(jìn)子節(jié)點(diǎn)的對(duì)比方式。如果我們直接按照深度優(yōu)先遍歷的方式,一個(gè)個(gè)去對(duì)比子節(jié)點(diǎn),子節(jié)點(diǎn)的順序發(fā)生改變,那么就會(huì)導(dǎo)致 diff 算法認(rèn)為所有子節(jié)點(diǎn)都需要進(jìn)行 replace,重新將所有子節(jié)點(diǎn)的虛擬 DOM 轉(zhuǎn)換成真實(shí) DOM,這種操作是十分消耗性能的。
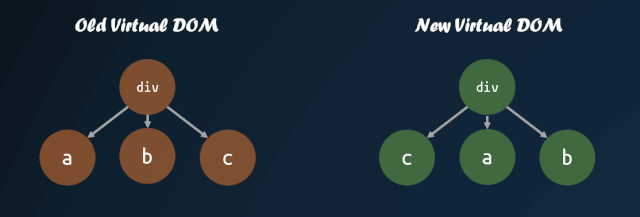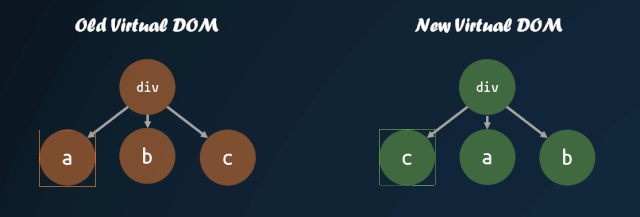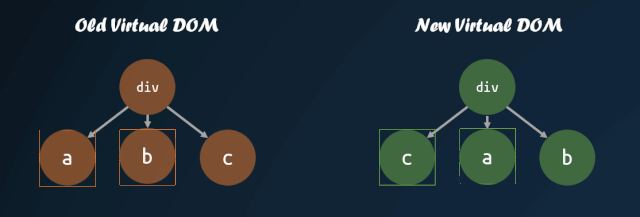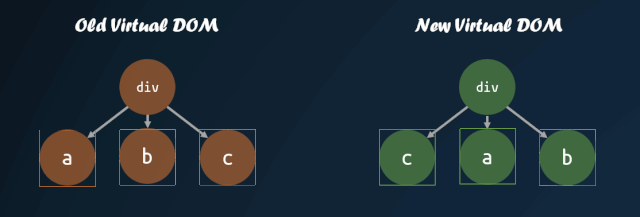
但是,如果我們能夠找到新舊虛擬 DOM 對(duì)應(yīng)的位置,然后進(jìn)行移動(dòng),那么就能夠盡量減少 DOM 的操作。
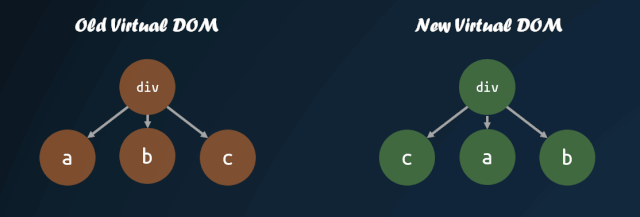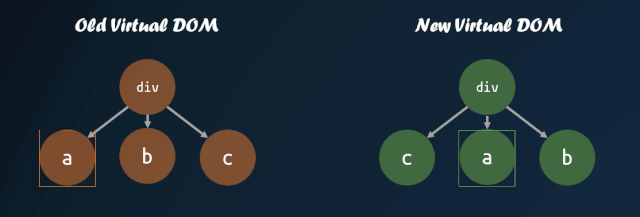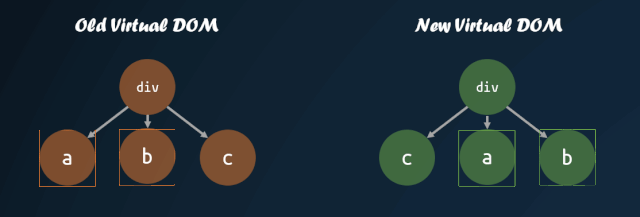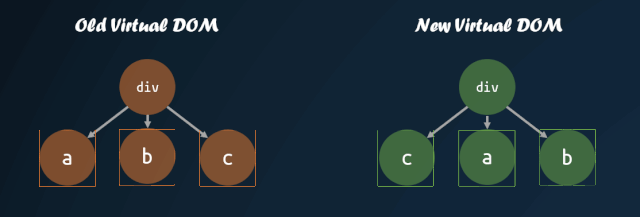
virtual-dom 在一開始就進(jìn)行了這方面的嘗試,對(duì)子節(jié)點(diǎn)添加 key 值,通過 key 值的對(duì)比,來判斷子節(jié)點(diǎn)是否進(jìn)行了移動(dòng)。通過 key 值對(duì)比子節(jié)點(diǎn)是否移動(dòng)的模式,被各個(gè)庫沿用,這也就是為什么主流的視圖庫中,子節(jié)點(diǎn)如果缺失 key 值,會(huì)有 warning 的原因。

具體是怎么對(duì)比的,我們先看代碼:
function diffChildren(oldNode, newNode, patches, patch, index) {
const oldChildren = oldNode.children
// 新節(jié)點(diǎn)按舊節(jié)點(diǎn)的順序重新排序
const sortedSet = sortChildren(oldChildren, newNode.children)
const newChildren = sortedSet.children
const oldLen = oldChildren.length
const newLen = newChildren.length
const len = oldLen > newLen ? oldLen : newLen
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
var leftNode = oldChildren[i]
var rightNode = newChildren[i]
index++
if (!leftNode) {
if (rightNode) {
// 舊節(jié)點(diǎn)不存在,新節(jié)點(diǎn)存在,進(jìn)行插入操作
patch = appendPatch(patch, {
type: PATCH.INSERT,
vNode: rightNode,
})
}
} else {
// 相同節(jié)點(diǎn)進(jìn)行比對(duì)
walk(leftNode, rightNode, patches, index)
}
if (isVNode(leftNode) && isArray(leftNode.children)) {
index += leftNode.children.length
}
}
if (sortedSet.moves) {
// 最后進(jìn)行重新排序
patch = appendPatch(patch, {
type: PATCH.ORDER,
moves: sortedSet.moves,
})
}
return patch
}
這里首先需要對(duì)新的子節(jié)點(diǎn)進(jìn)行重排序,先進(jìn)行相同節(jié)點(diǎn)的 diff ,最后把子節(jié)點(diǎn)按照新的子節(jié)點(diǎn)順序重新排列。
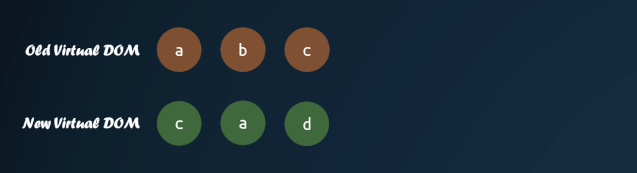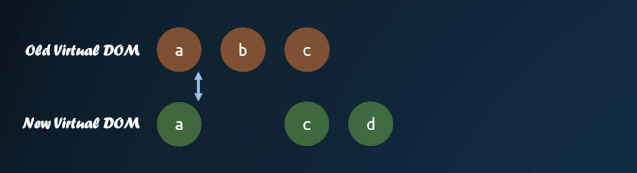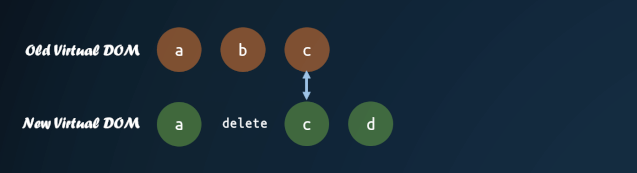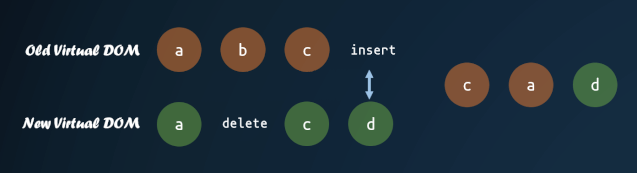
這里有個(gè)較復(fù)雜的部分,就是對(duì)子節(jié)點(diǎn)的重新排序。
function sortChildren(oldChildren, newChildren) {
// 找出變化后的子節(jié)點(diǎn)中帶 key 的 vdom (keys),和不帶 key 的 vdom (free)
const newChildIndex = keyIndex(newChildren)
const newKeys = newChildIndex.keys
const newFree = newChildIndex.free
// 所有子節(jié)點(diǎn)無 key 不進(jìn)行對(duì)比
if (newFree.length === newChildren.length) {
return {
children: newChildren,
moves: null,
}
}
// 找出變化前的子節(jié)點(diǎn)中帶 key 的 vdom (keys),和不帶 key 的 vdom (free)
const oldChildIndex = keyIndex(oldChildren)
const oldKeys = oldChildIndex.keys
const oldFree = oldChildIndex.free
// 所有子節(jié)點(diǎn)無 key 不進(jìn)行對(duì)比
if (oldFree.length === oldChildren.length) {
return {
children: newChildren,
moves: null,
}
}
// O(MAX(N, M)) memory
const shuffle = []
const freeCount = newFree.length
let freeIndex = 0
let deletedItems = 0
// 遍歷變化前的子節(jié)點(diǎn),對(duì)比變化后子節(jié)點(diǎn)的 key 值
// 并按照對(duì)應(yīng)順序?qū)⒆兓笞庸?jié)點(diǎn)的索引放入 shuffle 數(shù)組中
for (let i = 0; i < oldChildren.length; i++) {
const oldItem = oldChildren[i]
let itemIndex
if (oldItem.key) {
if (newKeys.hasOwnProperty(oldItem.key)) {
// 匹配到變化前節(jié)點(diǎn)中存在的 key
itemIndex = newKeys[oldItem.key]
shuffle.push(newChildren[itemIndex])
} else {
// 移除變化后節(jié)點(diǎn)不存在的 key 值
deletedItems++
shuffle.push(null)
}
} else {
if (freeIndex < freeCount) {
// 匹配變化前后的無 key 子節(jié)點(diǎn)
itemIndex = newFree[freeIndex++]
shuffle.push(newChildren[itemIndex])
} else {
// 如果變化后子節(jié)點(diǎn)中已經(jīng)不存在無 key 項(xiàng)
// 變化前的無 key 項(xiàng)也是多余項(xiàng),故刪除
deletedItems++
shuffle.push(null)
}
}
}
const lastFreeIndex =
freeIndex >= newFree.length ? newChildren.length : newFree[freeIndex]
// 遍歷變化后的子節(jié)點(diǎn),將所有之前不存在的 key 對(duì)應(yīng)的子節(jié)點(diǎn)放入 shuffle 數(shù)組中
for (let j = 0; j < newChildren.length; j++) {
const newItem = newChildren[j]
if (newItem.key) {
if (!oldKeys.hasOwnProperty(newItem.key)) {
// 添加所有新的 key 值對(duì)應(yīng)的子節(jié)點(diǎn)
// 之后還會(huì)重新排序,我們會(huì)在適當(dāng)?shù)牡胤讲迦胄略龉?jié)點(diǎn)
shuffle.push(newItem)
}
} else if (j >= lastFreeIndex) {
// 添加剩余的無 key 子節(jié)點(diǎn)
shuffle.push(newItem)
}
}
const simulate = shuffle.slice()
const removes = []
const inserts = []
let simulateIndex = 0
let simulateItem
let wantedItem
for (let k = 0; k < newChildren.length; ) {
wantedItem = newChildren[k] // 期待元素: 表示變化后 k 的子節(jié)點(diǎn)
simulateItem = simulate[simulateIndex] // 模擬元素: 表示變化前 k 位置的子節(jié)點(diǎn)
// 刪除在變化后不存在的子節(jié)點(diǎn)
while (simulateItem === null && simulate.length) {
removes.push(remove(simulate, simulateIndex, null))
simulateItem = simulate[simulateIndex]
}
if (!simulateItem || simulateItem.key !== wantedItem.key) {
// 期待元素的 key 值存在
if (wantedItem.key) {
if (simulateItem && simulateItem.key) {
// 如果一個(gè)帶 key 的子元素沒有在合適的位置,則進(jìn)行移動(dòng)
if (newKeys[simulateItem.key] !== k + 1) {
removes.push(remove(simulate, simulateIndex, simulateItem.key))
simulateItem = simulate[simulateIndex]
// if the remove didn't put the wanted item in place, we need to insert it
if (!simulateItem || simulateItem.key !== wantedItem.key) {
inserts.push({ key: wantedItem.key, to: k })
}
// items are matching, so skip ahead
else {
simulateIndex++
}
} else {
inserts.push({ key: wantedItem.key, to: k })
}
} else {
inserts.push({ key: wantedItem.key, to: k })
}
k++
}
// 該位置期待元素的 key 值不存在,且模擬元素存在 key 值
else if (simulateItem && simulateItem.key) {
// 變化前該位置的元素
removes.push(remove(simulate, simulateIndex, simulateItem.key))
}
} else {
// 如果期待元素和模擬元素 key 值相等,跳到下一個(gè)子節(jié)點(diǎn)比對(duì)
simulateIndex++
k++
}
}
// 移除所有的模擬元素
while (simulateIndex < simulate.length) {
simulateItem = simulate[simulateIndex]
removes.push(
remove(simulate, simulateIndex, simulateItem && simulateItem.key)
)
}
// 如果只有刪除選項(xiàng)中有值
// 將操作直接交個(gè) delete patch
if (removes.length === deletedItems && !inserts.length) {
return {
children: shuffle,
moves: null,
}
}
return {
children: shuffle,
moves: {
removes: removes,
inserts: inserts,
},
}
}
function keyIndex(children) {
const keys = {}
const free = []
const length = children.length
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
const child = children[i]
if (child.key) {
keys[child.key] = i
} else {
free.push(i)
}
}
return {
keys: keys, // 子節(jié)點(diǎn)中所有存在的 key 對(duì)應(yīng)的索引
free: free, // 子節(jié)點(diǎn)中不存在 key 值的索引
}
}
function remove(arr, index, key) {
arr.splice(index, 1) // 移除數(shù)組中指定元素
return {
from: index,
key: key,
}
}
這一部分比較復(fù)雜,具體可以查看 virtual-dom 的兩個(gè) pr ,這兩個(gè) pr 里面討論了關(guān)于 diff 子節(jié)點(diǎn)重新排序的優(yōu)化邏輯。
Rewrite reorder Rewrite reorder (part 2)
更新 DOM
在拿到了 VDOM 的 diff 結(jié)果后,需要將得到的 patches 更新到視圖上。
function patch(rootNode, patches) {
if (!patches || patches.length === 0) return
// 取得對(duì)應(yīng) index 的真實(shí) DOM
const nodes = domIndex(rootNode)
patches.forEach((patch, index) => {
patch && applyPatch(nodes[index], patch)
})
}
function domIndex(rootNode) {
const nodes = [rootNode]
const children = rootNode.childNodes
if (children.length) {
for (let child of children) {
if (child.nodeType === 1 || child.nodeType === 3) {
if (child.nodeType === 1) {
nodes.push(...domIndex(child))
} else if (child.nodeType === 3) {
nodes.push(child)
}
}
}
}
return nodes
}
遍歷patches,然后得到每個(gè)真實(shí) DOM 和其對(duì)應(yīng)的 patch,然后在真實(shí) DOM 上進(jìn)行更新:
function applyPatch(node, patchList) {
for (let patch of patchList) {
patchOp(node, patch)
}
}
function patchOp(node, patch) {
const { type, vNode } = patch
const parentNode = node.parentNode
let newNode = null
switch (type) {
case PATCH.INSERT:
// 插入新節(jié)點(diǎn)
break
case PATCH.REMOVE:
// 刪除舊新節(jié)點(diǎn)
break
case PATCH.REPLACE:
// 替換節(jié)點(diǎn)
break
case PATCH.ORDER:
// 子節(jié)點(diǎn)重新排序
break
case PATCH.VTEXT:
// 替換文本節(jié)點(diǎn)
break
case PATCH.PROPS:
// 更新節(jié)點(diǎn)屬性
break
default:
break
}
}
這里每一步操作,不進(jìn)行具體展開,感興趣的話可以在我的 github 查看完整代碼。
2?? cito.js
cito 其他步驟與 virtual-dom 類似,最大的差異點(diǎn)就在子節(jié)點(diǎn)的對(duì)比上,而且 cito 移除了 patch 更新,在 diff 的過程中,直接更新真實(shí) DOM ,這樣省去了 patch 的存儲(chǔ),一定程度上節(jié)省了內(nèi)存,后面其他的 VDOM 庫基本使用這種方式。
我們?cè)賮砜纯?cito 在子節(jié)點(diǎn)的對(duì)比上,到底有何優(yōu)化?
其實(shí)前面我們已經(jīng)介紹過了,cito 主要變化就是引入了兩端對(duì)比,將 diff 算法的速度提升了幾個(gè)量級(jí)。

/**
* 子節(jié)點(diǎn)對(duì)比
* @param {Element} domNode 父節(jié)點(diǎn)的真實(shí)DOM
* @param {Array} oldChildren 舊的子節(jié)點(diǎn)
* @param {Array} children 新的子節(jié)點(diǎn)
*/
function updateChildren(domNode, oldChildren, children) {
const oldChildrenLength = oldChildren.length
const childrenLength = children.length
let oldEndIndex = oldChildrenLength - 1
let endIndex = childrenLength - 1
let oldStartIndex = 0
let startIndex = 0
let successful = true
let nextChild
// 兩端對(duì)比算法
outer: while (
successful &&
oldStartIndex <= oldEndIndex &&
startIndex <= endIndex
) {
successful = false
let oldStartChild = oldChildren[oldStartIndex]
let startChild = children[startIndex]
while (oldStartChild.key === startChild.key) {
// 子節(jié)點(diǎn)對(duì)比
updateNode(oldStartChild, startChild, domNode)
oldStartIndex++
startIndex++
if (oldStartIndex > oldEndIndex || startIndex > endIndex) {
break outer
}
oldStartChild = oldChildren[oldStartIndex]
startChild = children[startIndex]
successful = true
}
let oldEndChild = oldChildren[oldEndIndex]
let endChild = children[endIndex]
while (oldEndChild.key === endChild.key) {
// 子節(jié)點(diǎn)對(duì)比
updateNode(oldEndChild, endChild, domNode)
oldEndIndex--
endIndex--
if (oldStartIndex > oldEndIndex || startIndex > endIndex) {
break outer
}
oldEndChild = oldChildren[oldEndIndex]
endChild = children[endIndex]
successful = true
}
while (oldStartChild.key === endChild.key) {
nextChild = endIndex + 1 < childrenLength ? children[endIndex + 1] : null
// 子節(jié)點(diǎn)對(duì)比
updateNode(oldStartChild, endChild, domNode)
// 移動(dòng)子節(jié)點(diǎn)
moveChild(domNode, endChild, nextChild)
oldStartIndex++
endIndex--
if (oldStartIndex > oldEndIndex || startIndex > endIndex) {
break outer
}
oldStartChild = oldChildren[oldStartIndex]
endChild = children[endIndex]
successful = true
}
while (oldEndChild.key === startChild.key) {
nextChild = oldStartIndex < oldChildrenLength ? oldChildren[oldStartIndex] : null
// 子節(jié)點(diǎn)對(duì)比
updateNode(oldEndChild, startChild, domNode)
// 移動(dòng)子節(jié)點(diǎn)
moveChild(domNode, startChild, nextChild)
oldEndIndex--
startIndex++
if (oldStartIndex > oldEndIndex || startIndex > endIndex) {
break outer
}
oldEndChild = oldChildren[oldEndIndex]
startChild = children[startIndex]
successful = true
}
}
}
子節(jié)點(diǎn)對(duì)比:
function updateNode(oldNode, node, domParent) {
if (node === oldNode) {
return
}
const tag = node.tag
if (oldNode.tag !== tag) {
// 標(biāo)簽不一致,創(chuàng)建新節(jié)點(diǎn)
createNode(node, domParent, oldNode, true)
} else {
const oldChildren = oldNode.children
const children = node.children
const domNode = oldNode.dom
node.dom = domNode // 真實(shí) DOM 掛在到 虛擬 DOM 上
// 子節(jié)點(diǎn)對(duì)比
if (children !== oldChildren) {
updateChildren(domNode, node, oldChildren, children)
}
const oldProps = oldNode.props
const props = node.props
// 屬性對(duì)比
if (props !== oldProps) {
updateAttributes(domNode, props, oldProps)
}
}
}
移動(dòng)子節(jié)點(diǎn):
function moveChild(domNode, child, nextChild) {
const domRefChild = nextChild && nextChild.dom
let domChild = child.dom
if (domChild !== domRefChild) {
if (domRefChild) {
domNode.insertBefore(domChild, domRefChild)
} else {
domNode.appendChild(domChild)
}
}
}
3?? kivi.js
kivi 的 diff 算法在 cito 的基礎(chǔ)上,引入了最長(zhǎng)增長(zhǎng)子序列,通過子序列找到最小的 DOM 操作數(shù)。
算法思想
“翻譯自 kivi/lib/reconciler.ts
該算法用于找到最小的 DOM 操作數(shù),可以分為以下幾步:
1. 找到數(shù)組中首部和尾部公共的節(jié)點(diǎn),并在兩端移動(dòng)
該方法通過比對(duì)兩端的 key 值,找到舊節(jié)點(diǎn)(A) 和新節(jié)點(diǎn)(B)中索引相同的節(jié)點(diǎn)。
A: -> [a b c d e f g] <-
B: [a b f d c g]
這里我們可以跳過首部的 a 和 b,以及尾部的 g。
A: -> [c d e f] <-
B: [f d c]
此時(shí),將嘗試對(duì)邊進(jìn)行比較,如果在對(duì)邊有一個(gè) key 值相同的節(jié)點(diǎn),將執(zhí)行簡(jiǎn)單的移動(dòng)操作,將 c 節(jié)點(diǎn)移動(dòng)到
右邊緣,將 f 節(jié)點(diǎn)移動(dòng)到左邊緣。
A: -> [d e] <-
B: [d]
現(xiàn)在將再次嘗試查找公共的首部與尾部,發(fā)現(xiàn) d 節(jié)點(diǎn)是相同的,我們跳過它。
A: -> [e] <-
B: [ ]
然后檢查各個(gè)列表的長(zhǎng)度是否為0,如果舊節(jié)點(diǎn)列表長(zhǎng)度為0,將插入新節(jié)點(diǎn)列表的剩余節(jié)點(diǎn),或者新節(jié)點(diǎn)列表長(zhǎng)度為0,將刪除所有舊節(jié)點(diǎn)列表中的元素。
這個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單的算法適用于大多數(shù)的實(shí)際案例,比如僅僅反轉(zhuǎn)了列表。
當(dāng)列表無法利用該算法找到解的時(shí)候,會(huì)使用下一個(gè)算法,例如:
A: -> [a b c d e f g] <-
B: [a c b h f e g]
邊緣的 a 和 g 節(jié)點(diǎn)相同,跳過他們。
A: -> [b c d e f] <-
B: [c b h f e]
然后上面的算法行不通了,我們需要進(jìn)入下一步。
2. 查找需要?jiǎng)h除或者插入的節(jié)點(diǎn),并且某個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)是否需要移動(dòng)
我們先創(chuàng)建一個(gè)數(shù)組 P,長(zhǎng)度為新子節(jié)點(diǎn)列表的長(zhǎng)度,并為數(shù)組每個(gè)元素賦值 -1 ,它表示新子節(jié)點(diǎn)應(yīng)該插入的位置。稍后,我們將把舊子節(jié)點(diǎn)中的節(jié)點(diǎn)位置分配給這個(gè)數(shù)組。
A: [b c d e f]
B: [c b h f e]
P: [. . . . .] // . == -1
然后,我們構(gòu)建一個(gè)對(duì)象 I,它的鍵表示新子節(jié)點(diǎn)的 key 值,值為子節(jié)點(diǎn)在剩余節(jié)點(diǎn)數(shù)組中的位置。
A: [b c d e f]
B: [c b h f e]
P: [. . . . .] // . == -1
I: {
c: 0,
b: 1,
h: 2,
f: 3,
e: 4,
}
last = 0
我們開始遍歷舊子節(jié)點(diǎn)列表的剩余節(jié)點(diǎn),并檢查是否可以在 I 對(duì)象的索引中找到具有相同 key 值的節(jié)點(diǎn)。如果找不到任何節(jié)點(diǎn),則將它刪除,否則,我們將節(jié)點(diǎn)在舊節(jié)點(diǎn)列表位置分配給數(shù)組 P。
A: [b c d e f]
^
B: [c b h f e]
P: [. 0 . . .] // . == -1
I: {
c: 0,
b: 1, <-
h: 2,
f: 3,
e: 4,
}
last = 1
當(dāng)我們?yōu)閿?shù)組 P 分配節(jié)點(diǎn)位置時(shí),我們會(huì)保留上一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)在新子節(jié)點(diǎn)列表中的位置,如果當(dāng)一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)的位置大于當(dāng)前節(jié)點(diǎn)的位置,那么我們將 moved 變量置為 true。
A: [b c d e f]
^
B: [c b h f e]
P: [1 0 . . .] // . == -1
I: {
c: 0, <-
b: 1,
h: 2,
f: 3,
e: 4,
}
last = 1 // last > 0; moved = true
上一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn) b位置為 “1”,當(dāng)前節(jié)點(diǎn) c 的位置 “0”,所以將 moved 變量置為 true。
A: [b c d e f]
^
B: [c b h f e]
P: [1 0 . . .] // . == -1
I: {
c: 0,
b: 1,
h: 2,
f: 3,
e: 4,
}
moved = true
對(duì)象 I 索引中不存在 d,則刪除該節(jié)點(diǎn)
A: [b c d e f]
^
B: [c b h f e]
P: [1 0 . . 3] // . == -1
I: {
c: 0,
b: 1,
h: 2,
f: 3,
e: 4, <-
}
moved = true
為節(jié)點(diǎn) e 分配位置。
A: [b c d e f]
^
B: [c b h f e]
P: [1 0 . 4 3] // . == -1
I: {
c: 0,
b: 1,
h: 2,
f: 3, <-
e: 4,
}
moved = true
為節(jié)點(diǎn) f 分配位置。
此時(shí),我們檢查 moved 標(biāo)志是否被打開,或者舊子節(jié)點(diǎn)列表的長(zhǎng)度減去已刪除節(jié)點(diǎn)的數(shù)量不等于新子節(jié)點(diǎn)列表的長(zhǎng)度。如果其中任何一個(gè)條件為真,我們則進(jìn)入下一步。
3. 如果 moved 為真,查找最小移動(dòng)數(shù),如果長(zhǎng)度發(fā)送變化,則插入新節(jié)點(diǎn)。
如果 moved 為真,我們需要在 P 數(shù)組中找到 最長(zhǎng)自增子序列,并移動(dòng)不屬于這個(gè)子序列的所有節(jié)點(diǎn)。
A: [b c d e f]
B: [c b h f e]
P: [1 0 . 4 3] // . == -1
LIS: [1 4]
moved = true
現(xiàn)在我們需要同時(shí)從尾端遍歷新的子節(jié)點(diǎn)列表以及最長(zhǎng)自增子序列(后面簡(jiǎn)稱 LIS),并檢查當(dāng)前位置是否等于 LIS 的值。
A: [b c d e f]
B: [c b h f e]
^ // new_pos == 4
P: [1 0 . 4 3] // . == -1
LIS: [1 4]
^ // new_pos == 4
moved = true
節(jié)點(diǎn) e 保持當(dāng)前位置
A: [b c d e f]
B: [c b h f e]
^ // new_pos == 3
P: [1 0 . 4 3] // . == -1
LIS: [1 4]
^ // new_pos != 1
moved = true
移動(dòng)節(jié)點(diǎn) f,移動(dòng)到下一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn) e 前面它。
A: [b c d e f]
B: [c b h f e]
^ // new_pos == 2
P: [1 0 . 4 3] // . == -1
^ // old_pos == -1
LIS: [1 4]
^
moved = true
節(jié)點(diǎn) h 在數(shù)組 P 中為 -1 ,則表示插入新節(jié)點(diǎn) h。
A: [b c d e f]
B: [c b h f e]
^ // new_pos == 1
P: [1 0 . 4 3] // . == -1
LIS: [1 4]
^ // new_pos == 1
moved = true
節(jié)點(diǎn) b 保持當(dāng)前位置
A: [b c d e f]
B: [c b h f e]
^ // new_pos == 0
P: [1 0 . 4 3] // . == -1
LIS: [1 4]
^ // new_pos != undefined
moved = true
移動(dòng)節(jié)點(diǎn) c ,移動(dòng)到下一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn) b 前面它。
如果 moved 為 false 時(shí),我們不需要查找LIS,我們只需遍歷新子節(jié)點(diǎn)列表,并檢查它在數(shù)組 P 中的位置,如果是 -1 ,則插入新節(jié)點(diǎn)。
關(guān)于 kivi
kivi 是作者對(duì)虛擬 DOM 性能提升的一些猜想,一開始它就向著性能出發(fā),所有它在實(shí)現(xiàn)上代碼可能并不優(yōu)雅,而且它的 api 也十分不友好。而接下來的 snabbdom 就在 kivi 的基礎(chǔ)上,大大提升了代碼的可讀性,很多講述虛擬 DOM 的文章也將 snabbdom 作為案例。
另外,kivi 的作者也創(chuàng)建了另一個(gè) 源碼以及 api 更友好的倉庫:ivi,感興趣可以了解一下。
4?? snabbdom
snabbdom 的優(yōu)勢(shì)就是代碼的可讀性大大提升,并且也引入了兩端對(duì)比,diff 速度也不慢。
我們可以簡(jiǎn)單看下 snabbdom 的兩端對(duì)比算法的核心代碼:
/**
* 子節(jié)點(diǎn)對(duì)比
* @param {Element} parentElm 父節(jié)點(diǎn)的真實(shí)DOM
* @param {Array} oldCh 舊的子節(jié)點(diǎn)
* @param {Array} newCh 新的子節(jié)點(diǎn)
*/
function updateChildren(parentElm, oldCh, newCh) {
let oldStartIdx = 0
let newStartIdx = 0
let oldEndIdx = oldCh.length - 1
let oldStartVnode = oldCh[0]
let oldEndVnode = oldCh[oldEndIdx]
let newEndIdx = newCh.length - 1
let newStartVnode = newCh[0]
let newEndVnode = newCh[newEndIdx]
let oldKeyToIdx
let idxInOld
let elmToMove
let before
while (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) {
// 跳過兩端不存在的舊節(jié)點(diǎn)
if (oldStartVnode == null) {
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx]
} else if (oldEndVnode == null) {
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
}
// 跳過兩端不存在的新節(jié)點(diǎn)
else if (newStartVnode == null) {
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
} else if (newEndVnode == null) {
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx]
}
/*
** 進(jìn)行兩端對(duì)比,分為四種狀況:
** 1. oldStart <=> newStart
** 2. oldEnd <=> newEnd
** 3. oldStart <=> newEnd
** 4. oldEnd <=> newStart
*/
else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx]
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode)
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode)
insertBefore(parentElm, oldStartVnode.dom, oldEndVnode.dom.nextSibling)
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx]
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode)) {
// Vnode moved left
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode)
insertBefore(parentElm, oldEndVnode.dom, oldStartVnode.dom)
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
}
// 上面四種情況都不存在,通過 key 值查找對(duì)應(yīng) VDOM 進(jìn)行對(duì)比
else {
// 構(gòu)造舊子節(jié)點(diǎn)的 map 表 (key => vdom)
if (oldKeyToIdx === undefined) {
oldKeyToIdx = createKeyToOldIdx(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
}
idxInOld = oldKeyToIdx[newStartVnode.key]
// 如果新的子節(jié)點(diǎn)在舊子節(jié)點(diǎn)不存在,進(jìn)行插入操作
if (idxInOld === undefined) {
insertBefore(parentElm, render(newStartVnode), oldStartVnode.dom)
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
}
// 如果新的子節(jié)點(diǎn)在舊子節(jié)點(diǎn)存在,進(jìn)行對(duì)比
else {
elmToMove = oldCh[idxInOld]
if (elmToMove.sel !== newStartVnode.sel) {
// key 值相同,但是 tag 不同,重新生成節(jié)點(diǎn)并替換
insertBefore(parentElm, render(newStartVnode), oldStartVnode.dom)
} else {
patchVnode(elmToMove, newStartVnode)
oldCh[idxInOld] = undefined // 該位置已經(jīng)對(duì)比,進(jìn)行置空
insertBefore(parentElm, elmToMove.dom, oldStartVnode.dom)
}
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
}
}
}
// 處理一些未處理到的節(jié)點(diǎn)
if (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx || newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) {
if (oldStartIdx > oldEndIdx) {
before = newCh[newEndIdx + 1] == null ? null : newCh[newEndIdx + 1].dom
addVnodes(parentElm, before, newCh, newStartIdx, newEndIdx)
} else {
removeVnodes(parentElm, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
}
}
}
關(guān)于 snabbdom ,網(wǎng)上有太多教程來分析它的 diff 過程了,不管是虛擬 DOM 的教程,還是 Vue 的源碼分析,這里就不再詳細(xì)講述了。但是可以明顯的看到,snabbdom 的 diff 算法是有 cito 和 kivi 的影子在的。
總結(jié)
毋庸置疑虛擬 DOM 帶給前端的意義是非凡的,虛擬 DOM 在現(xiàn)如今還有更多新鮮的玩法。比如 omi 將虛擬 DOM 與 Web Component 的結(jié)合,還有 Taro 和 Chameleon 帶來的多端統(tǒng)一的能力。
另外,文中相關(guān)的代碼都可以在我的 github 查看,這篇文章更多是對(duì)自己學(xué)習(xí)的一個(gè)記錄,如果有什么錯(cuò)誤的觀點(diǎn),歡迎進(jìn)行指正。
